MSC
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
1
New cards
autotrophic
make their own energy (photosynthesis)
2
New cards
heterotrophic
obtain energy from consuming others
3
New cards
suspension feeders
use appendages to strain particulate food from water
4
New cards
filter feeders
take in water and filter food particles and expel water
5
New cards
deposit feeders
process mud and remove food particles (sand dollars)
6
New cards
Littoral zones (intertidal) characteristics
-depth depends on tidal range
-extreme temp
-altering flooding/dessication
-changing salinity/temp
-organisms tolerant to extremes
-extreme temp
-altering flooding/dessication
-changing salinity/temp
-organisms tolerant to extremes
7
New cards
Interstitial organisms (meiofauna)
-live in the sand
-low biodiversity and competition (few large orgs)
-tolerant to wave impact/ dessication
-low biodiversity and competition (few large orgs)
-tolerant to wave impact/ dessication
8
New cards
Epifauna
organisms that live ON the surface
9
New cards
Infauna
organisms that live IN the surface
10
New cards
Salt marsh
coastal wetland flooded by sal by tides
11
New cards
Estuary
inlet of ocean water towards freshwater and freshwater flowing outside
-marine nurseries
-flunctuating salinity
-marine nurseries
-flunctuating salinity
12
New cards
euryhaline species
organisms tolerable to changing environments
13
New cards
mangrove wetlands
-habitat for birds
-nursery for fish
-rich nutrient source
-nursery for fish
-rich nutrient source
14
New cards
seagrasses
-highest primary productivity
-stabilize sediment
-tolerate various salt concentrations
-stabilize sediment
-tolerate various salt concentrations
15
New cards
coral reef limiting factors
- light (water clarity/depth)
-temperature (latitudinal limits)
-salinity (little flunctuation)
-wave energy (turbulence)
-nutrients (algae overgrowing)
-sedimentation (river runoff=coral buried/tired of cleaning themselves)
-temperature (latitudinal limits)
-salinity (little flunctuation)
-wave energy (turbulence)
-nutrients (algae overgrowing)
-sedimentation (river runoff=coral buried/tired of cleaning themselves)
16
New cards
Coral characteristics
-cnidarians
-nematocysts
-CaCO3 skeleton
-nematocysts
-CaCO3 skeleton
17
New cards
Coral symbiotic relationship with Zooxanthellae
Coral gives zooxanthellae cells shelter and their waste which the cells use as nutrients for photosynthesis creating a higher coral calcification rate
18
New cards
Coral reef threats
coral bleaching (loss of zooxanthellae) due to:
-temperature stress
-UV radiation
-high O2 tension due to increased photosynthesis bc too much light
-high eutrophication+algae covering algae
-temperature stress
-UV radiation
-high O2 tension due to increased photosynthesis bc too much light
-high eutrophication+algae covering algae
19
New cards
eutrophication
high amount of nutrients due to sewages, runoffs, fertilizers causing algae growth covering corals
20
New cards
organisms adaptations at intertidal zones
motiles: crawl under rocks
sessiles: have tough shells and stick tightly to surfaces
sessiles: have tough shells and stick tightly to surfaces
21
New cards
hydrothermal vents
-chemosynthesis
-microbes and bacteria form at base
-found in divergent boundaries
-discovered in 1970s
-microbes and bacteria form at base
-found in divergent boundaries
-discovered in 1970s
22
New cards
chemosynthesis
process by which food (glucose) is made by bacteria using chemicals as energy source instead of sunlight
23
New cards
compensation depth
depth where primary production=respiration depth
-O2 accumulates above and no net loss below
-O2 accumulates above and no net loss below
24
New cards
Polar areas productivity levels
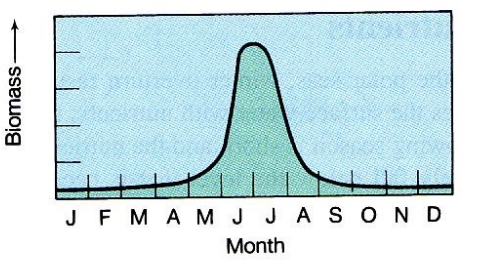
25
New cards
temperate areas productivity levels
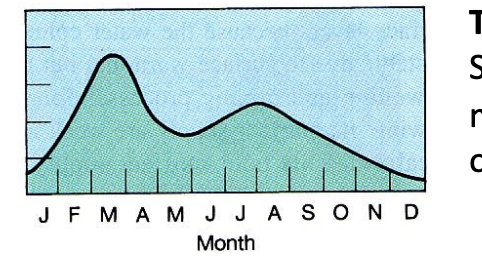
26
New cards
subtropical area productivity levels
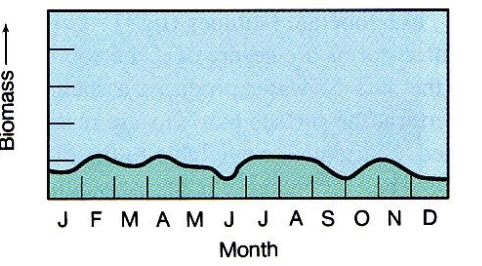
27
New cards
4 groups of phytoplankton
-Cyanobacteria
-Diatoms
-Dinoflagellates
-Coccolithophores
-Diatoms
-Dinoflagellates
-Coccolithophores
28
New cards
Cyanobacteria
-most tiny and abundant
-"sea green algae"
-"sea green algae"
29
New cards
diatoms
-silica skeletons
-abundant in polar regions
-abundant in polar regions
30
New cards
dinoflagellates
-2 flagella for motility
-large phytoplankton
-form red tides
-bioluminescent
-large phytoplankton
-form red tides
-bioluminescent
31
New cards
coccolithophores
covered in calcium carbonate plates (chalk)
32
New cards
primary production
conversion of dissolved inorganic carbon (CO2) and nutrients to biomass
33
New cards
major factors for primary production
-light
-temperature
-nutrients
-temperature
-nutrients
34
New cards
who makes primary production
microbes and phytoplankton (bacteria and eukaryotes)
35
New cards
gross primary production (GPP)
biomass created from photosynthesis
\
\
36
New cards
net primary production (NPP)
the difference between the amount of carbon produced through photosynthesis (GPP) and the amount used for respiration
NPP= GPP- RESPIRATION
NPP= GPP- RESPIRATION
37
New cards
how to measure primary production?
-satellite measuring amount of chlorophyll (green)
-oxygen in light and dark bottles incubation
-oxygen in light and dark bottles incubation
38
New cards
photosynthesis
ENERGY+CO2+H2O------->ORGANIC MATTER+O2
39
New cards
respiration
ORGANIC MATTER+O2------->ENERGY+CO2+H2O
40
New cards
phytoplankton growth factors
Redfield ratio
C:N:P
106:16:1
C:N:P
106:16:1
41
New cards
holoplankton
planktonic for entire life cycle
42
New cards
meroplankton
planktonic for part of their life
43
New cards
holoplankton examples
-copepods
-cnidarians
-ctenophores (comb jelly)
-chaetognaths (arrow worms)
-euphosids (krill)
-pteropods (sea butterflies)
-cnidarians
-ctenophores (comb jelly)
-chaetognaths (arrow worms)
-euphosids (krill)
-pteropods (sea butterflies)
44
New cards
meroplankton examples
-ichtyoplankton (fish eggs and larvae)
-mollusks
-mollusks
45
New cards
importance of studying icthtyoplankton
-monitor trends in population if rising/declining faster and earlier
-cheaper sampling
-cheaper sampling
46
New cards
plankton stresses
-predation
-sinking
-food availability
-sinking
-food availability
47
New cards
diel vertical migration
journey of organisms from surface to deep to reduce vulnerabilty with predators
-day in the deep and night in the surface
-day in the deep and night in the surface
48
New cards

heterocercal (sharks)
49
New cards

lunated
50
New cards

forked
51
New cards

turnicated
52
New cards

rounded
53
New cards
fusiform
torpedo shape
speed
speed
54
New cards
laterally compressed
short burst of speed
quick turns
quick turns
55
New cards
flattened
sea floor adapted
56
New cards
elonagted
hiding
57
New cards
irregular
camouflage
58
New cards
oviparous
organisms that lay eggs
59
New cards
viviparous
organisms that give birth
60
New cards
ovoviviparous
organisms that give birth with no embryo connection, yolk sacs instead (seahorses)
61
New cards
anandromous
live in ocean and spawn in freshwater
62
New cards
catadromous
live in freshwater and spawn in ocean
63
New cards
shoaling
unstrcutured, mixes species
64
New cards
schooling
tightly organized, single species
65
New cards
advantages of schooling
mating
safety
effective traveling
safety
effective traveling
66
New cards
how do fish breath?
take in water with dissolved oxygen through mouth and pump water out with their gills, releasing CO2
67
New cards
buccal pumping
water through mouth and past gills by muscles called gill pumps
68
New cards
ram ventilation
water through mouth and past gills by forward swimming
69
New cards
poikilothermic (cold blooded)
body temp same as exterior env
70
New cards
homeothermic (warm blooded)
body temp independent of external env
71
New cards
rate mireable
arteries use countercurrent blood flow within net to retain heat generated by swimming muscles
72
New cards
agnatha
jawless snake liked
73
New cards
chondricthyes
sharks/rays
cartilagnious fish no swimm bladder
cartilagnious fish no swimm bladder
74
New cards
osteichtyes
bony fish
75
New cards
cephalopods
squid, octopus, cuttlefish
76
New cards
lateral line
sensory body line to detect movement and vibration
77
New cards
ampullae of lorenzini
electrive sensitive cells for prey
78
New cards
fisheries challenges
high nutrients to feed fish
antibiotics for diseases
possible escape of invasive fish
antibiotics for diseases
possible escape of invasive fish
79
New cards
magnuson-stevenson act
governs marine fisheries management in U.S. federal waters.
80
New cards
maximum sustainable yield
highest amount of population that can be fished while maintaning stable population
81
New cards
impacts of abundance in fisheries
-mortality rate
-dispersal (movement of fish to adult recruit)
-succesful settlement of new adult habitats
-dispersal (movement of fish to adult recruit)
-succesful settlement of new adult habitats
82
New cards
cetaceans
whales,dolphins, porposises
83
New cards
pinnipeds
seals,sea lions, walruses
84
New cards
sirenians
manatees, dugongs
85
New cards
fissipeds
polar bears, otters
86
New cards
2 types of cetaceans
mysticetes: baleen whales
odontocetes: toothed whales
odontocetes: toothed whales
87
New cards
marine mammals risks
-historical whaling
climate change (melting ice and warm sea)
slow reproduction
sound disruptions
climate change (melting ice and warm sea)
slow reproduction
sound disruptions
88
New cards
how to study marine mammals
visual survey
acolustics sound tags
satellite tags
necropsies (study dead animals)
acolustics sound tags
satellite tags
necropsies (study dead animals)
89
New cards
How do we study Earth’s past climate?
paleo proxy
-oxygen isotopes in the ice cores
-carbon isotopes in carbonate shells in sediment cores
-thickness of tree rings
-oxygen isotopes in the ice cores
-carbon isotopes in carbonate shells in sediment cores
-thickness of tree rings
90
New cards
What things can we infer from paleo proxies?
-temperature
-evaporation/precipitation
-ice volume/sea level
-evaporation/precipitation
-ice volume/sea level
91
New cards
What processes have controlled Earth’s climate over hundreds of millions of years?
-plate tectonics: weathering of rocks consumes CO2, exchange CO2 with atmosphere
-solar intensity
-orbital change
-solar intensity
-orbital change
92
New cards
solar forcing
incoming solar radiation or insolation (how much energy comes in from the sun)
93
New cards
solar forcing factors
intensity of the sun
orbital forcing
orbital forcing
94
New cards
orbital forcing
orbit of earth around sun defines insolation balance
95
New cards
radiative balance
how much incoming radiation is reflected (albedo) versus absorbed, how much outgoing radiation is absorbed by atmosphere and re-emitted (feedback)
96
New cards
radiative balance factors
-albedo
-greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
-ice dynamics
-greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
-ice dynamics
97
New cards
feedback process example
less ice-less albedo-ocean absorbs more heat-ocean warms...
98
New cards
ocean role in CO2
-large reservoir of dissolved CO2
-transfer CO2 out of atmosphere (changes in circulation and photosynthesis)
-transfer CO2 out of atmosphere (changes in circulation and photosynthesis)
99
New cards
Biological
carbon
pump
carbon
pump
moving carbon from the surface to the deep
100
New cards
When was the last ice age (Last Glacial Maximum)?
20,000 years ago