Baillargeon’s theory of infant abilities
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Background - early research in knowledge of the physical world
Who? believed that babies less than _- _months of age (s____ stage) have a very p_____ (basic, simple) understanding of the nature of the physical world.
For example, he claimed that babies lack knowledge of what? and what was his reasoning based on?
R____ B_____ suggested otherwise:
she suggested that young babies had a b____ u____ of the physical world than P____ had suggested.
She proposed that the lack of understanding of o____ p___ could be explained differently. - how?
Background - early research in knowledge of the physical world
Piaget believed that babies less than 8-9 months of age (sensorimotor stage) have a very primitive (basic, simple) understanding of the nature of the physical world.
For example, he claimed that babies lack knowledge of object permanence → reasoning was based on his research showing that babies would lose interest in an object once the object was out of sight.
Renée Baillargeon suggested otherwise:
she suggested that young babies had a better understanding of the physical world than Piaget had suggested.
She proposed that the lack of understanding of object permanence could be explained differently→ for example young babies might lack the necessary motor skills to pursue a hidden object or they may just lose interest because they are easily distracted.
Violation of expectation research
Baillargeon needed new techniques to investigate her belief in b____' s____ a____.
what is the technique she developed?
Baillargeon (2004) explains VOE as follows: 'In a typical experiment, [babies] see two test events - an e_____ event, which is c____ with the e____ examined in the experiment, and an u_____ event, which v____ this e____.
So if the VOE method is used to test o____ p____, infants will typically see two c___ in which o___ pass in and out of s___.
Violation of expectation research
Baillargeon needed new techniques to investigate her belief in babies' superior abilities.
One of the techniques she developed is the violation of expectation (VOE) method.
Baillargeon (2004) explains VOE as follows: 'In a typical experiment, [babies] see two test events - an expected event, which is consistent with the expectation examined in the experiment, and an unexpected event, which violates this expectation.
So if the VOE method is used to test object permanence, infants will typically see two conditions in which objects pass in and out of sight.
Violation of expectation research
In an early VOE experiment B______ and G____ (19___) showed ___ babies, aged _-__ months, a what? passing behind a screen with a window.
In the familiarisation event , a baby is what? disappearing as they pass behind a screen - as fits our expectations of o_____ p_____.
why is the familiarisation event is shown first?
Violation of expectation research
In an early VOE experiment Baillargeon and Graber (1987) showed 24 babies, aged 5-6 months, a tall and a short rabbit passing behind a screen with a window.
In the familiarisation event , a baby is shown a short rabbit and a tall rabbit disappearing as they pass behind a screen - as fits our expectations of object permanence.
The familiarisation event is shown first to help the infant become used to the objects and the basic situation. it allows infants to understand the setup (screen, window, rabbits).
Violation of expectation research
After, the familiarisation event, there are two conditions - what are these conditions
Violation of expectation research
After, the familiarisation even, there are two conditions :
the expected event
the unexpected event
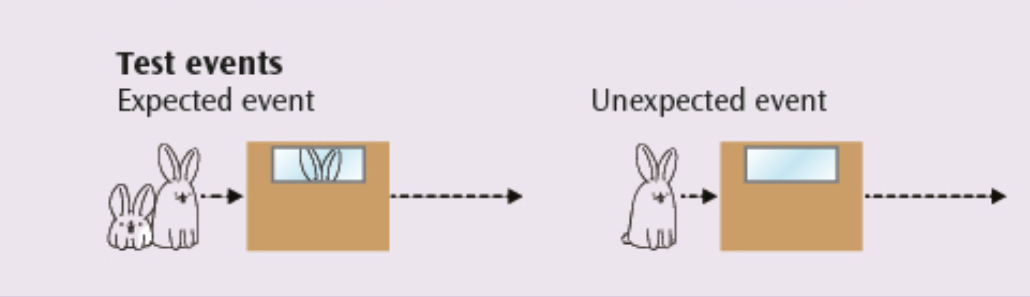
Violation of expectation research → expected event
what could the 2 expected events be?
Violation of expectation research → expected event
where a short rabbit passes behind a screen with a window and, because the height of the window, the short rabbit is not visible until it appears on the other side
OR
the another expected event might also be the tall rabbit passing behind the window and being seen.

Violation of expectation research → unexpected event
what’s the unexpected event
how would a baby with object permeance react?
Violation of expectation research → unexpected event
the tall rabbit would not be seen through the window as it moves from one side of the screen to other
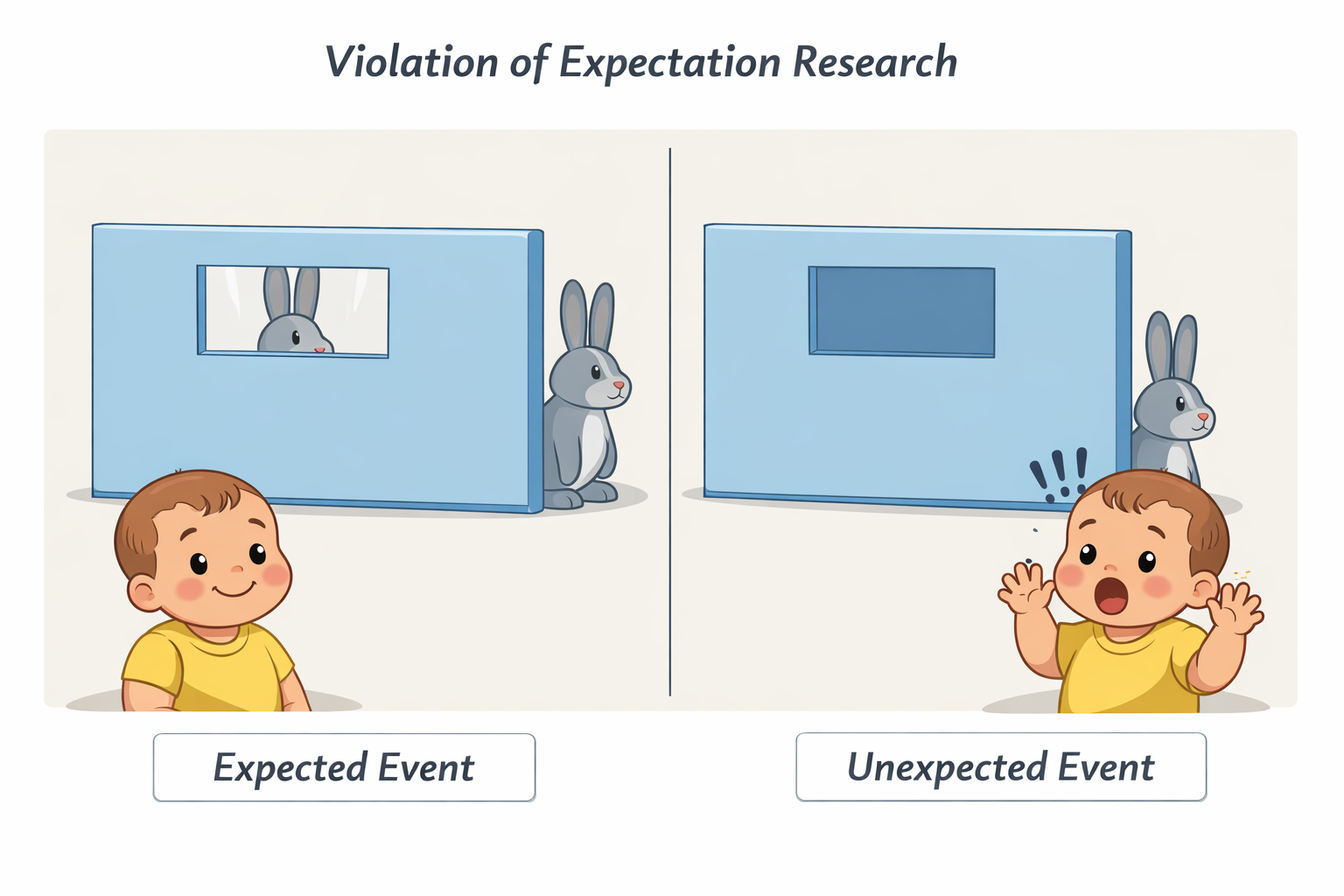
a baby with object permeance would show surprise when shown the unexpected event as it shows the baby understands that objects continue to exist even when they cannot be seen.
Violation of expectation research → Findings
The babies looked for an average of ____ seconds at the u____ event compared to ____ seconds at the e_____ event.
The researchers interpreted this as what?
For them to be surprised it follows that they must have known what?
(✘- what is a limitation that arises here?)
Violation of expectation research → Findings
The babies looked for an average of 33 seconds at the unexpected event compared to 25 seconds at the expected event.
The researchers interpreted this as meaning that the babies were surprised at the unexpected condition.
For them to be surprised it follows that they must have known that the tall rabbit should have reappeared at the window. This demonstrates a good understanding of object permanence.
( ✘ - A key limitation of violation is that it relies on subjective interpretation of infants’ behaviour. The researchers assume that longer looking times indicate surprise and therefore understanding of object permanence. However, infants may look longer at the unexpected event for alternative reasons, e.g visually interesting, rather than because it violates their expectations.)
other research
The Baillargeon and Graber study with the rabbits is an example of an occlusion study → what does this mean?
VOE experiments have also been used to test infant understanding of containment and support.
what does containment mean?
what does support?
In all these cases infants have shown that they pay more attention to u___ (impossible) events and so appear to have a good understanding of the p____ w____ (H_____ and B_____ 2008).
other research
The Baillargeon and Graber study with the rabbits is an example of an occlusion study → when an object blocks another object from view so researchers can test whether babies understand the hidden object still exists
VOE experiments have also been used to test infant understanding of containment and support.
'Containment' is the idea that when an object is seen to enter a container it should still be there when the container is opened.
'Support' is the idea that an object should fall when unsupported but not when it is on a horizontal surface.
In all these cases infants have shown that they pay more attention to unexpected (impossible) events and so appear to have a good understanding of the physical world (Hespos and Baillargeon 2008).
Baillargeon's theory of infant physical reasoning
B_____ et al. (2012) proposed that humans are born with a P____ R_____ S_____ ( PRS) :
we are born hardwired with what 2 things?
Initially we have a p____ a____ of the p______ properties of the world and this becomes more s______ as we learn from experience
. One aspect of the world of which we have a c____( basic) understanding from birth is object p___.
This is roughly the same idea as what? and why?
Baillargeon's theory of infant physical reasoning
Baillargeon et al. (2012) proposed that humans are born with a Physical Reasoning System ( PRS) :
we are born hardwired with both a basic understanding of the physical world and also the ability to learn more details easily.
Initially we have a primitive awareness of the physical properties of the world and this becomes more sophisticated as we learn from experience
. One aspect of the world of which we have a crude( basic) understanding from birth is object persistence. (where’s piagets says it emerges later in infancy)
This is roughly the same idea as Piaget's object permanence - it is the idea that an object remains in existence and does not spontaneously alter in structure.
Baillargeon's theory of infant physical reasoning
Development of object persistence proceeds as follows:
in the first few weeks of life babies begin to i____ e____ c___ with each event category corresponding to one way in which o____ i____ → for example, occlusion events take place when?
Because a baby is born with a basic understanding of o____ p____ and quickly learns what., by the time they are tested in tasks like Baillargeon and Graber's VOE with tall and short rabbits, babies actually have a g____ u______ that the tall rabbit should a___ at the window.
so, why does The 'unexpected' event captures the baby's attention ?
Baillargeon's theory of infant physical reasoning,
Development of object persistence proceeds as follows:
in the first few weeks of life babies begin to identify event categories. with each event category corresponding to one way in which objects interact. → for example, occlusion events take place when one object blocks the view of another.
Because a baby is born with a basic understanding of object persistence and quickly learns that one object can block their view of another, by the time they are tested in tasks like Baillargeon and Graber's VOE with tall and short rabbits, babies actually have a good understanding that the tall rabbit should appear at the window.
The 'unexpected' event captures the baby's attention because the nature of their PRS means they are predisposed to attend to new events that might allow them to develop their understanding of the physical world.
evaluation of Baillargeon’s theory of infant abilities - strengths
✓- One strength of Baillargeon's research is the validity of the VOE method.
The VOE method is seen as more v____ and a l_____ of Piaget's research e.g - what assumption?
Piaget's method of studying o____ p____ cannot distinguish between this and what alternative possibility?
The VOE method overcomes this because 'd____' would not affect the outcome.
In the VOE the only thing being measured is what? - what would not be recorded?
This means that Baillargeon's VOE method has greater v____ than P____ because a confounding variable is c___. This also provides support for her theory explaining early cognitive development.
evaluation of Baillargeon’s theory of infant abilities - strengths
✓- One strength of Baillargeon's research is the validity of the VOE method.
The VOE method is seen as more valid and a limitation of Piaget's research e.g his assumption that when a baby loses interest in a hidden object they no longer believe it exists.
Piaget's method of studying object permanence cannot distinguish between this and the alternative possibility that the baby simply became distracted by other visual stimuli and therefore stopped looking in the original place.
The VOE method overcomes this because 'distraction' would not affect the outcome.
In the VOE the only thing being measured is how long the baby looks at the visual scene - looking away from the scene would not be recorded.
This means that Baillargeon's VOE method has greater validity than Piaget's because a confounding variable is controlled. This also provides support for her theory explaining early cognitive development.
evaluation of Baillargeon’s theory of infant abilities - strengths
✓- A further strength of Baillargeon's explanation is its ability to explain u____ understanding of the physical world.
H____ and V___ M____ (2012) point out we all have a very good understanding of what? regardless of c____ and p____ e____.
explain example of keys
This does not require past experience what?
This universal understanding suggests that a basic understanding of the physical world is i____. If it were not innate we would expect s_____ c____ and i____ d_____
This i____ basic understanding of the physical world suggests what is correct?
EXTENSION:
Baillargeon’s theory contributes to which side of the nature–nurture debate ?
evaluation of Baillargeon’s theory of infant abilities - strengths
✓- A further strength of Baillargeon's explanation is its ability to explain universal understanding of the physical world.
Hespos and Van Marle (2012) point out we all have a very good understanding of the basic characteristics of the physical world regardless of culture and personal experience.
For example, everyone understands that if we drop a key ring it will fall to the ground.
This does not require past experience of dropping keys or even a culture that makes use of keys.
This universal understanding suggests that a basic understanding of the physical world is innate. If it were not innate we would expect significant cultural and individual differences
This innate basic understanding of the physical world suggests that Baillargeon' PRS is correct.
EXTENSION:
Baillargeon’s theory contributes to the nature–nurture debate by supporting the nature side, as it suggests that core knowledge of the physical world is innate rather than learned through experience.
evaluation of Baillargeon’s theory of infant abilities - limitations
✘- One limitation of Baillargeon's research is the assumption that response to VOE is linked to u_____ and hence object permanence.
Piaget suggested that babies respond to u____ e____ but that this does not mean they truly understand it.
A further methodological issue is that babies' response may not even be to the u____ of the event.
All VOE shows is that babies find certain events more i____. We are i____ a link between this response and object permanence.
Although the different length of time spent looking at two different events may well reflect one being more interesting than the other, this may not be because the baby sees it as unexpected. It could be interesting for some other reason.
This means that the VOE method may not be an entirely valid way to study a veryyoung child's understanding of the physical world.
evaluation of Baillargeon’s theory of infant abilities - limitations
✘- One limitation of Baillargeon's research is the assumption that response to VOE is linked to unexpectedness and hence object permanence.
Piaget suggested that babies respond to unexpected events but that this does not mean they truly understand it.
A further methodological issue is that babies' response may not even be to the unexpectedness of the event.
All VOE shows is that babies find certain events more interesting. We are inferring a link between this response and object permanence.
Although the different length of time spent looking at two different events may well reflect one being more interesting than the other, this may not be because the baby sees it as unexpected. It could be interesting for some other reason.
This means that the VOE method may not be an entirely valid way to study a veryyoung child's understanding of the physical world.