Bio Final one big flashcards
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/398
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
399 Terms
1
New cards
Dorsal
Refers to the back of an organism
ex- dorsal fin on the back of a whale
ex- dorsal fin on the back of a whale
2
New cards
Ventral
Opposite of dorsal
refers to the front/chest area of an organism
refers to the front/chest area of an organism
3
New cards
Anterior
Refers to the head of an animal
4
New cards
Posterior
Refers to the butt of an organism
5
New cards
Lateral
Refers to the sides of an organism
6
New cards
Median
Refers to the middle of an organism
7
New cards
Mouth
Designed specifically to aid the body with the mechanical and chemical digestion of food. It does this by use of the teeth, salivary glands, and hard and soft pallates
8
New cards
Salivary Glands
Produce saliva and enzymes (that include Amylase) and adds water to the mouth. It’s fluids can be reused when saliva is swallowed.
9
New cards
Amylase
An enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (amylose)
Present in saliva and aids in the chemical digestion of starches
Present in saliva and aids in the chemical digestion of starches
10
New cards
Hard and soft pallate
Helps determine what we should and shouldn’t eat
Hard pallate is located in the front top of the mouth
Soft pallate is located in the back top of the mouth
The soft palate makes up the posterior third of the palate and is a posterior continuation of the hard palate. The soft palate consists of muscle fibers and connective tissue
The hard palate, which composes two-thirds of the total palate area, is a plate of bone covered by a moist, durable layer of mucous-membrane tissue
Hard pallate is located in the front top of the mouth
Soft pallate is located in the back top of the mouth
The soft palate makes up the posterior third of the palate and is a posterior continuation of the hard palate. The soft palate consists of muscle fibers and connective tissue
The hard palate, which composes two-thirds of the total palate area, is a plate of bone covered by a moist, durable layer of mucous-membrane tissue
11
New cards
Digestive System
Closed sytem
Food particles travel all the way through it
Acts as a long tube
Food particles travel all the way through it
Acts as a long tube
12
New cards
Excretory system
The purpose of this system is to remove toxins
13
New cards
Pharynx
The connection between the mouth and nose
The reason why some people are mouth breeders
Can cause fluids to come out of your nose when you laugh
The reason why some people are mouth breeders
Can cause fluids to come out of your nose when you laugh
14
New cards
Nasopharynx
The space posterior to the nasal cavities and soft pallate
contiguous with the Oropharynx
contiguous with the Oropharynx
15
New cards
Oropharynx
Throat
Space posterior to the mouth
Posterior extension of the Nasopharynx
Space posterior to the mouth
Posterior extension of the Nasopharynx
16
New cards
Esophogus
Long tube made out of smooth muscle
It’s porcess of peristalsis pushes food through the digestive system, making it so you could technically eat upside down
No digestion takes place inside of it
Can be found in dissection by reaching down the mount with a blunt probe
Located behind the trachea
It’s porcess of peristalsis pushes food through the digestive system, making it so you could technically eat upside down
No digestion takes place inside of it
Can be found in dissection by reaching down the mount with a blunt probe
Located behind the trachea
17
New cards
Liver
Located right below the ribcage
One of the two organs in the body that can regenerate
helps to detoxify our blood, making it part of the circulatory system as drugs brought into the bloodstream have to be detoxified by the liver
Serosis can occur when too high a consumption of alchohol over a lifespan causes this organ to stop working
Produces a ton of enzymes (such as alchohol dehydrogenase) that aid the digestive system to break down things into simple parts for the body to use
Produces the digestive fluid Bile
Important for chemical digestion
Involved in excretion, digestion, and circulation
Presence of processed foods cause trouble in the organ
One of the two organs in the body that can regenerate
helps to detoxify our blood, making it part of the circulatory system as drugs brought into the bloodstream have to be detoxified by the liver
Serosis can occur when too high a consumption of alchohol over a lifespan causes this organ to stop working
Produces a ton of enzymes (such as alchohol dehydrogenase) that aid the digestive system to break down things into simple parts for the body to use
Produces the digestive fluid Bile
Important for chemical digestion
Involved in excretion, digestion, and circulation
Presence of processed foods cause trouble in the organ
18
New cards
Bile
\
Digestive fluid produced in liver and stored in the gallbladder that helps to break down lipids
Digestive fluid produced in liver and stored in the gallbladder that helps to break down lipids
19
New cards
Gallbladder
Injects Bile through the duodenum giving it a green cover. This organ is located on the right side of the liver and looks like a little green pouch
20
New cards
Cardiac Sphincter
Connects the stomach to the esophogus
Located next to the heart
Inflamation of this results in what is known as heartbearn
Located next to the heart
Inflamation of this results in what is known as heartbearn
21
New cards
Pyloric Sphincter
located between the stomach and the small intestine, specifically at the junction of the stomach's pylorus and the duodenum. It regulates the flow of partially digested food from the stomach into the small intestine
22
New cards
Stomach
Found right behind the ribs on the left side of the body
Has a two way sphincter system
Has a Ph between 1-2 which allows it to de-nature food using enzymes and hydrochloric acid
Breaks down protein by using pepsin
Designed in a special way to make sure it does not digest itself
Has a mucus lining that could break down and cause ulcers
Like a washing machine that churns food around
Has a two way sphincter system
Has a Ph between 1-2 which allows it to de-nature food using enzymes and hydrochloric acid
Breaks down protein by using pepsin
Designed in a special way to make sure it does not digest itself
Has a mucus lining that could break down and cause ulcers
Like a washing machine that churns food around
23
New cards
Pepsin
Enzyme in the stomach that breaks down peptide bonds
Aids in the chemical digestion of protein
Aids in the chemical digestion of protein
24
New cards
Pancreas
An organ and gland
Produces insulin which regulates glucos level in the bloodstream
It’s insulin level can be properly maintained with a healthy diet
Part of digestive and endocrine systems
Chemical digestion only
Produces insulin which regulates glucos level in the bloodstream
It’s insulin level can be properly maintained with a healthy diet
Part of digestive and endocrine systems
Chemical digestion only
25
New cards
Exocrine Glands
Glands that inject hormones directly through a duct
26
New cards
Endocrine Glands
Glands that inject hormones directly into the blood
27
New cards
Insulin Insensitivity
When cells can’t respond to insulin, causing type 2 diabetes to occur.
28
New cards
Doudenum
First part of the small intestine
29
New cards
Small intestine
About 21 feet long
Where a majority of chemical digestion and absorption takes place
No mechanical digestion occurs, only chemical
Everything is broken down in the small intestine
Contains microvilli which aid in the absorption of nutriets
Where a majority of chemical digestion and absorption takes place
No mechanical digestion occurs, only chemical
Everything is broken down in the small intestine
Contains microvilli which aid in the absorption of nutriets
30
New cards
Microvilli
Increase the surface area of the walls of the small intestine and contain blood vessels and capilaries that absorb nutrients
31
New cards
Large Intestine(Colon)
Produces vitamin K with bacteria
Where water from food is absorbed
The last stop in the digestive system to pull stuff out of food
About 8 feet long
Includes the ascending(right) transverse, and descending colon(leads to the rectum)
Has a green color due to the reabsorption of bile
Where water from food is absorbed
The last stop in the digestive system to pull stuff out of food
About 8 feet long
Includes the ascending(right) transverse, and descending colon(leads to the rectum)
Has a green color due to the reabsorption of bile
32
New cards
Rectum
storage organ for feces until eliminated through the anus
33
New cards
Bladder
Stores urine
34
New cards
Kidney
Filters the blood to removes excess water and nitrogenous waste
Removes urea from urine, which is un-needed as it contains excess nitrogen
Removes salts
Removes urea from urine, which is un-needed as it contains excess nitrogen
Removes salts
35
New cards
Uriter
The connection between the kidney and the bladder
Accumulation of calcium salts in the uriter causes the formation of a kidney stone
Accumulation of calcium salts in the uriter causes the formation of a kidney stone
36
New cards
Absorption processes
\
absorption of drugs take place in stomach
absorption of nutrients take place in the small intestine
absorption of water takes place in the large intestine
absorption of drugs take place in stomach
absorption of nutrients take place in the small intestine
absorption of water takes place in the large intestine
37
New cards
Surface area to Volume relationships
High surface area of the microvilli allows food to be digested and absorbed
High surface area of alveoli allows for more gas exchange along the capillaries
High surface area of alveoli allows for more gas exchange along the capillaries
38
New cards
Excretory organs
\
bladder: right under umbilical flap of pig(excretes urine)
skin: excrete sweat and boils
lungs: excrete H2O and CO2
Kidney: excrete excess water and nitrogenous waste
Liver: excrete any of the toxins that we need to get out of our body
bladder: right under umbilical flap of pig(excretes urine)
skin: excrete sweat and boils
lungs: excrete H2O and CO2
Kidney: excrete excess water and nitrogenous waste
Liver: excrete any of the toxins that we need to get out of our body
39
New cards
Atria
The two upper chambers of the heart that receive and store blood from the veins and pump it into the ventricles. They are responsible for the contraction that fills the ventricles with blood.
40
New cards
Right ventricle
Passes blood into the pulmonary arteries
41
New cards
Left ventricle
Located on the biggest side of the heart and pumps blood to the whole body
42
New cards
Septum
Separation between left and right side of the heart
43
New cards
Heart valves
Structures within the heart that regulate blood flow by opening and closing in response to pressure changes. There are four valves in the heart: the tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve, mitral valve, and aortic valve. These valves ensure that blood flows in the correct direction through the heart and prevent backflow. Dysfunction of heart valves can lead to various cardiovascular diseases.
44
New cards
SA Node(pacemaker)
Sends an electric signal to the heart telling it to speed up or slow down
Like a band conducter for the heart
Like a band conducter for the heart
45
New cards
Aorta
Biggest artery in the whole body
Pumps oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body
The blood pumped out by the aorta exchanges oxygen for carbon dioxide and the system cardiovascular restarts itself
Pumps oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body
The blood pumped out by the aorta exchanges oxygen for carbon dioxide and the system cardiovascular restarts itself
46
New cards
Superior Vena Cava
On the top of the right side of the heart
Brings in de-oxygenated blood down from areas above the heart
Brings in de-oxygenated blood down from areas above the heart
47
New cards
Inferior Vena Cava
Bottom left of heart
Brings in blood coming from the feet/bottom of the body
Brings in blood coming from the feet/bottom of the body
48
New cards
Arteries
Push blood away from heart
49
New cards
Pulmonary arteries
Only arteries that carry de-oxygenated blood
Push blood from the heart to the lungs
Push blood from the heart to the lungs
50
New cards
Veins
Carry blood to the heart
51
New cards
Pulmonary Veins
Only veins that carry oxygenated blood
Carry blood from lungs to the heart
Carry blood from lungs to the heart
52
New cards
Capilaries
so thin that blood cells can go through one at a time
exchange of nutrients and waste between arteries and veins
exchange of nutrients and waste between arteries and veins
53
New cards
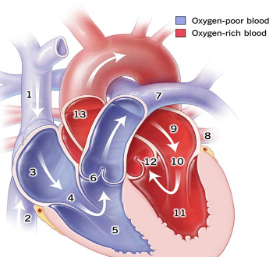
1
Superior Vena Cava
54
New cards
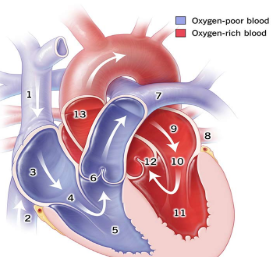
2
Inferior Vena Cava
55
New cards
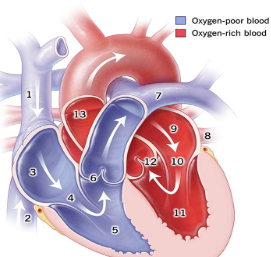
3
right atrium
56
New cards
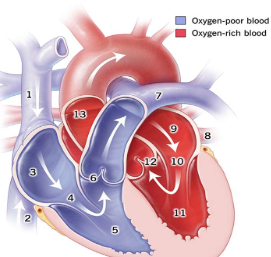
5
right ventricle
57
New cards
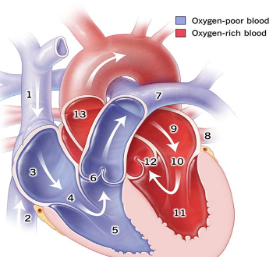
7
pulmonary artery
58
New cards
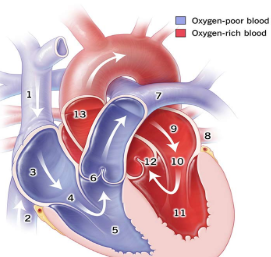
8
pulmonary vein
59
New cards
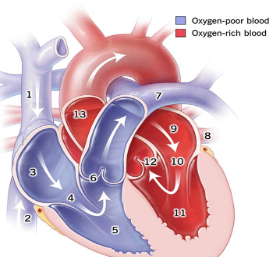
9
Left atrium
60
New cards
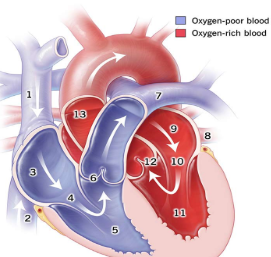
11
Left Ventricle
61
New cards
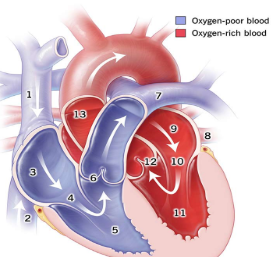
13
Aorta
62
New cards
Diastolic Pressure (80mmHg)
Heart pressure when the heart is relaxing
63
New cards
Systolic Pressure
\
when your heart is beating
higher pressure when heart contracts more
high pressure can be alleviated with diet and exercise
when your heart is beating
higher pressure when heart contracts more
high pressure can be alleviated with diet and exercise
64
New cards
Red blood cells function
Main function is to carry oxygen and carbon dioxide
65
New cards
White Blood Cell Function
Fighting infection
66
New cards
Platelets
Used to help form blood clots to slow or stop bleeding and to help wounds heal.
67
New cards
Trachea(windpipe)
Branches down into the lungs
cartilaginous springs can be felt from under the larynx
cartilaginous springs can be felt from under the larynx
68
New cards
Larynx(voicebox)
adams apple
sound gets transferred through when mouth is opened
sound gets transferred through when mouth is opened
69
New cards
Epiglottis
Tissue that covers up the windpipe to prevent choking on food
70
New cards
Bronchi
Branch off of the tree trunk to the lungs
71
New cards
Bronchioles
Brach off of left and right bronchi and carry oxygen through the lungs
72
New cards
Alveoli
The little air sacs at the end of bronchioli
73
New cards
Diaphragm
Tissue above liver
contracts during inspiration and relaxing during expiration
contracts during inspiration and relaxing during expiration
74
New cards
Axial skeleton
Looking at the skelton from head to tailbone, not related to appendages
75
New cards
Appendicual skeleton
related to appendages (arms, legs, shoulders)
76
New cards
Skeletal muscle
Muscle we usually eat
Any muscle involved in moving the skeleton
Voluntary muscles that the brain
Any muscle involved in moving the skeleton
Voluntary muscles that the brain
77
New cards
Smooth muscle
Makes up most organs and glands
Involuntary
Involuntary
78
New cards
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary muscle
Only covers the walls of the heart
Only covers the walls of the heart
79
New cards
Cartilidge
Protects the bones from grinding against eachother
80
New cards
Ball and Socket Joint
Found in shoulders and hips
Form allows for it to be rotated all around
Form allows for it to be rotated all around
81
New cards
Hinge joints
Simmilar to a door hinge
Found in knee and elbow, allowing for it to move up and down
Found in knee and elbow, allowing for it to move up and down
82
New cards
Pivot joints
Ex- neck
Allows movement from side to side
Allows movement from side to side
83
New cards
Saddle joints
Found in carpal bones and trapezium
help with grasps and allow the hands to be dexterious
help with grasps and allow the hands to be dexterious
84
New cards
endocytosis
when a cell takes in an external substance through the cell membrane by creating vesicles (sacks) to “hug” it in
85
New cards
exocytosis
to get rid of macromolecules that are too big for the cell, it releases macromolecules by fusing the vesicle with the plasma membrane
86
New cards
large cell size makes it…
hard to move nutrients into the cell
87
New cards
cells function best when
there is a larger surface area to volume ratio
88
New cards
small cell size makes it…
easy to absorb nutrients and excrete waste
89
New cards
unicellular organisms…
reproduce/clone asexually via cell division
90
New cards
multicellular organisms…
use cell division to grow and develop, and repair and renew cells once fully grown
91
New cards
interphase
when a cell grows and copies its DNA in prep for mitosis--90% of the cell cycle happens here
92
New cards
G1 phase “first gap”
cell growth and protein synthesis
93
New cards
S phase (synthesis)
dna replicated
94
New cards
G1/S Checkpoint
if cell does not pass cell cycle stops completely
Cell goes into senescence
Cell goes into senescence
95
New cards
G2 phase“second gap”
growth, protein synthesis, and organelle development
96
New cards
mitosis
division of nucleus, then division of cytoplasm (cytokinesis)
97
New cards
G2/M checkpoint
if cell does not pass, cycle stops to prepare DNA
98
New cards
G0 (senescence)
cell retirement home, waiting to die
99
New cards
apoptosis
cellular suicide…cell is damaged/gets signal proteins, shrinks, proteins help break down cell components, enzymes break down nucleus, cell parts removed from the body
100
New cards
in plant cells, vesicles form…
a cell plate