AP Environmental Science Unit 8
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
non-point source pollution
Are diffused and can therefore be difficult to identify, such as pesticide spraying and urban runoff.
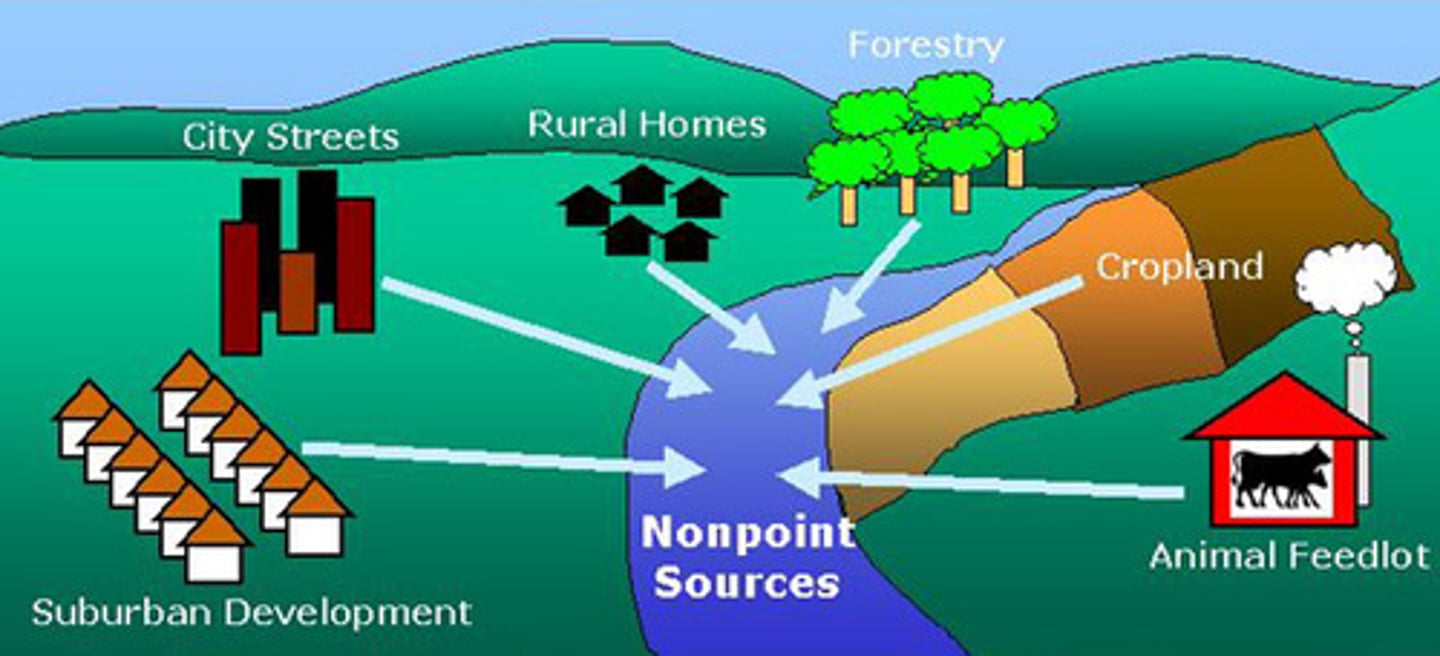
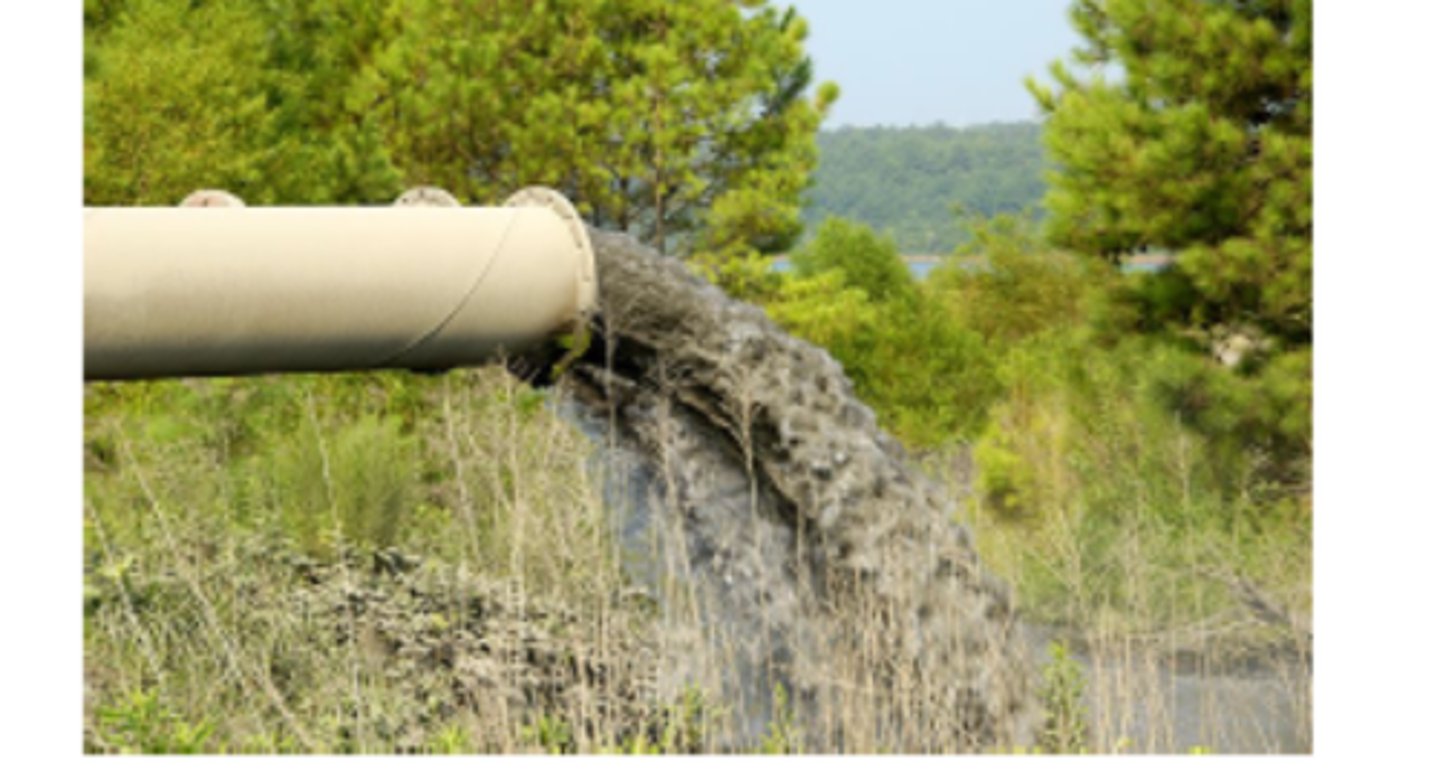
point source pollutant
Single, identifiable source of pollutant, such as a smokestack or waste disposal discharge pipe.

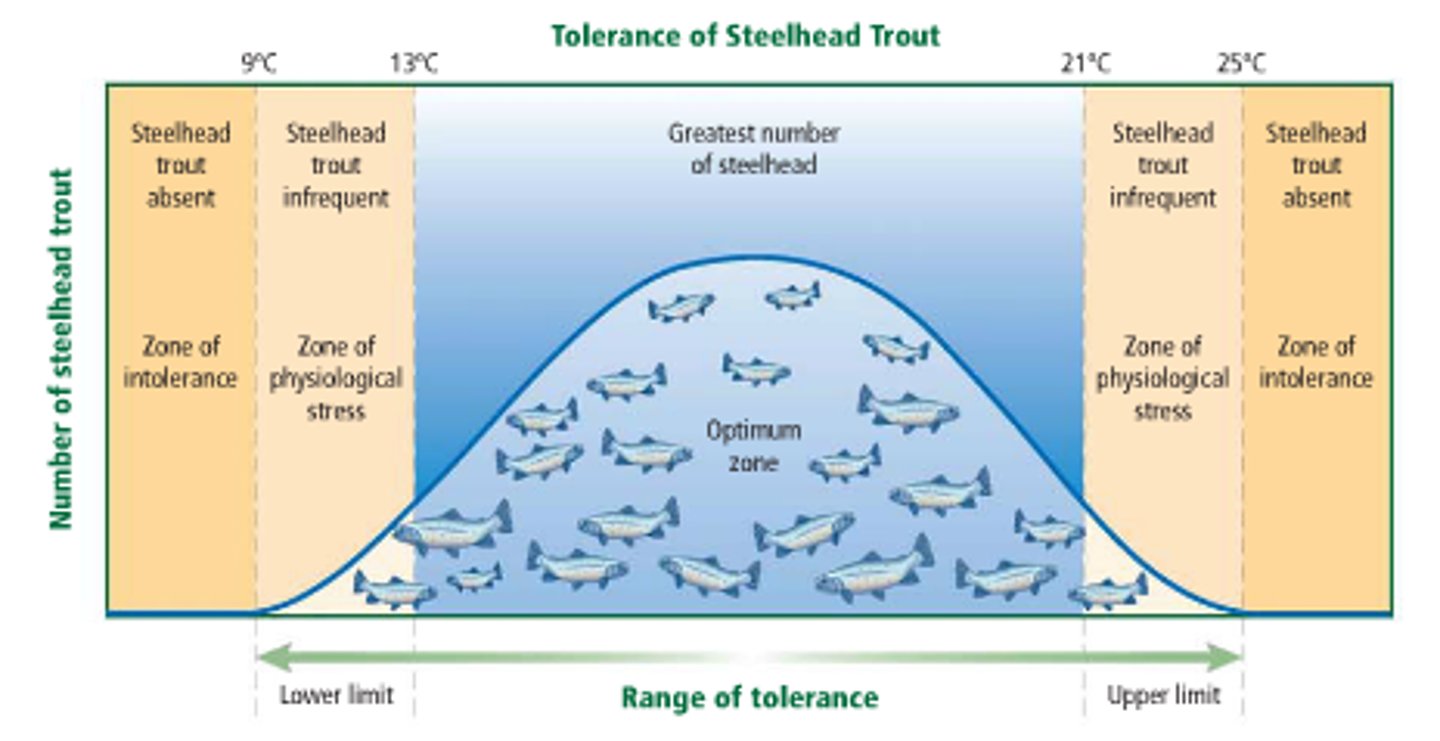
range of tolerance
the limits to the abiotic conditions that a species can tolerate
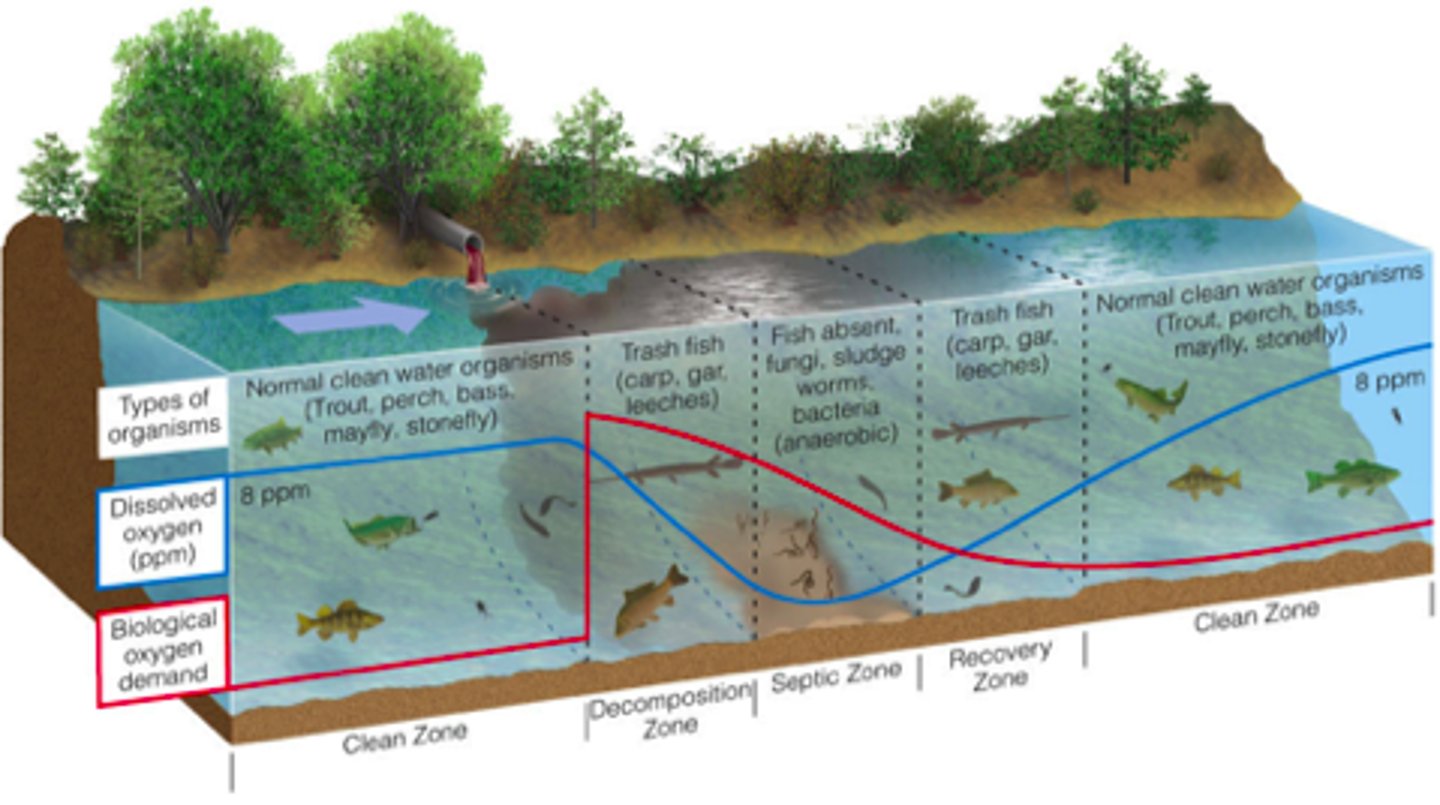
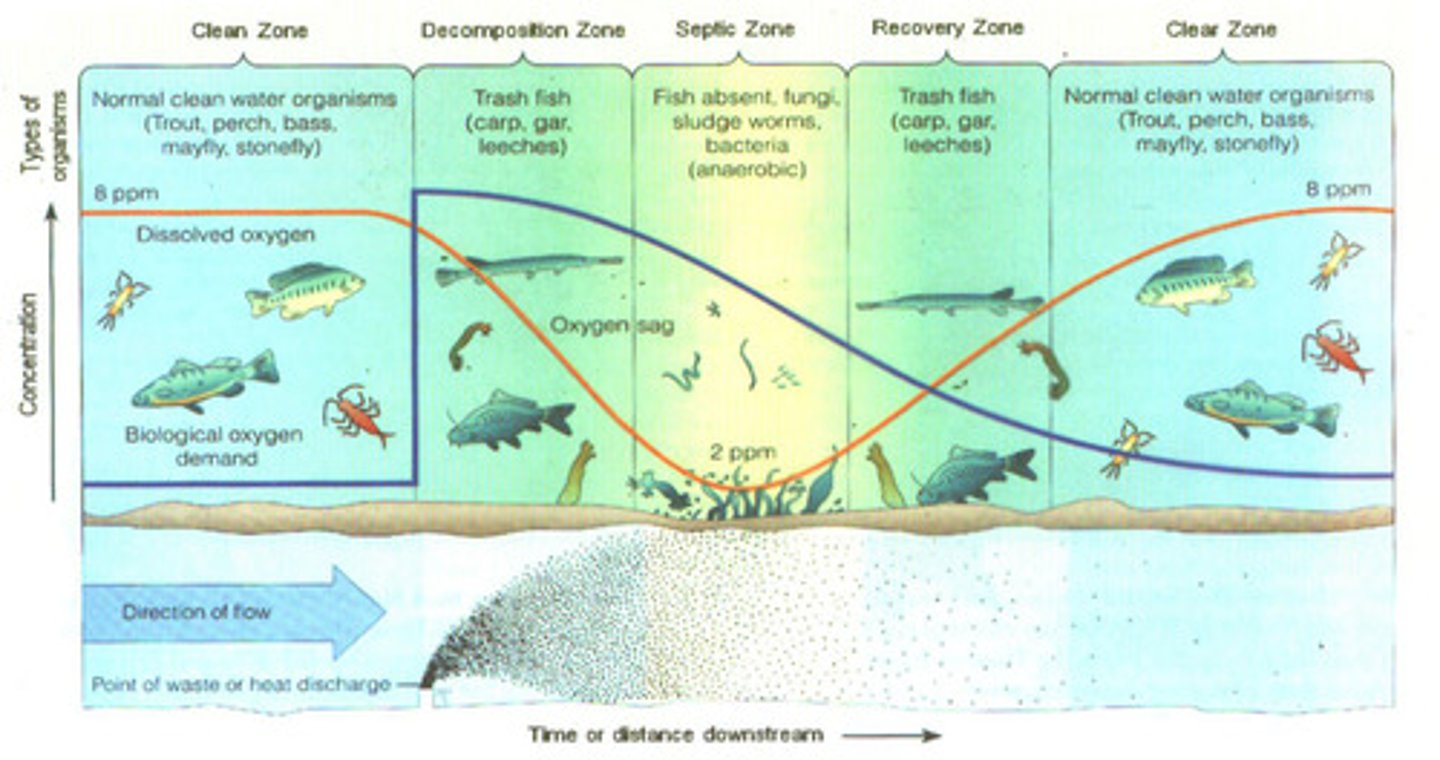
oxygen sag curve
is a plot of dissolved oxygen levels versus the distance from a source of pollution.
Oil Spill Mitigation Strategies
Clean up, burning, physical removal, chemical dispersants.
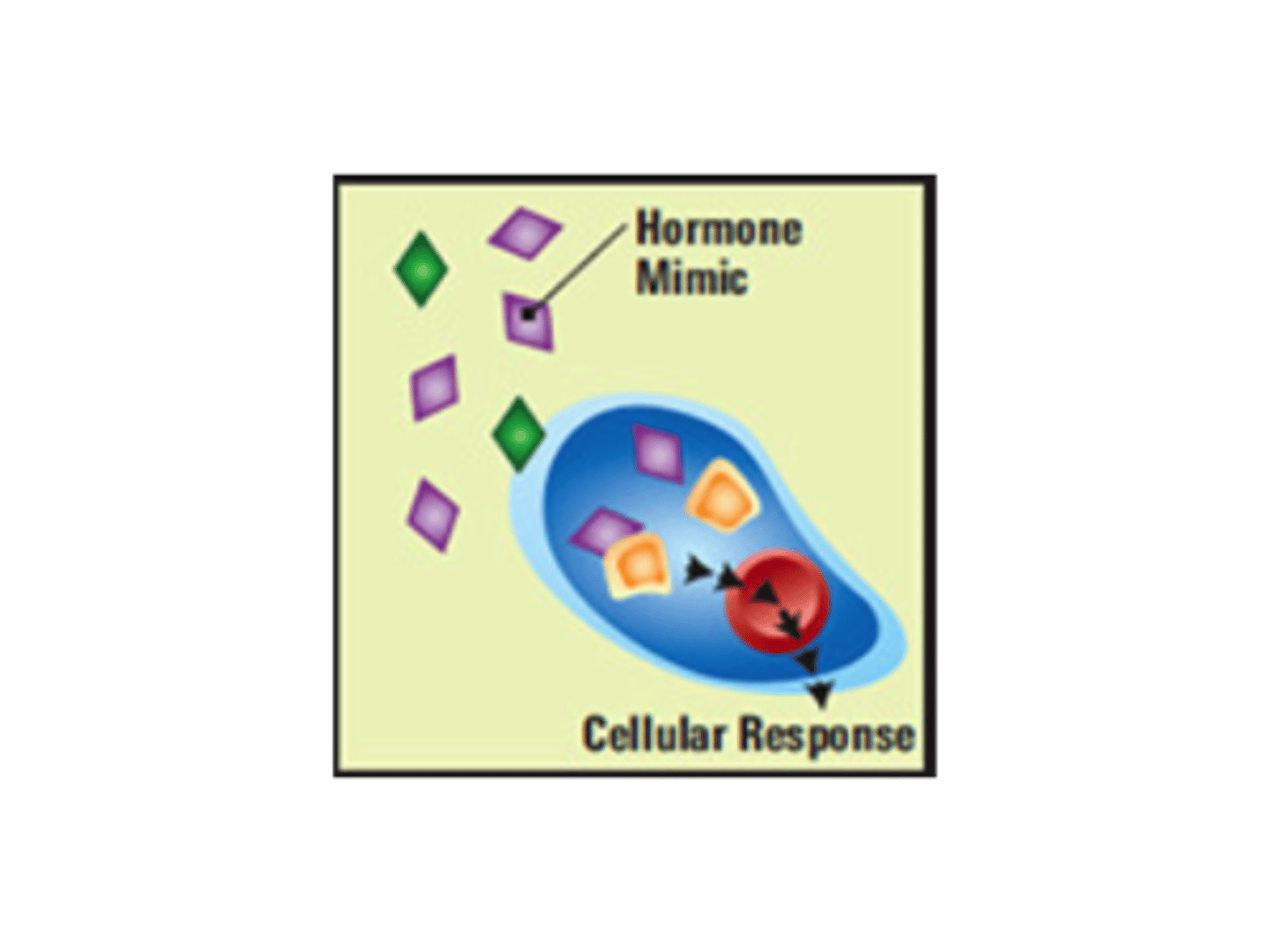
endocrine disruptors
chemicals that interfere with endocrine (hormonal) systems of animals. Endocrine disruptors bind to cell receptors meant for natural hormones, either blocking or amplifying the effects of the hormone.
Arsenic
a naturally occurring chemical element, found naturally in bedrock, used in the production of pesticides and wood preservatives, and causes poisoning
Lead
found in paint and its a neurotoxin and endocrine disrupter.
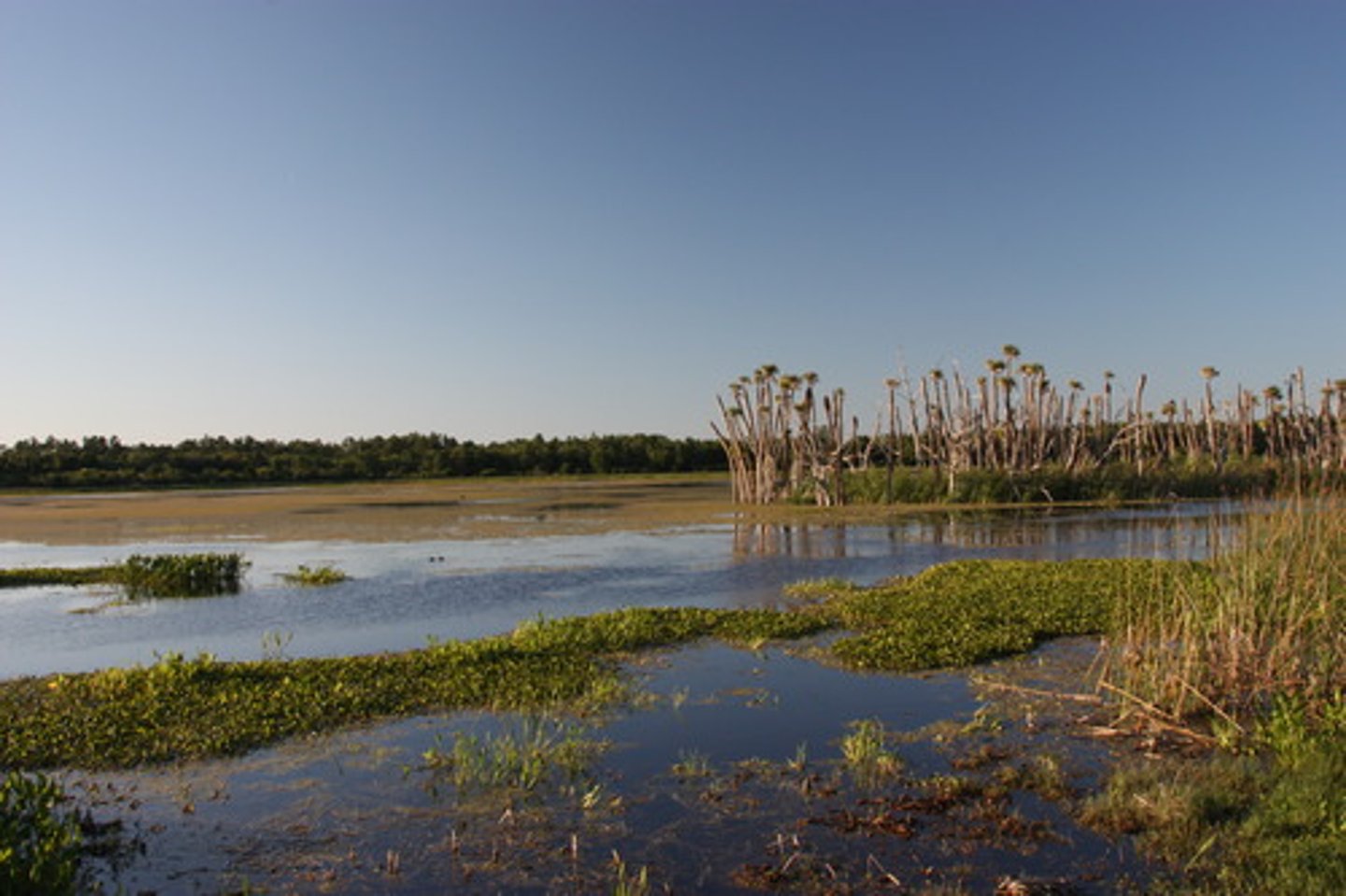
Wetlands
Areas with soil submerged/saturated plants in water for at least part of the year, but shallow enough for emergent plants.

ecosystem services
provisioning, regulating, supporting, cultural
provisioning services
products obtained from ecosystems
regulating services
benefits obtained from regulation of ecosystem processes
cultural services
The non-material benefits people obtain from ecosystems through recreation and aesthetic experience, etc.
supporting services
ecosystem services "that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services" - nutrient dispersal and cycling, seed dispersal, primary production
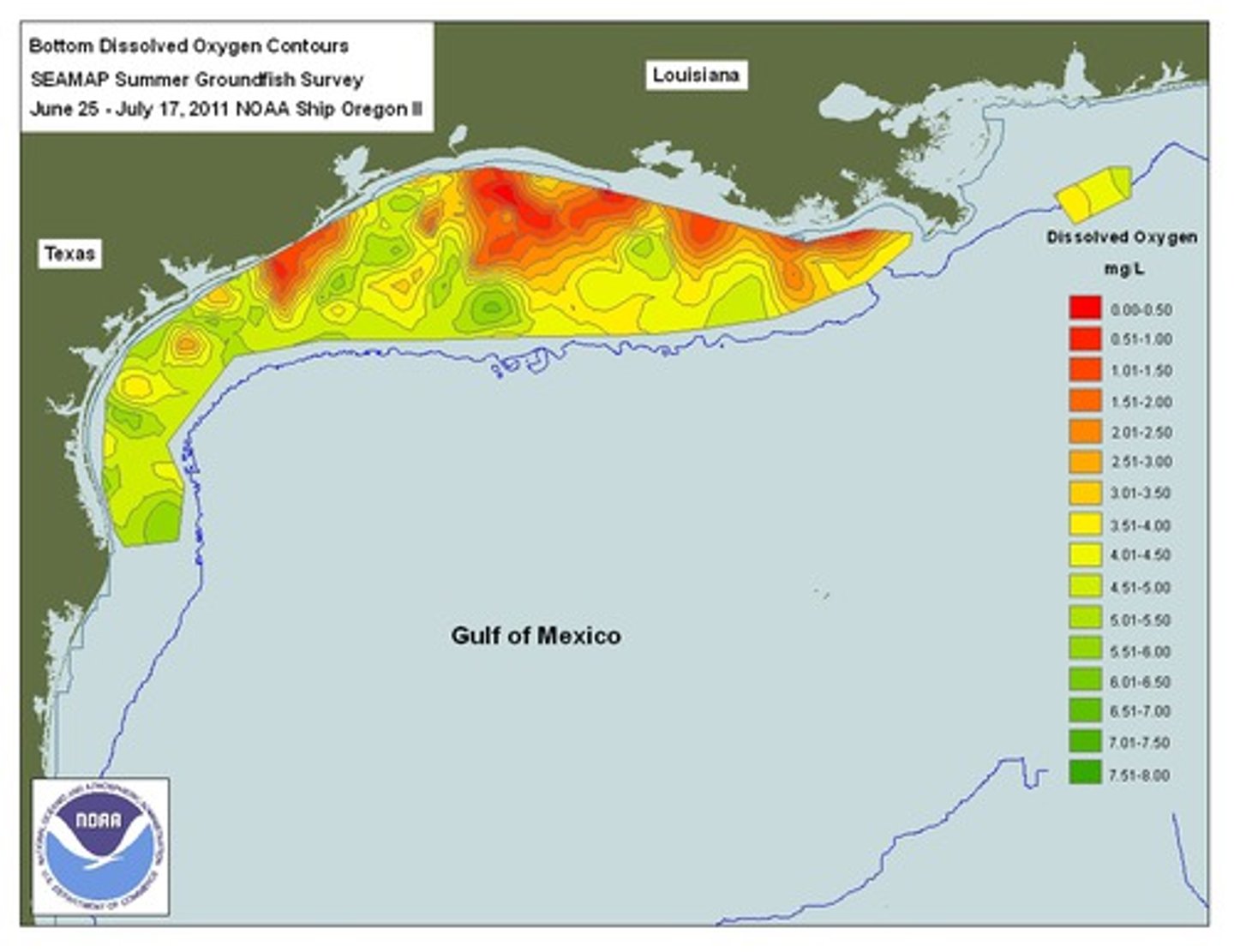
Hypoxic
low oxygen environment
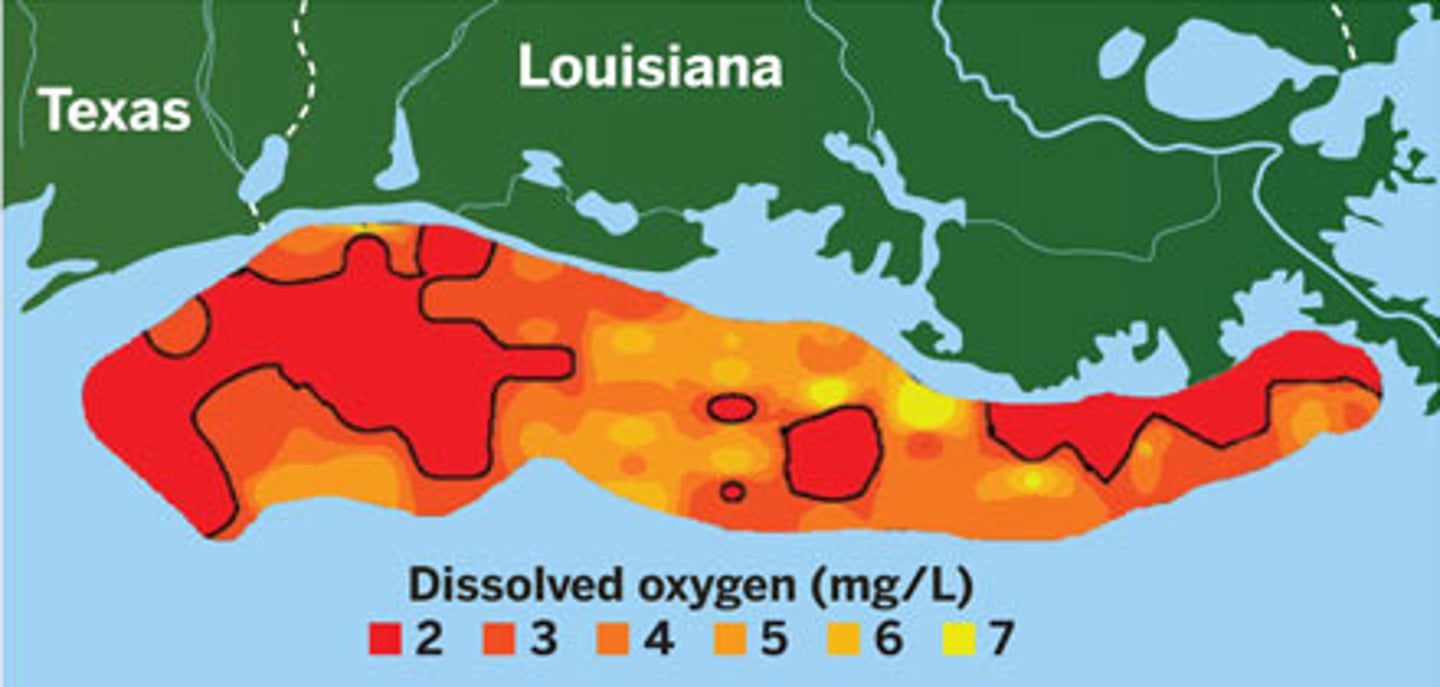
Eutrophic
A body of water with high nutrients
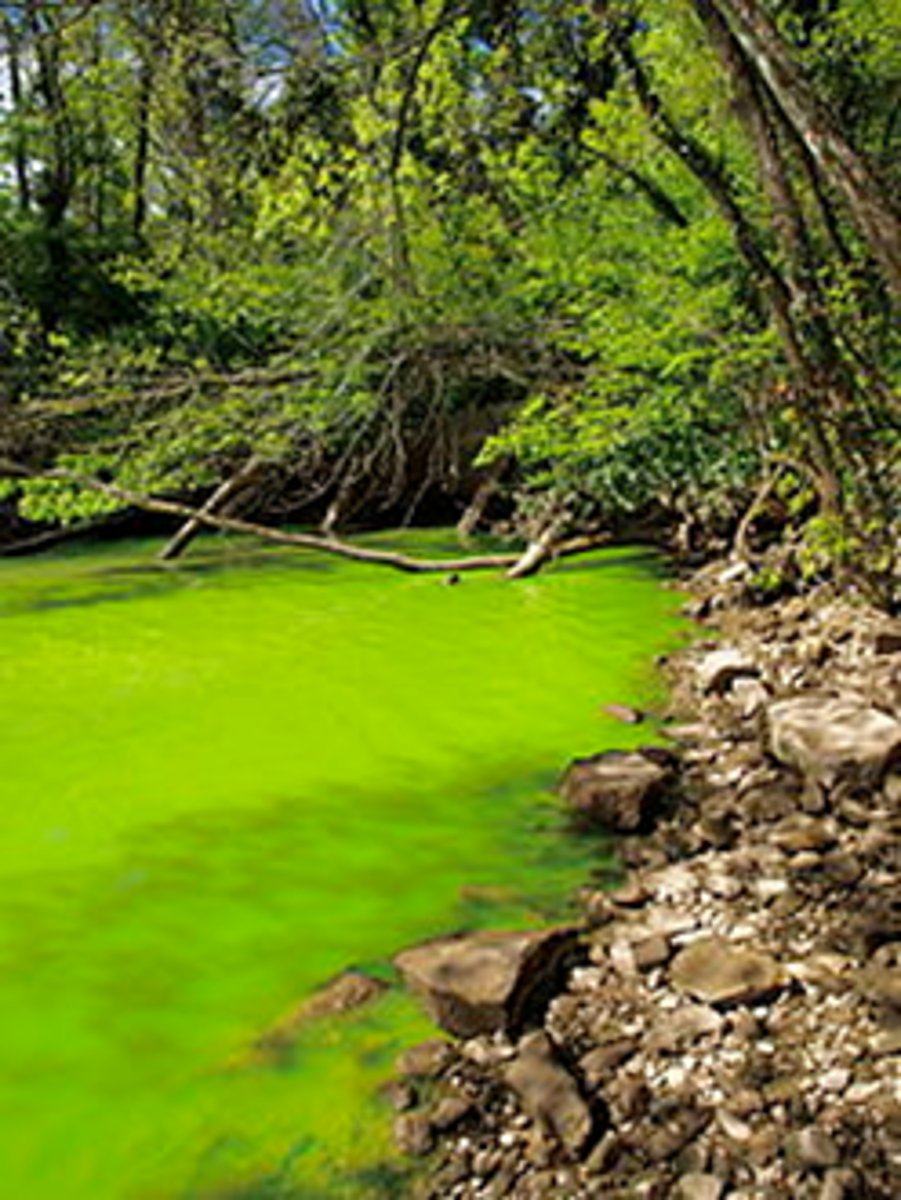

dead zone
In a body of water, an area with extremely low oxygen concentration and very little life.
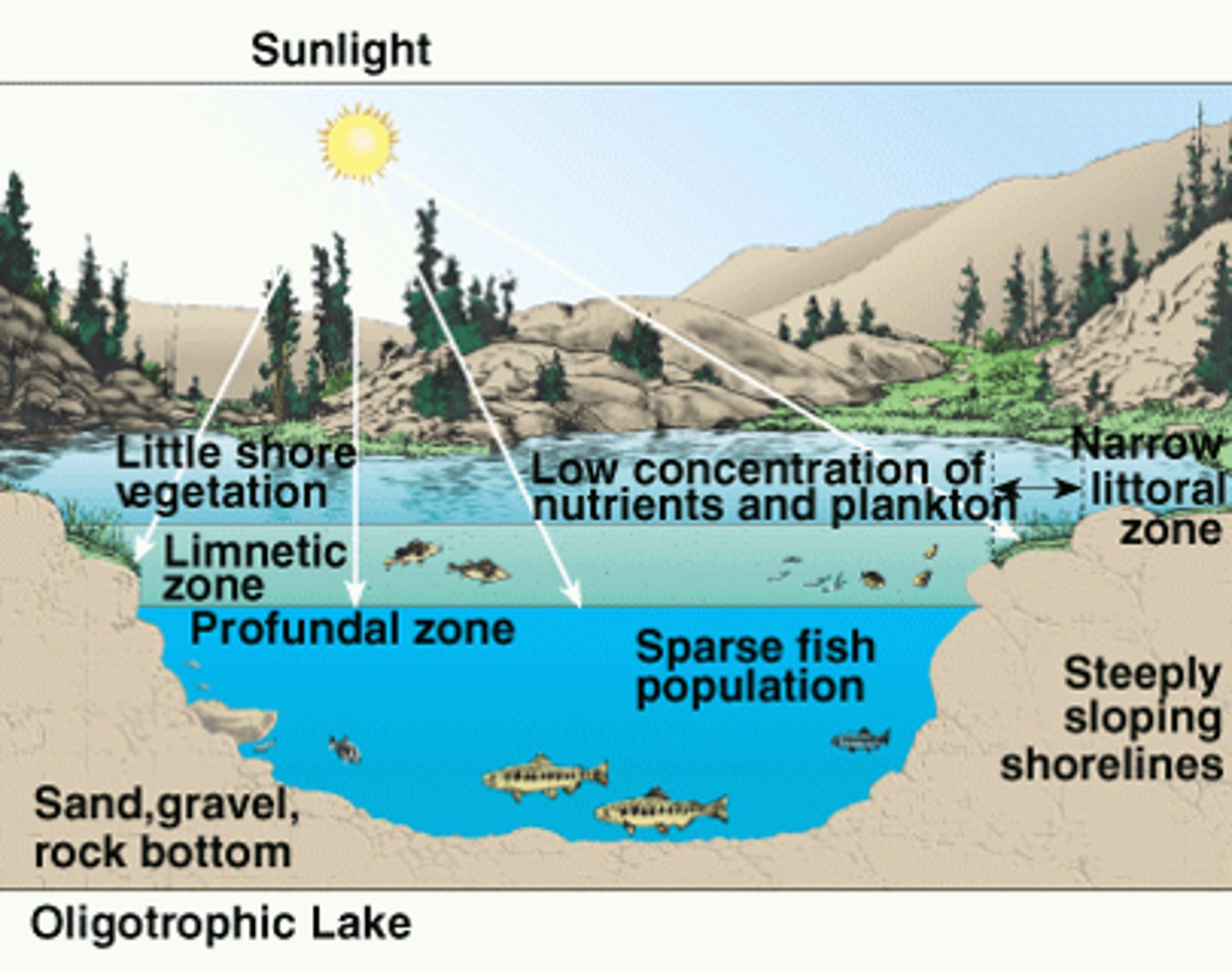
Oligotrophic
A body of water that is low in nutrients and high in dissolved oxygen.
algal bloom
The rapid growth of a population of algae
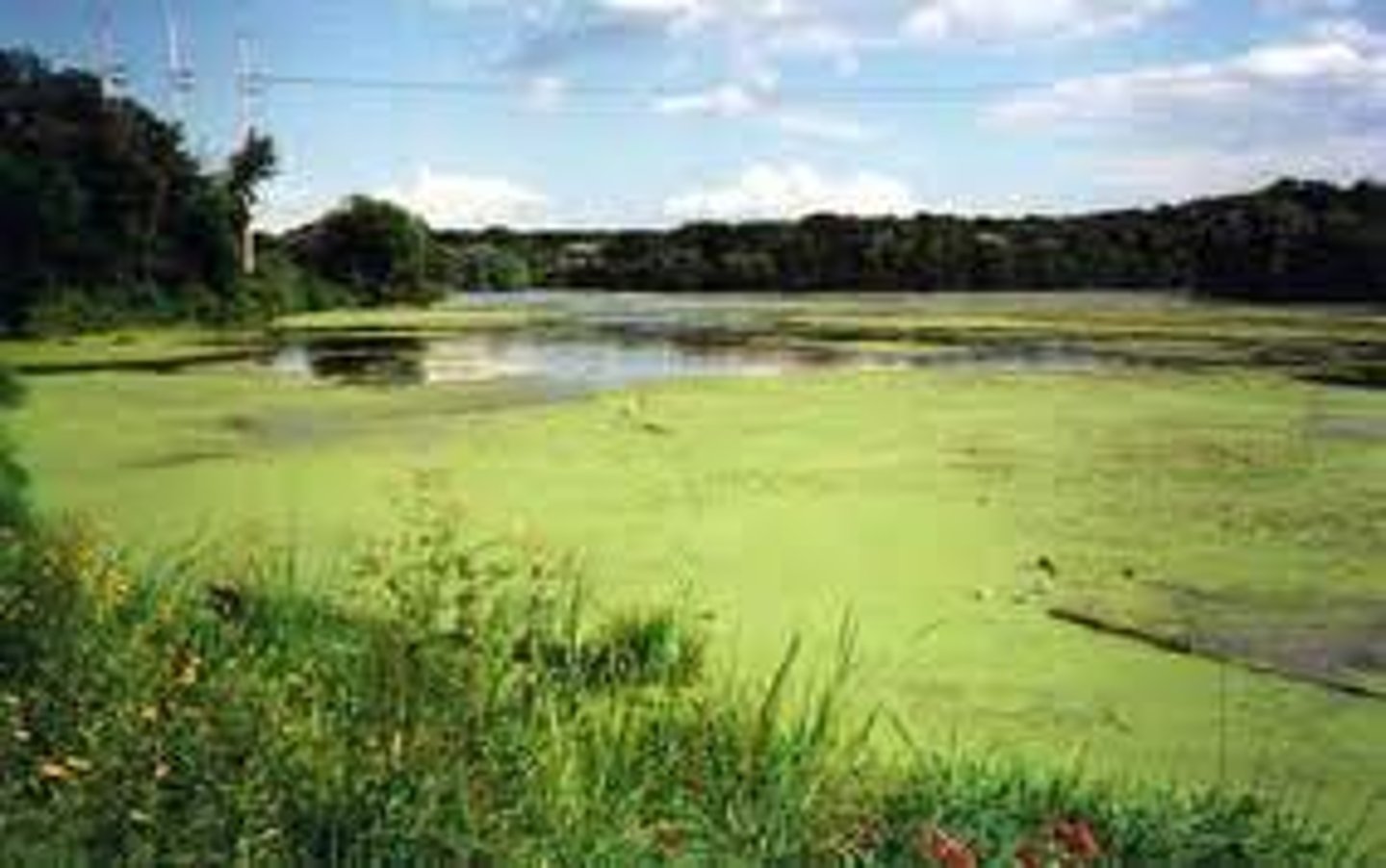

Biological Oxygen Demand
amount of dissolved oxygen needed by aerobic decomposers to break down organic materials
Eutrophication process
Nutrients into water
Increased plankton (algae) - GPP - algal blooms blanket water surface - increase in total biomass - increase in dead organic matter - increase in BOD - decline in O2 levels
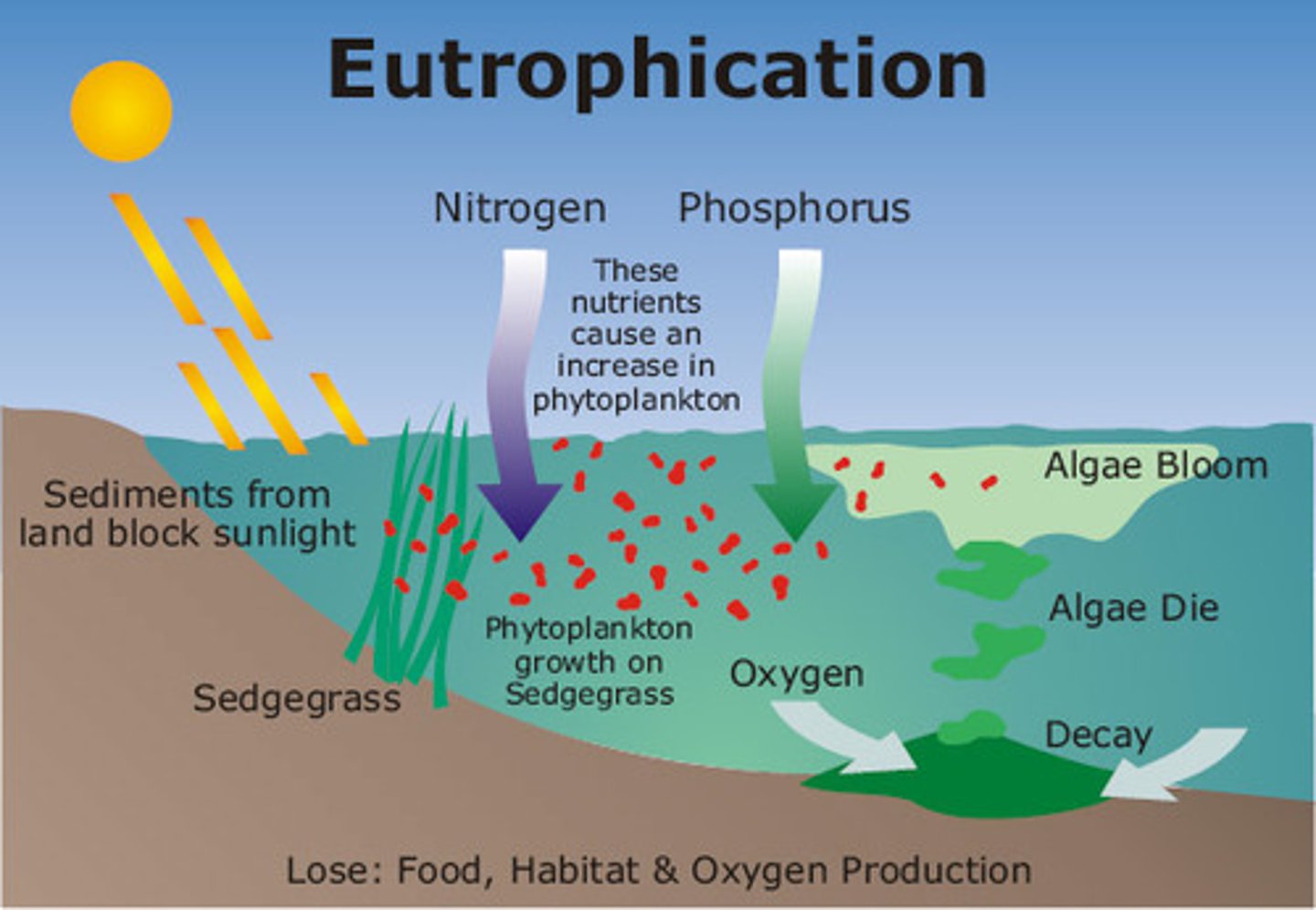
cultural eutrophication
is the process that speeds up natural eutrophication because of human activity. Sediments accumulate over time in the benthic zone.
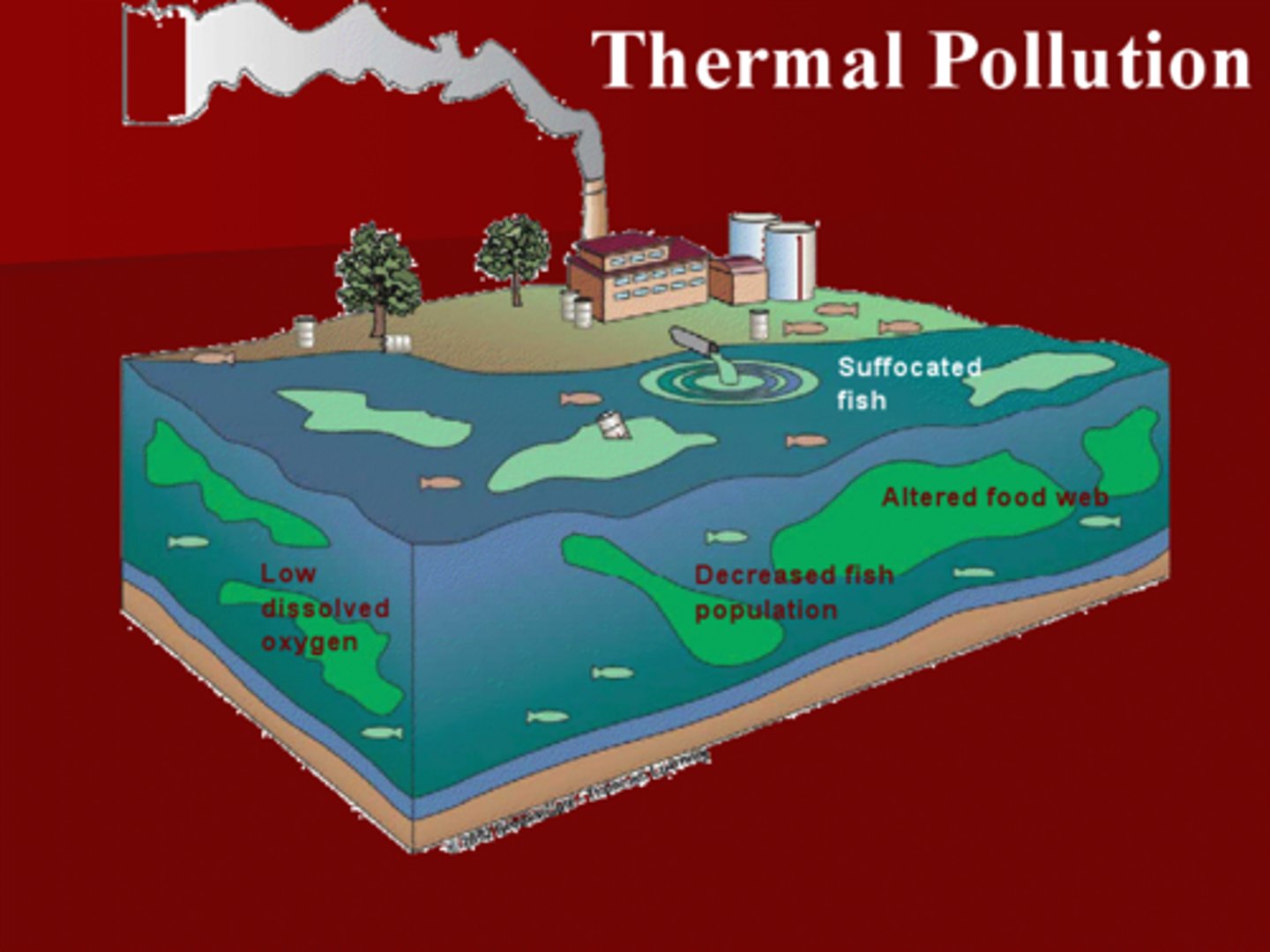
Thermal pollution
is a sudden increase or decrease in temperature of a natural body of water by human influence.
persistent organic pollutants (POPs)
Chemical compounds that persist in the environment and retain biological activity for a long time.

Characteristics of POPs
Persistent, toxic, synthetic, hydrophobic, etc.
DDT
an insecticide that is also toxic to animals and humans

PCBs
synthetic chemicals containing chlorine that are used in the manufacture of plastics and other industrial products, become stored in the tissue of animals, and also persist in the environment
Clean Air Act
Set emission standards for cars, and limits for release of air pollutants
Clean Water Act of 1972
Establishes and maintains goals and standards for U.S. water quality and purity. It has been amended several times, most prominently in 1987 to increase controls on toxic pollutants, and in 1990, to more effectively address the hazard of oil spills.
Safe Drinking Water Act (1974)
Establishes drinking water standards for tap water safety, and requires rules for groundwater protection from underground injection; amended in 1986 and 1996. The 1996 amendments added a fund to pay for water system upgrades, revised standard: setting requirements, required new standards for common contaminants, and included public "right to know" requirements to inform consumers about their tap water.
Resource Conservation and liability act (1980)
to address the problem of remediating abandoned hazardous waste sites, by establishing legal liability, as well as a trust fund for cleanup activities.
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Act (1976)
to clean up uncontrolled or abandoned hazardous-waste sites as well as accidents, spills, and other emergency releases of pollutants and contaminants into the environment. And the transportation of the hazardous waste
Bioaccumulation
The accumulation of a substance, such as a toxic chemical, in various tissues of a living organism.
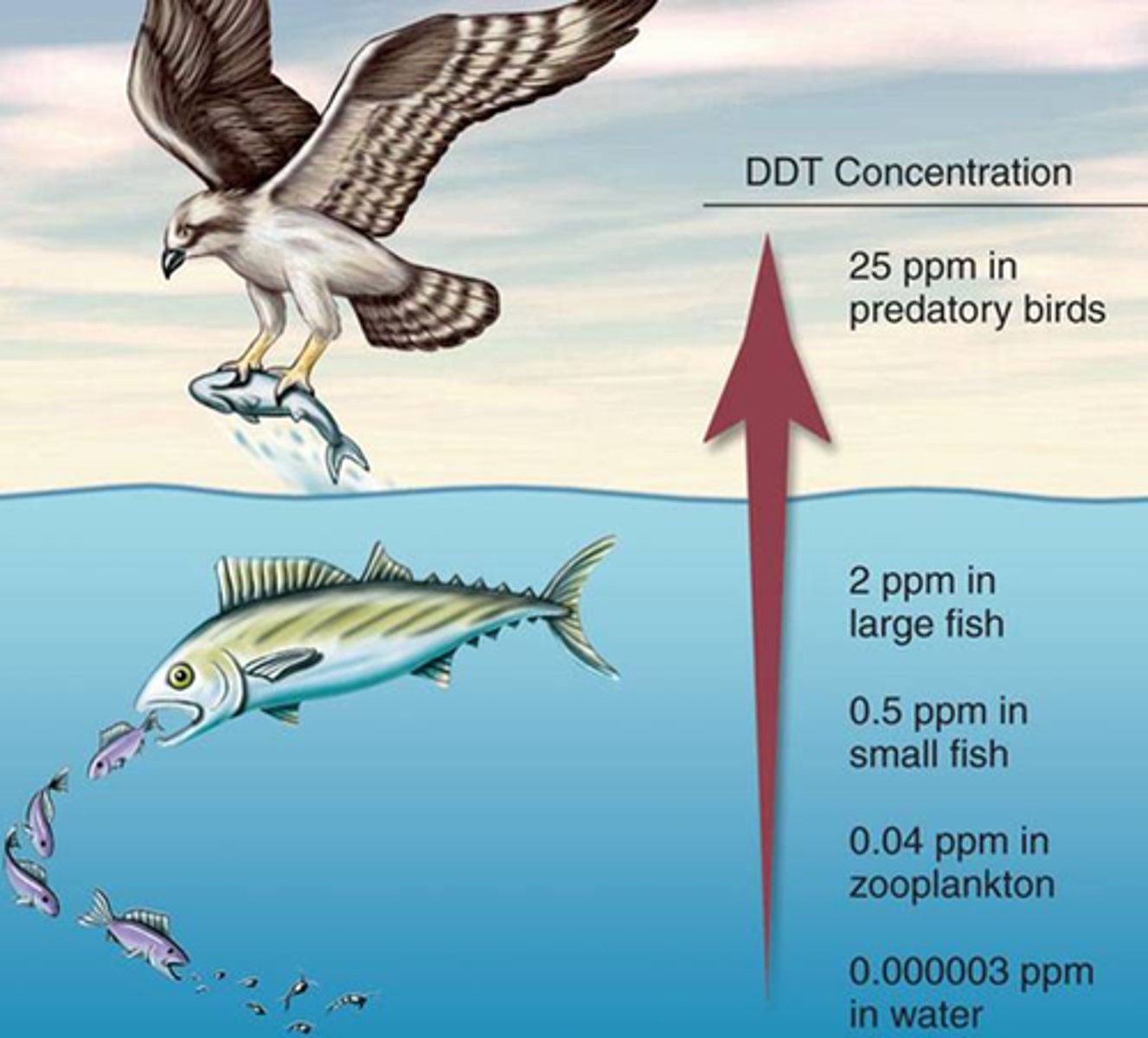
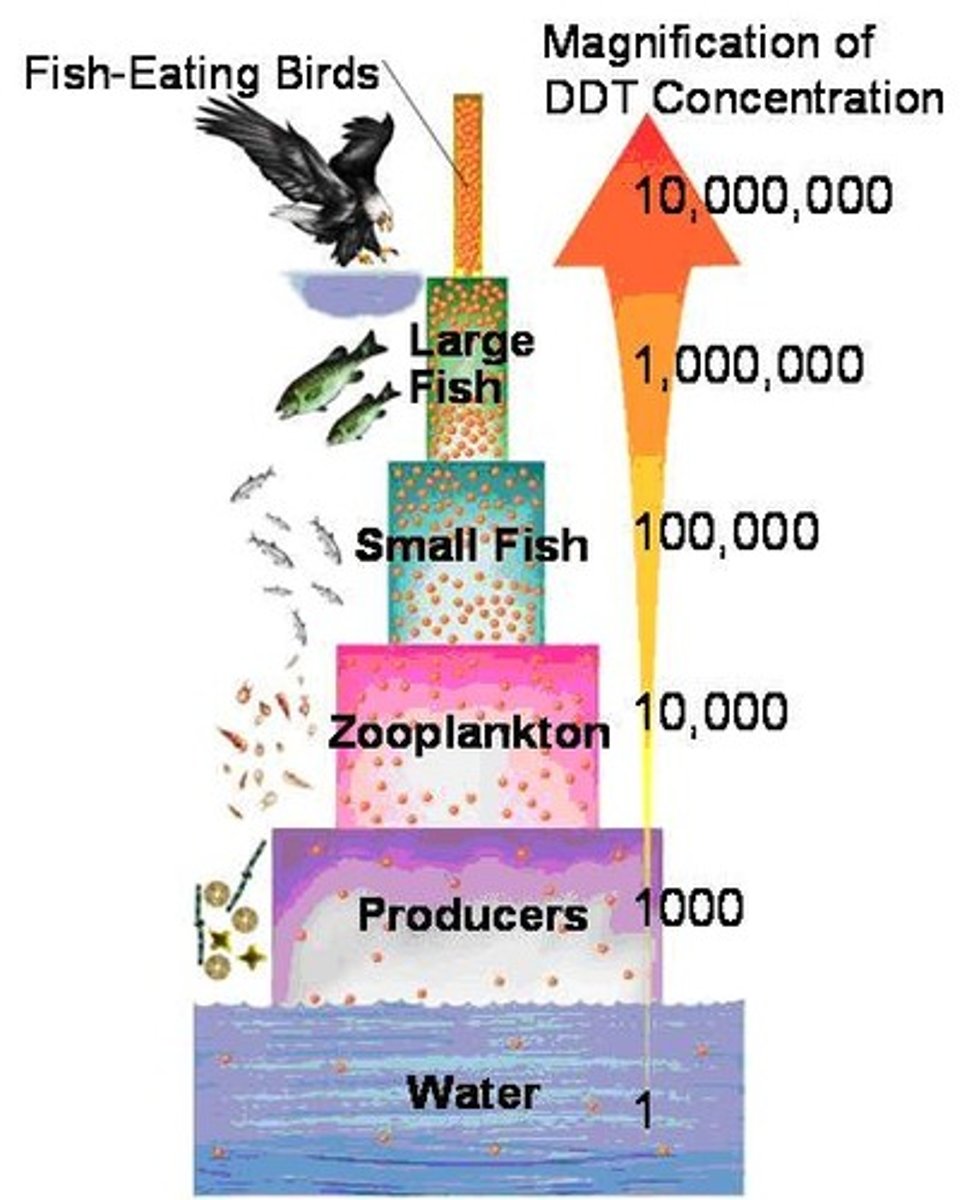
Biomagnification
accumulation of pollutants at successive levels of the food chain
Steps of wastewater treatment/sewage treatment
-Primary(physical removal of large debris)
-Secondary(biological breakdown of organic matter)
-Tertiary(chemical process of removing remaining pollutants)
-Disinfection(treated water is exposed to disinfectants)
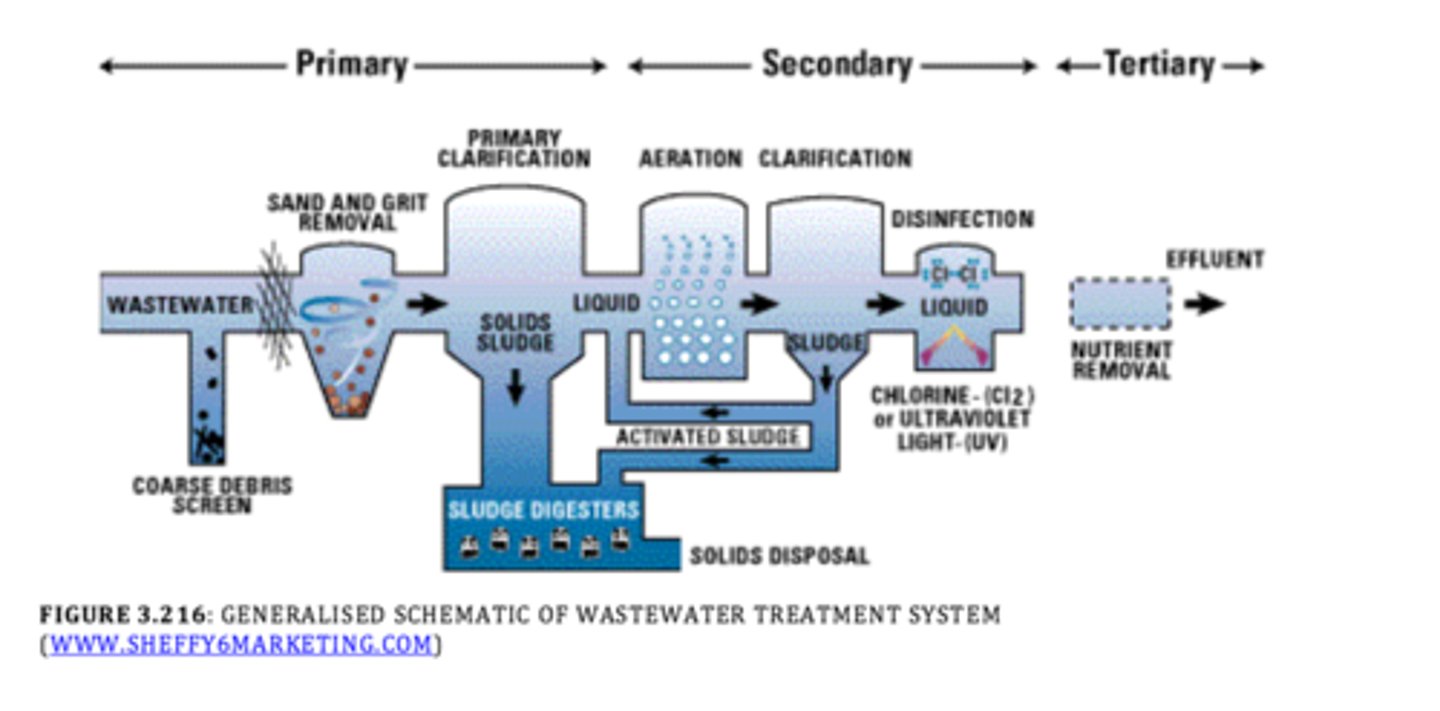
effluent
liquid waste or sewage discharged into a river or the sea.

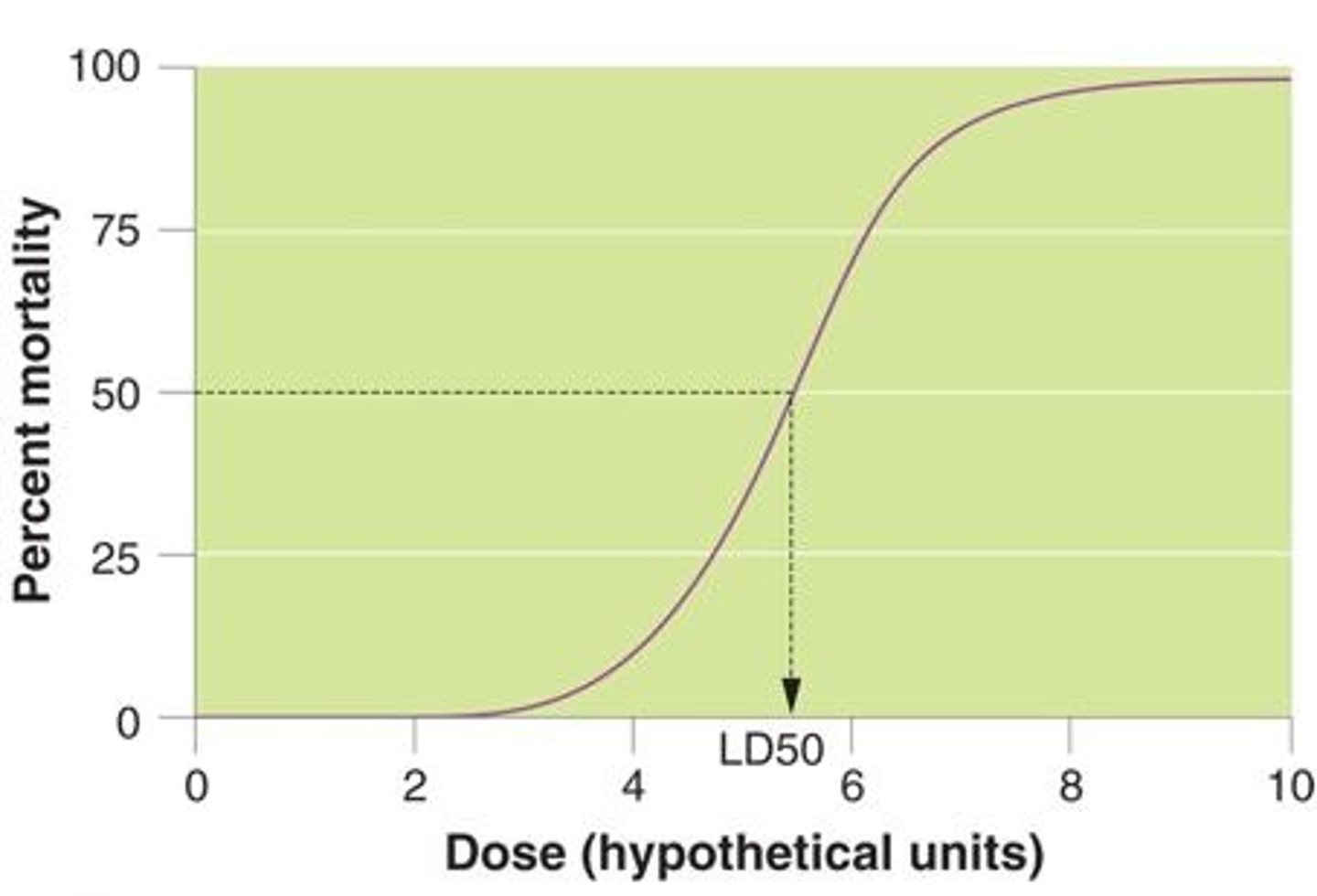
LD50
the amount of a chemical that kills 50% of the population being tested
Synergism
combination of two drugs causes an effect that is greater than the sum of the individual effects of each drug alone
dysentery
caused by human or animal fecal contamination of food or water. Causes intestinal inflammation
mesothelioma
Caused by inhaled asbestos fibers and causes shortness of breath and chest pain
Pathogens
disease causing agents
infectious disease
A disease that is caused by a pathogen and that can be spread from one individual to another.
non-infectious disease
a disease that cannot spread from one person to another
Vectors
Living organisms capable of carrying and transmitting infectious pathogens to other organisms.

Bubonic Plague
Caused by bacterium, flea bite, swollen lymph nodes.
Tuberculosis
An infectious disease that may affect almost all tissues of the body, especially the lungs. caused by bacterium
Malaria
A disease caused by mosquitoes implanting parasites in the blood.
West Nile Virus
spread to humans by the bite of an infected mosquito
Zika Virus
from mosquitoes
Cholera
an acute intestinal infection caused by ingestion of contaminated water or food
SARS
severe acute respiratory syndrome (virus)
COVID-19
A contagious viral respiratory disease that may cause serious complications, especially in people who are more than 60 years old and/or who already have serious health concerns.
DO
Dissolved Oxygen.