psych/neuro - Anticonvulsants
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
how can you measure seizure activity
EEG
what are the 3 key features of seizure classification?
1) where the seizure starts (onset)
2) pt level of awareness during a seizure
3) other symptoms during a seizure
why is understanding seizure onset important?
onset affects choice of seizure medication later on
what are the 2 categories of seizures?
(1) Focal (3-types)
(2) Generalized onset (2 major types)
what are the main types of focal seizures?
(1) focal aware
(2) focal impaired awareness
(3) focal to bilateral tonic-clonic convulsions (AKA grand mal = GTC)
what are the main types of generalized onset seizures?
(1) generalized onset w/ motor seizures (impaired awareness)
⚫️ generalized onset tonic-clinic "grand mal", "GTC"
(2) generalized onset w/ non-motor seizures (impaired awareness
⚫️ Childhood Absence Epilepsy (CAE)
____ of common epilepsies are drug-resistant
30-40%
what is the goal of therapy for ADEs
complete cessation of symptoms
what are subjective symptoms of epilepsy
seizures per pt and eyewitness report:
(1) motor
(2) non-motor
what are the motor symptoms of epilepsy
(1) stiffening (tonic)
(2) jerking (clonic)
(3) automatisms (lip-smacking, chewing, blocking)
what are non-motor symptoms of epilepsy
(1) sensory (visual, auditory, gustatory, olfactory)
(2) autonomic (increased HR, feeling in pit of stomach, nausea/vomiting)
(3) cognitive (sense of deja-vu)
what is focal onset w/o impaired awareness
starts with motor or non-symptoms + CAN remember events
what is focal onset w/ impaired awareness
starts with any motor or non-motor sx + CANNOT remember events (often progresses to "staring episodes" 1-2 minutes long)
what is focal-to-bilateral convulsions
(1) total loss of consciousness
(2) "flopping to ground"
(3) whole-body tonic-clonic convulsions, with tongue biting and urinary incontinence
what is generalized onset motor sxs
tonic-clonic
what is generalized onset non-motor sxs
short staring spellings 3-5 seconds long -> absence seizures are typical of childhood absence epilepsy (CAE)
what are objective clinical evaluation for epilepsy
(1) EEGs - gold standard for epilepsy diagnosis
(2) MRIs
what percent of the time will EEGs catch epilepsy
50%
does a single normal EEG rule epilepsy
no; need to repeat test 3x to be sure
what does a brain MRI show
abnormal brain damage (from stroke, traumatic brain injury)
does a normal MRI rule out epilepsy
no
epilepsy is a _______ diagnosis
clinical; not diagnosed by any single test
a diagnosis of epilepsy can be made if:
1) at least 2 unprovoked seizures occurring greater than 24 hours apart
2) 1 unprovoked seizure + 1 other finding
⚫️ (i.e. 1 seizure + abnormal EEG or MRI)
what are dose-related ASM side effects
(1) neurotoxic = sedation
(2) cognitive impairment
what is idiosyncratic ASM side effect
not dose related, can be severe
(1) rash progressing to SJS or TEN
(2) aplastic anemia (abnormal blood cells OR hepatotoxicity
what are long term ASM side effects
(1) gingival hyperplasia
(2) osteoporosis
what is the difference in efficacy of the >25 ASMs?
SIMILAR efficacy
what differs between ASMs
side effects, PK, DDIs
what are the steps when starting therapy for epilepsy
1) start with monotherapy first, check for side effects and efficacy
2) then try monotherapy with 2nd agent, check for side effects and efficacy
3) then try dual and combination therapies, check for side effects and efficacy
what are the first gen ASMs
(1) Carbamazepine
(2) Clonazepam
(3) Ethosuximide
(4) Phenytoin
(5) Phenobarbital
(6) Primidone
(7) Valproic Acid (Depakene)
-"C2E3PvalprOic"
Carbamazepine
(0) Indication + Generation
(1) Efficacy
(2) Comorbid conditions
(3) Side Effects
(4) DDI
(5) Therapeutic Range
Carbamazepine
(0) Indication: epilepsy - 1st gen ASM
(1) Efficacy: narrow: may exacerbate generalized sz d/o including CAE
(2) Comorbid conditions:
⚫️mood stabilizer (bipolar d/o)
⚫️trigeminal neuralgia
(3) Side Effects
⚫️ hepatotoxicity, hyponatremia
⚫️ idiosyncratic rash in Asians (risk of SJS/TEN) gene testing required
(4) DDI: INDUCER
⚫️ auto-induction (induces its OWN metabolism)
(5) Therapeutic Range: TMD required (narrow TR)
Ethosuximide
(0) Indication + Generation
(1) Efficacy
(2) Therapeutic Range
(3) Side effects
Ethosuximide
(0) Indication: epilepsy - 1st gen ASM
(1) Efficacy: gold standard for Childhood Absence Epilepsy (CAE)
(2) Therapeutic Range: TDM required (narrow)
(3) Side effects:
⚫️ hepatotoxicity
⚫️ rash
what is hyponatremia?
low Na+ levels in blood
what are the main AEDs associated with hyponatremia?
(1) Carbamazepine
(2) Oxcarbazepine
(3) Eslicarbazpine
-"COE"
If a pt already has hyponatremia, what do you want to avoid?
you want to avoid starting pts on "COE" as it will worsen the baseline hyponatremia
Phenytoin
(1) Indication + Class
(2) Efficacy
(3) Comorbid uses
(4) Side effects
(5) DDI
(6) Therapeutic Range
(7) PK
(8) Binding
Phenytoin
(1) Indication: epilepsy - 1st gen ASM
(2) Efficacy: narrow --- may exacerbate generalized seizures, including CAE
(3) Comorbid uses: N/A
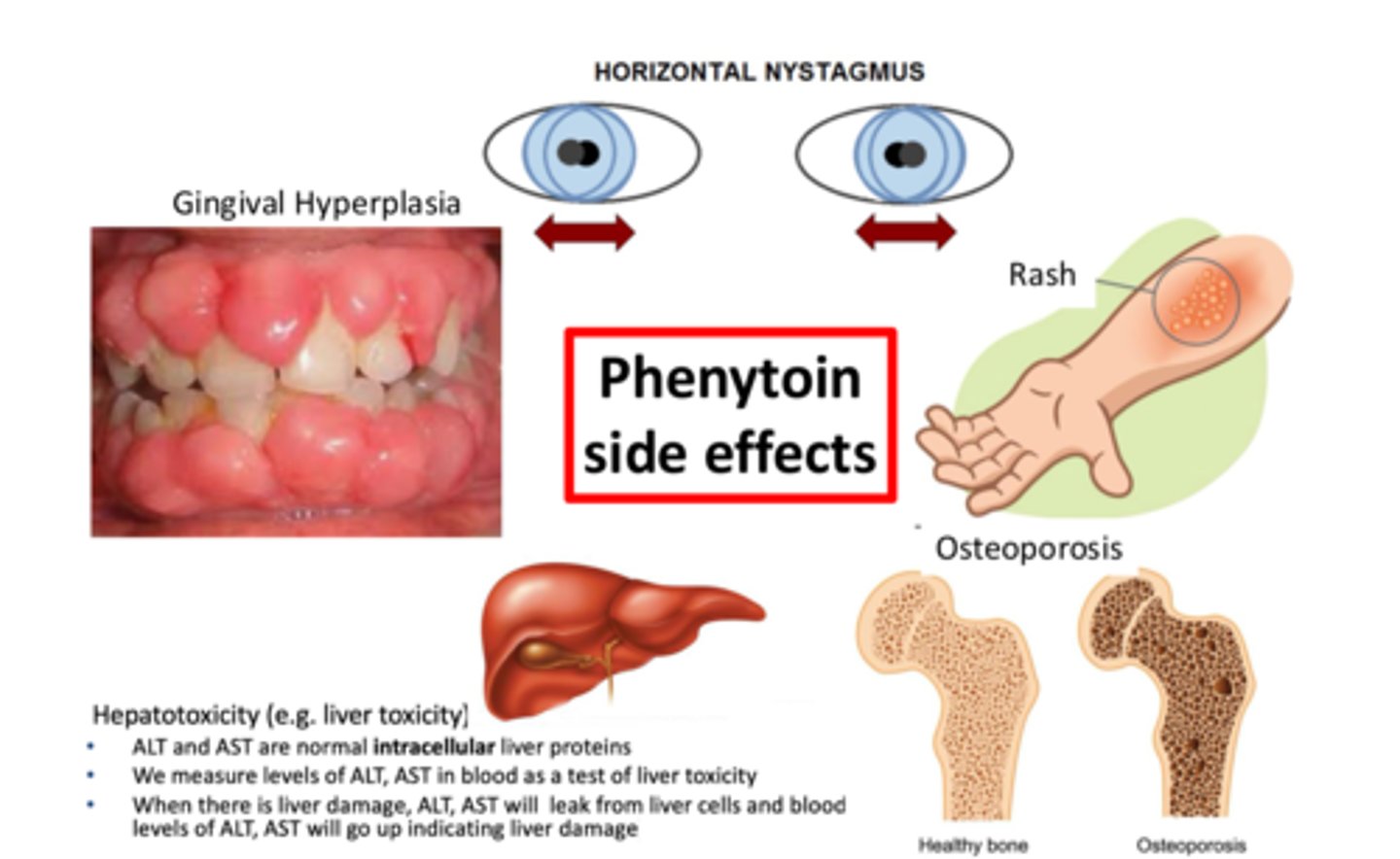
(4) Side effects:
⚫️All Na+ channel inhibitors are "neurotoxic" - ataxia, sedation, decreased cognition
⚫️ Nystagmus common exam finding
⚫️ Long-term causes: gingival hyperplasia, osteoporosis
⚫️ idiosyncratic rash, hepatotoxicity
(5) DDI: INDUCER
(6) Therapeutic Range: TDM required (narrow)
(7) PK: Non-linear kinetics
(8) Binding: Lots of protein binding
Phenobarbital
(1) Indication + Class
(2) Efficacy
(3) Side Effects
(4) DDI
(5) Therapeutic Window
Phenobarbital
(1) Indication: epilepsy - 1st gen ASM
(2) Efficacy: exacerbate CAE
(3) Side Effects:
⚫️ rash
⚫️ hepatoxicity
(4) DDI: inducer
(5) Therapeutic Window: TDM required (narrow)
Primidone
(0) Class
(1) Indication
(2) Metabolic relationship
Primidone
(0) 1st gen ASM
(1) Indication: not really used in epilepsy = used in tremor
(2) Metabolic relationship: prodrug of phenobarbital
Valproic Acid (________)
(1) Indication + Class
(2) Additional Names
(3) Efficacy
(4) Cormorbid conditions
(5) Side effects
(6) DDI
(7) Therapeutic Range
Valproic Acid (Depakene)
(1) Indication: epilepsy - 1st gen ASM
(2) Additional names: divalproex (Depakote)
(3) Efficacy in different seizures:
⚫️Broad spectrum (good for both focal & generalized onset) (often used 2nd line in CAE)
(4) Comorbid conditions:
⚫️Bipolar d/o - mood stabilizer
⚫️Migraines - preventative treatment
(5) Side effects
⚫️ Hepatotoxicity
⚫️ Rash
⚫️ Teratogenic
⚫️ Weight gain
⚫️ Pancreatitis
(6) DDI: lots = "classic" inhibitor
(7) Therapeutic Range: TDM required (narrow)
what is the efficacy of carbamazepine
narrow
what might carbamazepeine exacerabate
generalized sz d/o including CAE
what comorbid conditions does carbamazepine treat
mood stabilizer (bipolar d/o), trigeminal neuralgia
what are the side effects for carbamazepine
hepatotoxicity, hyponatremia, idiosyncratic rash in Asians (risk of SJS/TEN) gene testing required
what are the DDIs for carbamazepine
INDUCER - auto induction
is TDM required for carbamazepine
yes
what is the efficacy for clonazepam
focal and generalized epilepsy
what comorbid conditions does clonazepam treat
sz d/o (clonazepam is a long-acting benzodiazepine)
t/f clonazepam may lead to drug abuse
true
what are the DDIs for clonazepam
none
what are the side effects for clonazepam
none
is TDM required for clonazepam
no
what is the efficacy for ethosuximide
gold standard for CAE
is TDM required in ethosuxide
no
what are the side effects for ethosuximide
hepatotoxicity and rash
what is hyponatremia
low Na+ levels
what AEDs may cause hypoatremia
carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, eslicarbazepine
what is the efficacy for phenytoin
narrow
what might phenytoin exacerbate
generalized seizures including CAE
what are the comorbid uses for phenytoin
none
what are the side effects for phenytoin
all Na+ channels are neurotoxic - ataxia, sedation, decreased cognition, nystagmus, gingival hyperplasia, osteoporosis, idiosyncratic rash, hepatotoxicity
what are the DDIs for phenytoin
INDUCER
is TDM required for phenytoin
yes
what are the kinetics for phenytoin
non-linear
what does phenytoin bind a lot to
protein
does phenobarbital exacerbate CAE
yes
who uses phenobarbital a lot
kids
what are the side effects for phenobaribital
rash, hepatotoxicity, agression in kids
what are the DDIs for phenobarbital
INDUCER
is TDM required in phenobarbital
yes
what is primidone mainly used for
not used in epilepsy, used for essential tremor
what is primidone the prodrug of
phenobarbital
what is valproic acid also known as
divalproex and valproate sodium IV
what is the efficacy for valproic acid
broad spectrum (good for both focal and generalized onset)
valproic acid is often used _____ line for CAE
2nd line
what comorbid conditions does valproic acid also help
bipolar d/o, migraines
what are the side effects of valproic acid
hepatotoxicity, rash, teratogenic, weight gain, pancreatitis
what are the DDIs for valproic acid
lots = classic inhibitor
is TDM required for valproic acid
yes
what are the 2nd gen ASMs
(1) Felbamate
(2) Gabapentin
(3) Lamotrigine
(4) Levetiracetam
(5) Oxcabazepine
(6) Tiagabine
(7) Topiramate
(8) Zonisamide
-"ForGetLLOTTZ"
Felbamate
(0) Indication + Class
(1) Efficacy
(2) Side effects
(3) DDI
Felbamate
(0) Indication + Class: epilepy + 2nd gen ASM
(1) Efficacy: broad
(2) Side effects: powerful but limited by fatal side effects:
⚫️ aplastic anemia
⚫️ hepatotoxicity
(3) DDI: CYP3A4
Gabapentin
(0) Indication + Class
(1) Efficacy
(2) Side effects
(3) DDI
Gabapentin
(0) Indication + Class: most commonly use forneuropathic pain (not epilepsy) - 2nd gen ASM
(1) Efficacy: not great -- adjunct ony
(2) Side effects:
⚫️ sedation
⚫️ weight gain
⚫️ well-tolerated
(3) DDI: n/a bc renally cleared
Lamotrigine
(0) Indication + Class
(1) Efficacy
(2) Side effects
(3) DDI
(4) Comorbid contions
(5) Pregnancy
Lamotrigine
(0) Indication + Class: epilepsy - 2nd gen asm
(1) Efficacy: probably broad
(2) Side effects: rash SJS/TEN associated w/ fast titration
(3) DDI: valproate inhibits LTG metabolism
⚫️ CHZ, PHT, PHB induces LTG metabolism
(4) Comorbid contions: mood stabilizer (bipolar d/o); good for elderly b/c has least cognitive side effects
(5) Pregnancy: Follow levels in pregnancy
Levetiracetam
(0) Indication + Class
(1) Efficacy
(2) Side effects
(3) DDI
(4) Comorbid uses
Levetiracetam
(0) Indication + Class: epilepsy - 2nd gen asm
(1) Efficacy: most commonly used ASM
(2) Side effects: irritability
(3) DDI: n/a bc renally excreted
(4) Comorbid uses: n/a
Oxcarbazepine
(0) Indication + Class
(1) Efficacy
(2) Side effects
(3) DDI
(4) Comorbid uses
(5) Me too
Oxcarbazepine
(0) Indication + Class: epilepsy + 2nd gen ASM
(1) Efficacy: probably exacerbates primary generalized epilepsies
(2) Side effects: MORE hyponatremia than CBZ, less rash than CBZ
(3) DDI: less that carbamazepine
(4) Comorbid uses: can treat bipolar, neuropathic pain
(5) Me too: 2nd gen me too of CBZ
Topiramate
(0) Indication + Class
(1) Efficacy
(2) Side effects
(3) DDI
(4) Comorbid uses
(5) Additional Notes:
Topiramate
(0) Indication + Class: epilepsy - 2ng gen ASM
(1) Efficacy: probably broad (multiple MOA)
(2) Side effects: "DOPAMAX" - neurotoxic effects calls for slow titration
(3) DDI: high dose decreases oral contraceptives
(4) Comorbid uses: promotes weight loss, used in migraine prevention
(5) Additional Notes: carbonic anhydrase inhibitor -- small risk of kidney stones (keep well hydrated), acid/base distrubances
Zonisamide:
(0) Indication + Class
(1) Efficacy
(2) Side effects
(3) DDS
Zonisamide:
(0) Indication + Class: epilepsy - 2nd gen asm
(1) Efficacy: probably broad
(2) Side effects:
⚫️Na+ channel inbitor so > neurotoxic ADEs
⚫️Also carbonic anhydrase inhibitor ==> small risk of kidney stones (keep well hydrated)
(3) DDS: few/none
what is the efficacy for felbamate
broad
what are the side effects for felbamate
fatal side effects aplastic anemia and hepatotoxicity, not used a lot due to severe side effects
what are the DDIs for felbamate
CYP3A4
what is the efficacy of gabapentin
not great, adjunct only
what comorbid condition is gabapentin used for
neuropathic pain
what are the side effects for gabapentin
sedation, weight gain, well-tolerated
what are the DDIs for gabapentin
none b/c its renally cleared
what is the efficacy for lamotrigine
probably broad
what comorbid conditions does lamotrigine treat
bipolar d/o, good for elderly b/c has least cognitive side effects
what are the side effects for lamotrigine
rash (SJS/TEN)
when might a side effect for lamotrigine occur
fast titration
what are the DDIs for lamotrigine
valproate inhibits LTG metabolism, CBZ, PHT, PHB induces LTG metabolism
what should you do when pregnant people on lamotrigine
follow levels
what is SJS
life-threatening skin condition in which cell death causes the separation of inner and outer skin and mucous membrane