E1: fractures/splinting & casting
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
what are the types of fractures?
comminuted
transverse, nondisplaced
oblique, nondisplaced
spiral
segmental
Salter-Harris Fracture Classification
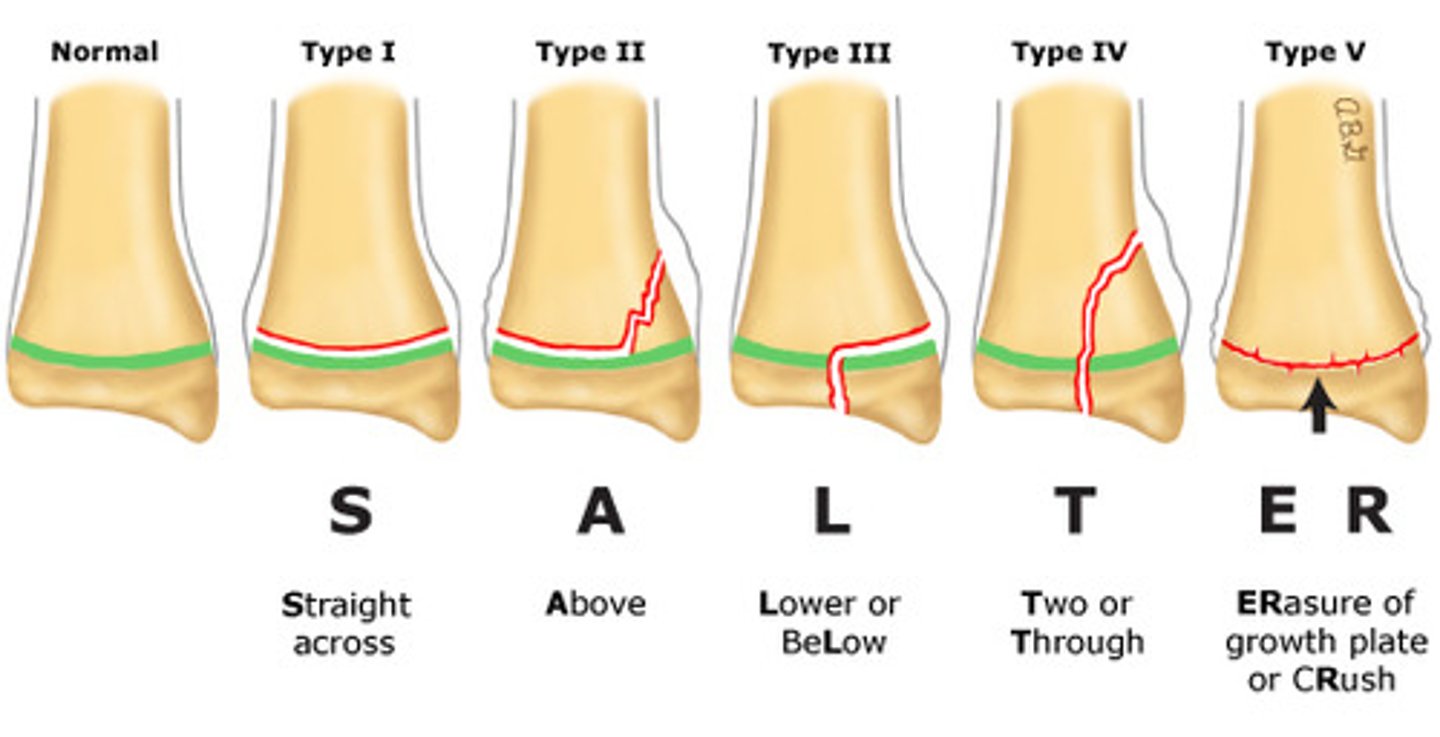
what are the most commonly missed fractures?
scaphoid
talar neck
radial head
tibial plateau
what are complications of fractures?
vascular compromise → cap refill > 2 sec and pulse not normal
nerve injury → contusion, crush, transection
what is a contusion (neuropraxic) associated with?
closed fx, dislocation or blunt trauma
what is axonotmesis (crush) associated with?
closed fx, dislocation or blunt trauma
what is neurotmesis (transection) associated with?
open fx
how long does nerve recovery take?
type 1 = 2-3 months (except knee)
type 2 = 1-2 cm/month → 95% recover by 6 mos
what are common sites of fx complications?
spiral fx humerus → radial nerve injury = wrist drop
tibial plateau fx → peroneal nerve injury = foot drop
what is the initial care (at scene) of a fx?
splint before transporting including joint above & below
always pad splints
elevate extremity
ice to control swelling
when should an orthopedic surgeon be consulted for a fracture?
- any open fx
- displaced intraarticular fx
- large/long bone fx (femur, spine, humerus)
- fx of both tibia and fibula
what factors delay healing of fractures?
smoking
elderly
DM
malnutrition
bleeding disorders
what are the methods of fracture management?
1. open or closed reduction w/ internal fixation
2. continuous traction followed by cast immobilization
3. closed reduction w/ external skeletal fixation
4. closed reduction followed by cast immobilization
is open or closed reduction with internal fixation preferred and why?
closed because it has less infection
what are the types of fracture that benefits from rigid internal fixation?
- a displaced joint fx (esp weight bearing joints)
- fx that can't be reduced or held closed (unstable fx)
- elderly pts w fps (allows for earlier activity)
- epiphyseal fx (salter Harris)
- joint fx (allows for early motion to prevent stiffness)
which method of fracture management is used for lower extremity fractures?
continuous traction → allows alignment & maintain reduction
what is external fixation?
using pins/hardware through the skin to stabilize fx
- hardware is placed above and below fx site
- typically incorporated into a cast
what is the most common form of fracture management?
closed reduction → using a cast to immobilize fx and allow for healing
what is the "periosteal hinge"?
the periosteum on the opposite side of the fx is still intact and is used to correct the fx
closed reduction is done on what type of fractures?
epiphyseal fx → distal portion is pushed back into place
transverse fx → reduced by simple traction
oblique "toggle" fx
how is closed reduction accomplished?
1. traction is applied to distal fragment w counter traction on proximal fragment
2. misalignment is corrected
3. distal fragment is reduced & angular deformity corrected
4. periosteal hinge prevents over reduction
5. cast holds position
how is adequate reduction done in adults vs children?
adults = angular deformities have to be completely corrected
child = angular deformity < 20 degrees that is close to a joint and in same plane of motion corrects itself
why do we cast fractures?
- immobilizes the ends of a fx
- allows for ambulation
- hold position of reduction
what are the 2 types of casts?
plaster and fiberglass
what is appropriate aftercare of an arm cast?
- keep elevated above heart (using a sling)
- watch for compartment syndrome
- watch for complications → Volkmann's ischemic contracture and tissue necrosis
how is itching from a cast treated?
ice, elevation, OTC antihistamines
what is proper casting for the arm?
cast does not extend beyond distal palmar creases
MCPs should be able to completely flex
pt should be able to fan fingers
elbow casts should be 90 degrees
what is the proper casting for a short leg cast?
- foot/ankle at 90 degrees (prevents Achilles tightness)
- always extend under metatarsal heads (support)
- toes exposed (no free pics tho)
- if a kid, can use weight-bearing cast and post-op shoe
should you wait for the swelling to go down before reducing a fracture?
NO!!!
an avulsion fx near a joint may signify?
ligament or tendon damage
does rotational misalignment correct itself in children?
no
what are the most common bones fractured from child abuse?
long bones → shaft (metaphysis) is most common
ribs → posterior, lateral
vertebral body compression fx
what plain film views do you want to do if you suspect child abuse?
AP & lateral (sometimes oblique)
- the more views the better!
what are S&S of senior abuse?
hand fx
unset broken bones
repeat fall injuries