Wind and Desert Landforms: Erosion, Deposits, and Geology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is wind?
Moving air (motion in the atmosphere) driven primarily by convection.
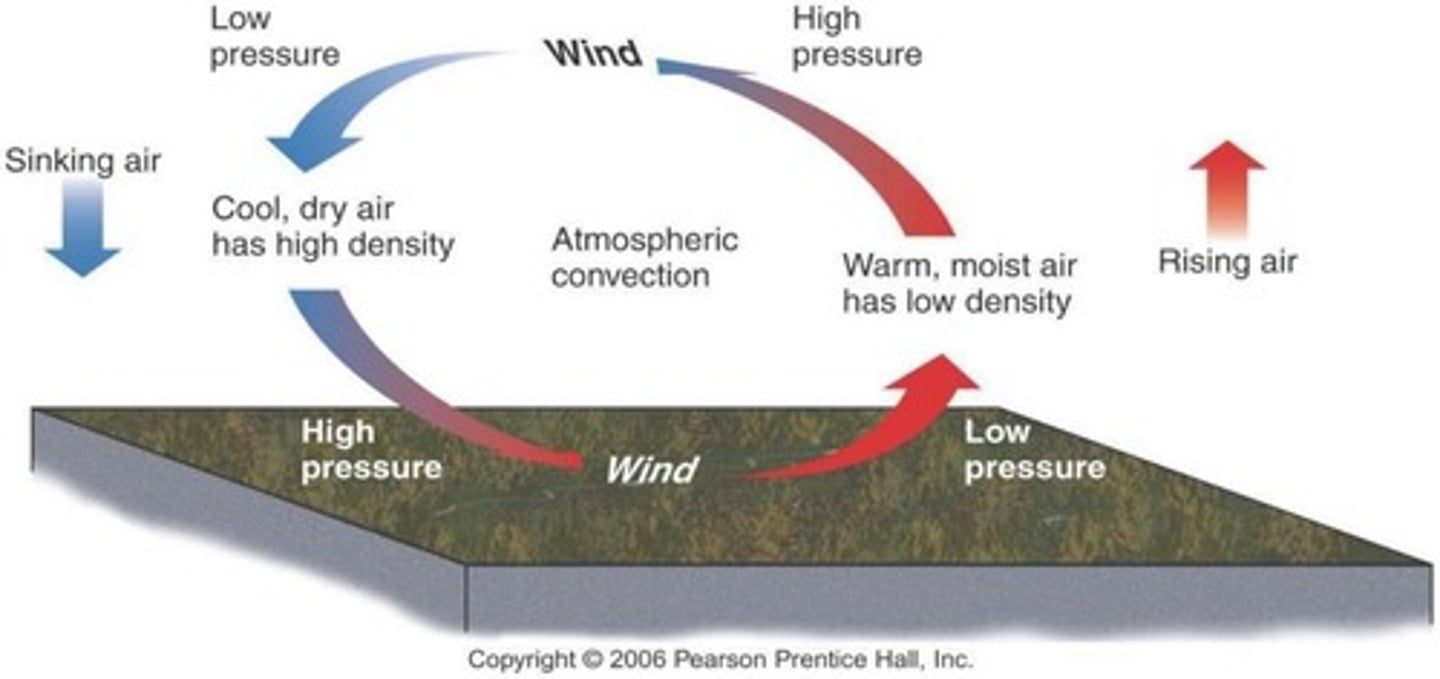
What primarily controls the movement of wind?
Pressure differences due to different air densities.
What factors affect air density?
Temperature and humidity; warm moist air is less dense and rises, while cool dry air is dense and sinks.
How do wind speeds vary?
Wind speeds are driven by pressure differences; greater differences lead to greater speeds.
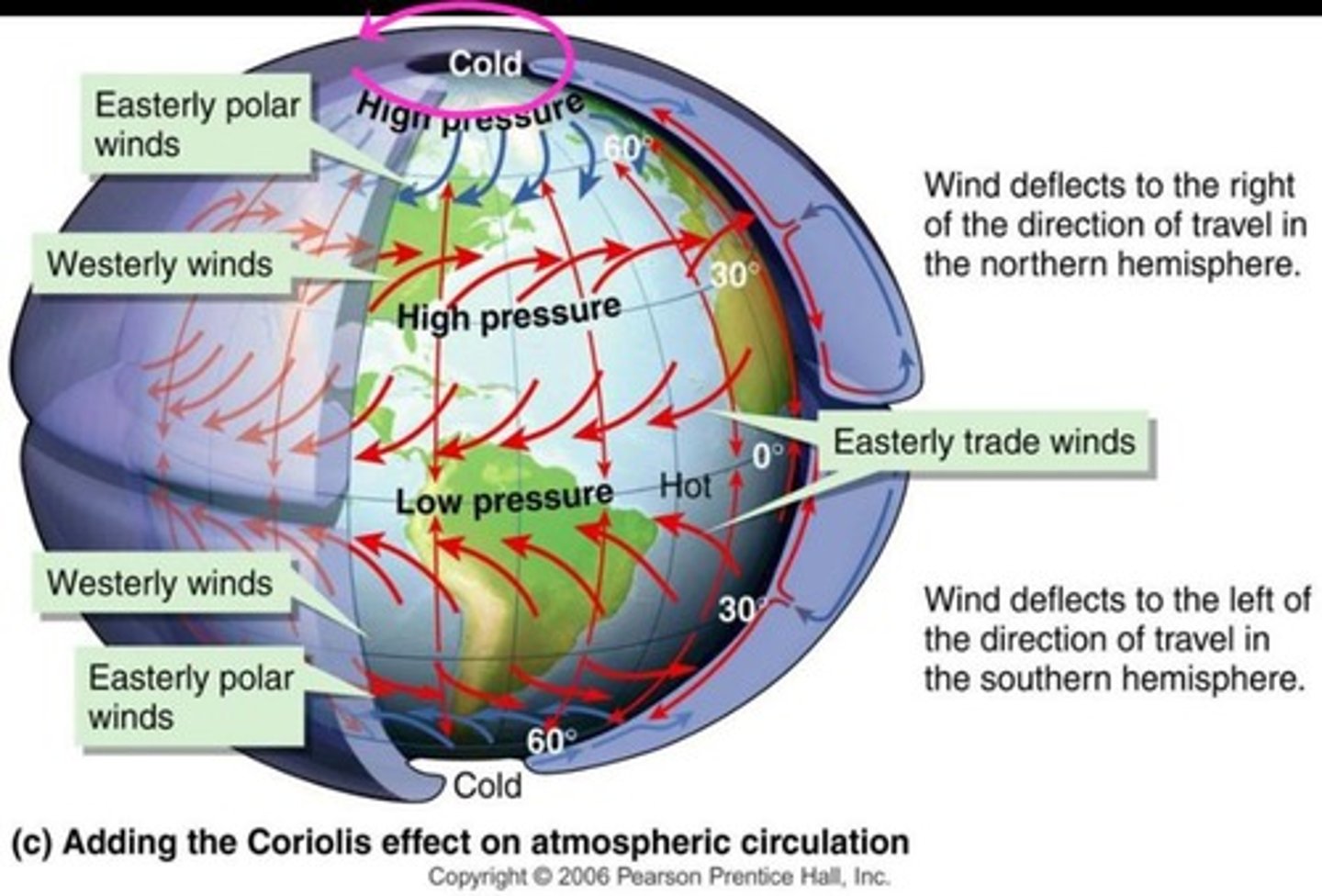
What is the Coriolis Effect?
The apparent curve of moving objects due to Earth's rotation.
What are the three requirements for wind erosion to occur?
Strong winds, little vegetation, and fine grain loose soils.
What defines a desert?
A region that receives less than 25 cm (~10 inches) of precipitation per year.
Where are most deserts located?
Close to 30°N and 30°S latitudes or downwind of major mountains.
What are subtropical deserts?
Deserts resulting from patterns of atmospheric convection, found from 20° to 30° N and S latitudes.
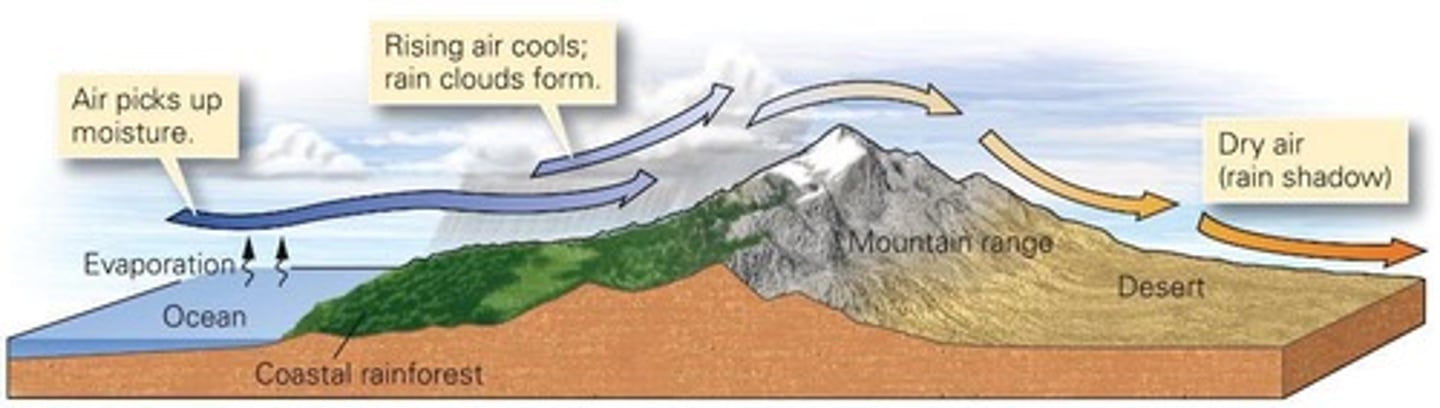
What is a rain-shadow desert?
A desert formed when moist air rises over mountains, cools, and loses moisture, leaving dry air on the leeward side.
What are coastal deserts?
Deserts that form along cold ocean currents where cold water decreases air's moisture capacity.

What is deflation in the context of wind erosion?
The lowering of elevation in an area due to the removal of material by winds.
What is abrasion in wind erosion?
Erosional process driven by wind-blown particles such as sand.
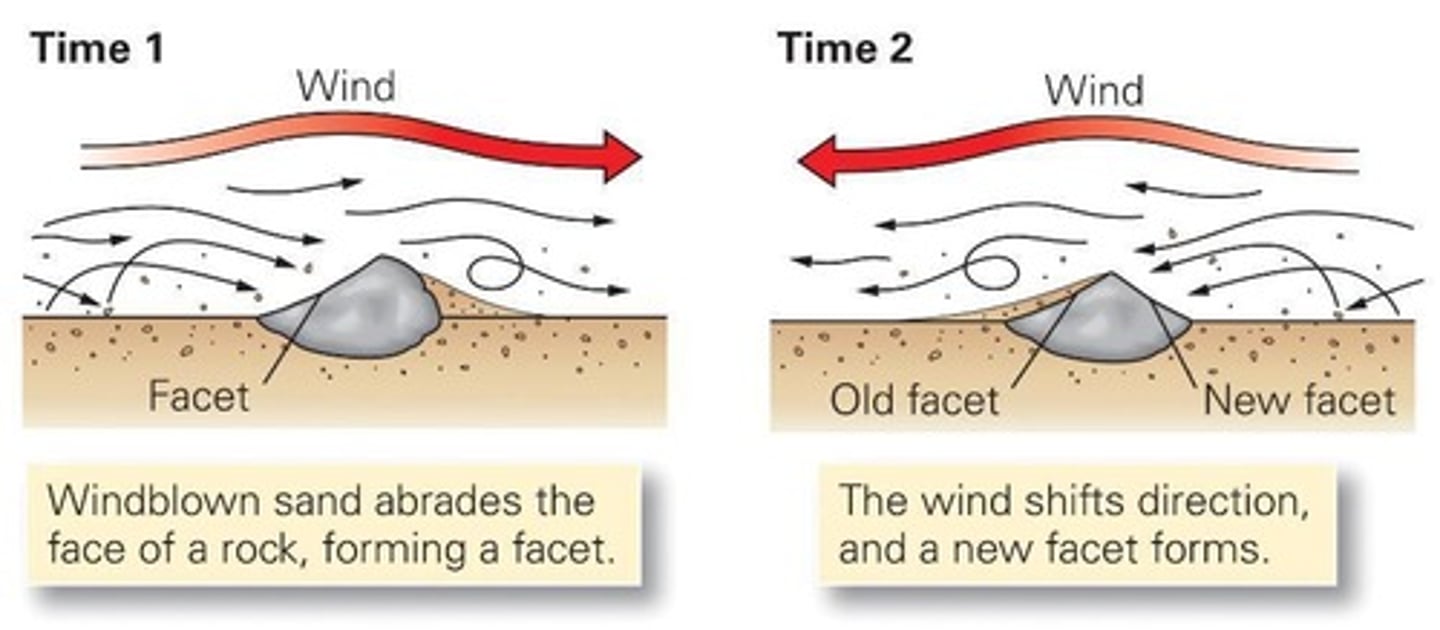
What are ventifacts?
Stones that have been sandblasted by wind.
What are yardangs?
Elongate ridges formed due to aeolian abrasion of bedrock, oriented parallel to prevailing wind direction.
How do sand dunes migrate?
Dunes migrate in the direction of prevailing winds over time.
What are barchan dunes?
Dunes with limited sediment supply, where 'horns' point downwind and migrate rapidly.
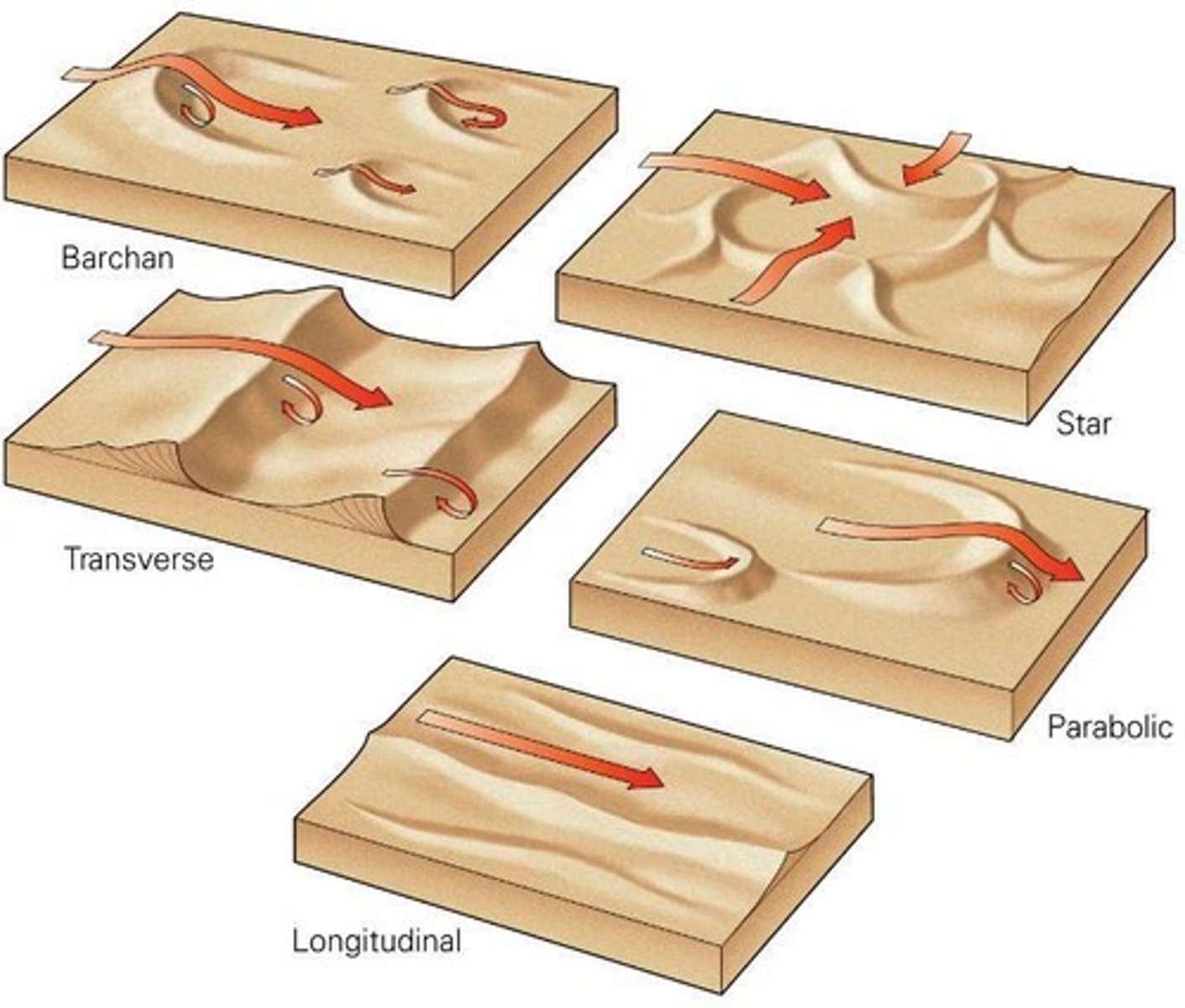
What are longitudinal (linear) dunes?
Dunes formed by bi-directional winds, characterized by ridges parallel to the mean wind vector.
What are transverse dunes?
Dunes that form parallel rows perpendicular to the prevailing wind, requiring lots of sand and constant wind direction.
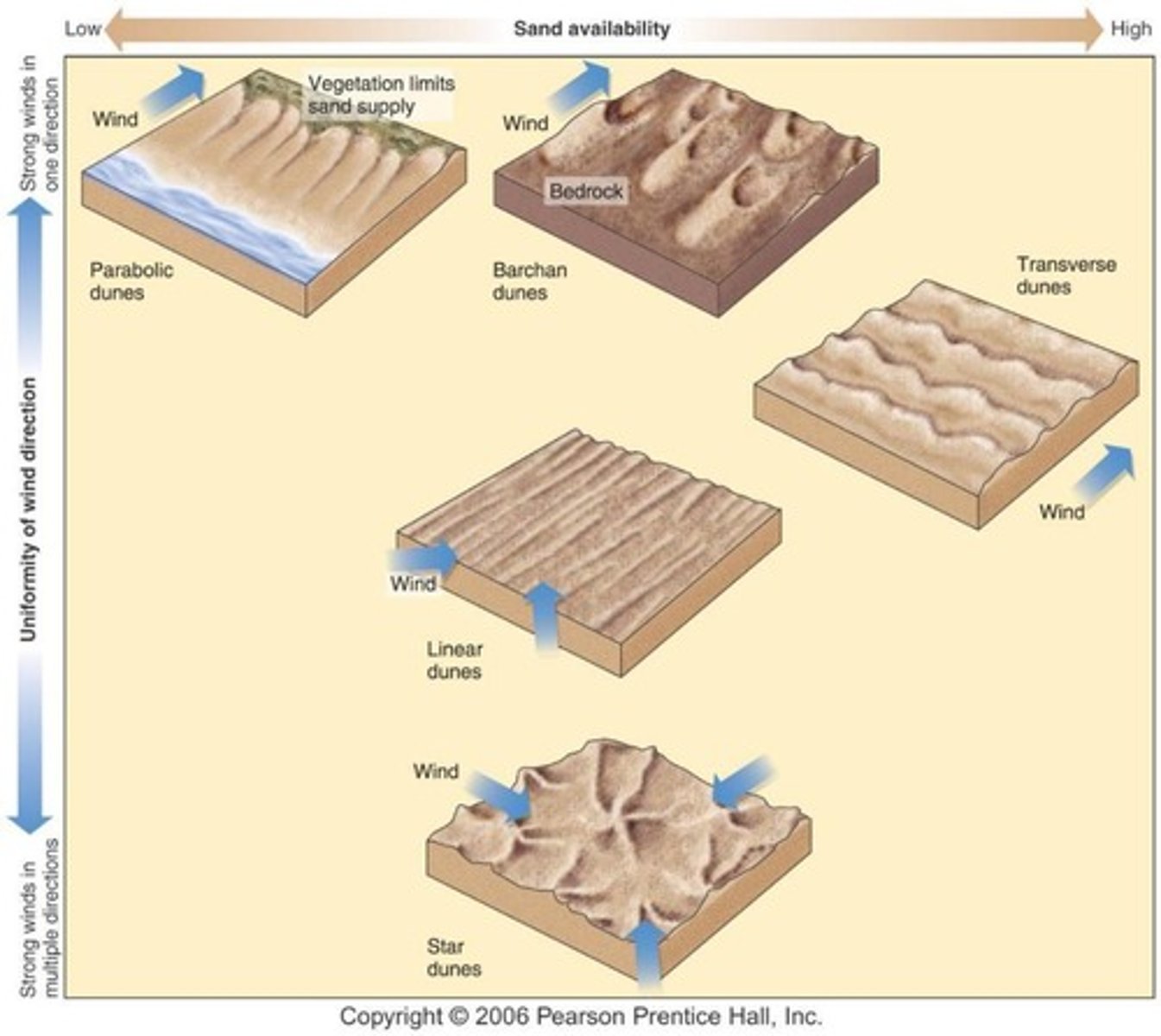
What are star dunes?
Dunes that appear star-shaped, formed by winds coming from different directions.
What is desert varnish?
A dark surface coating of iron and manganese oxides that forms slowly through bacterial activity and dust.
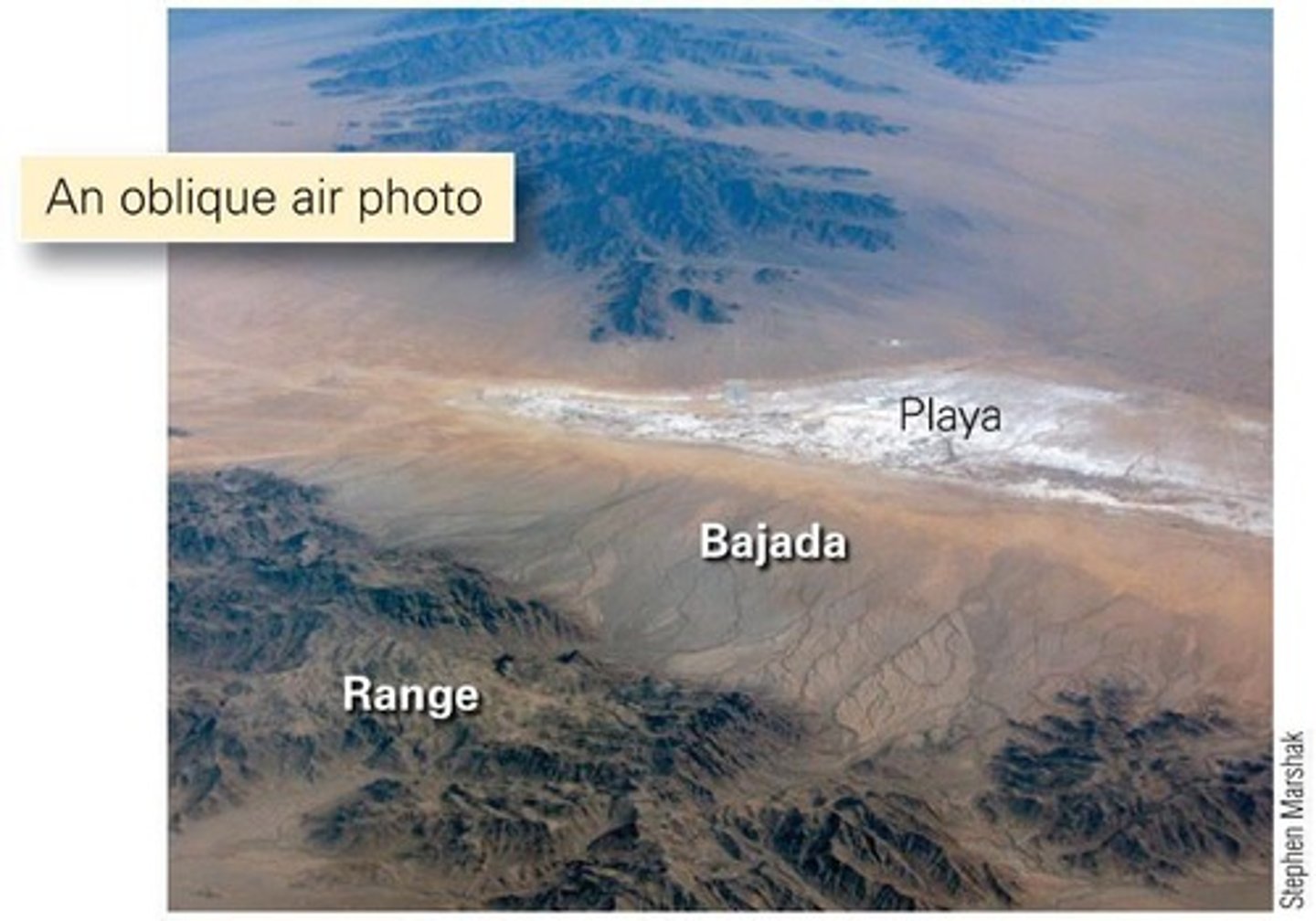
What are alluvial fans?
Conical accumulations of sediment formed when water exits a canyon and spreads out.
What are playas?
Desert lakes with no outlet streams, where dissolved solids crystallize out as water evaporates.

How do cliffs and mesas form?
Bedrock controls landforms; erosion and weathering create cliffs, plateaus, mesas, buttes, and chimneys.
What is the role of weathering in landform appearance?
Resistant rocks form steep cliffs, while weak rocks weather to form slopes at the angle of repose.
What is the purpose of topographic maps?
To present complex information simply and visualize data/trends.
What do contour lines on a topographic map represent?
Imaginary lines of equal elevation above a reference point.
What does closely spaced contour lines indicate?
A steep slope where elevation changes rapidly.
What is the significance of widely spaced contour lines?
They indicate a gentle slope or relatively flat terrain.
What is the 'V' shape formed by contour lines crossing a stream?
The point of the 'V' always points upstream, towards higher elevation.
What is orogenesis?
The process of mountain building.
What are the three types of plate boundaries?
Convergent, divergent, and transform.
What is the definition of 'fault' in geology?
Fractures where rock slides past one another.
What is the difference between brittle and ductile deformation?
Brittle deformation involves cracking, while ductile deformation involves bending without cracking.
What factors influence whether rock deforms in a brittle or ductile manner?
Temperature, confining pressure, rate of deformation, and type of rock.
What happens to rock response as temperature increases?
Rock response becomes more ductile.
What is the brittle-ductile transition depth range?
Between 10 to 15 km depth.
What is the definition of 'strain' in geology?
The change in shape caused by deformation.
What are the three types of stress in geology?
Compression, tension, and shear.
What does 'displacement' refer to in rock deformation?
A change in location.
What does 'rotation' refer to in rock deformation?
A change in orientation.
What does 'distortion' refer to in rock deformation?
A change in shape.
What are orogenic belts?
Regions where mountains are formed and have a finite life span.
What is the practical importance of understanding geologic structures?
It helps in locating economic resources like oil and gas traps.
What is a geologic cross-section?
A representation showing the distribution of different structures and rock formations.
What are veins in geology?
Deposits of ore minerals formed by hot fluids migrating along faults.
What is the significance of the scale on a map?
It represents the relationship between distance on the map and distance on the ground.
What are the key components of a map?
Title, date, legend, scale, and direction.
What is the angular distance for latitude measured from?
Earth's center, north or south of the equator.
What is the angular distance for longitude measured from?
Earth's center, east or west of the prime meridian.