Origin of Life & Perspectives on Earth History
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Man
A recent agent of changea recent agent of change
“death of planet Earth”
Loss of internal heat and its consequence called _____________ form part of the destiny of this planet.
10000 Years
Amount of time before a fault or volcano is considered inactive after showing no activity. Similarly, age of remains before being considered a “fossil”
Anthropocene
Proposed (accepted) addition to the Geologic Timescale, splitting the Holocene Epoch into two by the major impact of man on the planet.
4.56 Billion Years Old
Age of Earth
Slow to Fast
Rates of Change of Earth
2-2.5 Mya (0.04% of Geologic Time)
The duration that Man has been on the Planet.
Fossils
Earth materials
Evidences used to record Earth History
Fossils
Actual remains, imprints, and traces of formerly living organisms older than 10K years
Actual remains (e.g., from Amber, Tar pits, Ice)
Body fossils: casts, molds
Trace (Ichnofossils): manifestation of activity--- burrows, coprolites, tracks
Chemical: molecules
Types of Fossils
Living Fossils
An organism that has remained essentially unchanged from earlier geologic times and whose close relatives are usually extinct
Eubacteria
Archaea
Eucarya
3 Major Domains of Life
Eucarya
Life with Eukaryotic Cells: with nuclear membrane
Many kinds of membranous organelles in cell
Eubacteria and Archaea
Life with Prokaryotic Cells: no nuclear membrane
Kerogen
Photosynthetic byproduct indicating possible photosynthetic life over 3.5Bya
Banded Iron Formations (BIF)
Ferric Iron-rich sediments in the ocean noting reaction of iron with oxygen-rich water. This suggests a significant amount of oxygen in the atmosphere at least 2.6 Bya
Phanerozoic
The Age of Visible/Evident Life (First Abundant Skeletons)
Organisms have developed preservable hard parts.
Vendian Revolution
End of the Proterozoic; Ocean iron now depleted, free O2 build up in the ocean and atmosphere forming the ozone.
Photosynthesizers, Eukaryotes, appear and tolerate/use O2. Prokaryotes dwindle.
Vendian/Ediacara Fauna
These were confirmed to be multicellular organisms
A set of remarkable animal (fauna) fossils first discovered in the Ediacara Hills of Southern Australia
Fossilized imprints of what were apparently soft-bodied organisms, preserved mostly on the undersides of slabs of quartzite and sandstone.
Most were round, disc-shaped forms that Sprigg dubbed "medusoids" from their seeming similarity to jellyfish. Others, however, resembled worms, arthropods, or even stranger things.
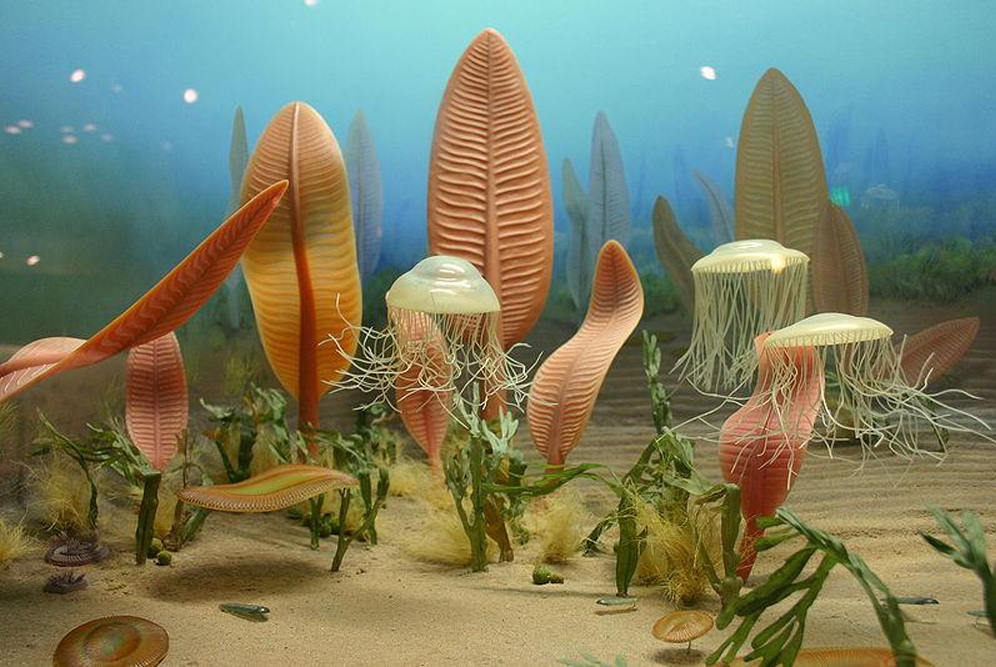

Vendian biota
(recently confirmed to be multicellular)
These soft-bodied fossils of the first animals from the Vendian are also known as the __________.
It is the first appearance of a group of large fossils in the rock record.
It gives us a good look at the first animals to live on Earth.


Phanerozoic Eon
540Mya - Present
Consisting of
Paleozoic
Mesozoic
Cenozoic
Precambrian Eon
Eon subdivided into Hadean, Archean, and Proterozoic eons dominated by single-celled organisms
Cambrian
Start of the Phanerozoic Eon
Charles D. Walcott
Discovered the Burgess Shale "fossil-bearing unit"
Burgess Shale
Most popular fossil site of sedimentary rocks containing the best record we have of Cambrian animal fossils, being one of the most diverse and well-preserved fossil localities in the world.
HYDROTHERMAL VENTS
A hotspring/geyser on the seafloor.
Continuously spews super-hot (~400C) mineral-rich water that helps support a diverse community of organisms.
LIFE ELSEWHERE ON THE SOLAR SYSTEM
Mid-Ocean Ridges
Volcanic Undersea mountain ranges in the Ocean Floor
Where hydrothermal vents are located (where they form)
3.5-4 Billion years Old
Discovered 1977
Age of Ocean vents and Year of Discovery
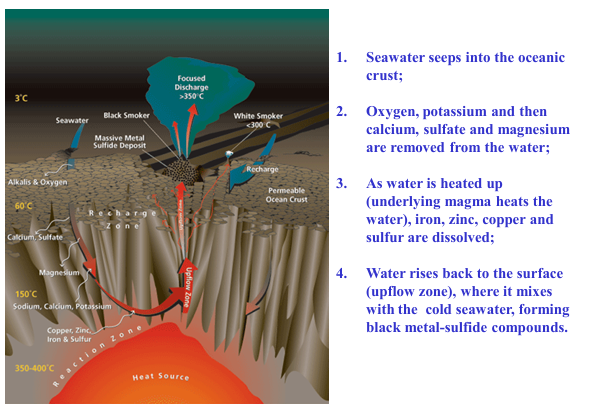
Hydrothermal vent process
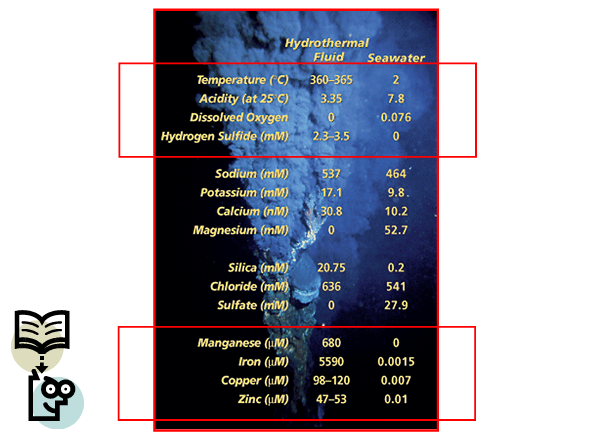
Higher Temperature
Highly acidic
Rich in Hydrogen Sulfide
Rich dissolved metals (Manganese, Iron, Copper, Zinc, etc)
Hydrothermal Fluid compared to Seawater

Black Smokers
hydrothermal vents of deeper recharge, metal-rich.
Superheated waters rich in Sulfide minerals precipitate massive sulfide or gold deposits in frigid (cold) water.

White Smokers
hydrothermal vents of shallower recharge, not as metal-rich.
Waters are depleted in Sulfide minerals and are not as hot as the other hydrothermal vent type.
Black Smokers
Vent ecosystems are more associated with this specific type of hydrothermal vent
Vent Ecosystem
The center of unique ecosystems beneath the seafloor that depend on microbes to tap into the chemical energy in vent water.
Archaea
Extremophiles
Prominent microbes that thrive in vent ecosystems. Converts heat, methane, and sulfur compounds into energy through chemosynthesis.
Chemosynthesis
The process through which extremophiles convert heat, methane, and sulfur compounds into energy through
Chemosynthetic bacteria
Base of the food chain in the vent ecosystem
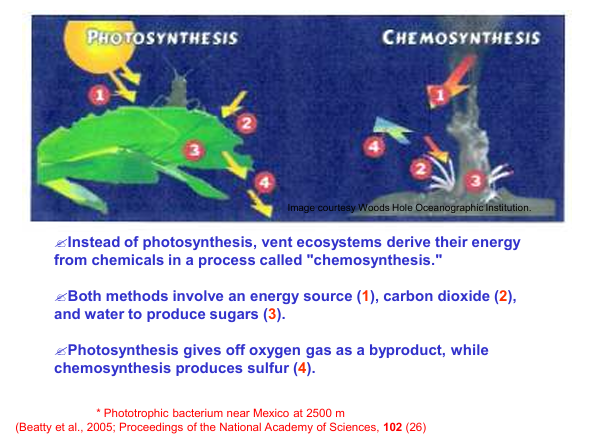
Photosynthesis vs Chemosynthesis
Surface, Oxygen
Hydrothermal vents, Sulfur
Location, Byproduct of 1. Photosynthesis, 2. Chemosynthesi

methane-sulfur-enriched Oil Seeps
An alternative energy source for cold, deep see areas without sunlight where chemosynthetic life is also found.
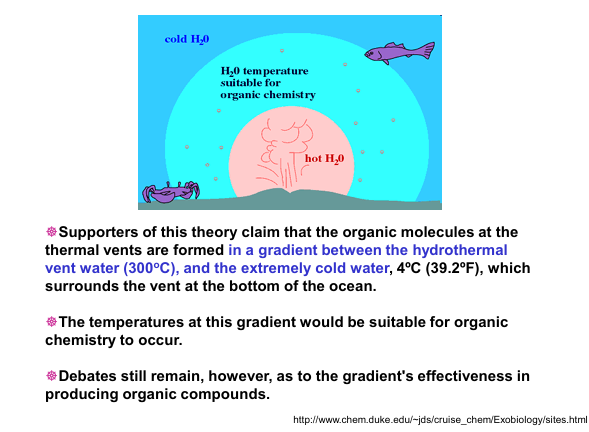
A temperature gradient exists around a vent that is suitable for organic chemistry
How life may have started in a hydrothermal vent


The Primordial Soup hypothesis
Hypothesis stating that life on earth began as a primordial soup in a lake or pond 4 bya.
Chemicals from the atmosphere combined with some form of energy necessary to make amino acids, the building blocks of protein, to create the first primitive organism and start the evolution of life.
The Miller-Urey Experiment
Stanley Miller and Harold Urey Experiment
An experiment that simulated hypothetical conditions of the early Earth, testing earlier hypothesis that conditions on the primitive Earth favored chemical reactions that synthesized organic compounds from inorganic precursors.
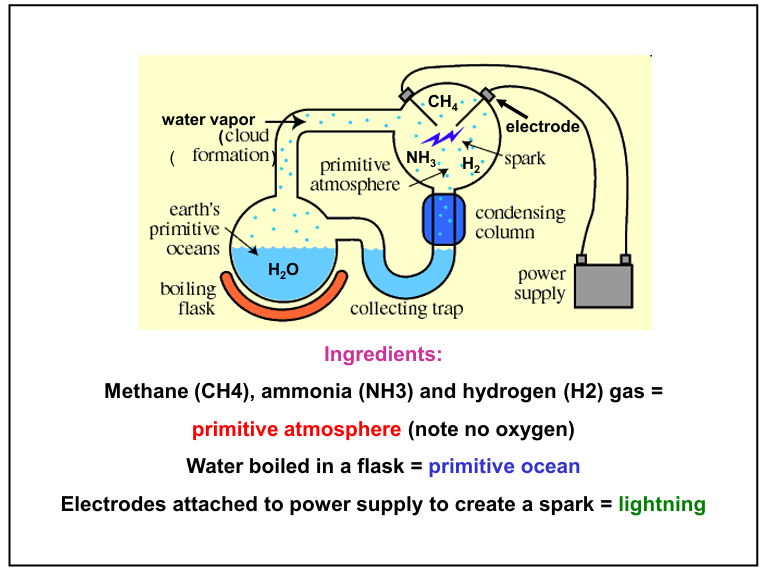
Reducing Atmosphere (low oxygen) and Abundant methane and ammonia
Hypothetical conditions of early Earth tested in the Miller-Urey experiment that comprise the ideal “primordial soup” for the origin of life.
Later experiments even produced 12 of the 20 most common amino acids needed for life!
Abiotic synthesis of amino acids only needs a source of chemicals and a reducing environment
They were able to form amino acids which are necessary ingredients for all life but not life itself. (Life itself required transformation of these amino acids to protein)
We were not sure that these conditions were identical to Earth 4.5 bya
Results of the Miller-Urey Experiment
LIFE FROM SPACE

PANSPERMIA
Life in a ready-made form is ubiquitous in the galaxy, brought by comets to planets
if comets supplied the raw materials to form life on Earth, life is also possible on other planets given the right conditions.
Impact/Implication of Panspermia Theory


Sunlight is not an absolute necessity for life. But so far water is.
Sunlight is not an absolute necessity for life. But so far water is.
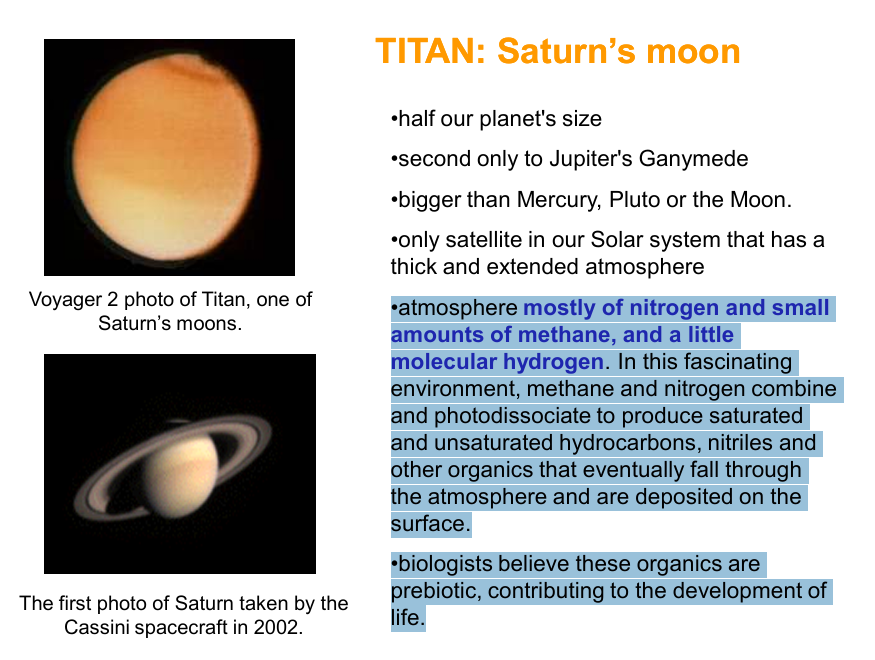
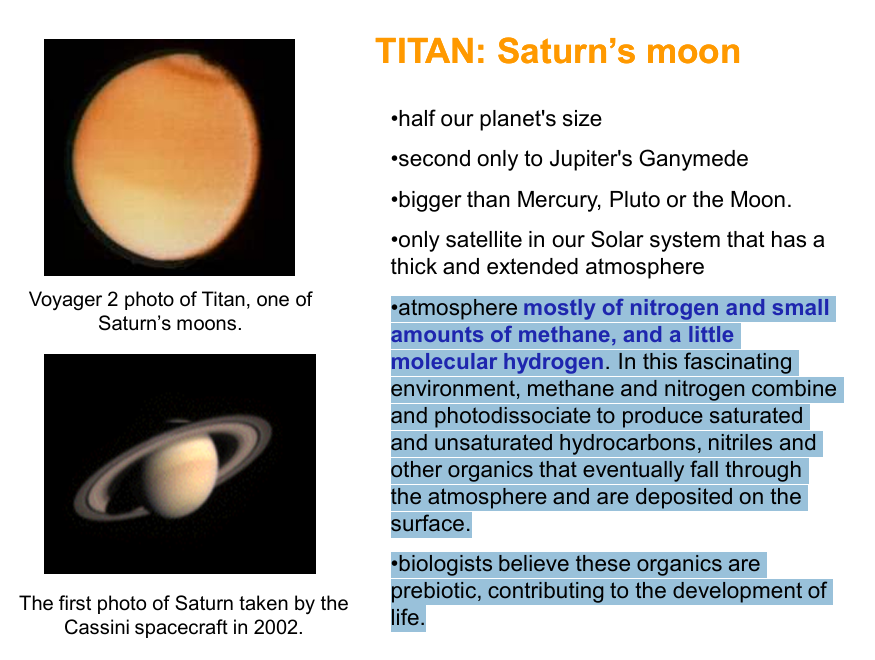
TITAN: Saturn’s moon
• atmosphere mostly of nitrogen and small amounts of methane, and a little molecular hydrogen. In this fascinating environment, methane and nitrogen combine and photodissociate to produce saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, nitriles and other organics that eventually fall through the atmosphere and are deposited on the surface.
• biologists believe these organics are prebiotic, contributing to the development of life.
TITAN
Saturn’s moon resembling the very young Earth before the appearance of life, when oxygen probably existed in the form of carbon dioxide and methane was abundant.
Observations also show presence of water vapor on this moon


Europa
Jupiter’s moon where water ice as predominant component on the surface. Possibly containing biology in its mantle where liquid water may be present and sunlight may pass.
Europa
Titan
(and Enceladus
Two Jupiter moons speculated to contain life and are found to have water
Mars appears to have had flowing water and an atmosphere
Mars appears to have had flowing water and an atmosphere
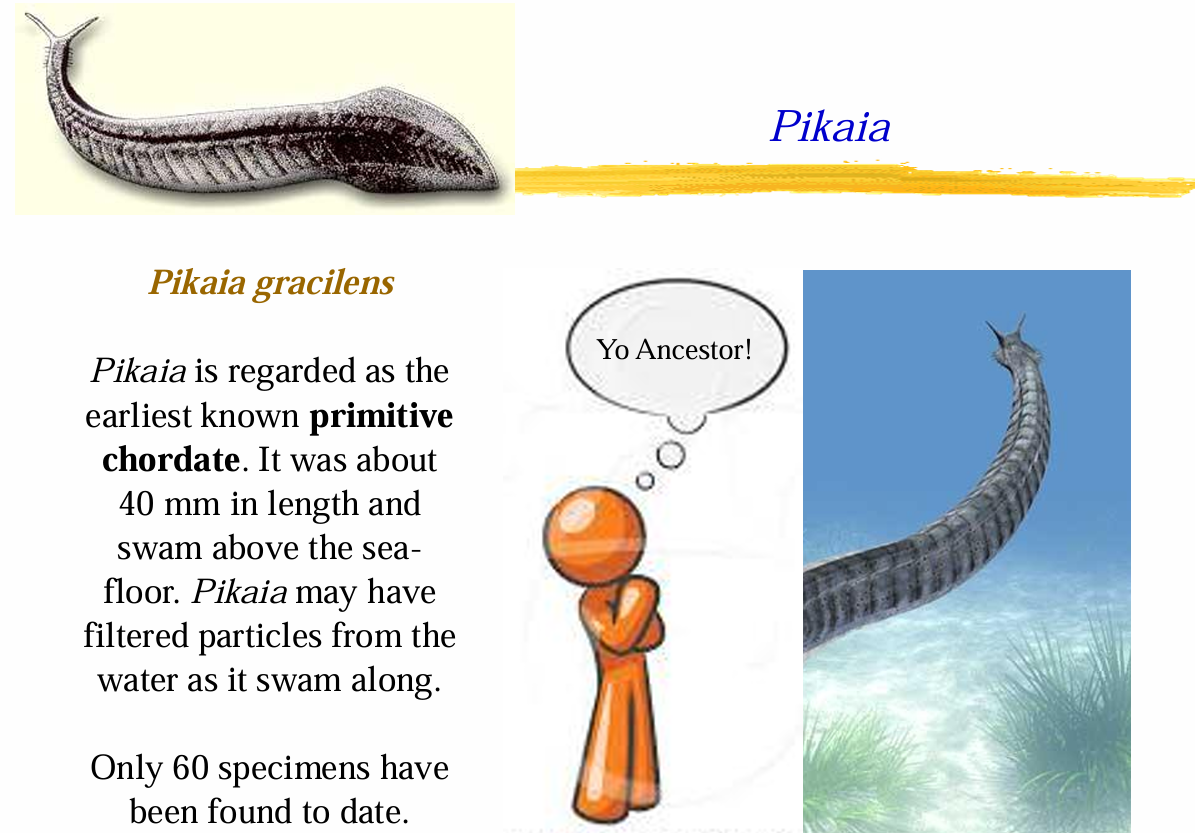
Pikaia
[Elite Ball Knowledge Question]
Earliest known primitive chordate


Cambrian Explosion
An evolutionary burst of animal origin.
INDEX FOSSILS
morphologic distinctiveness - should not be confused with other taxa
common occurrence - shouldn’t be very rare
worldwide geographic range - widespread
restricted stratigraphic range - short age range of time of appearance and extinction
Fossils very useful in establishing the age of rocks,
A fossil that identifies and dates the strata in which it is found; especially any fossil taxon that combines morphologic distinctiveness with relatively common occurrence and that has a broad, even worldwide geographic range and a narrow or restricted stratigraphic range.
The best index fossils include swimming or floating organisms that evolved rapidly and were distributed widely.
The best index fossils include swimming or floating organisms that evolved rapidly and were distributed widely.
The best index fossils include ________…

Ordovician Period
Diverse marine invertebrates (e.g., trilobites, brachiopods);
Appearance of coral fossils, but reef ecosystem is dominated by algae and sponges;
Jawless armored fish became common (ostracoderms – appeared during the Late Cambrian).
Colonization of land: Cells, cuticle and spores of early land plants (first non-vascular plants).
Silurian Period (436-408 Ma)
Widespread radiation of crinoids and brachiopods;
Oldest known coral reefs (times of major reef building);
Reefs are dominated by tabulate and colonial rugose corals and stromatoporoids;
First jawed fish (acanthodians);
jawless armored fish became abundant;
First known freshwater (non-marine) fish fossil
Colonization of land
a. First land animals (arthropods; millipedes are the oldest land animals);
b. First vascular plants and widespread non-vascular plants
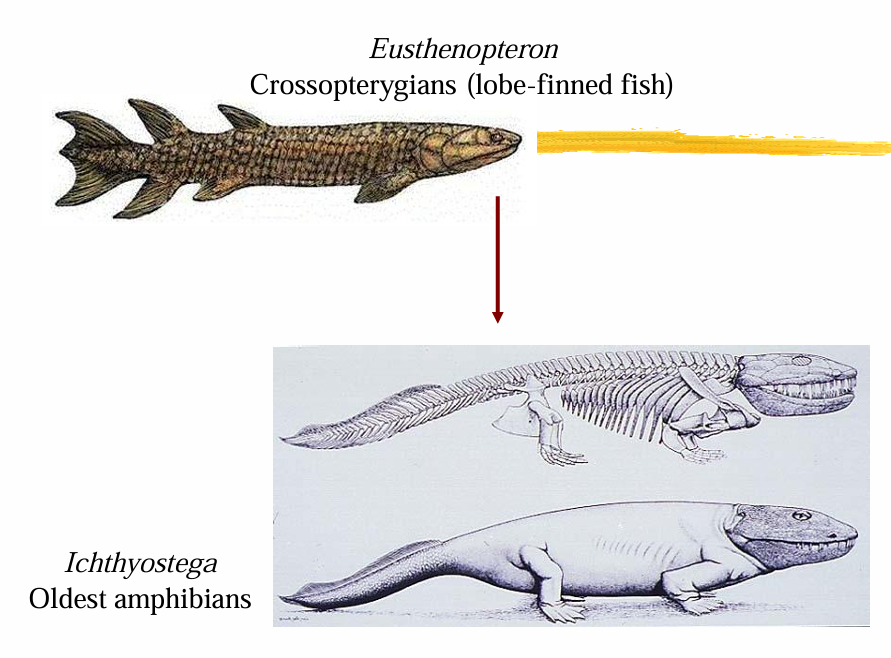
Devonian Period (408-360 Ma)
“Age of Fish”/Rapid diversification in fish
Besides the two fish groups, cartilaginous and bony fish also evolved
Colonization of land
a. Many new kinds of insects (e.g., scorpions, flightless insects);
b. Amphibians on land: Ichthyostega
c. Diverse seedless vascular plant flora (first forests)
d. First seed plants (seed ferns: Late Devonian)
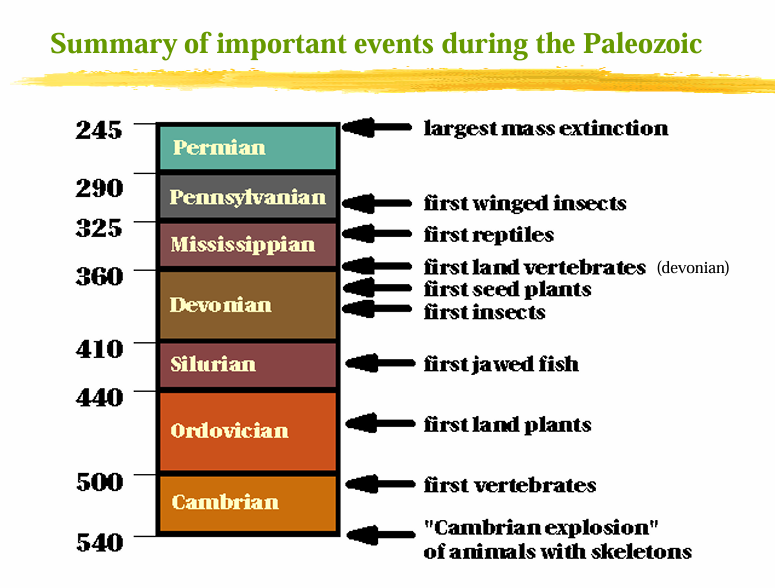
Lower Carboniferous = Mississippian;
Upper Carboniferous = Pennsylvanian
Periods comprising the Carboniferous
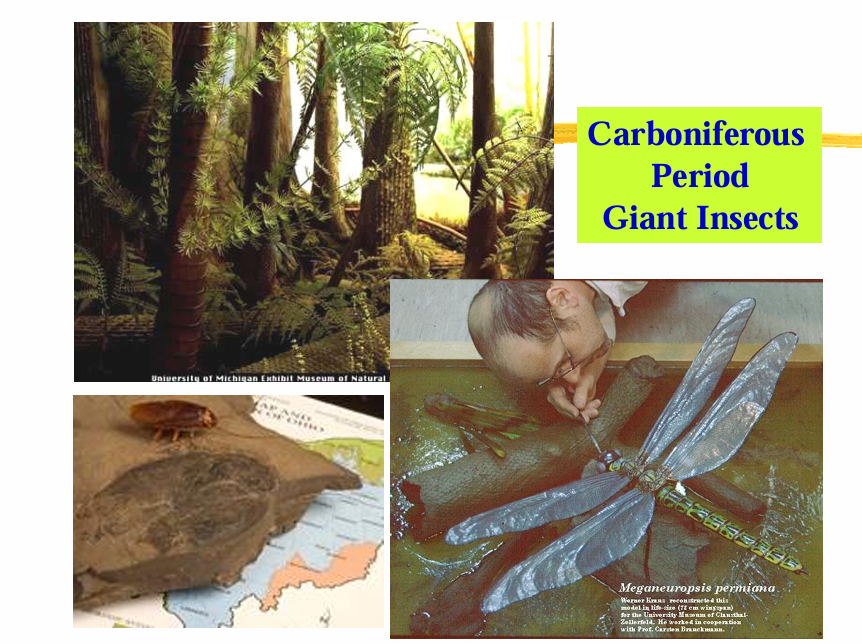

Carboniferous Period (360-286 Ma)
Period denoted by rich deposits of coal


Permian Period (286-245 Ma)
End period of the paleozoic era.
With the largest mass extinction event

PERMO-TRIASSIC EXTINCTION
The ________ extinction event, also known as the Great Dying, occurred approximately 251.9 million years ago and is the most severe extinction event in Earth's history, resulting in the loss of about 90% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial vertebrate species, over 95% of all organisms.
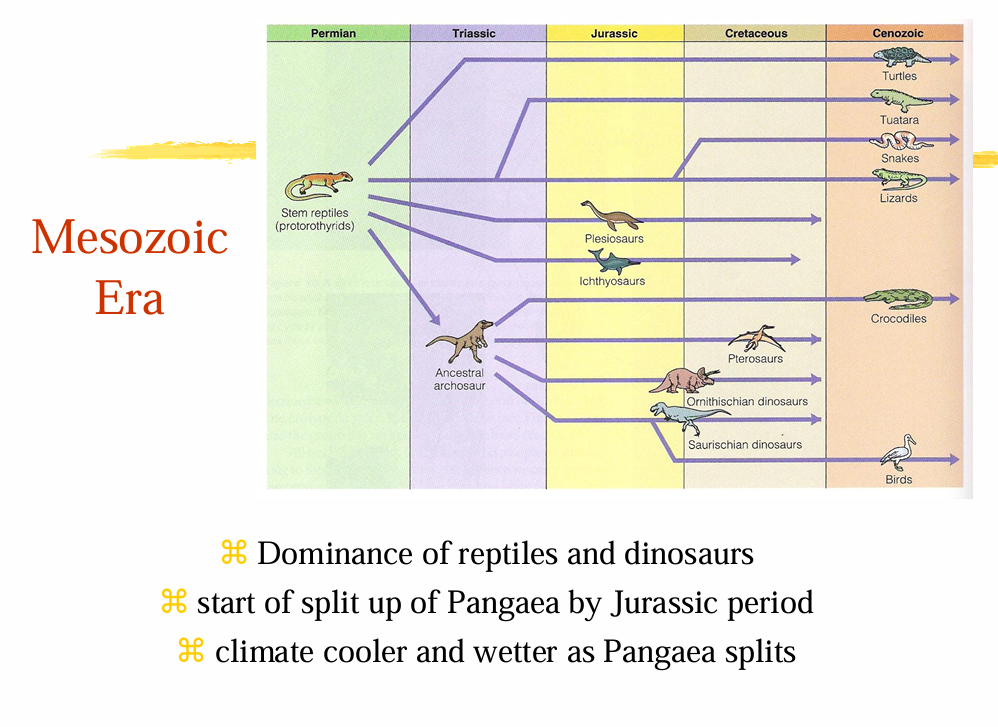
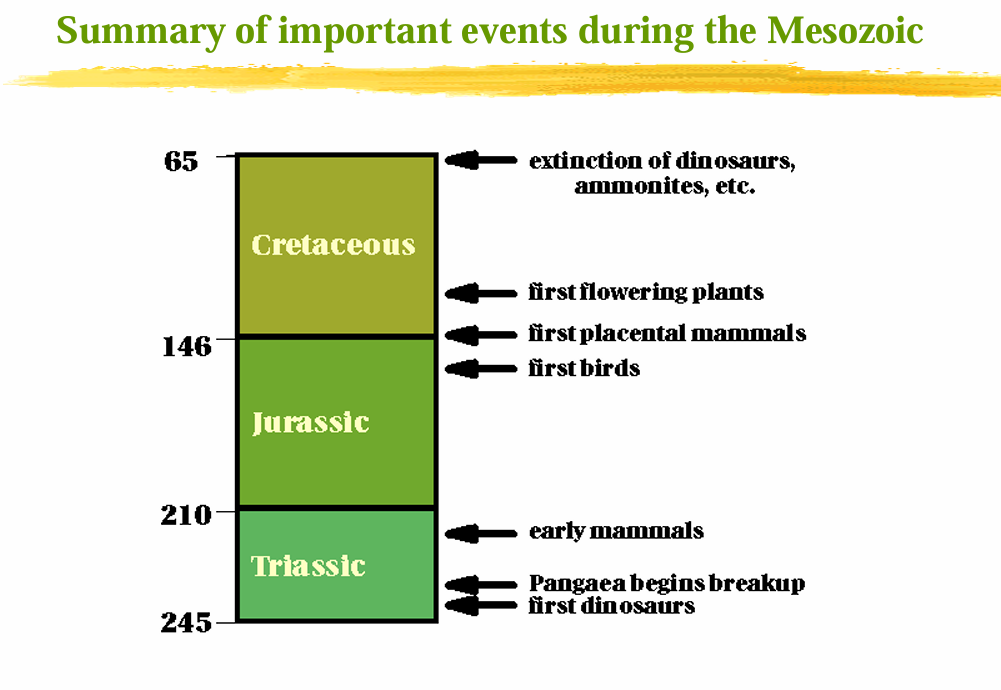
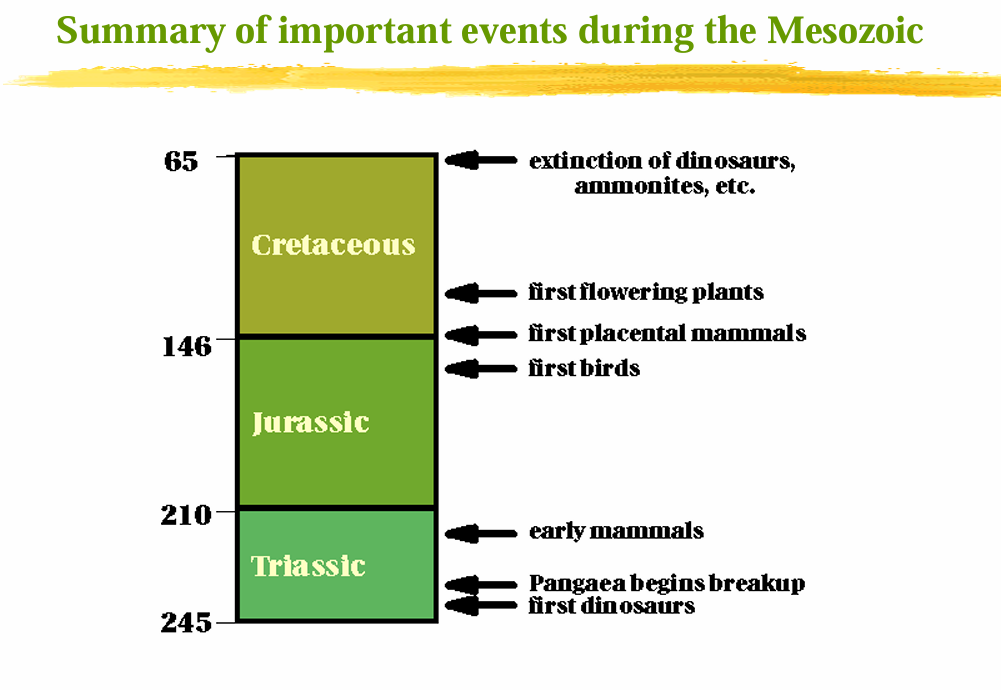
Mesozoic Era
Age of the Reptiles (Era)

Ammonites
The fishes of the Mesozoic
Jurassic
Triassic
Cretaceous
Periods of the Mesozoic Era
K-T Extinction
Extinction of ammonites, rudists, planktonic foraminifera, dinosaurs, flying and marine reptiles and some marine invertebrates at the end of the Cretaceous.

Dinosaurs
Remember that the term dinosaurs is not used for the flying reptiles (pterosaurs) Nor is the term “dinosaurs” used for the large marine reptiles that lived during that time
Name literally means “terrible lizards”
Land reptiles that lived from the Late Triassic to the Cretaceous (65-230 million years ago)
T
T OR F
Birds evolved from Saurischian (Lizard-Hipped) dinosaurs.
Ornithischian (bird-hipped)
Saurischian (lizard-hipped)
Divisions of dinosaurs into groups based on pelvic bones

Bird hipped Dinosaurs
Stegosaurus (Tiled Lizard or Armed Lizard)
Triceratops
Ankylosaurus
Hadrosaurus
Examples of Ornisthischians

Lizard-Hipped Dinosaurs
Tyrannosaurus
Apatosaurus = Brontosaurus
Compsognathus
Oviraptor
Examples of Saurischians
Archaeopteryx
Late Jurassic
The earliest known bird
Pterosaurs
flying reptiles
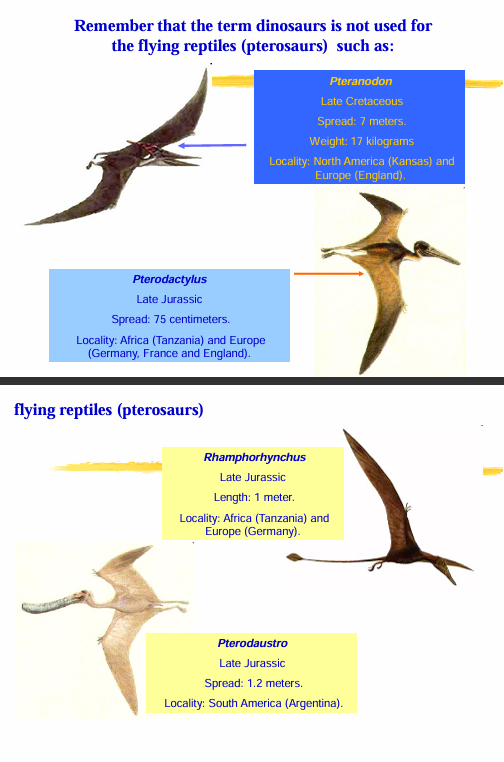
flying reptiles
Pteranodon
Pterodactylus
Rhamphorhynchus
Pterodaustro
Examples of pterosaurs
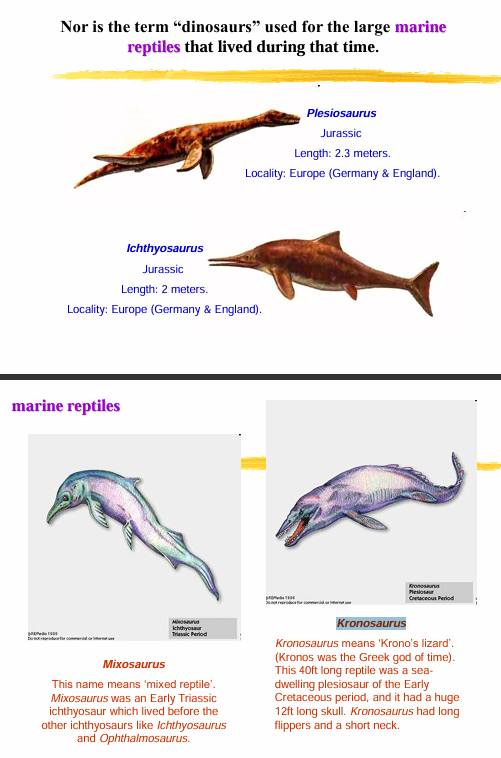
Plesiosaurus
Ichthyosaurus
Mixosaurus
Kronosaurus
Example of Mesozoic marine reptiles
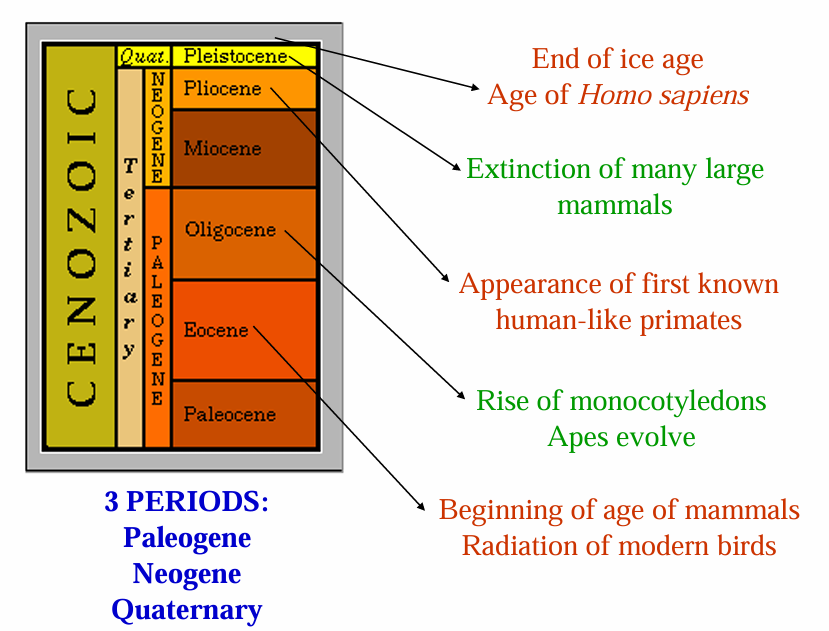
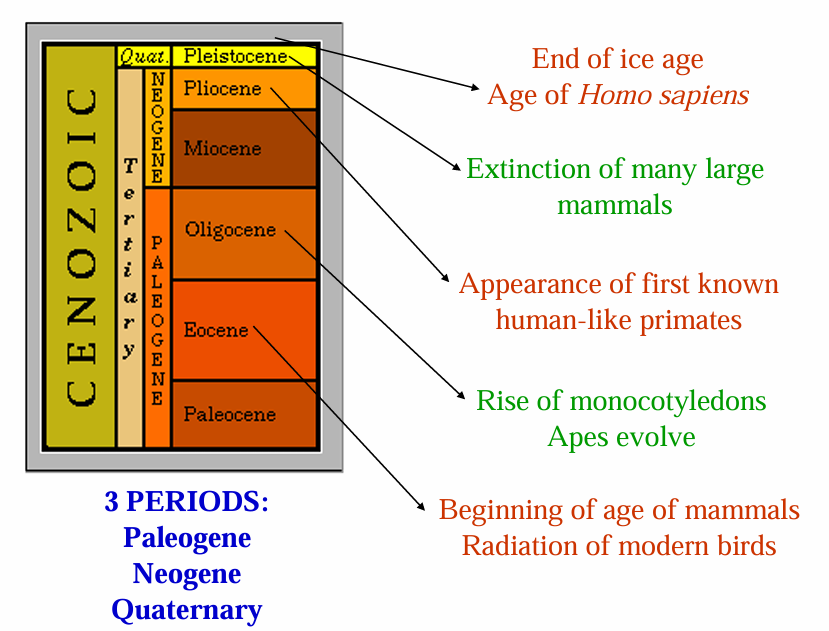
Tertiary
Paleogene
Neogene
Quaternary
Periods of the Cenozoic
Cenozoic Era (65 Ma-Present)
Dominant: flowering plants & mammals
Man as an agent of extinction