Chapter 10: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Secondary Structure
Three-dimensional arrangement of nucleic acid strands.
Denaturation
Process of separating double-stranded DNA.
Renaturation
Re-association of separated DNA strands.
Circular DNA
DNA molecules that form a closed loop.
Eukaryotic Chromosomes
Linear DNA structures found in eukaryotic cells.
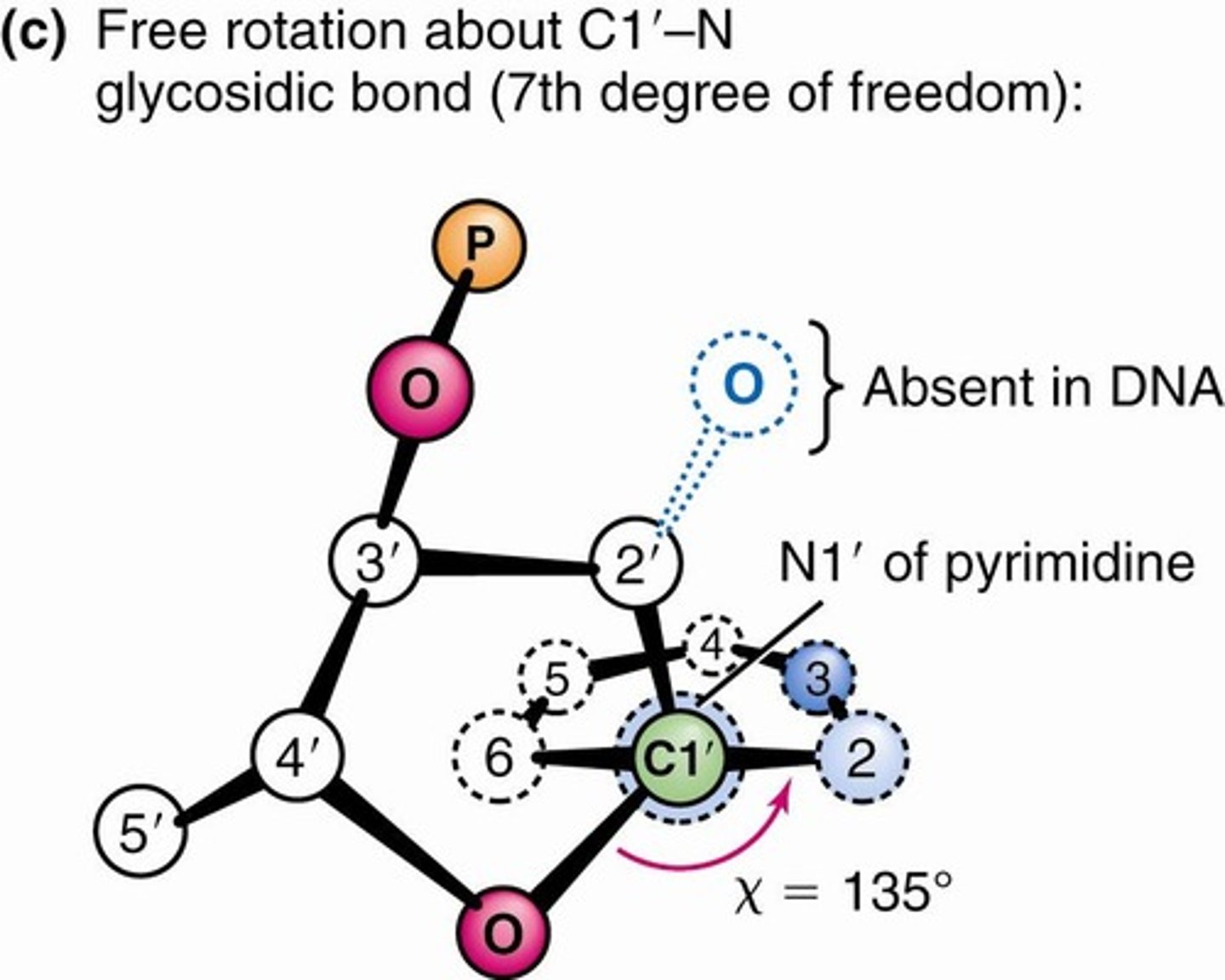
Rotational Degrees of Freedom
Flexibility in polynucleotide strand structures.
Deoxyribose-Phosphate Backbone
Structural framework of DNA composed of sugars and phosphates.
C1'-N Glycosidic Bond
Bond allowing rotation in nucleotide structure.
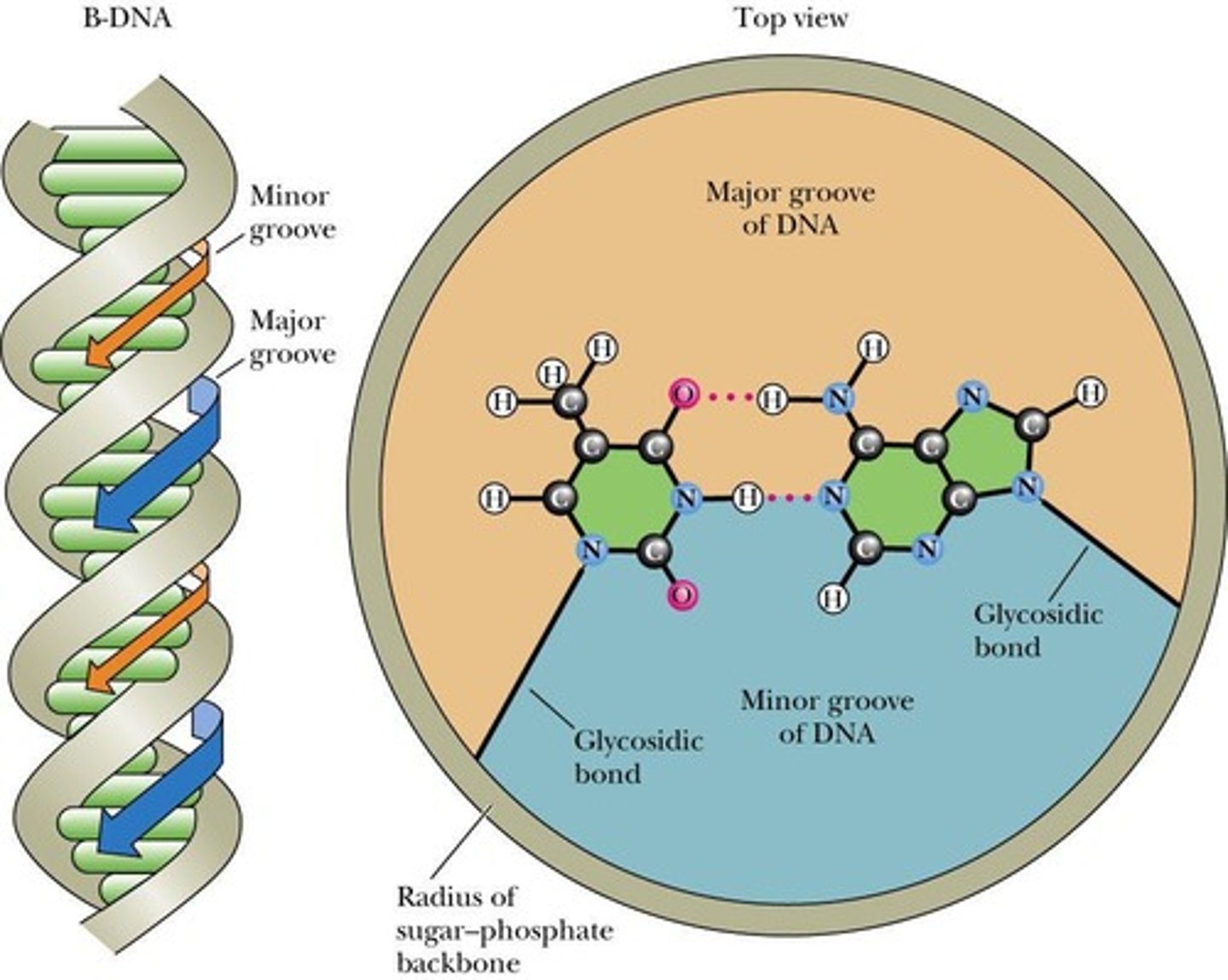
Base Pairing
Hydrogen bonding between complementary DNA bases.
Electrostatic Interactions
Repulsion of negatively charged phosphate groups.
Base-Pair Stacking
Hydrophobic interactions between aromatic base rings.
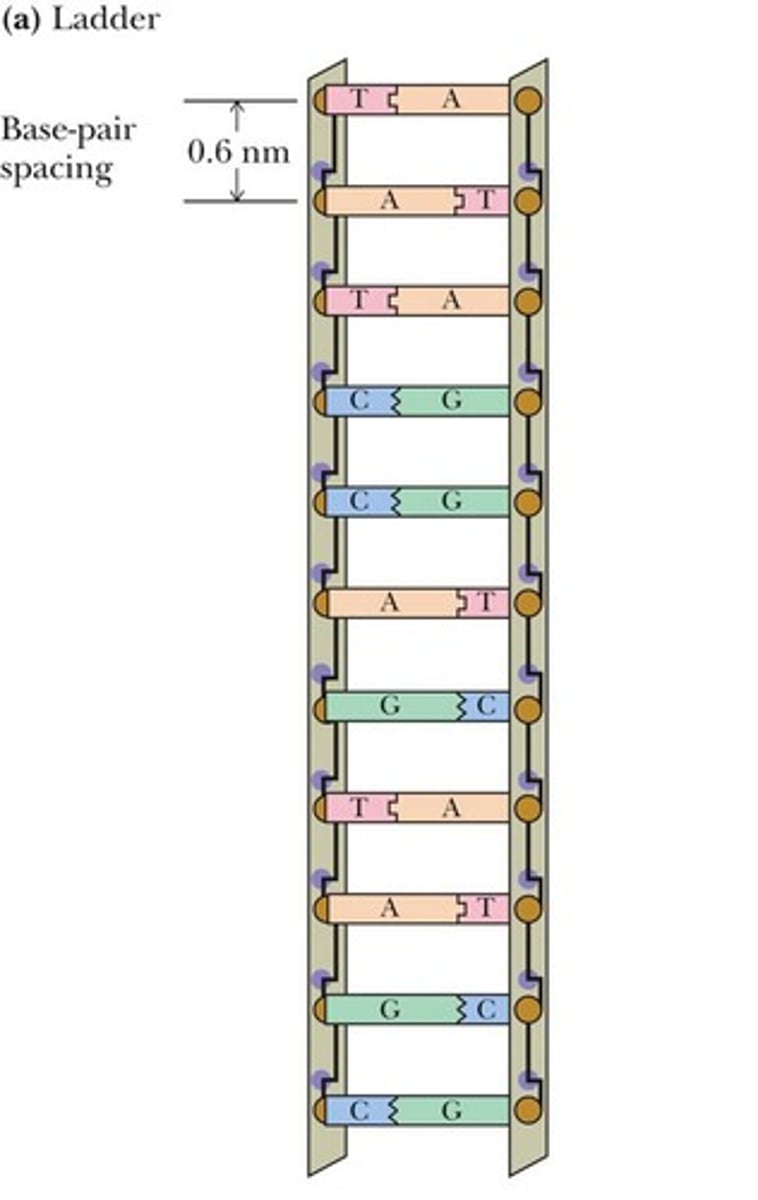
B-DNA
Most common DNA form in solution.
A-DNA
Shorter, fatter DNA helix, dehydrated form.
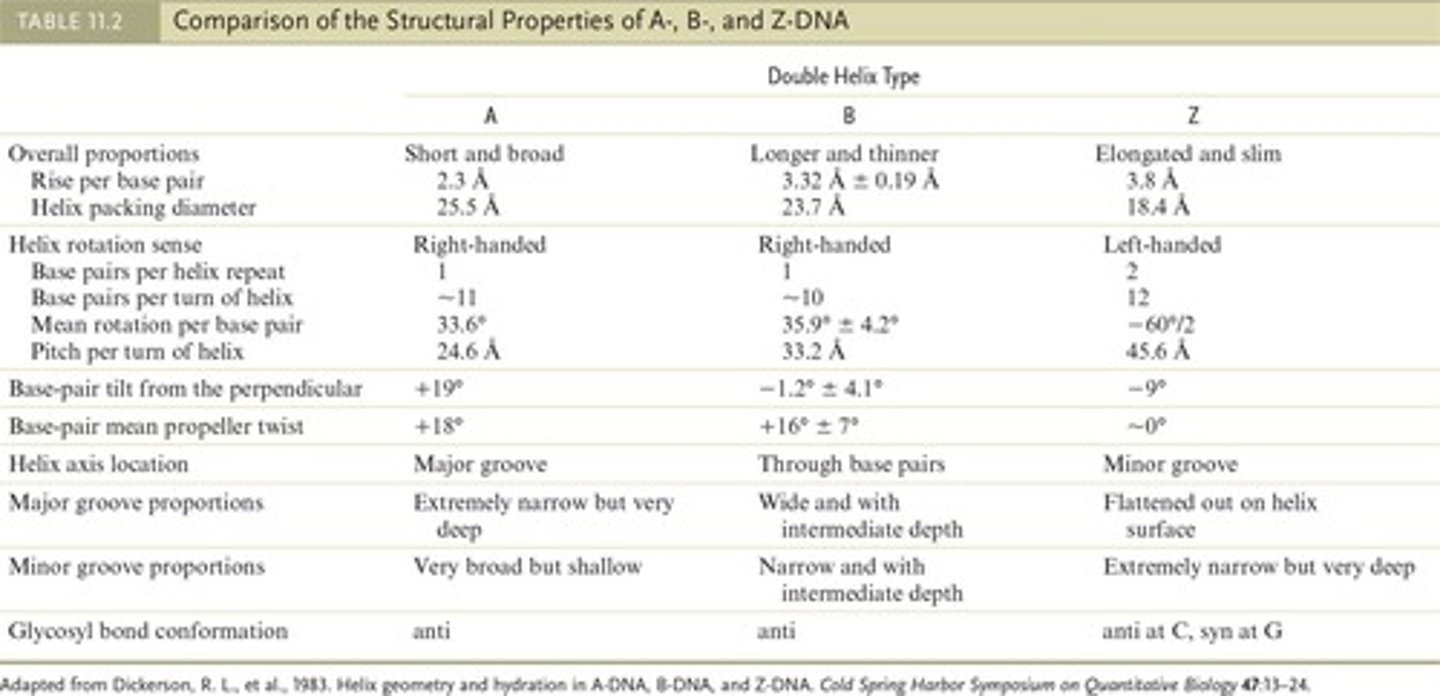
Z-DNA
Left-handed DNA helix, involved in gene regulation.
Major Groove
Wide groove in DNA, protein-binding site.
Minor Groove
Narrow groove in DNA, less accessible to proteins.
Pitch of B-DNA
34 Å per turn of the helix.
Base Pair per Turn
10 base pairs in B-DNA helix.
Hydrophobic Interactions
Interactions contributing to DNA stability.
Transcription Factors
Proteins that bind to DNA regulatory regions.
Physiological Relevance of Z-DNA
Potential role in regulating DNA expression.
H-DNA
Triplex DNA with one purine-rich strand.
Cruciform DNA
Secondary structure with four-way junction in DNA.
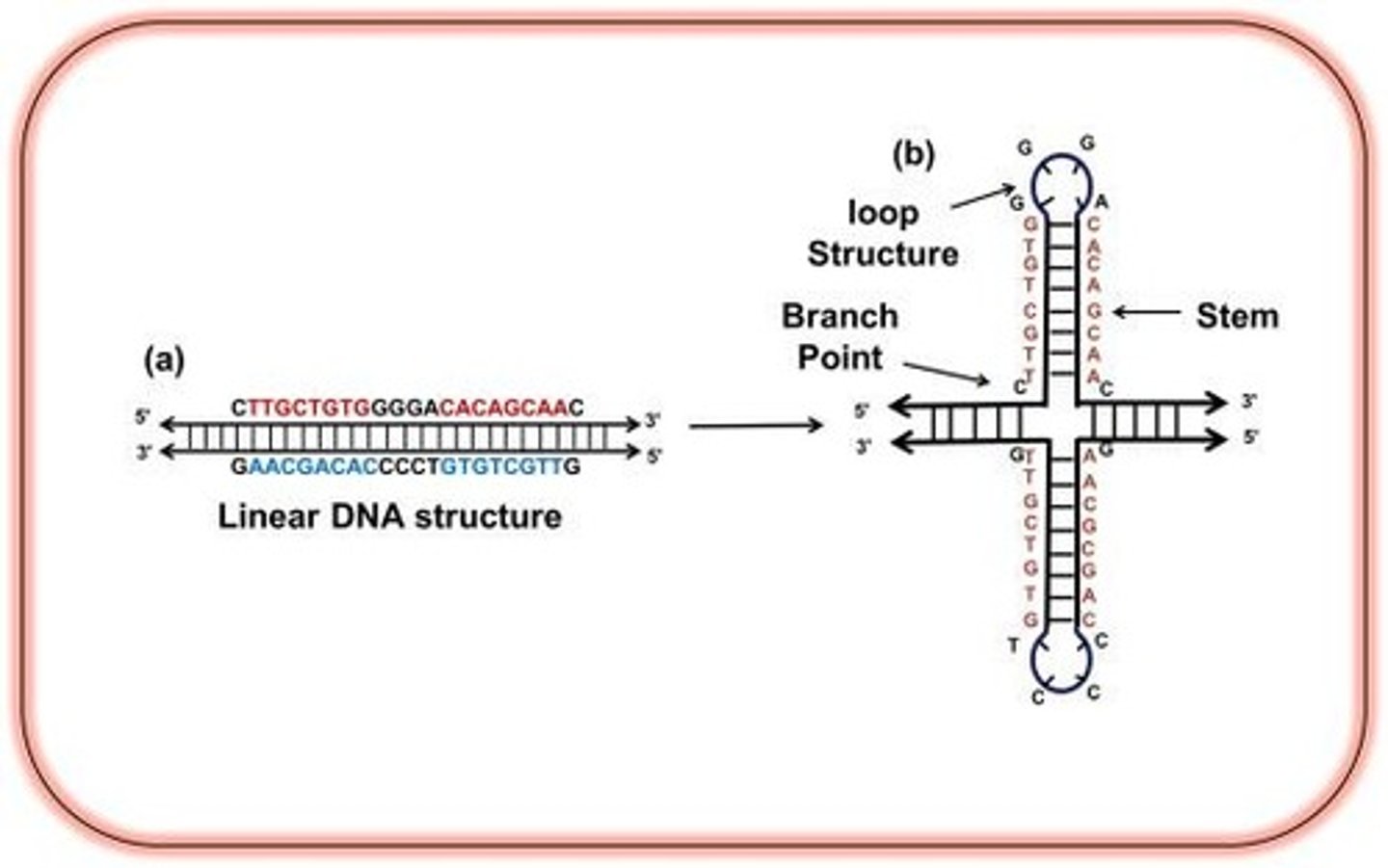
Palindromic regions
DNA sequences that read the same forwards and backwards.
Cytosine methylation
Addition of methyl groups to cytosine residues.
5-methylcytosine
Methylated form of cytosine in DNA.
Epigenetics
Study of heritable changes without nucleotide sequence alteration.
Intercalating agents
Molecules that insert between DNA base pairs.
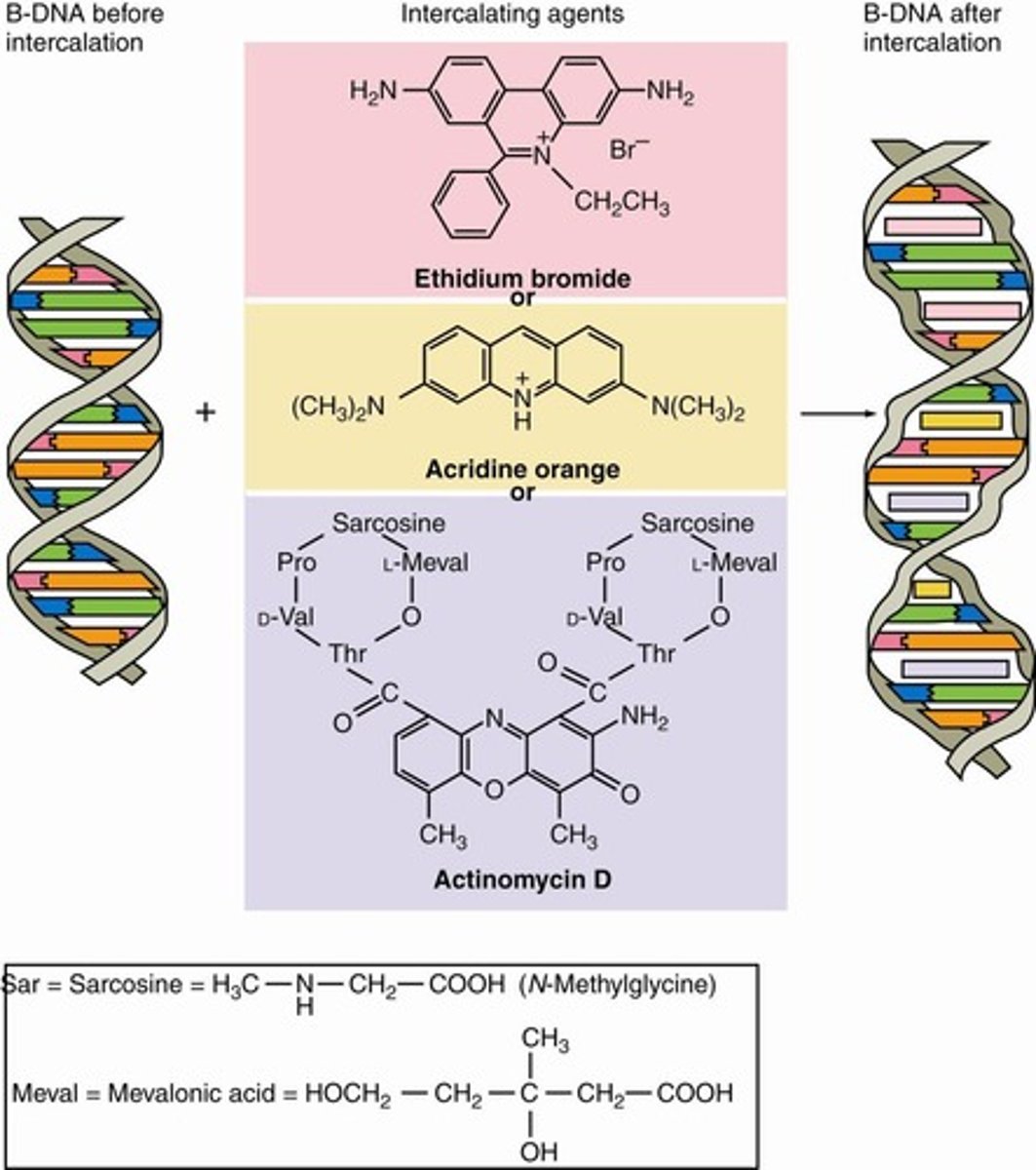
Ethidium bromide
Intercalating agent used in DNA visualization.
Renaturation
Reassociation of denatured DNA strands into duplex.
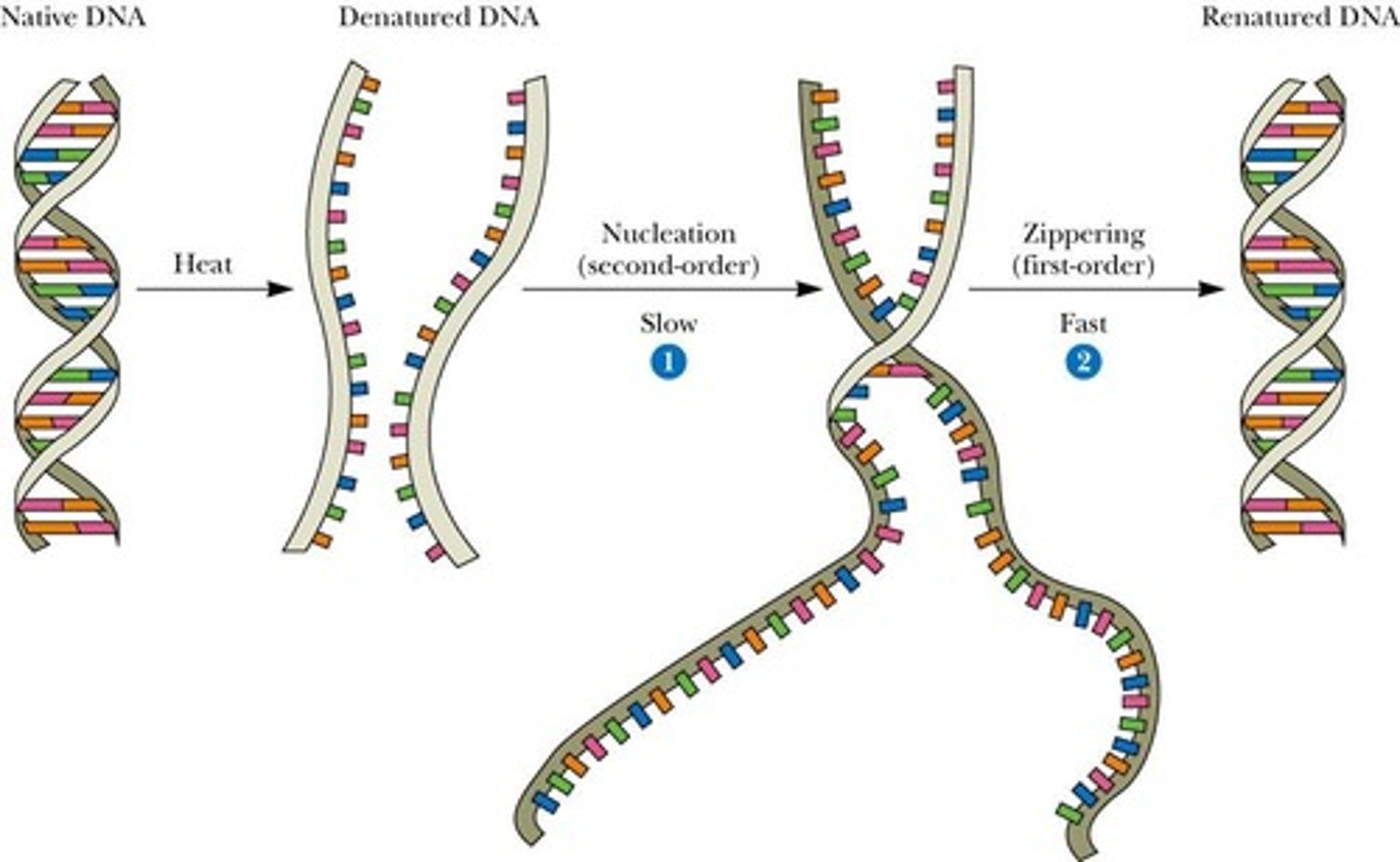
Reannealing
Process of realigning complementary DNA bases.
Hybrid duplexes
DNA from different species forming stable pairs.
Sequence similarity
Degree of resemblance between different DNA sequences.
Supercoiled DNA
Circular DNA with altered helical turns.
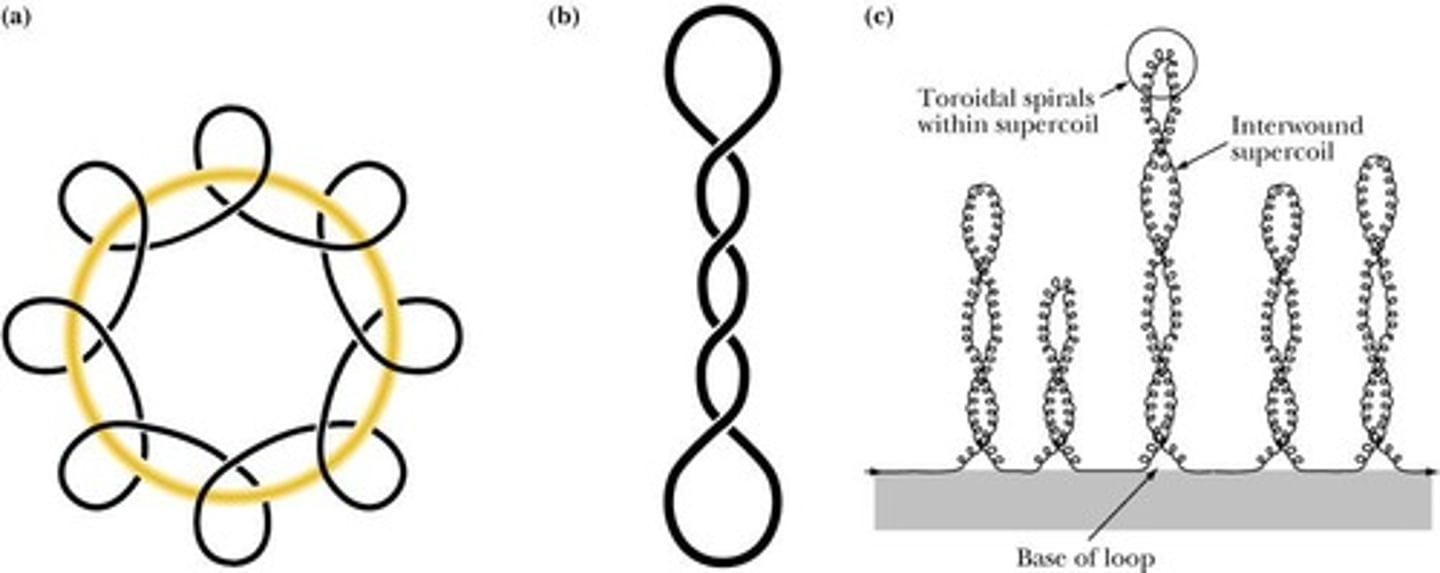
Linking number (L)
Sum of twist (T) and writhe (W) in DNA.
Twist (T)
Number of helical turns in DNA structure.
Writhe (W)
Supercoiling of DNA in three-dimensional space.
DNA gyrase
Topoisomerase introducing negative supercoils into DNA.
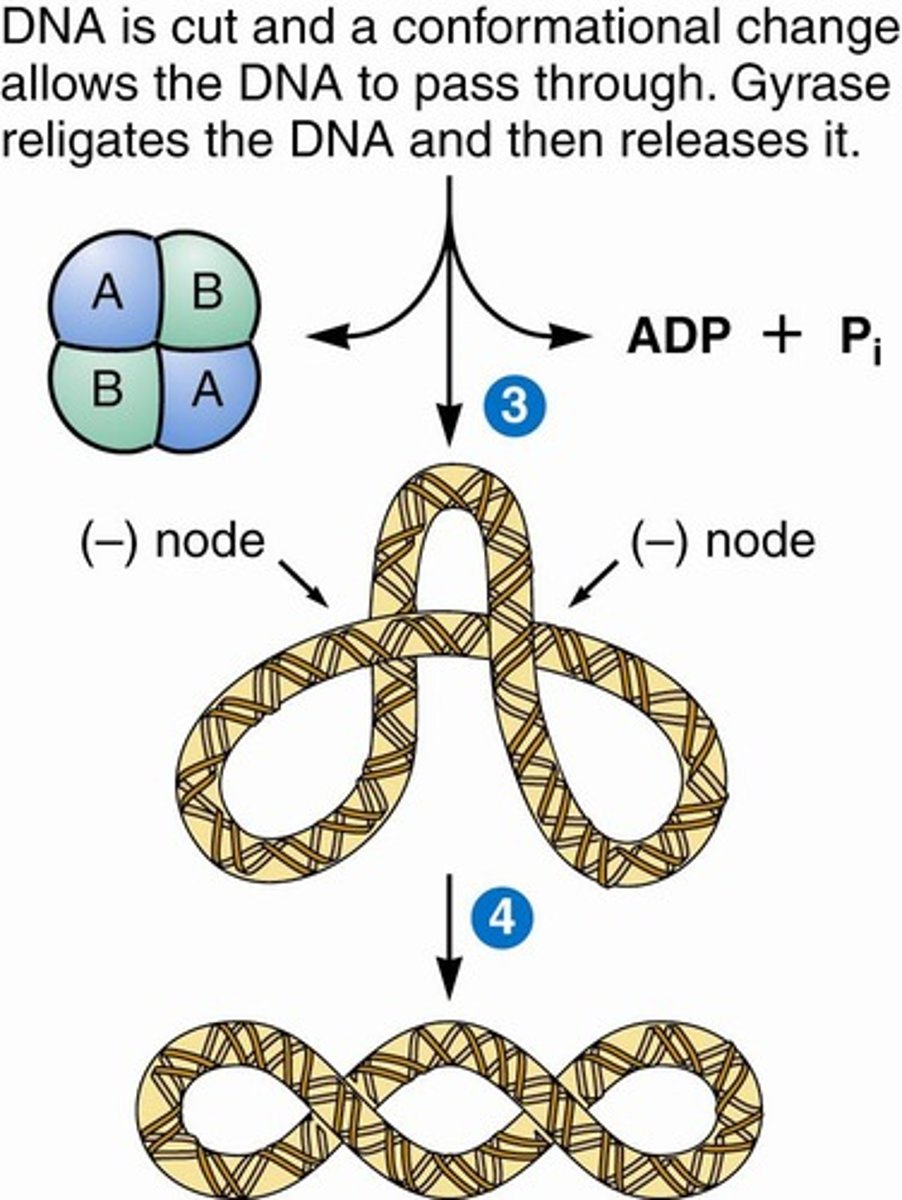
Negative supercoiling
Underwinding of DNA, facilitating strand separation.
Topoisomerases
Enzymes that alter DNA supercoiling.
Human DNA length
Total length of human DNA is approximately 2 meters.
Aromatic macrocycles
Flat hydrophobic molecules that intercalate in DNA.
Actinomycin D
Antibiotic that intercalates into DNA, inhibiting transcription.
Nucleus
Cellular structure about 5 micrometers in diameter.
Compression
DNA is compressed over 100,000 times.
Nucleosomes
DNA wrapped around protein spools for packaging.
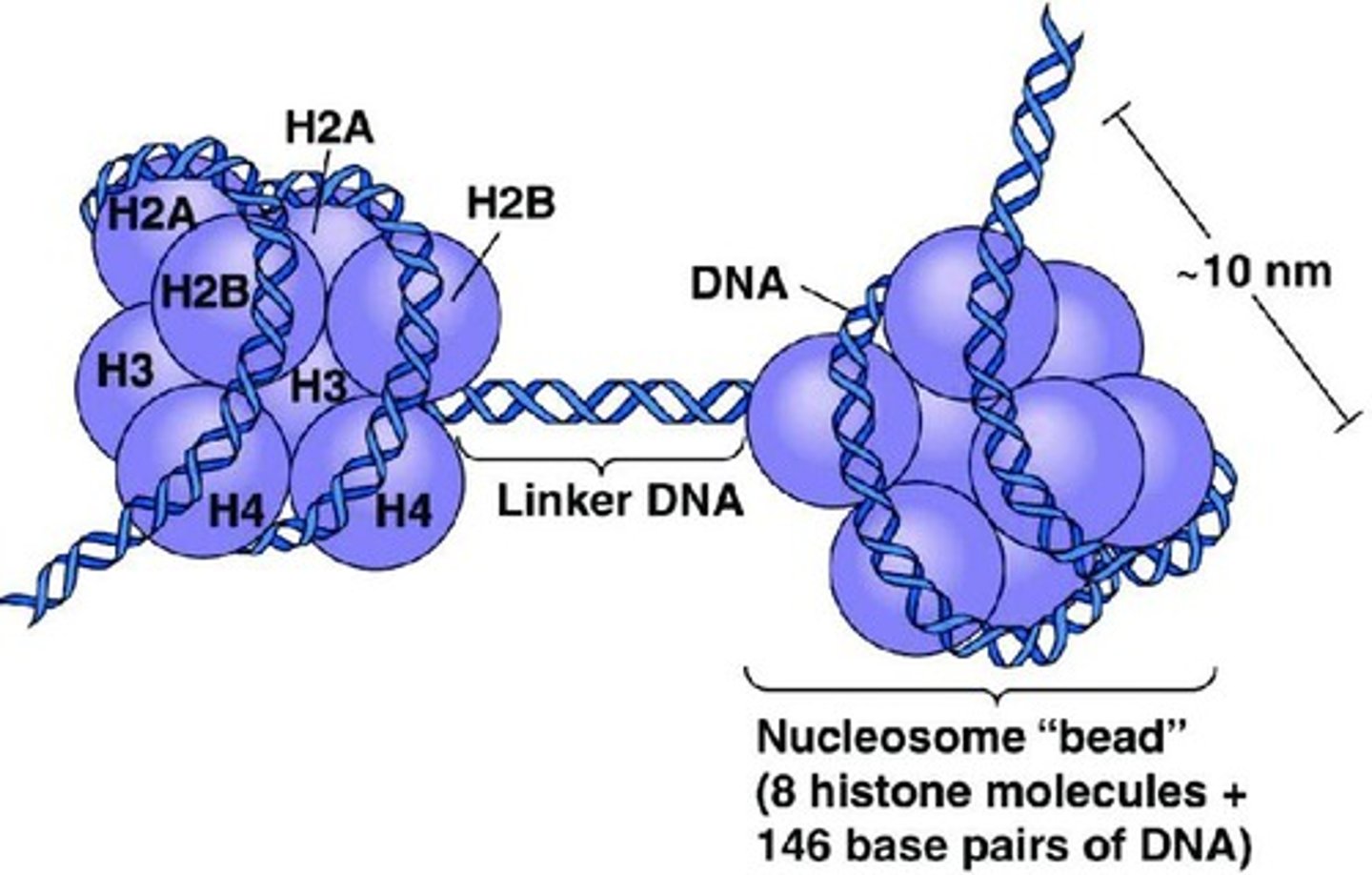
Histone Proteins
Two classes of chromatin proteins: histones and nonhistones.
Distinct Histones
Five known histones: H1, H2A, H2B, H3, H4.
Octameric Core
Histones H2A, H2B, H3, H4 form octamer structures.
Chromatin
Nucleoprotein complex of histones and nonhistone proteins.
Beads-on-a-string
Primary chromatin structure motif resembling beads on string.
30-nm Fiber
Secondary chromatin structure formed by nucleosome arrays.
Long Loops
30-nm fiber forms loops of 60,000-150,000 bp.
Miniband Unit
18 loops arranged radially in chromosome structure.
SMC Proteins
Aid chromosome organization and dynamics during mitosis.
RNA Structure
RNA is typically single-stranded with high conformational freedom.
Intrastrand Base Pairing
Complementary RNA sequences join within the same strand.
Secondary Structures of RNA
Includes stems, loops, bulges, and junctions.
Hairpin Structures
Formed by imperfect base pairing in RNA.
Tertiary Structures of RNA
Arise from coaxial stacking and pseudoknot formation.
tRNA
Contains 73-94 nucleotides with extensive intrastrand base pairing.
L-shaped tRNA
Phenylalanine tRNA adopts an 'L' shape.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Makes up about 2/3 of ribosome structure.
X-ray Crystallography
Technique revealing detailed ribosome tertiary and quaternary structures.
Quaternary Structure
Interactions between ribosomal proteins and rRNAs in ribosome.
Conserved Secondary Structures
Secondary features of rRNA are conserved across types.