Exam II - Positive Sense RNA Viruses and Prions
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Picornavirus
a family of naked positive sense virus containing single stranded RNA. They have icosahedral symmetry and are very small.
naked
is picornavirus naked or enveloped?
positive sense
is picornavirus positive or negative sense?
Icosahedral symmetry
describe the shape of picornavirus.
Polio virus
picornavirus part of the enterovirus class causing infection of the Peyer's patches of the intestines and motor neurons. Mostly irradicated but still seen in India, Pakistan, and Nigeria.
Fecal oral route
route of transmission of polio virus
Peyers patches and motor neurons
tropism of polio virus
vaccine available and improved sanitation
two reasons for decreased poliovirus infection
flaccid asymmetric paralysis
the main complication of polio virus infection. Occurs due to the destruction of presynaptic motor neurons in the anterior horn of the spinal cord as well as the destruction of postsynaptic neurons exiting the cord.
Coxsackievirus (A and B)
picornavirus part of the enterovirus first identified in New York, but is widely distributed worldwide. Most cases (60%) are subclinical.
Fecal oral, respiratory droplets, saliva, contaminated water
four modes of transmission of coxsackievirus
Coxsackie A
form of coxsackievirus primarily causing skin and mucosal infections. Ie) hand foot mouth disease, herpangina, and acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis
2-6, 8, 10
three coxsackie A serotypes causing herpangia
5, 10, 16
three coxsackie A serotypes causing hand, foot, and mouth disease
24
coxsackie A serotype causing acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis.
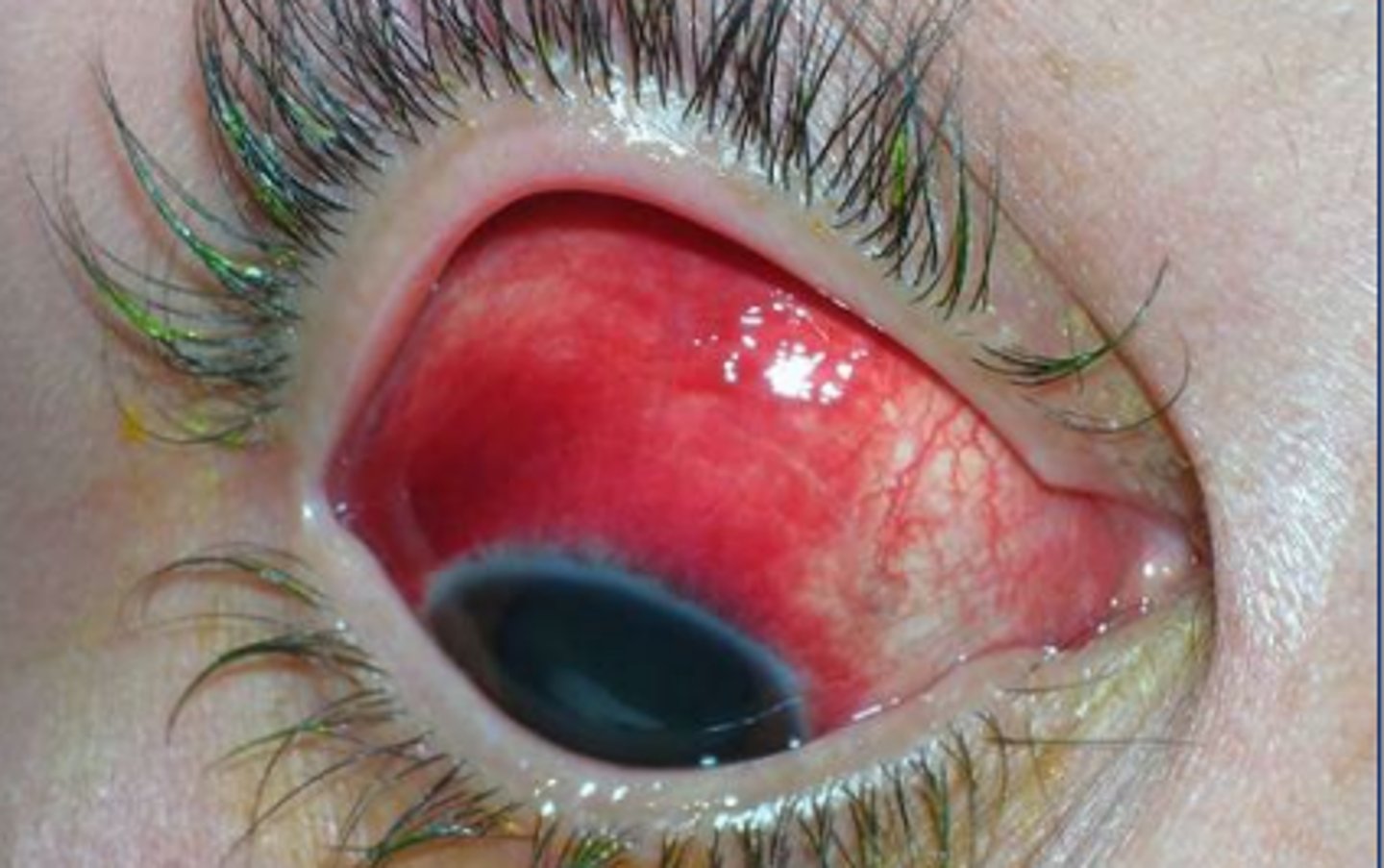
Coxsackie B
form of coxsackievirus primarily causing pleurodynia and myocarditis/pericarditis.
Rhinovirus
picornavirus which replication in surface epithelium of nasal mucosal and spread via contact with infected secretion. Produces a common cold due to infection.
epithelium of nasal mucosa
where does rhinovirus replicate?
Direct contact, fomites, self inoculation
three routes of transmission for rhinovirus
Togavirus/Rubivirus
family of enveloped positive sense virus containing single stranded RNA. They have icosahedral symmetry
enveloped
is rubivirus naked or enveloped?
positive sense
is rubivirus positive or negative sense?
icosahedral symmetry
describe the shape of togavirus
E1
glycoprotein of togavirus/rubivirus that interacts with host receptors to facilitate viral attachment to the host.
E2
glycoprotein of togavirus/rubivirus that interacts with capsid and E1 to reach the host golgi for assembly.
Acquired infection
infection of rubivirus where the virus enters the repiratory tract. It then disseminates via blood and lymph to other tissues. A rash develops and the virus is shed from the oropharynx.
respiratory tract, blood and lymph, oropharynx
in acquired infection of rubivirus the virus enters the _____. It then disseminates via _____ (2) to other tissues. A rash develops and the virus is shed from the ______
Respiratory tract secretions
transmission of acquired rubella virus infection
Congenital infection
infection of rubivirus that occurs due to maternal viremia. It is spread trans placentally to the fetus. After birth infants excrete the virus in the throat and urine. Infections that occur earlier in pregnancy are more severe.
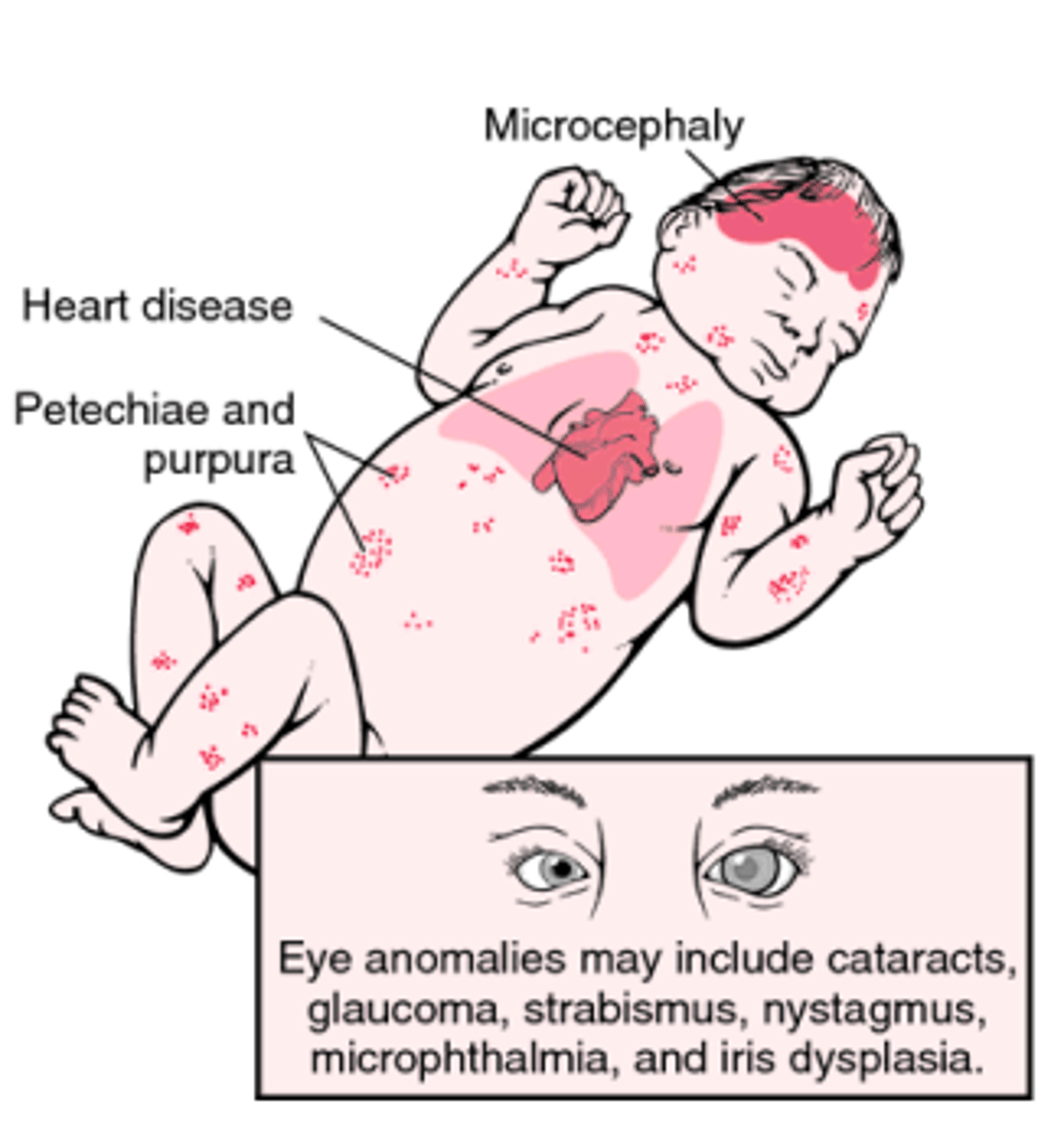
Cataracts, cardiac abnormalities, deafness
triad of congenital rubella infection
Retrovirus
a family of enveloped positive sense virus containing single stranded linear diploid RNA which is translated in the reverse direction via reverse transcriptase to form double stranded DNA. Has the ability to then incorporate itself into the host genome.
positive sense
is HIV positive or negative sense?
HIV/retrovirus
name one positive sense RNA virus that is unique in that it replicates in the nucleus
enveloped
is HIV naked or enveloped?
Icosahedral symmetry
shape of immature retrovirus/HIV. Become cylindrical shaped when they mature
Plasma membrane
host cell structure that HIV derives its envelope from
Protease
proteins of HIV that destroy host proteins
Reverse transcriptase
protein of HIV that converts viral RNA to DNA which can be incorporated into the host genome.
Integrase
protein of HIV that integrate viral genetic material into the host genetic material
Capsid proteins
protein of HIV that is measurable in serum during early infection
Matrix proteins
protein of HIV that holds glycoprotein spikes in the cell envelope
Sexual contact (via small ulcerations), blood transfusion, needles, transplacental
transmission of HIV
CD4+ T cells
tropism of HIV including other immune cells such as macrophages, monocytes, and CNS dendritic cells.
Clinical latency
HIV infection stage where that is asymptomatic, but there is still viral replication. Occurs for about 8 years.
400-200
levels of CD4 cells in HIV infection where there is a wasting syndrome that occurs. Opportunistic infections also occur.
AIDS
HIV infection stage where CD4 count is less than 200. The immune system fails and severe opportunistic infections occur.
<50
CD4 levels in HIV infection where there is almost no immune response and the patient is highly susceptible to opportunistic infections.