Chemistry - Chapter 5 and 6
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1
New cards
Wavelength
The distance
between two
waves
between two
waves
2
New cards
Amplitude
The height of a wave
3
New cards
Frequency
How often a wave
goes up and down
goes up and down
4
New cards
The speed of light
c = 3.0 x 10^8 m/s
5
New cards

FOR THE LEFT SIDE: say if it has (short or long) or (lowest or highest): wavelength, energy, and frequency
Short Wavelength
High energy
High frequency
High energy
High frequency
6
New cards

FOR THE RIGHT SIDE: say if it has (short or long) or (lowest or highest): wavelength, energy, and frequency
Long Wavelength
Low energy
Low frequency
Low energy
Low frequency
7
New cards
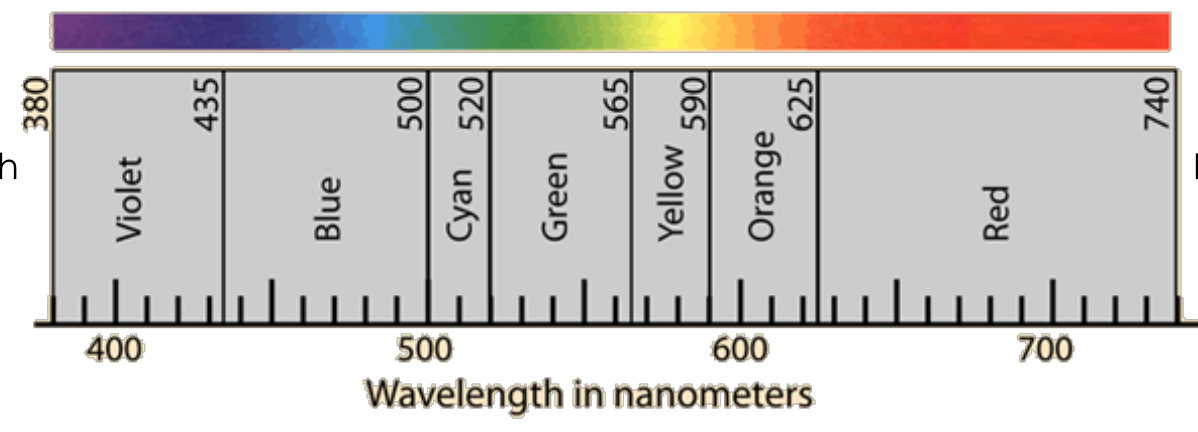
FOR THE LEFT SIDE: say if it has (short or long) or (least or most) (lowest or highest): wavelength, energy, and frequency
Short wavelength
Most energy
Highest frequency
Most energy
Highest frequency
8
New cards
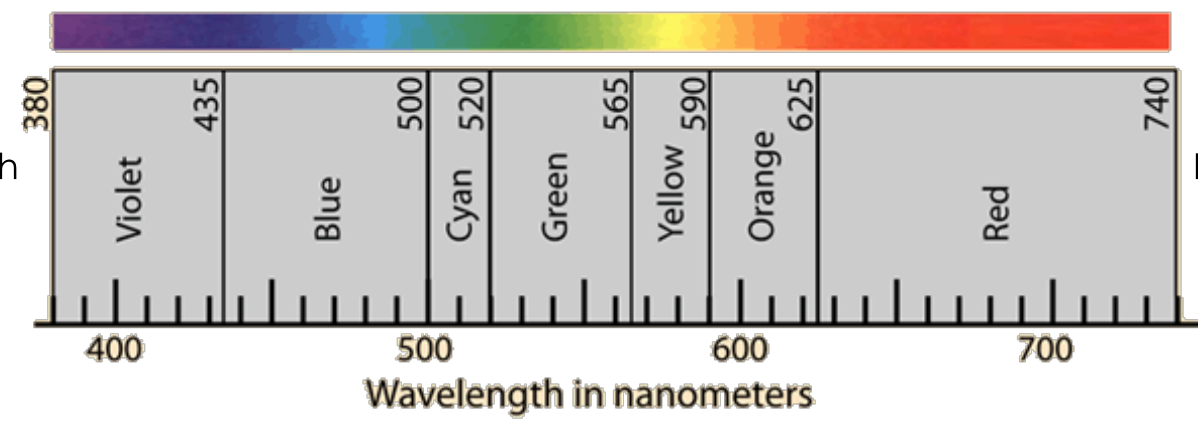
FOR THE RIGHT SIDE: say if it has (short or long) or (least or most) (lowest or highest): wavelength, energy, and frequency
Long wavelength
Least energy
Lowest frequency
Least energy
Lowest frequency
9
New cards
In order for an electron to move to
another level they have to...
another level they have to...
...absorb a specific amount
of energy
of energy
10
New cards
Excited State
When electrons absorbs energy
and moves to a higher energy
level
and moves to a higher energy
level
11
New cards
Ground State
When electrons "fall" back to their
original energy level, they release light
original energy level, they release light
12
New cards
Are excited states stable or unstable?
Unstable
13
New cards
How does the Emission Spectra connect to changing the color of light?
The higher the fall the more
energy is released,
changing the color of light
produced.
energy is released,
changing the color of light
produced.
14
New cards
What are the 3 rules for Electron Configurations?
• Aufbau principle
• Pauli Exclusion Principle
• Hund’s Rule
• Pauli Exclusion Principle
• Hund’s Rule
15
New cards
Aufbau
Electrons occupy orbitals of lower energy first.
16
New cards
Pauli Exclusion Principle
An orbital can hold only two electrons and they must have
opposite spin.
opposite spin.
17
New cards
Hund's Rule
In a set of orbitals, the electrons will fill the orbitals in a
way that would give the maximum number of parallel spins
(maximum number of unpaired electrons).
way that would give the maximum number of parallel spins
(maximum number of unpaired electrons).
18
New cards
In the configuration: 1s^2, what does 1 mean?
The MAIN energy level
19
New cards
In the configuration: 1s^2, what does "s" mean?
Sublevels
20
New cards
In the configuration: 1s^2, what does ^2 mean?
Number of electrons in the sublevel
21
New cards
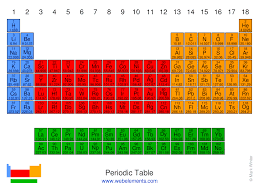
What is the block for the blue area?
s
22
New cards
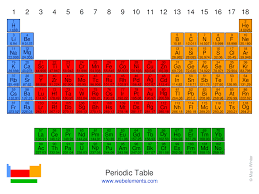
What is the block for the red area?
d
23
New cards
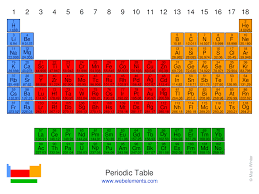
What is the block for the orange area?
p
24
New cards
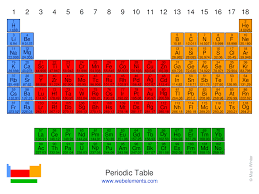
What is the block for the green area?
f
25
New cards
How to calculate the noble gas abbreviation.
1. Use the last noble gas that is located in
the periodic table right before the
element.
2. Write the symbol of the noble gas in
brackets.
3. Write the remaining configuration after
the brackets.
Ex: Fluorine: [He] 2s^2 2p^5
the periodic table right before the
element.
2. Write the symbol of the noble gas in
brackets.
3. Write the remaining configuration after
the brackets.
Ex: Fluorine: [He] 2s^2 2p^5
26
New cards
A family is a ? on the periodic table
Column
27
New cards
Where are the alkali metals?
First column
28
New cards
Where are the alkaline earth metals?
Second column
29
New cards
Where are the transition metals?
Middle section
30
New cards
Where are the metalloids?
Staircase
31
New cards
Where are the halogens?
Second to last column
32
New cards
Where are the noble gases?
Last column
33
New cards
Atomic radius
the size of the atom. PLURAL : Atomic radii
34
New cards
Atomic radius gets (smaller/larger) going down a group and why?
Larger, because we are adding another valence shell.
35
New cards
Atom raduis get (smaller/larger) across a period and why?
Smaller, because the charge in the nucleus is increasing.
36
New cards
Electronegativity
A measure of the attraction an atom has for electrons when bonded.
37
New cards
Electronegativity gets (smaller/larger) going down a group.
Smaller
38
New cards
Electronegativity gets (smaller/larger) going across.
Larger
39
New cards
Which element has the most electronegativity?
F (Fluorine) has the greatest electronegativity at
4.0
4.0
40
New cards
Ionization Energy
The energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion.
41
New cards
Ionization Energy gets (smaller/larger) going across.
Larger
42
New cards
Ionization Energy gets (smaller/larger) going down.
Smaller
43
New cards
Electron Affinity
Energy released when an electron is added to the atom.
44
New cards
Electron shielding
Atoms with more energy levels can't hold onto their valence
electrons as strongly. The pull from the nucleus is partially blocked by each layer of electrons.
electrons as strongly. The pull from the nucleus is partially blocked by each layer of electrons.
45
New cards
(Easier/harder) to remove an electron with more shielding?
Easier
46
New cards
Cation
When atoms lose valence electrons, they become positively charged ions.
47
New cards
Cations are always (smaller/larger) than the original atom.
Smaller
48
New cards
Anions
Atoms that gain electrons become negatively charged
ions. Atoms gain electrons in their outermost
shell.
ions. Atoms gain electrons in their outermost
shell.
49
New cards
Anions are always (smaller/larger) than the original atom.
Larger
50
New cards
Most reactive NON-metal?
Fluorine - F
51
New cards
Most reactive METAL?
Francium - Fr