Chapter 4- Equilibrium
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what is a closed system?
a system where reactants and products can neither be added or removed
what occurs at dynamic equilibrium?
the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the backward reaction
both the forward reaction and backward reactions are still taking place
the concentrations of the reactants and products stays constant and the reaction is continuous
what is le chatelier’s principle?
when conditions on a system in equilibrium are changed, the equilibrium moves in the direction to minimise effects of the change
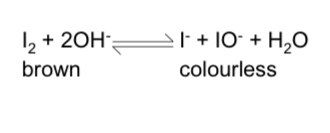
effect of concentration on equilibrium?
increasing concentration of OH- ions causes the equilibrium to shift to oppose this and move in the forward direction to remove OH- ions
the position of equilibrium will shift to the right, giving a higher yield of I- and IO-
the colour would change from brown to colourless
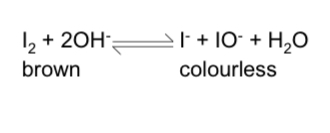
rules for the effect of concentration on equilibrium?
increasing conc of reactants ——> shifts PoE to the right to use up excess reactant
decreasing conc of reactants ——> shifts PoE to the left to produce more reactant
increasing conc of the products ——→ shifts PoE to the left to consume added product
decreasing conc of the products ——> shifts PoE to the right to produce more product (use up reactants)
effect of temperature on equilibrium?
if temp is increased, the equilibrium will shift to oppose this and move in the endothermic direction to try to increase the temp by absorbing heat
if temp is decreased, the equilibrium will shift to oppose this and move in the exothermic direction to try and increase the temp by giving out heat
effect of pressure on equilibrium?
increasing pressure causes equilibrium to shift to the side with fewer moles of gas to oppose the change and therefore reduce the pressure
decreasing the pressure will cause the equilibrium to shift to the side with more moles of gas to oppose the change and therefore increase the pressure
if the number of moles of gas is the same on both sides of the equation, then changing pressure will have no effect on position of equilibrium
explain why actual conditions used in the chemical industry might be different from what may be stated in questions?
too expensive to use a high pressure
too expensive to use a low temperature
what is a catalyst?
a substance that alters the rate of a reaction without being used up
substance that lowers the activation energy of a reaction by providing an alternative route
effect of catalysts on equilibrium?
no effect on position of equilibrium, but speeds up the rate at which the equilibrium is achieved
it speeds up/ alters both the forward and backward rate equally/ by the same amount
why are catalysts used in the industry?
because they lower the costs of the reaction process
they allow lower temps and pressures to be used, whilst achieving the same rate of reaction
they can also give a higher atom economy
how do catalysts increase the sustainability of a reaction?
reactions can be carried out at lower temperatures
reducing energy demand from the combustion of fossil fuels
this results in a reduction of CO2 emissions/ less fossil fuels burnt
what are homogeneous catalysts?
catalysts that are in the same phase as the reactants
what are heterogeneous catalysts?
catalysts that are in a different phase to the species in the reaction
example is in the haber process: solid iron catalyst used to speed up the reaction between hydrogen and nitrogen gases
transition metal catalysts?
electrons are transferred to produce a reactive intermediate and speed up the reaction rate
they make good catalysts because they have variable oxidation states
example is vanadium oxide, used in the contact process
what is ammonia used for?
making fertilisers
making nitric acid
pressure and temperature needed for the haber process?
pressure: 50 - 1000 atm
temperature: 200 - 600 C
describe and explain why the conditions for the haber process are a compromise between rate and equilibrium?
rate
increased pressure increases rate because molecules are closer together
increased temp increases rate because molecules have more kinetic energy
equilibrium
increased pressure pushes equilibrium to the RHS because there are fewer moles on the RHS
increased temp pushes equilibrium to LHS because forward reaction is exothermic
compromise
if temp is too high, low yield
if temp is too low, slow rate
if pressure is too high, increased costs/ safety issues
what is the contact process?
the process used to make sulfuric acid
stage 1 of the contact process?
sulfur is burnt in air to produce sulfur dioxide
stage 2 of the contact process?
sulfur dioxide is reacted with oxygen to produce sulfur trioxide in a reversible reaction
conditions: 450C, 10atm, catalyst- V2O5
stage 3 of the contact process?
sulfur trioxide is dissolved in 98% sulfuric acid to produce fuming sulfuric acid
this is then diluted to produce concentrated sulfuric acid
compromise between rate of reaction and product yield?
e.g- decreasing the temp of a reaction with forward endothermic reaction would increase the product yield, but decrease the rate of reaction
therefore, a compromise is made
reaction conditions are selected to give both a relatively good product yield and a relatively fast rate of reaction.
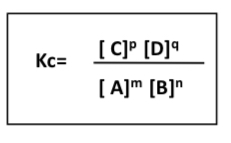
what is the expression for the equilibrium constant Kc?
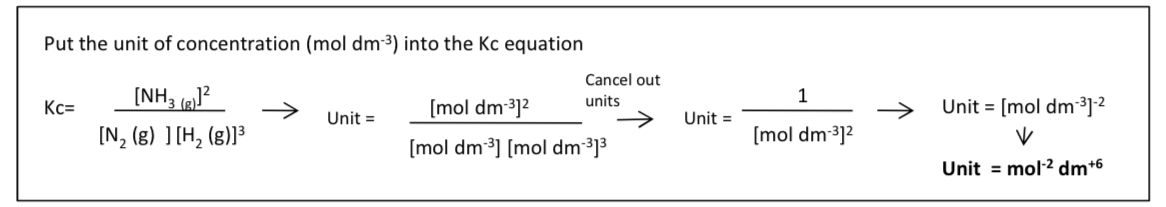
how to work out the unit of Kc?
*the unit of Kc changes and depends on the equation
what does the magnitude of Kc tell us?
the relative proportions of reactants and products in the equilibrium system?
magnitude of Kc?
a Kc value of 1 shows that the PoE is halfway between the reactants and productsw
a Kc value of greater than 1 shows that the PoE is leaning towards the products
a Kc value of less than 1 shows that the PoE is leaning towards the reactants
therefore, the larger the value of Kc, the further the position of equilibrium lies to the right hand side and the greater the concentrations of the products compared to the reactants