Vertebrate Morphology Lab: Anatomy of Sharks, Fish, Frogs, and Pigs
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Dermal Denticles
Tough protective covering on skin that resemble tiny teeth. Hydrodynamic properties. Sharks
Nares
Incurrent and excurrent apertures, used in odor detection. Sharks
Ampullae of lorenzini
Specialized sensory cells that are capable of detecting weak electric fields at short ranges. Sharks
Spiracle
First gill slit that may be highly reduced or absent in most fast moving sharks. Provides for oxygenated blood directly to the eye and brain. Sharks
Gill slits
Exit for water that has passed through the gills after entering the mouth. Sharks
Claspers
Male copulatory organs
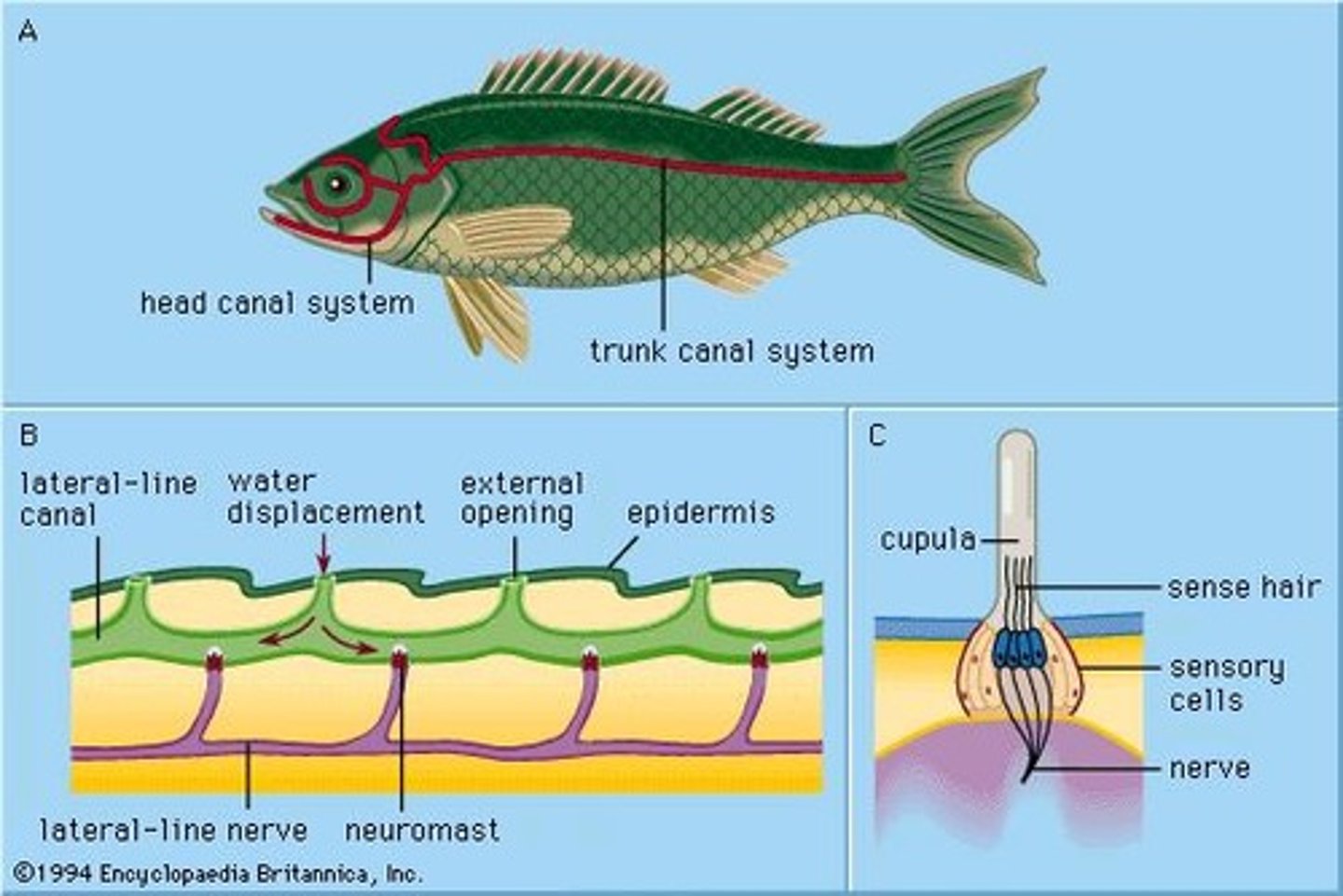
Lateral line
Series of small fluid filled canals lying just beneath the skin. Transforms underwater sound into nerve impulses.
Stomach (shark)
Three parts: cranial, fundic, and pyloric. Food storage and digestion
Pancreas (shark)
a flattened white gland that secretes digestive juices and insulin
gall bladder (shark)
a green sac that holds bile for enzymatic digestion
intestine (shark)
contains the spiral valve, which is an internally twisted or coiled organ that serves to increase the absorptive surface of the intestine
liver (shark)
bile secretion, glycogen and vit D storage. Large, soft, oily organ which occupies 25% of body cavitiy. Produces and holds oil for buoyancy
spleen (shark)
maintenance of blood (destroys old RBC and makes new RBC)
heart (shark)
muscular s-shaped tube with 2 chambers for pumping blood
ventricle (shark)
pumping chamber
atrium (shark)
collecting point of blood for all veins
gill lamellae (shark)
feather-like portion of the gills responsible of gas exchange
kidneys (shark)
elimination of waste and regulation of internal environment
rectal gland (shark)
acts as a salt gland for osmoregulation by removing excess NaCl from blood and secreting it through duct in rectum
ovaries/testes (shark)
female: egg and hormone production
male: gonads for sperm production
cloaca (shark)
a common chamber receiving the openings of the urinary tract, oviduct and intestine
unpaired fins (fish)
two dorsal fins, caudal fin and anal fin
What is the function of the spiny dorsal fin?
stabilization and defense
What is the function of the soft dorsal fin?
low speed swimming
What is the function of caudal fin?
propulsion.
What is the function of anal fin?
stabilization
operculum (fish)
gill cover. Serves as bellows to help pump water over gills
branchiostegal membrane (fish)
seals operculum and prevents backflow of water into gill chamber
nares (fish)
consist of both incurrent and excurrent aperatures, used in odor detection, not breathing
caudal peduncle (fish)
generates power to caudal fin for swimming
stomach (fish)
food storage and digestion.
pyloric caeca aids in both digestion and absorption
gall bladder (fish)
a sac, usually green, holds bile for enzymatic digestion
intestine (fish)
simple intestines for digestion
pancreas (fish)
secretion of digestion juices and insulin.
diffuse organ in fish, over the full surface of the intestine, interspersed with adipose and other connective tissue and blood vessles.
liver (fish)
bile secretion, glycogen and vit D storage
heart (fish)
2 chambers, atrium and ventricle
gill rakers (fish)
strains water and retains food
gill arches (fish)
supports the gills
gill lamellae (fish)
feather like portion of the gills responsible of gas exchange
kidneys (fish)
elimination of waste and regulation of internal environment
gonads (fish)
female, ovaries: egg and hormone production.
Male, testes: sperm production
cloaca (fish)
common chamber receiving the openings of urinary tract, oviduct, or vas deferens and the intestine
swim bladder (fish)
hydrostatic balancing and sound production
myomeres (fish)
blocks or bundles of skeletal muscle. Space between them is myosepta.
Tympanic membrane (frog)
senses vibrations, hearing
nictitating membranes (frog)
covers and protects eye
vomerine teeth (frog)
grasping
maxillary teeth (frog)
chewing
tongue (frog)
attached to anterior of floor of mouth, catching prey
stomach (frog)
mechanical and chemical digestion of food, contains rugae
rugae (frog)
stomach interior folds that increase the surface area of stomach for increased absorption efficiency
small intestine (frog)
chemical digestion and nutrient absorption
large intestine (frog)
water absorption and fecal packing
pancreas (frog)
secretion of digestive juices, insulin
gall bladder (frog)
greenish sac, holds bile for enzymatic digestion
liver (frog)
makes bile, stores carbs, metabolizes fats and other compounds (3 lobes)
fat bodies (frog)
energy storage
heart (frog)
3 chambers
right atrium (frog)
collects blood from sinus venous
kidneys (frog)
elimination of waste, regulation of internal environment
cloaca (frog)
common chamber receiving the openings of the urinary tract, the oviducts or vas deferens, and the intestine.
teats (pig)
mammary papillae
urogenital oriface(pig)
combined urine and reproductive system opening
male: located posterior to umbilical cord
female: located anterior to anus
genital papilla (pig)
female; small fleshy protuberance anterior to urogenital oriface
scrotum (pig)
male; contains testes
palate (pig)
forms roof of mouth, hard palate is anterior portion, soft is posterior
glottis (pig)
opening to trachea
rectum (pig)
passage between intestine and anus
heart (pig)
four chambers
muscular diaphragm (pig)
separates thoracic from abdominal cavities, lung expansion
uterine horns (pig)
provides space for multiple embryos to develop (litter)
spermatic cord (pig)
includes vas deferens
taxonomy
The scientific study of how living things are classified
scientific class for shark
chondrichthyes
scientific class for fish
actinopterygii
scientific class for frog
amphibia
scientific class for pig
mammalia
how many names shark species are there
>500
reproduction in sharks
internal fertilization, produces small numbers, long gestation period, long maturation period, large young
scales of fish
ctenoid or cycloid
osmoregulation in fish
freshwater: no salts enter gut, large volume of urine, salt absorbed by gills, does not drink
saltwater: the opposite of freshwater
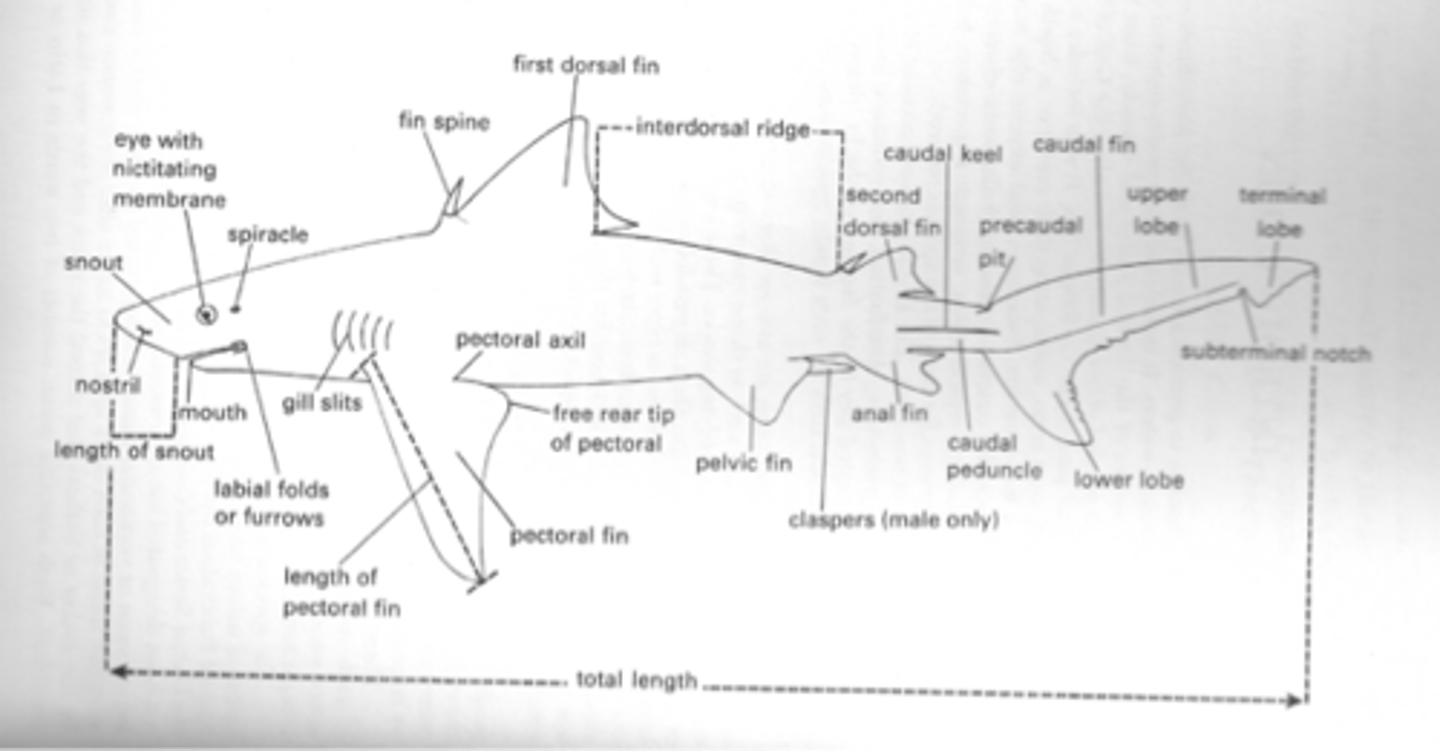
external anatomy of shark
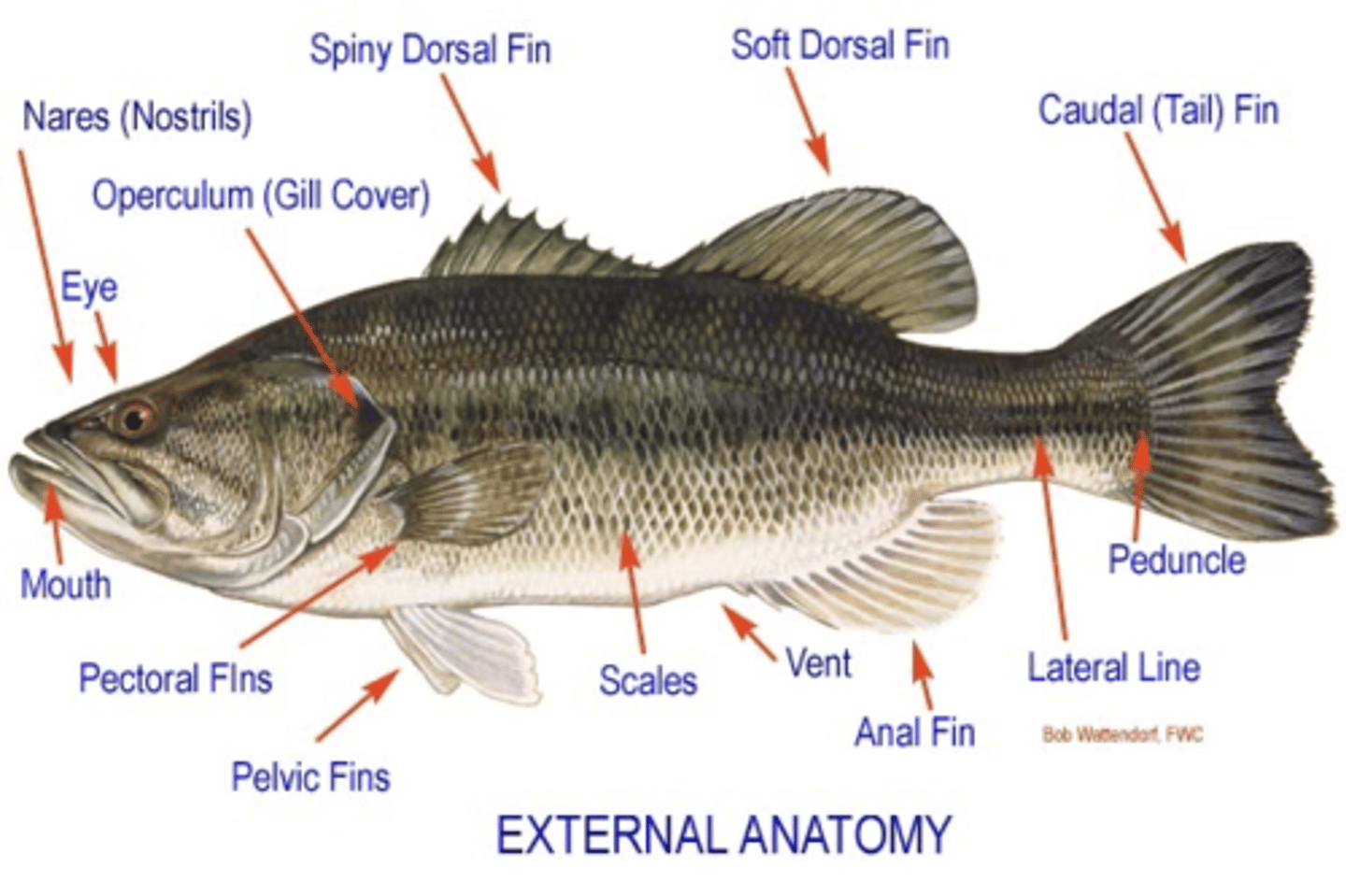
External anatomy of bony fish
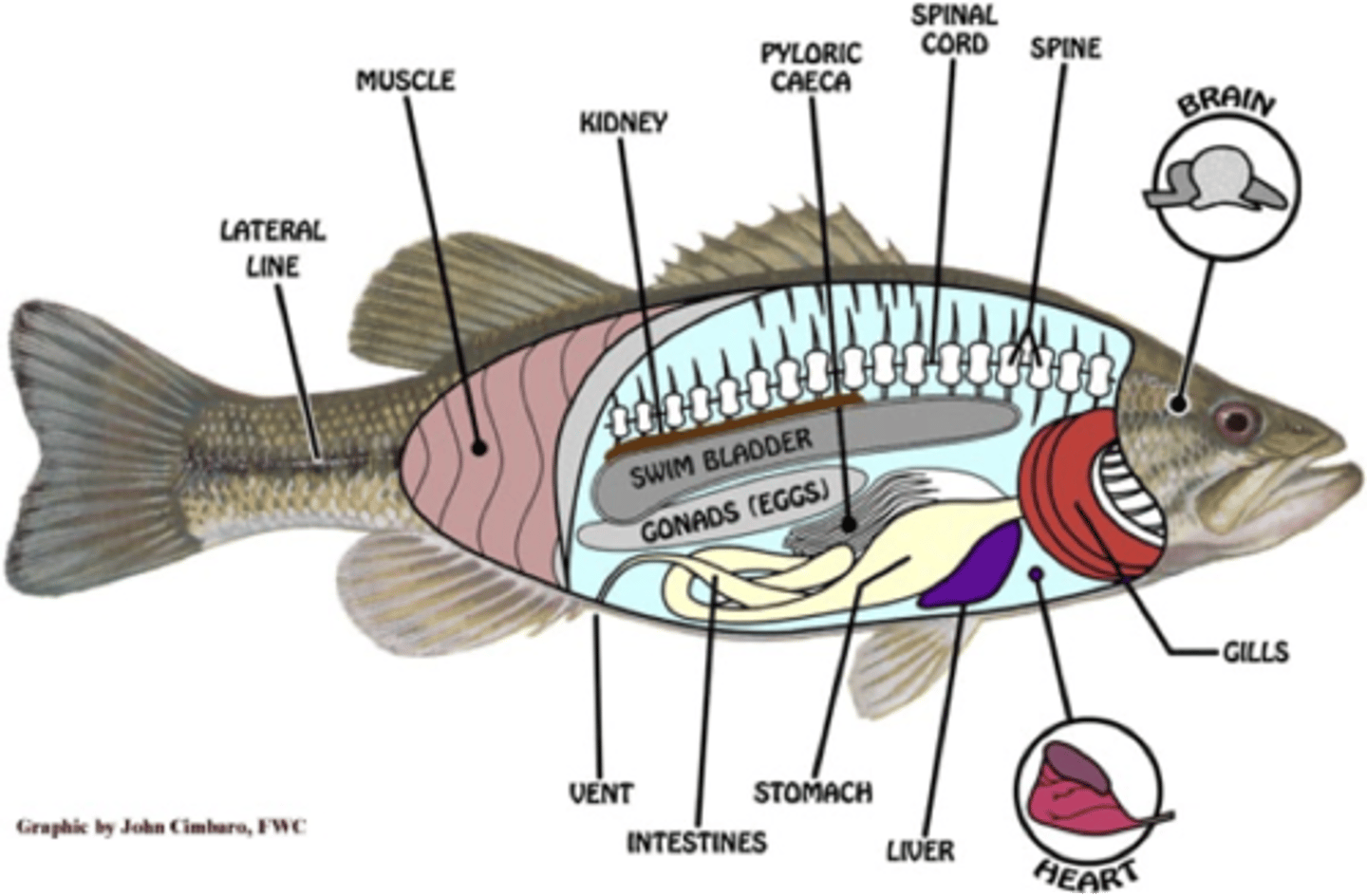
internal anatomy of fish
what did amphibia evolve from
lobe-finned fishes
what type of respiration do amphibia have
cutaneous
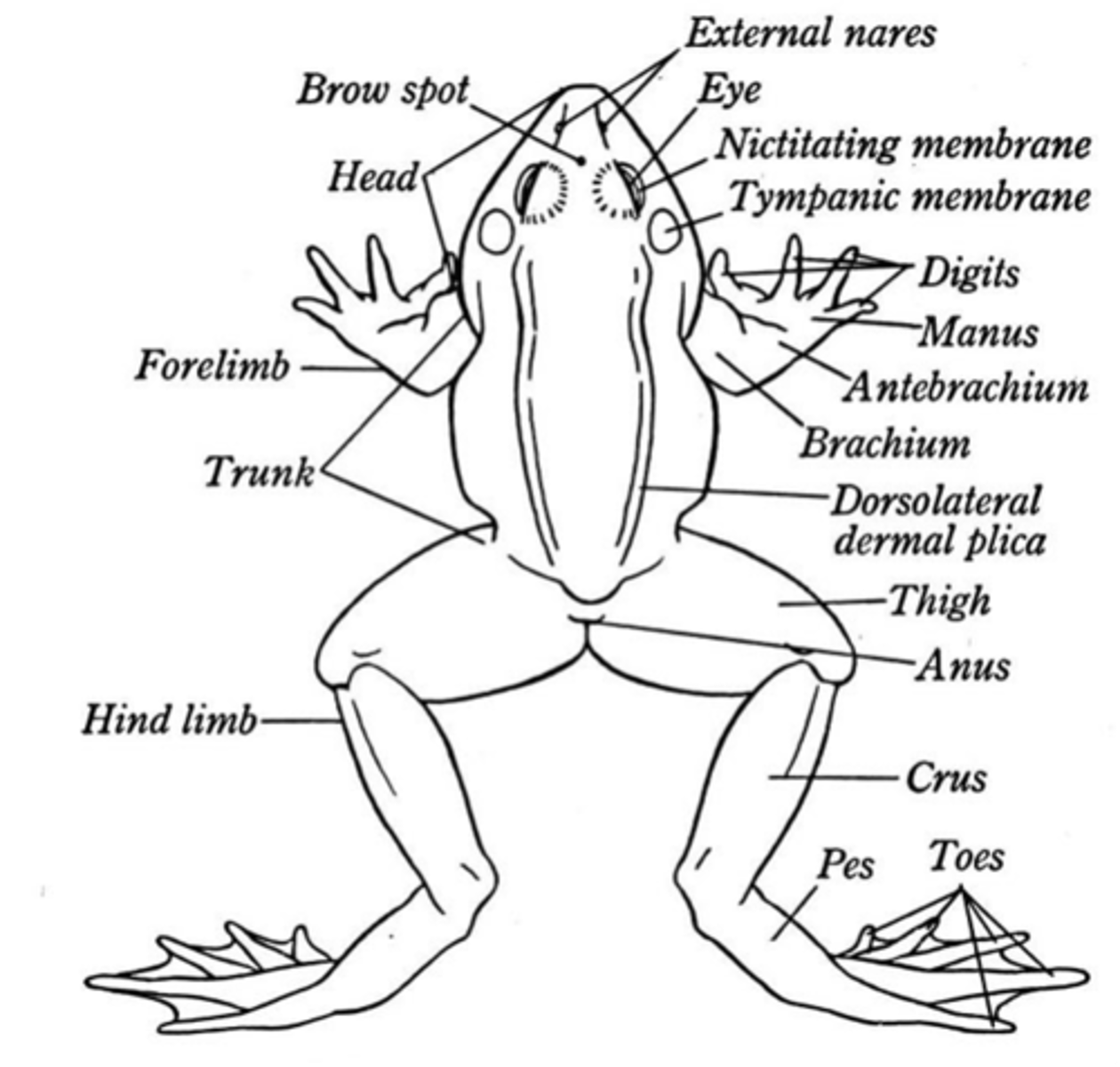
external frog anatomy
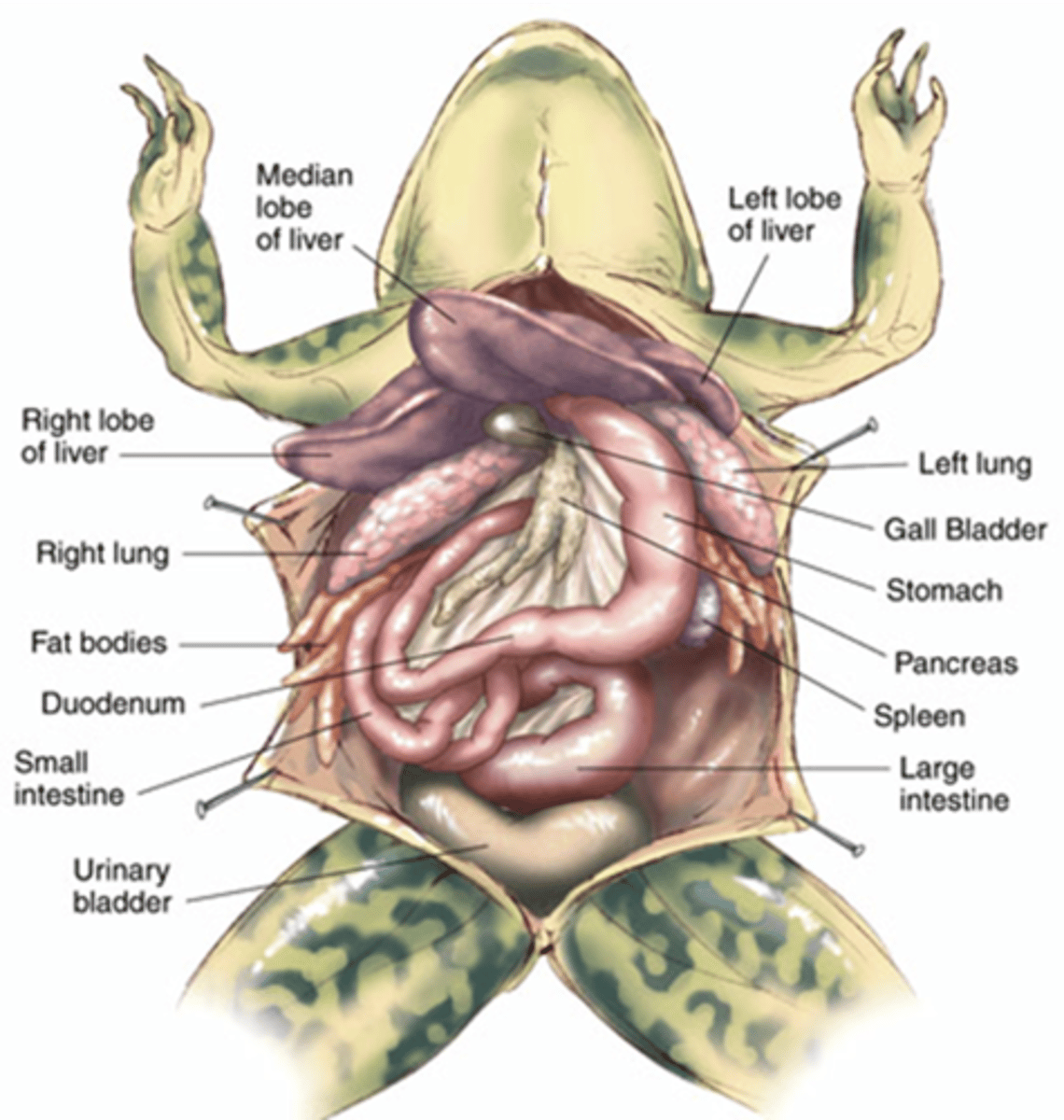
internal frog anatomy
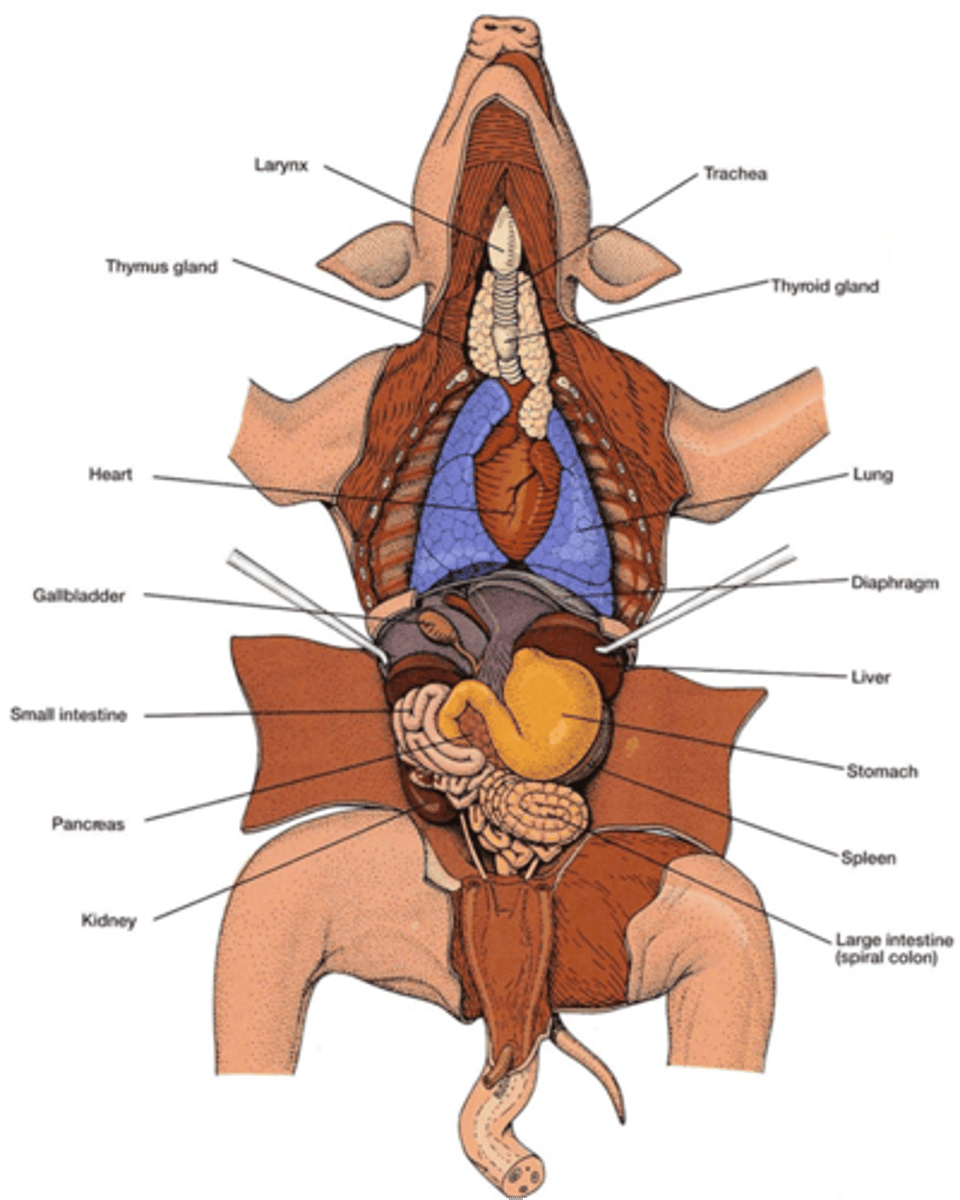
internal pig anatomy