Immunizations & Allergies
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
cell-mediated response
produces t-cell lymphocytes in response to some infections and malignancies
humoral immune response
produces b-cell lymphocytes when the body is exposed to an antigen and also develops antibodies for that antigen; specific to the antigen
nonspecific immune response
causes inflammation in body tissue due to injury; inflammation involves chemical, vascular, and leukocyte activities in the tissues around the injury
specific immune response
activates when inflammation alone is insufficient to manage the infection
neutrophils (polymorphonuclear leukocytes)
specialized blood cells react to infection that threatens the health of the body cells and protects those cells from damage
monocytes
WBCs that eventually mature into macrophages and perform phagocytosis
eosinophils
WBCs that are attracted to cells and parasites coated with C2B substances; they secrete chemicals to erode the walls of the invading organism
basophils
WBCs important in hypersensitivity reactions in the allergic response
lymphocytes
WBCs responsible for the antigen-antibody response and sensitization (memory) to antigens to which the body has been exposure to previously
natural immunity
the body's inherent ability to fight infections through physical barriers and immune responses without prior exposure to specific pathogens
acquired immunity
results from being exposed to a disease or being immunized through vaccinations
active immunity
long-term immunity and often lasts for the person’s lifetime; immunizations typically lead to active immunity
passive immunity
temporary immunity gained through the transfer of antibodies from one individual to another, such as from mother to child during breastfeeding
immunodeficiency diseases
occur when the immune system is unable to fight the disease and protect the body
autoimmune disorders
occur when the body perceives part of its own body as a foreign substance and develops self-antigens to that part in order to destroy it
hypersensitivity and allergy reactions
occur when the body becomes inflamed and organs become dysfunctional when a foreign substance enters the body
autoimmune hemolytic anemia
the body does not recognize the body’s RBCs and they are destroyed by b-cells
multiple sclerosis
chronic or progressive neurological disorder that affects the myelin sheath
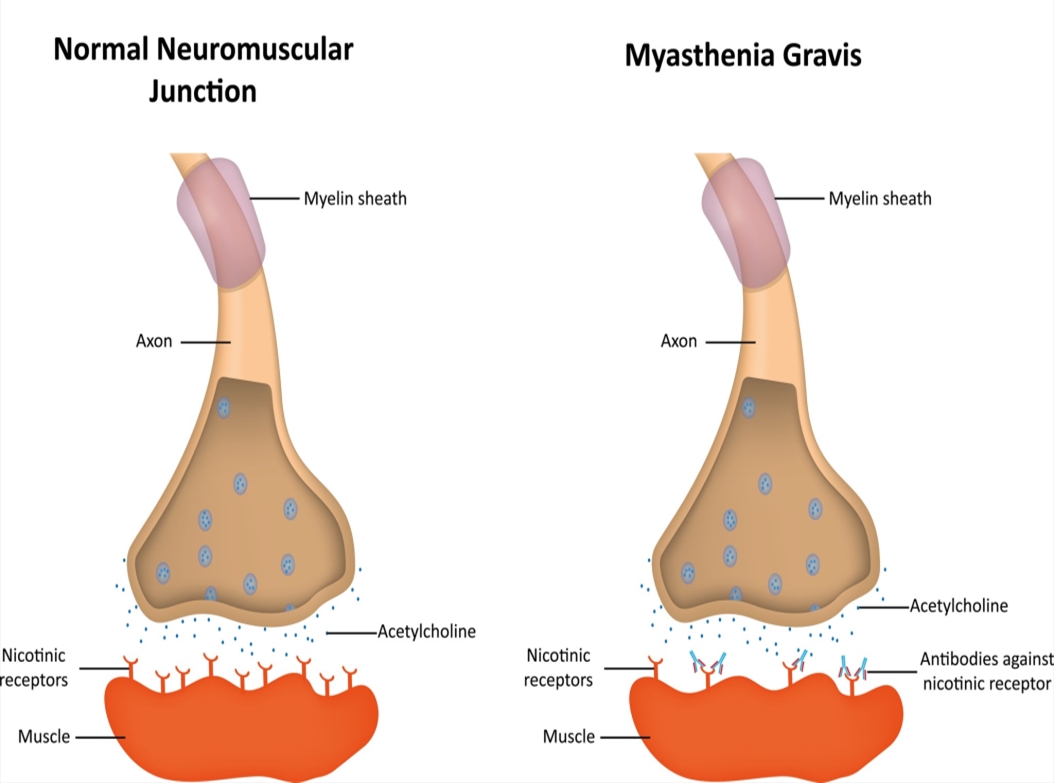
myasthenia gravis
neuromuscular disease that shoes sporadic weakened muscles, espcially after strenuous activity
pernicious anemia
inherited autoimmune blood cell production disorder and results from a deficiency of intrinsic factor in which RBCs develop abnormally when B12 is deficient
rheumatoid arthritis
chronic diseases that causes an inflammation and destruction of synovial membranes of the joints; the cartilage and bone erode over time and become deformed
systemic lupus erythematosus
chronic systemic disorder that can affect connective tissue throughout the body
hypersensitivity
allergy to a substance to which a person does not normally react
allergic reaction
a local or generalized reaction of an organism to contact with a specific allergen
hay fever
seasonal respiratory reaction to allergens such as pollen
asthma
serious respiratory reaction in which the bronchial tubes constrict, causing serious breathing difficulties
urticaria
spreading of reddened and elevated lesions (hives)
anaphylaxis
a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction that occurs when the body’s immune system overreacts to a substance (allergen)
intradermal allergy testing
a skin test where a small amount of a suspected allergen is injected under the skin to check for an allergic reaction
skin patch allergy testing
a medical procedure where small amounts of potential allergens are applied to the skin under patches
scratch allergy testing
an allergist or nurse will put a tiny bit of an allergen on the skin, then make a small scratch or prick on the skin
CBC
the CBC test identifies and counts the 7 types of cells found in the blood