Grade 9 - Cells and Tissue
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
(F) Who discovered the cell
Robert Hooke
(F) Who discovered first living cell
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
(F) Ho coined term protoplasm
Purkinje
(F) Who discovered the nucleas
Robert Brown
(F) Who worked on the cell theory
Theodor Schwann , Matthias Schleiden , Rudolf Virchow
(SA) Plasma Membrane
It acts as an outer covering of the cell
It consists of a selectively permeable membrane
Osmosis takes place through the plasma membrane
(D) Osmosis
The movement of solvent (water) molecules through a semipermeable membrane from an area of it’s higher concentration to it’s lower concentration.
(LA) Explain the different types of solutions
Isotonic Solution
The concentration of solute and water is equal in the medium and inside the cell
There is no net movement of water.
The size of the cell stays the same
Hypertonic Solution
The concentration of water (solvent) is lower in the medium than inside the cell.
There is a movement of water outside the cell. This is called endosmosis
The cell will shrink
Hypotonic Solutions
The concentration of water (solvent) is higher in the medium surrounding the cell than inside the cell
There is a movement of water inside the cell. This is called endosmosis.
The cell will swell up.
(SA) Cell wall
Cell wall is a covering in addition to plasma membrane present in plant cells.
It is made up of cellulose
It allows the plant to witsand hypotnic solutions
When put in a hypotonic solution due to osmosis the contents of the cell shrink away from the cell wall. This is known as plasmolysis
(F) What solutions can be used to stain the cell.
Iodine solutions , safranin solution , methylene blue
(LA) Nucleus
The nucleus is a double membrane bound spherical structure that contains genetic material
It is covered by a double layered membrane known as nuclear membrane
The membrane contains nuclear pores which allow the transfer of materials between cytoplasm and nucleus
The nucleus contain chromosomes which are used for cell reproduction
Chromosomes are formed from chromatin material when the cell is ready for reproduction
Chromosomes are made of DNA and Protein
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It stores the genetic information necessary for the construction and organisation of a cell.
The functional segments of DNA are called genes
Prokaryotes lack a membrane bound nucleus they consist of nucleoid
In prokaryotes chlorophyll is not stored in plastids but membraneous vesicles
(D) Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is the fluid content enclosed within the plasma membrane
(LA) Differentiate between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Prokaryotic Cell
They are very small is size ranging from 1 - 10 micrometers
They do not have a membrane bound nucleus but only a region containing nucleic acid known as nucleoid
They only have one chromosome
Membrane bound cell organelles are absent
Eukaryotic Cell
They are larger in size ranging from 5 - 100 micrometers
They have a double membrane bound nucleus
They contain multiple chromosmes
Membrane bound cell organelles are present
(LA) Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membrane bound vesicles.
There are two types of ER , Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
RER appears rough as they contain ribosomes and synthesise proteins
SER synthesise lipids and fats
These proteins , lipids and fats sometimes act as regulating hormones
SER plays a crucial role in detoxifying many poisons and drugs
The ER acts as a medium of transport of substances mainly proteins through the cell
The ER form the cytoplasmic framework which act as a surface for biochemical activities of the cell
Some of the proteins and lipid molecules synthsized help build the cell membrane in a process known as membrane biogenesis
(LA) Golgi Appartus
The Golgi apparatus consists of membrane bound vesicles that form sacs called cisterns
They package and transport the materials synthesised in the ER to various targets inside and outside the cell.
The functions of the Golgi Complex include storage , transportation and packaging of materials
It was discovered by Camilio Golgi
It produces lysosomes.
(SA) Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes produced by the ER.
They help clean up the cell by breaking down waste materials and worn out organelles
They also break down foreign particles such as bacteria that enter the cell.
In certain conditions , such as if a cell is damaged the lysosomes release their enzymes digesting the cell itself
(SA) Mitochondria
Mitochondria is a double membranous organelle that produces energy for the cell in the form of Adenosine Triphosphate.
ATP is used to create new chemical compounds and perform mechanical work
The outer covering of mitochondria is porous while the inner covering of mitochondria is deeply folded to increase the surface area for ATP production
They have their own dna which allows them to be semi autonomous , manufacture their own proteins and duplicate themselves in times of need,
(LA) Plastids
Chromoplasts - pigment containing plastids
Leucoplasts - transparent plastids that store starch , sugars etc.
Chloroplats - plastids that contains chlorphyll
Properties of Plastids
They have a double membrane
They have their own DNA and ribosomes
They consist of membrane layers embedded in a material called stroma
(SA) Vacuoles
They are storage sacs in the cell
They are alrger in plant cells than animal cells
THey contain cell sap and providde turgidity and rigidity to the pcell
It stores many important substances like amino acids , sugars and organic acids , proteins.
In some unicellular organisms the vacuoles help in expelling excess water and some wastes from the cell
(SA) Meristematic Tissue
Meristematic tissue are the tissues that divide and help grow the plant
They have a dense cytoplasm , large nucleus , thin wall
Vacuoles are absent
(SA) Types of Meristematic Tissue
Apical Meristem - present on the growing tips of plants and helps increase the height
Lateral Meristem - present on the lateral side of stem and it helps increase it’s thickness and girth
Intercalary Meristem - It is presentt near the node and help grow new leaves , stem and buds
(LA) Differentiate between animal and plant tissue
Plant Tissue
They are designed to be stationary
Consist of living and non living cells
Use less energy
Have unlimited growth
Undergo differentiation
Animal Tissue
They are designed for movement
Consist of only living cells
Uses more energy
Have limited growth
Do not undergo differentiatiion
(D) Differentiation
The process in which meristematic tissues stop dividing and take up a specific role or function.
(LA) Simple Meristematic Tissue and it’s types
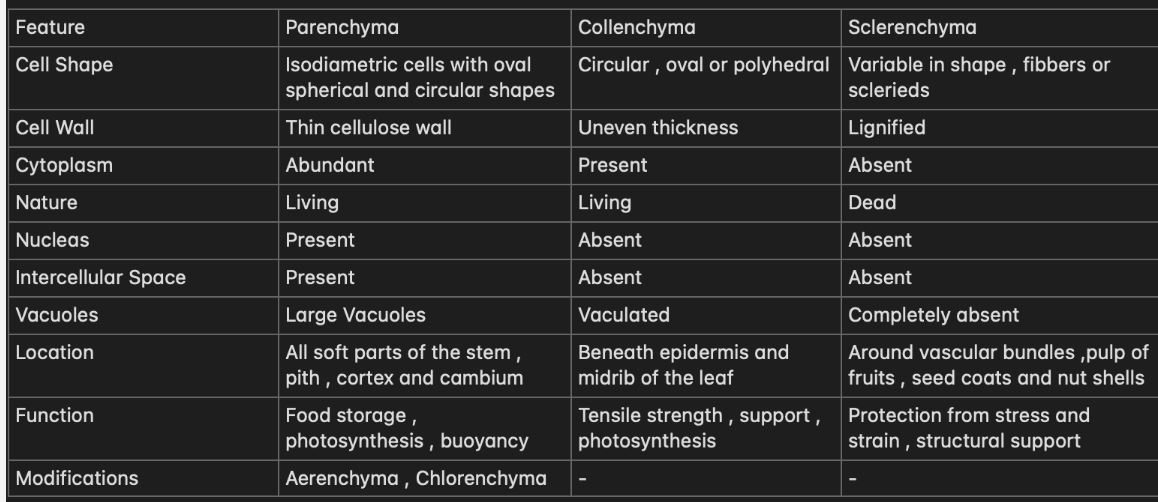
(D) Cutin , Lignin , Suberin
Lignin is present in the sclerenchyma and given it it’s hardness
Cutin is the waxy coating on the epidermis in some plants to prevent the water loss
Suberin is present in the cork cell and makes it impervious to gas and water
(LA) Epidermis Functions

(LA) Differentiate between xylem and phloem
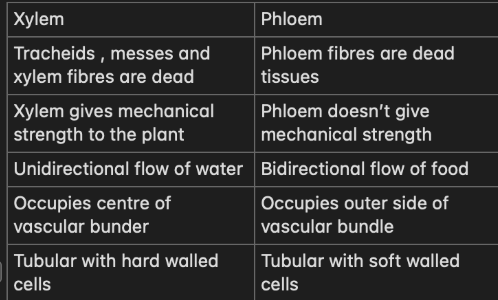
(SA) Xylem and it’s parts
Tracheids - they are dead cells with pits and they help in the vertical movement of water
Xylem Vessels - they are dead cells with pits that help in the conduction and movement of water
Xylem parenchyma - only living cells of xylem , it stores food for the tissue and helps in sideways conduction of water
Xylem Fibres - also dead cells that the xylem in its functions. They are not perforated
(SA) Phloem and it’s parts
Sieve tubes - tubular cells with perforated walls
Sieve cells - sieve cells do not form into sieve tubes and lack sieve plates
Companion cells - small elongated cells that help in the translocation of food
Phloem fibres - the only dead cells which are made of sclerenchyma
Phloem parenchyma - stores food for the phloem and helps in lateral conduction
(SA) Differentiate between meristematic tissue and permanent tissue
Meristematic Tissue
Cells divide rapidly
Vacuoles are absent
Always living cells
Its types are apical . lateral and intercalary
Permanenet Tissue
Cells do not divide as they have undergone differentiation
Vacuoles are present
Can be living or dead
Mention its types
(F) What is collagen
substnace present in the basement membrane of epithelium
(SA) Epithelial Tissue
It form a barrier to keep different body parts seprated
It covers most organs and cavitiies of the bodu
The basement membrane containg collagen seprates the epitehlium from the underlying tissues
(LA) Types of Epithelium
Squamous Epithelium - single layered flat cells that cover the linings of blood vessels and alveoli where substance transport occurs
Stratified squamous - found in the skin , it is a squamous epithelium with cells aranged in many layers to prevent wear and tear
Cuboidal - manily provides mechanical support , also performs functions of absorbtion and secretion found mostly in salivary glands and kidney tubules
Columnar - tall pillar like cells usually found in the inner lining of the small intestine that perform the functions of absorbtio and secretion
Ciliated Columnar - they have cilia which help in pushing or moving substances like mucus forward. It is found in the repiratory tract , spermducts and oviducts
Glandular epithelium - when epithelial tissue folds inwards to form a multicellular gland it is called a glandular epithelium
(F) what minerals are present in bone
calcium and phosphorous
(SA) Charecteristics of connective tissue
The cells are loosly spaced and embedded in an intercellular matrix which may be solid or liquid
(SA) DIfferentiate between tendons and ligament
Ligament
Joins bone to bone
Elastic and flexible
Made of yellow fibrous tissue
Tendon
Joins muscle to bone
Rigid and tough
Mad of white fibrous tissue
(SA) Differentiate between areolar and adipose tissue
(SA) Differentiate between striated , non striated and cardiac muslce tissue
Striated
Multinucleated
Cylindrical in shape
Present in limbs , face , neck etc.
Unbranched fibres
Voluntary in action
Unstriated
Uninucleated
Spindle Shaped
Present in iris , alveoli , uterus etc.
Unbranched fibres
involuntary in action
Cardiac
Uninucleated
Cylindrical
Present in heart
branched fibres
involuntary in action
(SA) Nerve tissue
The nerve tissue carries electrical signals throught the body from the brain.It’s structure consists of
Dendrites which receive signals from other neurons and allow transmission
Cell body - contains all the normal things like nucleus , golgi body etc.
Axon - the tube like long structure that carries the impulse
Synapse - it is the chemical junction between the terminal of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron