Baylor BIO 1105 Midterm Exam
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
What is the function of a dissecting microscope?
To examine and dissect biological specimens.
Eyepiece lens
the part of a compound light microscope that magnifies an image, usually 10 times, also called an ocular lens
objective lens
the part of a compound light microscope that is located directly above the specimen and that magnifies the image of the specimen
arm
Supports the tube and connects it to the base
Base
supports the microscope
stage plate
Platform on which a specimen is placed
stage clips
holds the slide in place on the stage
magnification adjustment
a knob on either side of the microscope that's used to adjust the magnification of the objective lens
focus adjustments
knobs on either side of the microscope that are used for focusing the microscope on the slide or specimen
light sources
transmitted light source- lighting from the base
reflected light source- light from above
brightness control
Used to control how bright or dim the light is. Located on the side of the microscope, at the bottom.
Research applications of a dissecting microscope
- view three dimensional objects and larger specimens
- study external features on an object
- examine structures not easily mounted onto flat slides
What is the function of a compound microscope?
viewing samples at a higher magnification that a dissecting microscope.
body tube
Connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses
Nosepiece
Holds the objectives and can be rotated to change the magnification
Diaphram
Controls the amount of light passing through the opening of the stage
coarse adjustment knob
this part moves the stage up and down to help you get the specimen into view (4x and 10x)
fine adjustment knob
this part moves the stage slightly to help you sharpen or "fine" tune your view of the specimen (10x and 40x)
stage
Supports the slide being viewed
stage control
These knobs move the stage left and right or up and down.
condenser lens
concentrates the light and makes illumination of the specimen more uniform
power switch
turns the microscope on and off
research applications of compound microscopes
- view small samples that cannot be identified with the naked eye
- viewing samples with high magnification
Advantage of knowing the FOV for each objective
If you know the FOV diameter, you can estimate the size of an organism.
Calculating the FOV of a high power objective using the measurements taken under low power
FOVlow x Mag low = FOV med/high X Mag med/high
How do you find the measurement of the cell size?
Divide the diameter of the FOVhigh by the number of stomata counted for the measurements of the cell
How to calculate the total magnification using the power of the eyepiece and the objective lens
Objective lens x ocular lens
Using imagej, how do you measure the surface area.
-Set scale using line tool & analyze
-Crop using rectangle tool
-Set the threshold so that the leaf is black and the background is white
-select the leaf with the wand tracing tool, analyze, and measure to collect SA
Using imagej, how do you measure the stomatal density
Count the number of stomata in the FOV given and divide by the total surface area to approximate stomatal density
Using imagej, how do you measure the stomatal size?
use the line tool to measure the length and width of the stomata
How to calculate the canopy area of a tree in the field?
Use a tape measure and find the distance from the edge of one drip line across the diameter of the canopy to the other edge; measure in at least 3 directions (field)-A=πr^2
Why is measuring a tree's canopy important to research?
- the relationships between the environment and the trees growing on a site cannot be distinguished.
- Without the detailed measurements we cannot understand the potential for growth contained within a single tree, a species, or a population.
- how much trees photosynthesize, biodiversity, and their roles in the carbon cycle
Describe the application and value of using GIS for scientific research
- geospatial analysis
- make a map of the campus that communicates the location of each tree and then lauers biological information
- archiving of trees
- analysis of descriptive information and exploration of patterns and relationships
How to find and map a tree using Google Earth Pro
-Type in coordinates
-Pin location
How to measure canopy area using the polygon tool on Google Earth
-Draw polygon tool
-New polygon
-Pick a color
-Outline the tree
-New polygon; measurements tab
-Set unit to meters
Advantages and disadvantages of using digitalized measurement tool
-Advantages:wide scale, collaborative research-Disadvantage:not very accurate
Describe the parts of a scientific paper
AIMRaD:
Abstract(BPMRD;main purpose and main results)
-Introduction
-Methods(determine the main steps in their protocols)
-Results
-Discussion
Recognize the general differences between a primary research article and a review article.
-Primary research: scientific journals, actual experiments, AIMRaD, peer reviewed
-Review Article: Scientific journals, summation of results, authors didn't do the experiments
metacognition
the awareness and understanding of your thought processes (scaffolds)
Growth mindset
belief that qualities can change/improve through effort
fixed mindset
the idea that we have a set amount of an ability that cannot change
planning
identifying goals and strategies
Monitoring
keeping track of your progress toward the goals
Evaluating
continually assessing the solutions and evaluating your strategies
What does Monitoring, Planning, and Evaluating have to do with learning and metacognition?
Metacognitive skills include planning your learning, monitoring whether your current learning strategies are successful, and evaluating results of your learning.
accuracy
Accuracy refers to the closeness of a measured value to a standard or known value
Precision
Precision refers to the closeness of two or more measurements to each other
micrometers
x1million
millimeters
1000x
centimeters
100x
meters
1x
kilometers
x1/1000
calculate the mean
average
calculate the standard deviation
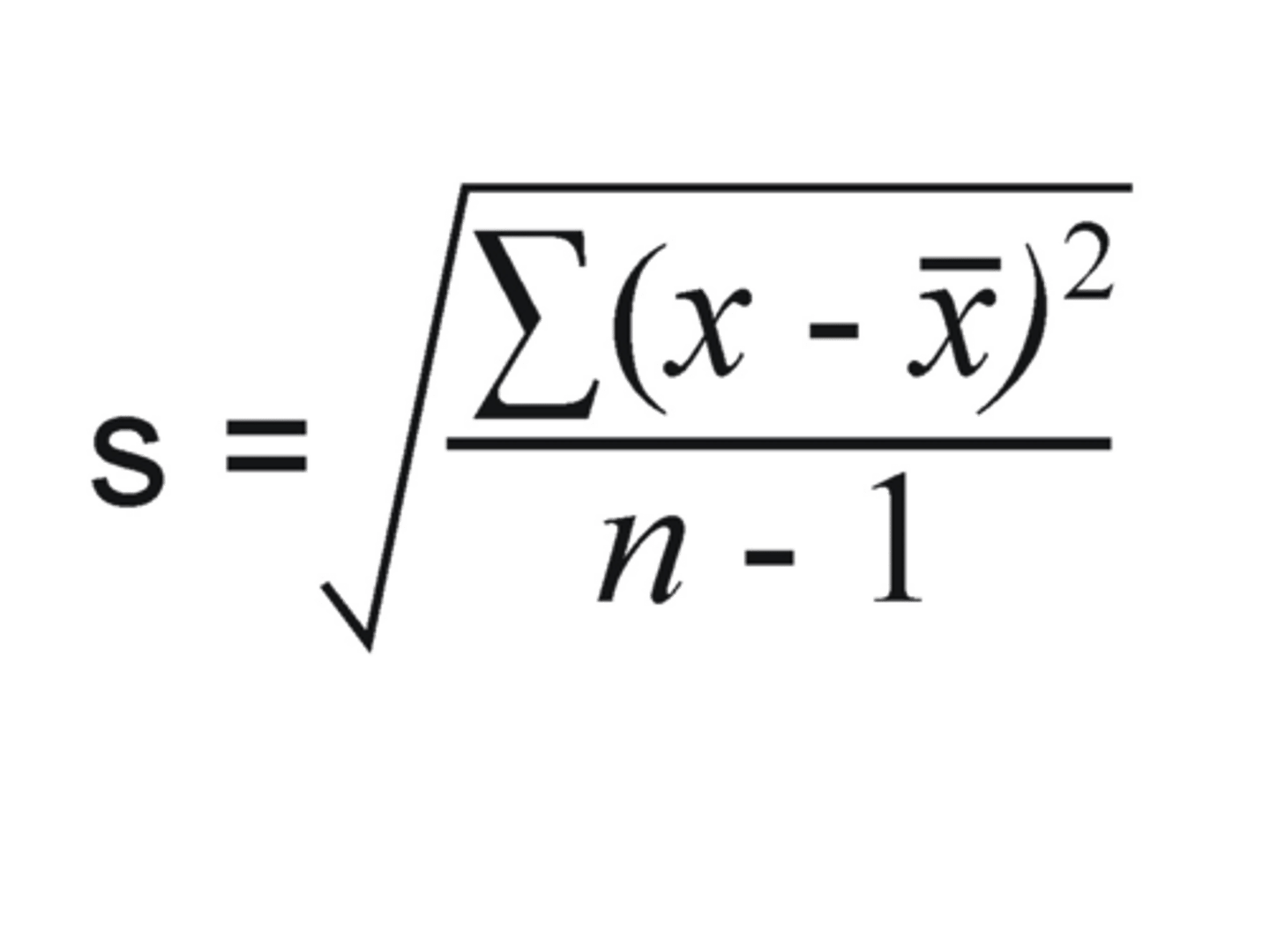
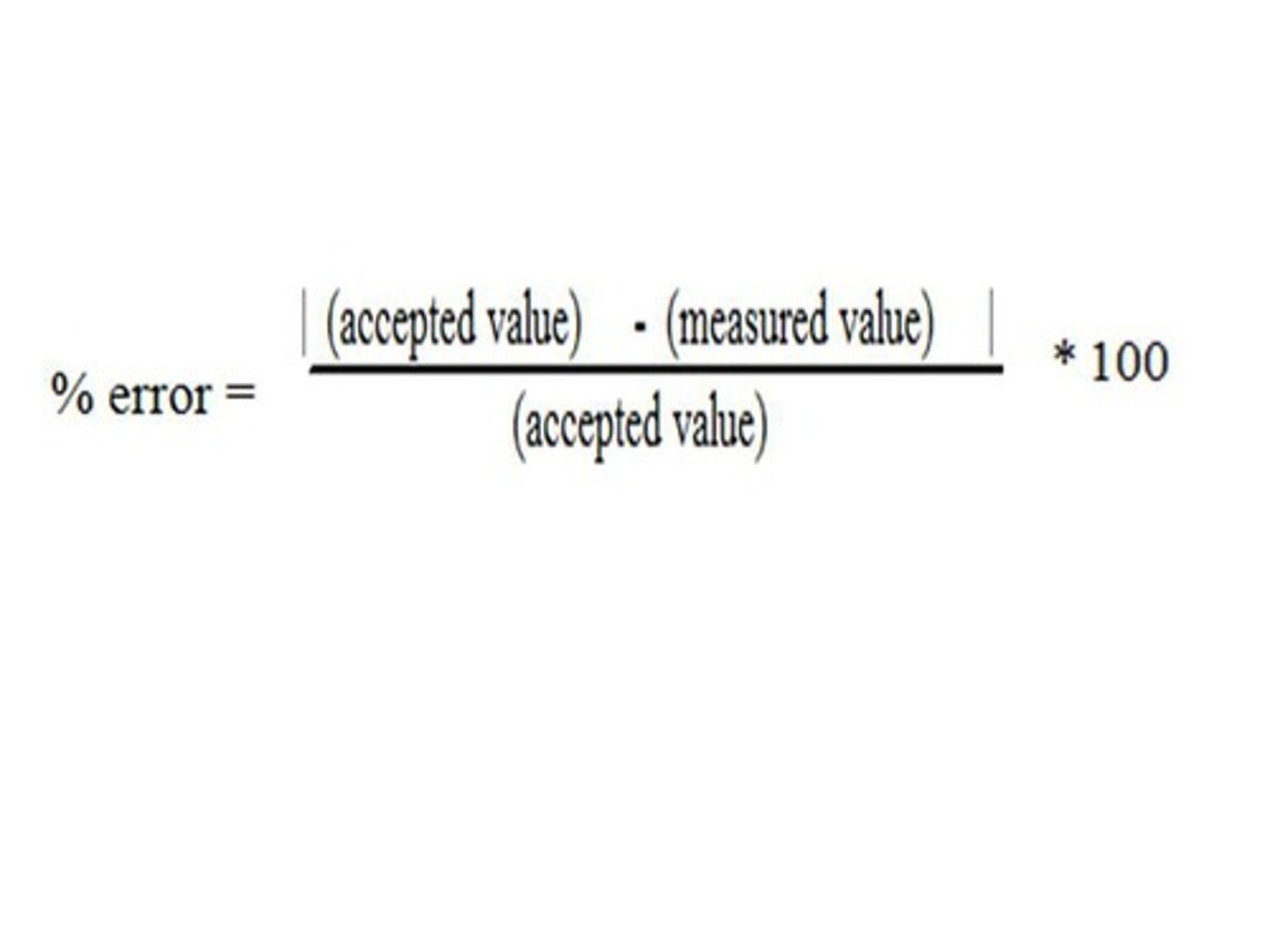
percent error
gives indication of accuracy with measurements since it compares the experimental value to a standard value
((value 1 - value 2) / avg value) x 100%
Percent difference
gives indication of precision since it takes all the experimental values and compares it to each other.
(|experimental values - accepted value| / accepted values) x 100%
Which formula would you use for comparing the field canopy area and the digital canopy area?
Percent error (accuracy)
Describe the global challenge of food insecurity and the role of science in addressing the challenge.
-GIS can help target the sources of food insecurity. It is our job as scientists to provide sufficient data that will help treat the problem.
-climate change aggravates food insecurity
-increase in CO2 increases photosynthesis but reduces the nutritional content of crops
-In our case, learning how guard cells form and function introduces important techniques and concepts that can address the global challenges associated with climate change.
Describe the global challenge of CO2 levels in the atmosphere
-traps infrared radiation heat in the atmosphere
-weathering rocks
-carbon source for plants
- not enough plants are able to take the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere
explain the role of science in addressing the challenge of CO2.
Options for removing CO2:
-forests
-farms
bio-energy with carbon capture
direct air capture
-carbon mineralization
How do we define a tree?
-woody plant characterized by a single dominant stem called a trunk.
-Many smaller woody branches that emerge from the trunk carry the leafy foliage of the tree. It is anchored by roots.
Explain how the structure of leaves can be used to classify plants.
-shape
-arrangements
-size
-leaf attachments
-leaf organization
-petiole features
-laminar shape
-laminar symmetry
-margin
-ventilation
Give examples of the variations that are found in leaf shape and arrangement.
compound leaves are able to spread out and have smaller SA. Found in the desert.
opposite arrangement
alternate arrangement
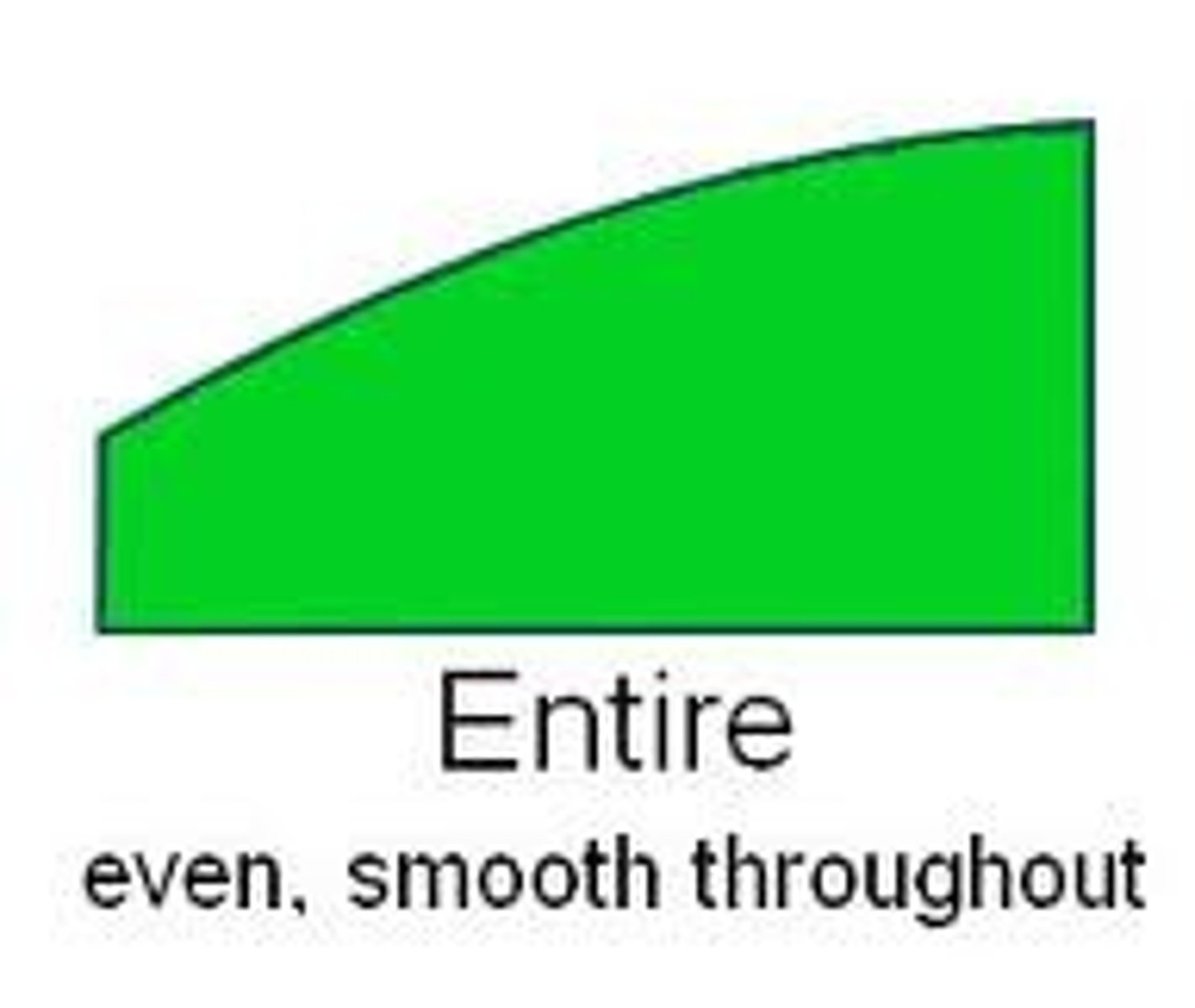
entire
even , smooth throughout
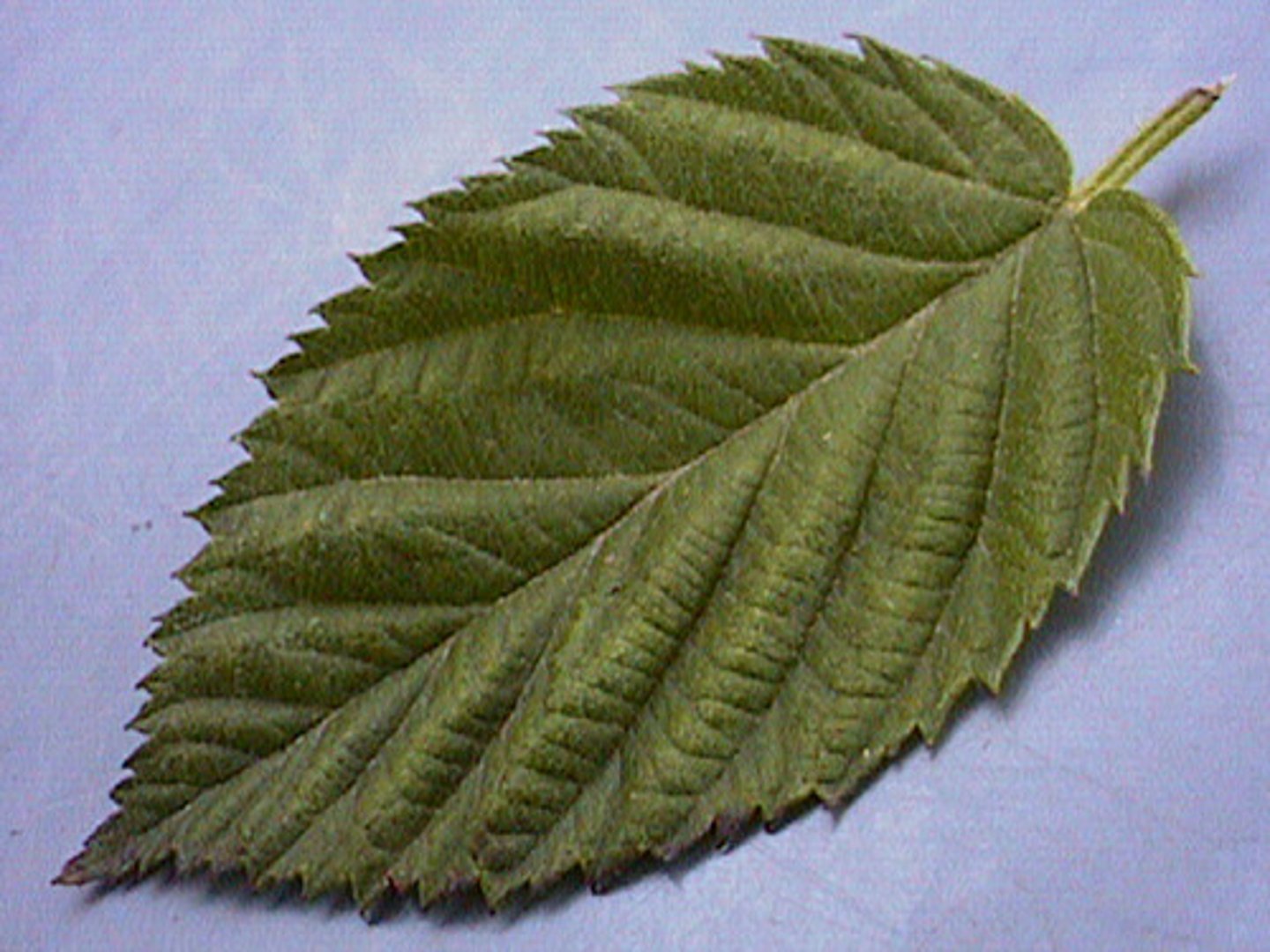
denate
with symmetrical teeth

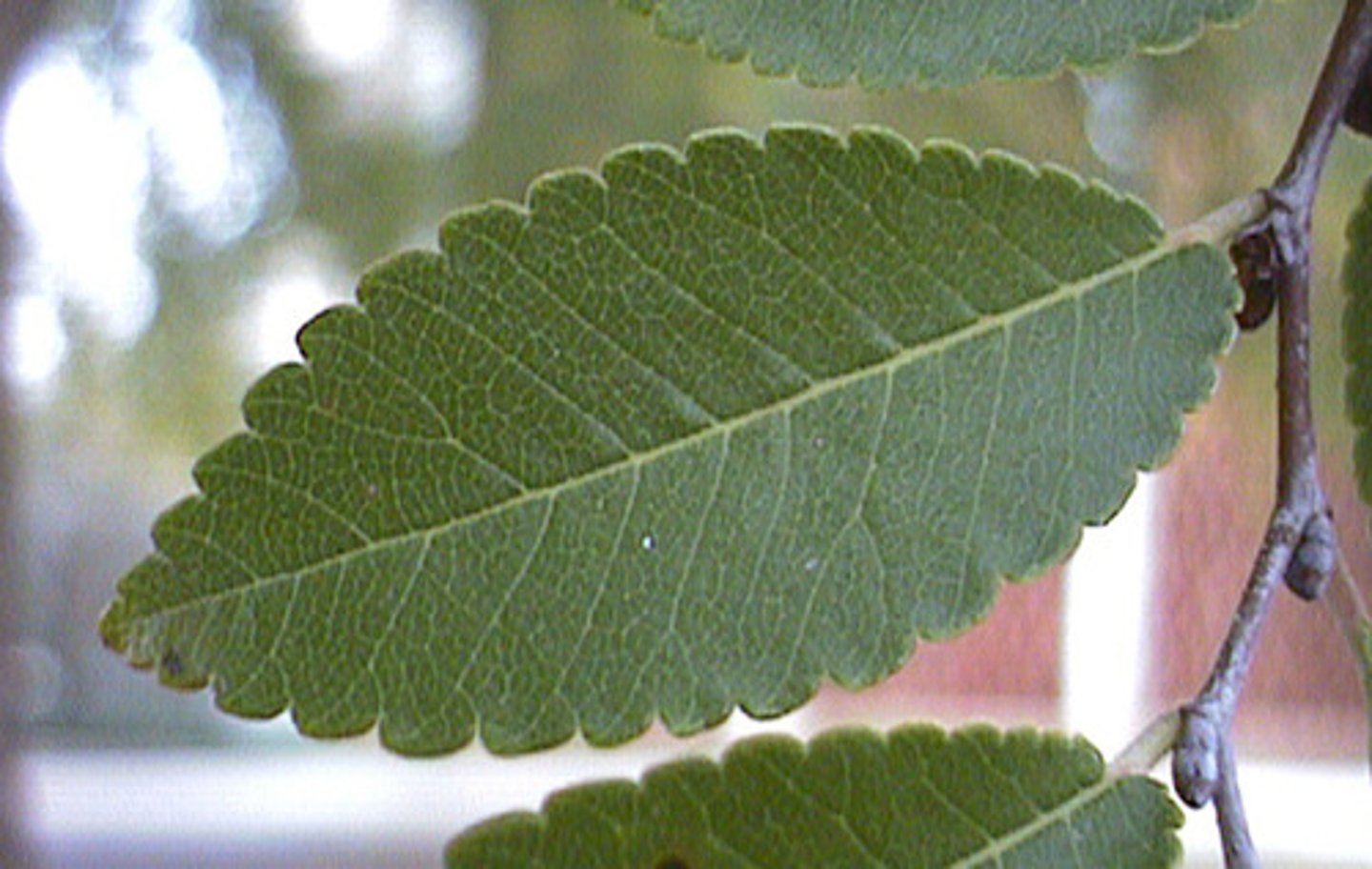
Crenate
with rounded teeth

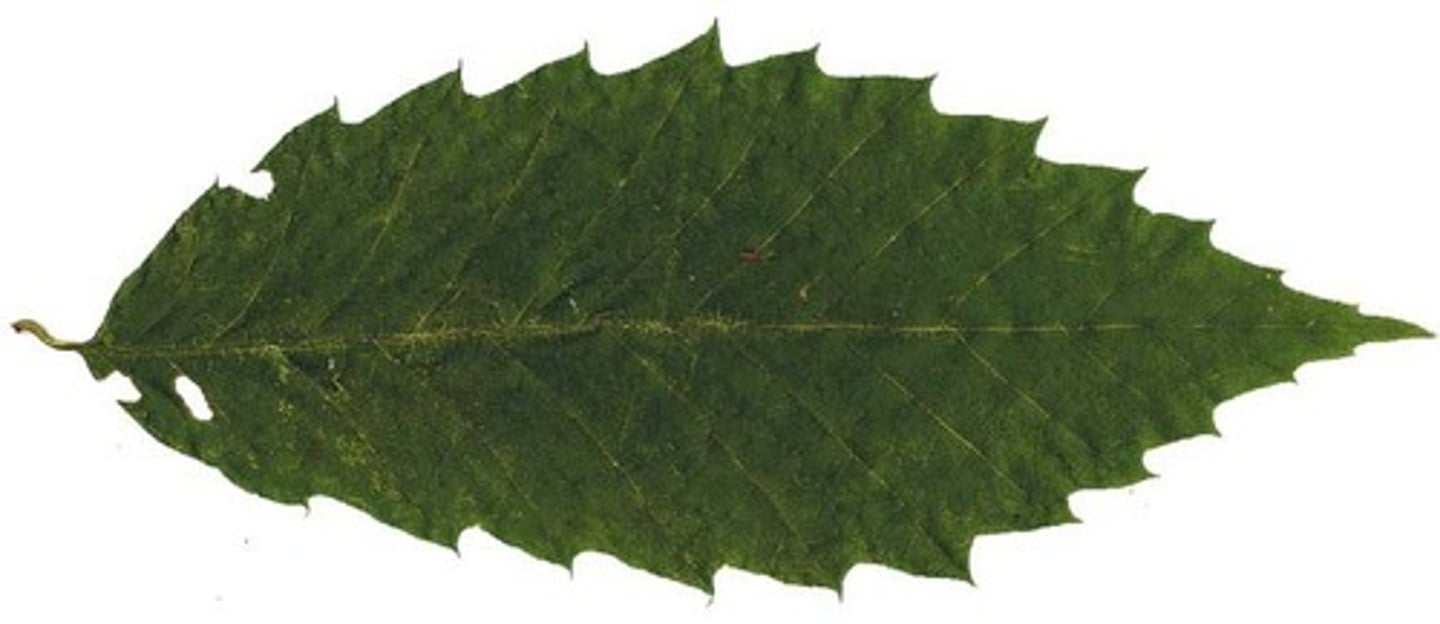
serrate
teeth forward-pointing

lobate
indented, but not to midline
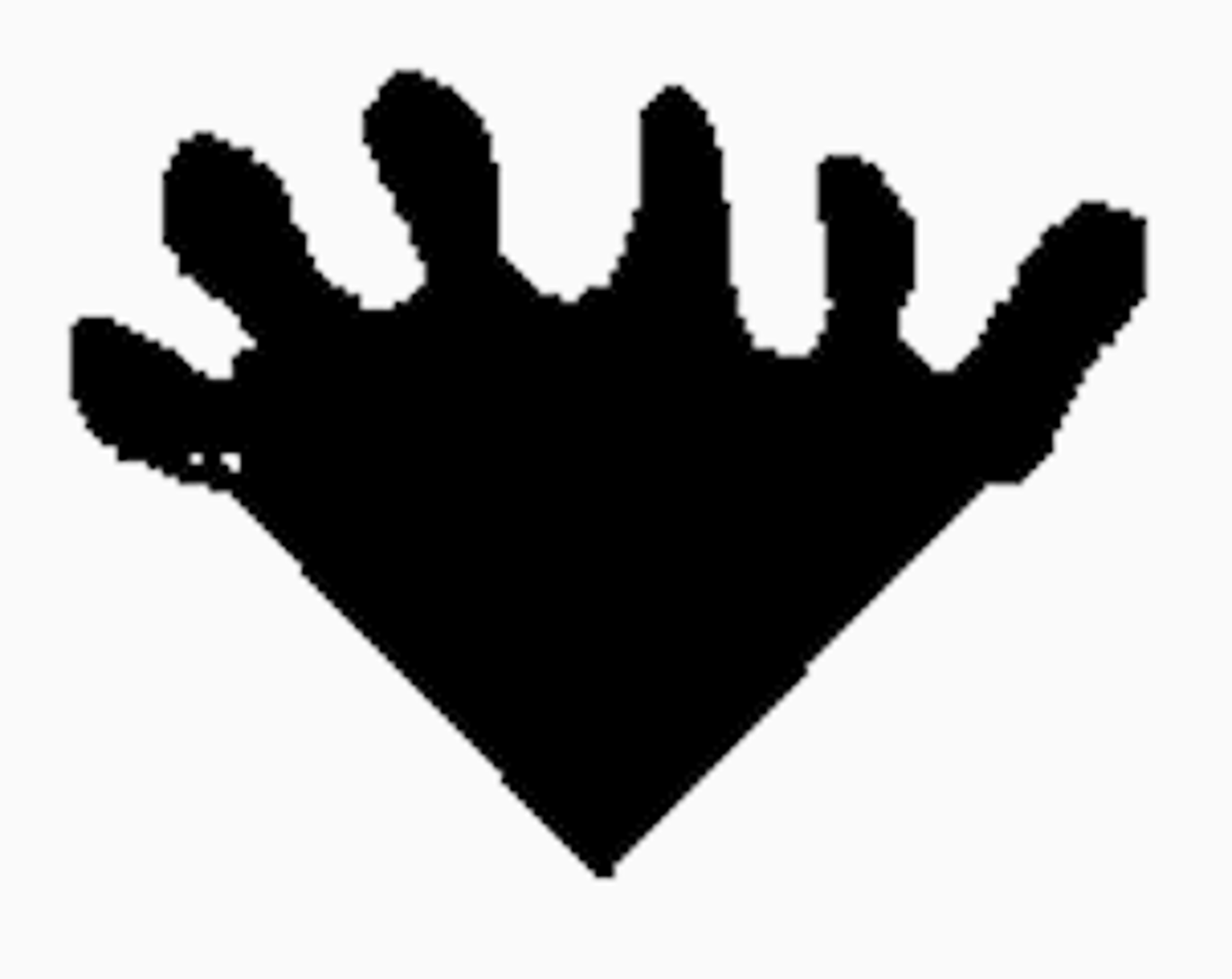

whorled
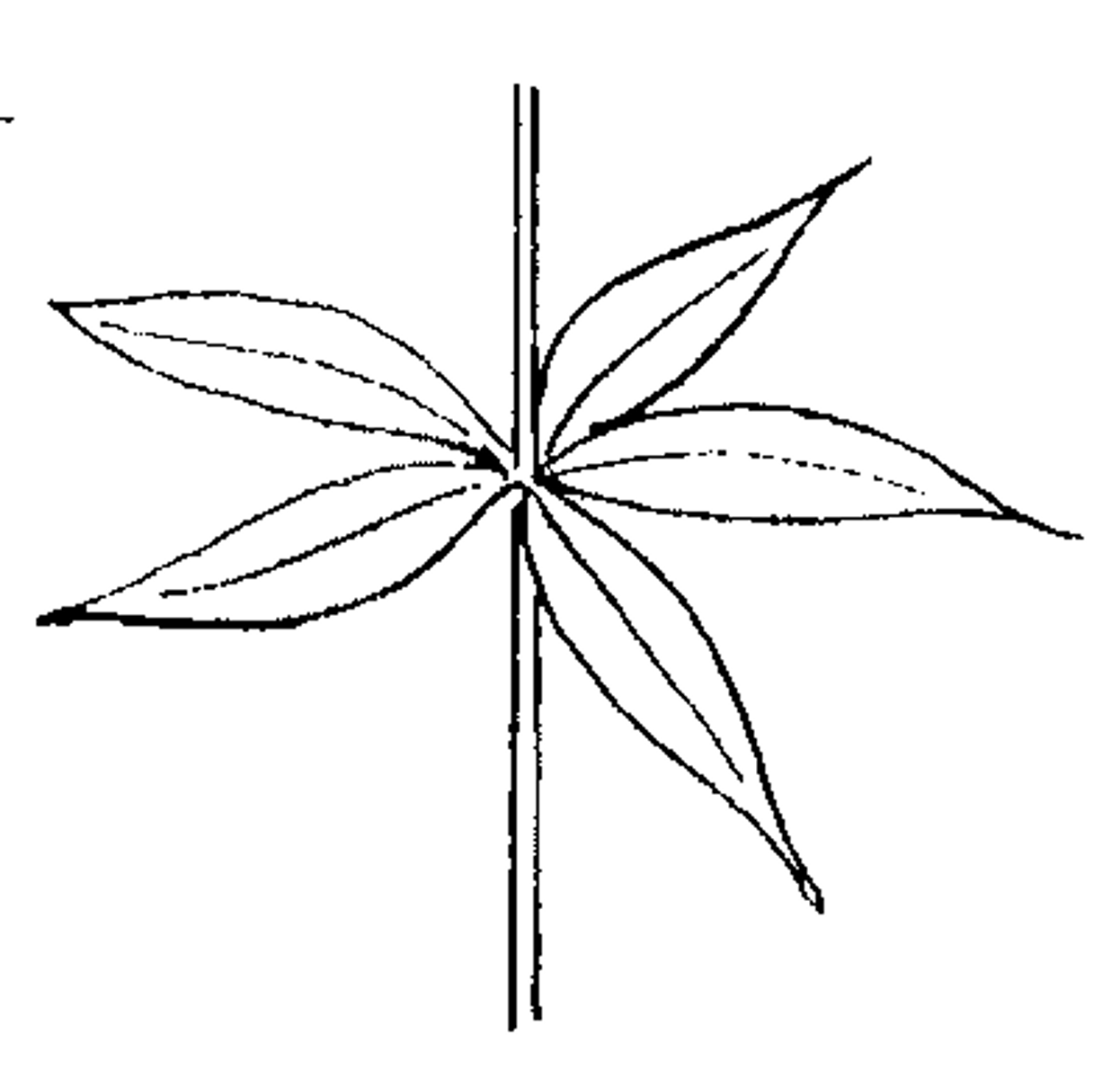
decussate
Obtuse leaf tip
bluntly tipped
obvate
egg-shaped, narrow at base

ovate
egg-shaped, wide at base

elliptic
oval-shaped, small or no point

pinnate
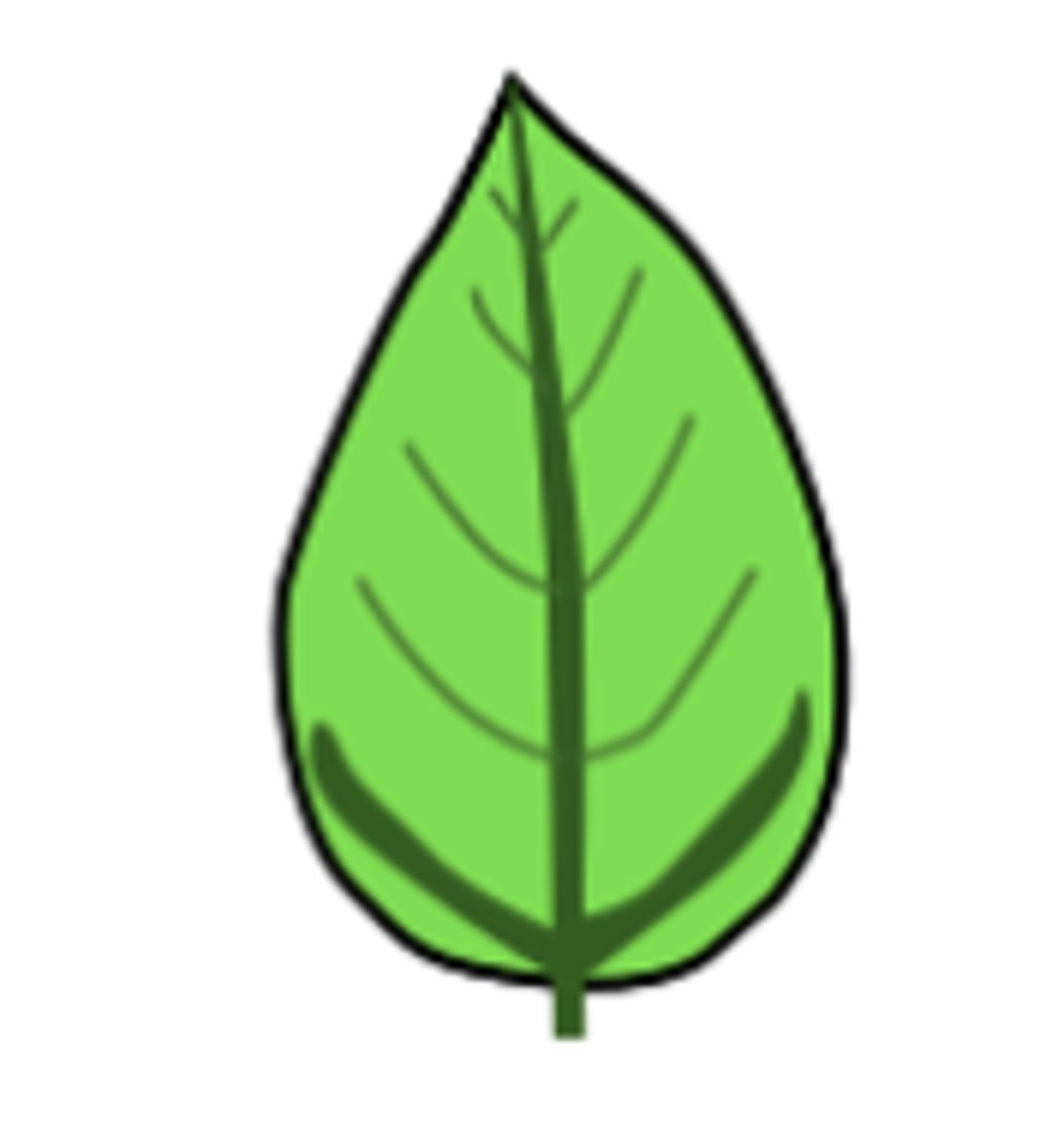
A leaf vein pattern that looks like a feather. There is one main vein that has smaller veins branching off sideways from it.

campylodromous

paralleldromous
palinactinodromous

flabellate
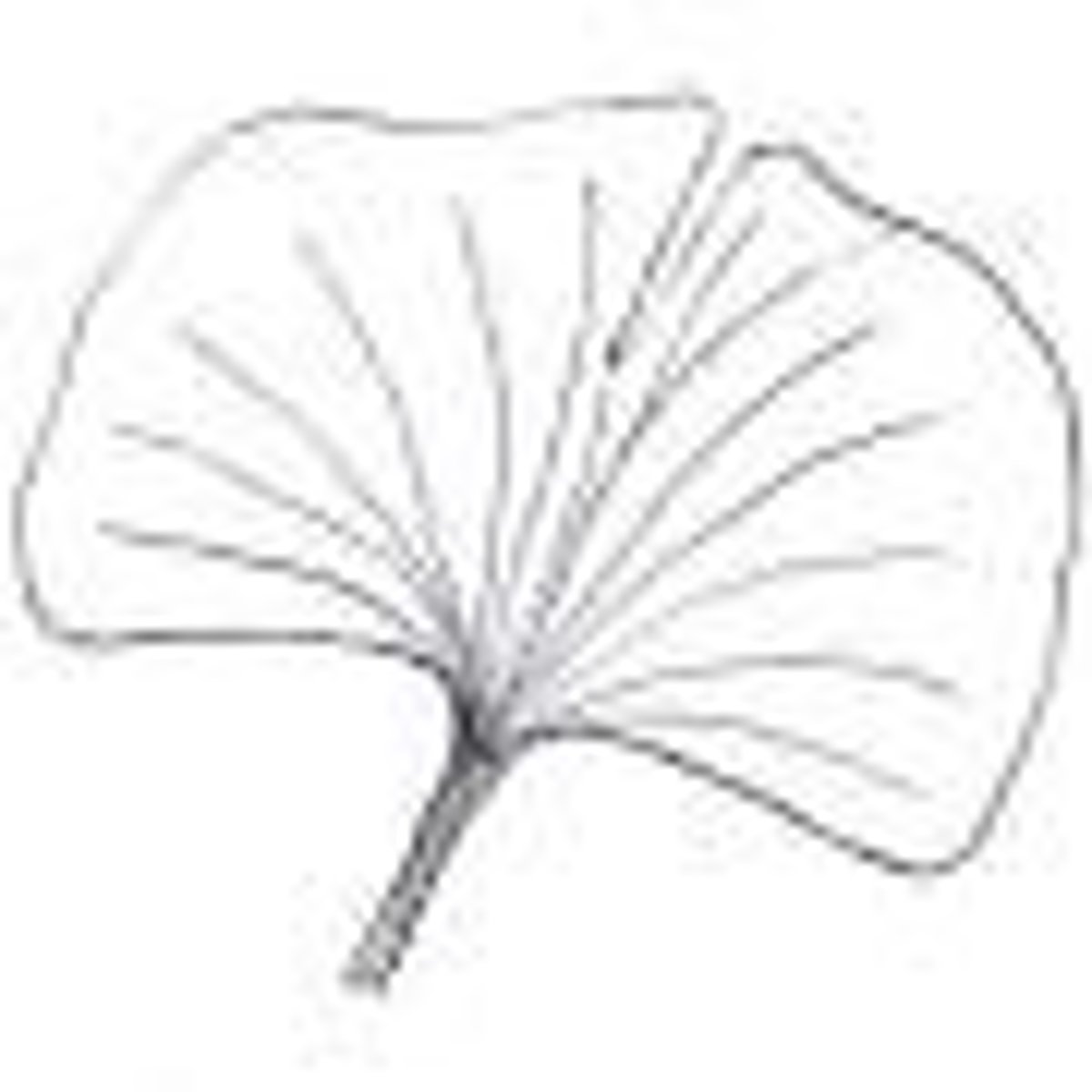
acrodromous
pertaining to a leaf in which the veins converge at the point
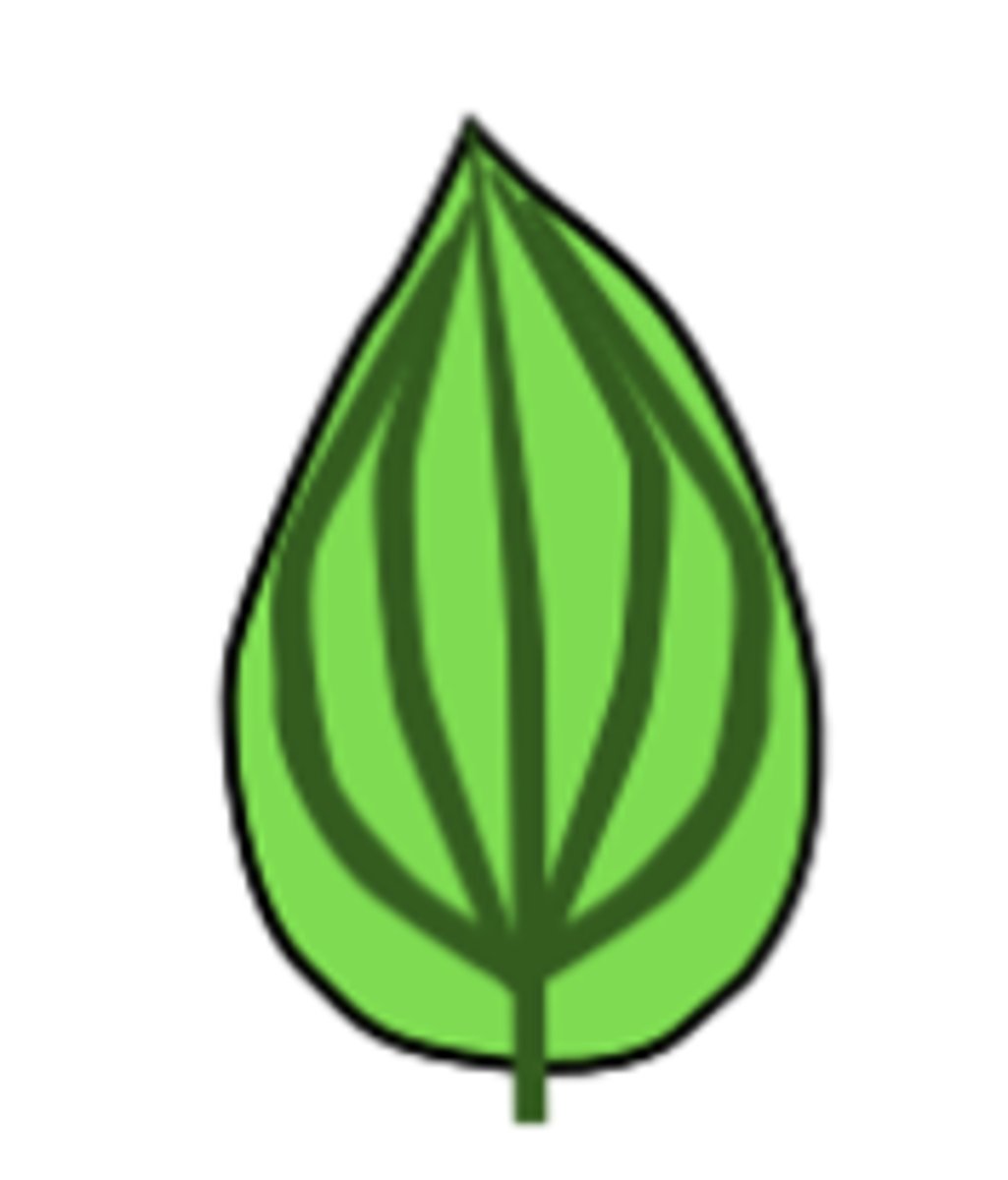

actindromous basal leaf
actinodromous suprabasal but veins go all the way to edge
actinodromous suprabasal

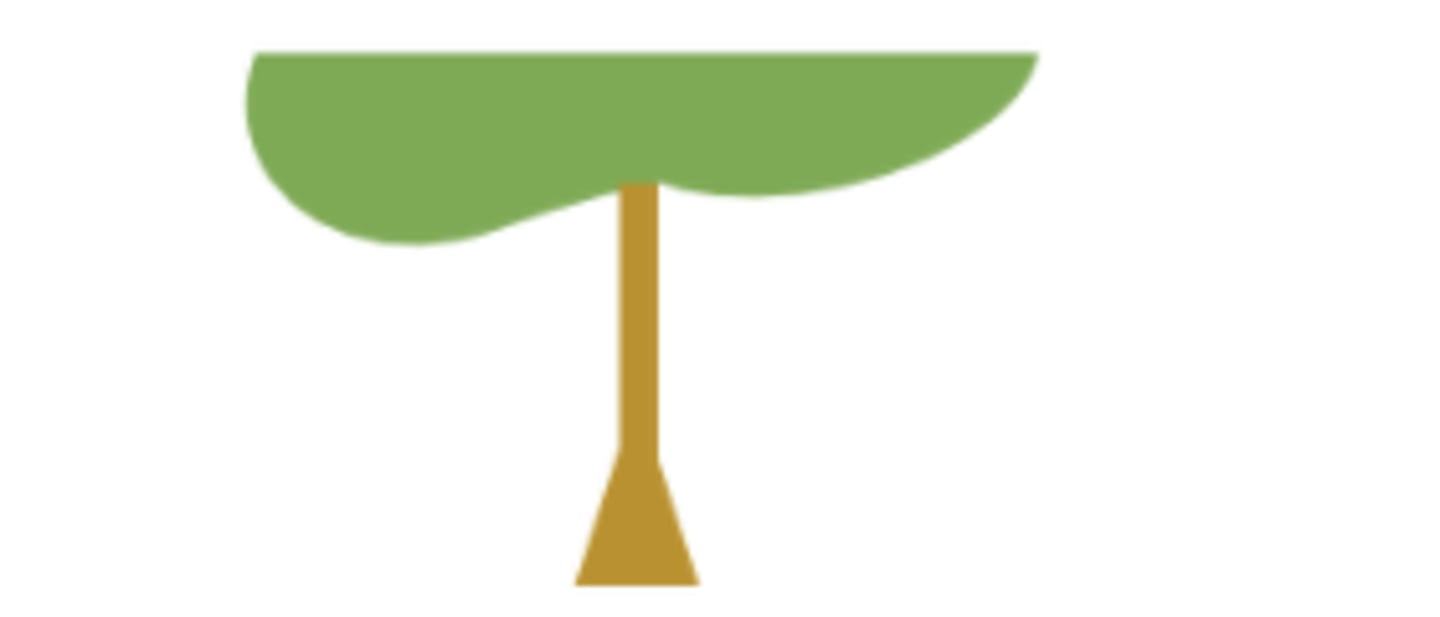
base swollen
petiole is thicker where it attaches at the base

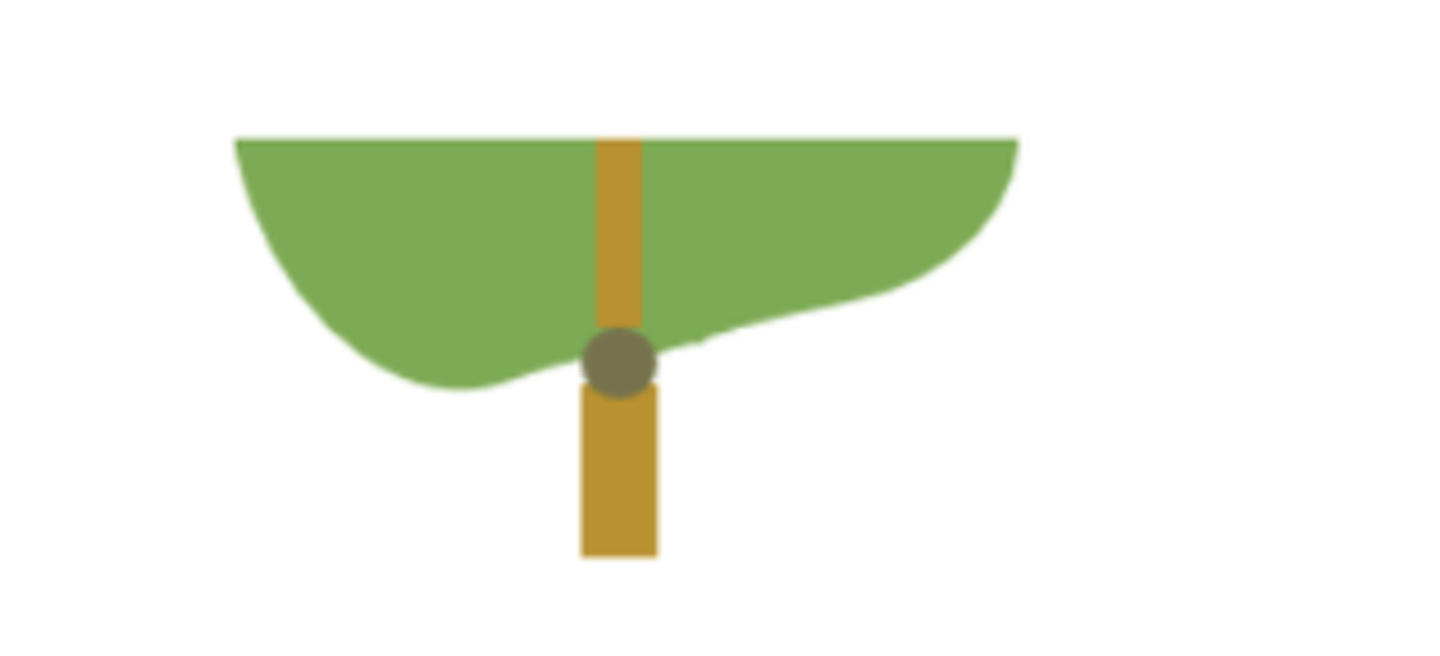
pulvinate
a flexible joint-like thickening around the base of the leaf

Describe three types of meristematic plant tissues:
1. apical - tip of the root, stem. help with growth of the root system and shoot system. cell division along the cellular enlargement help in the growth of the stem above ground and the root below the ground.
2. intercalary- located at the internodes or the base of the leaves. help increase the length of the internode. usually seen in monocotyledonous plants
3. lateral- present on the lateral side of the stem and root of a plant. help increase the thickness of the plants. ex. cambium
vascular
transports water and sugars throughout the plant
dermal
-forms a protective waxy coating, leaf hairs, secretory glands
-protect the plant from injury and water loss
Ground
-store starch, perform photosynthesis, support the structure of the plant
-storing the carbohydrates
Xylem
-waters; moves up
-transports water and dissolved minerals
Phloem
-sugars;moves up & down
-transport food nutrients such as sucrose
mesophyll
The cells in the middle, have many photosynthetic chloroplasts
Guard cells
opening and closing the stomata
Stomata
the pores of the leaf that let water out, while permitting oxygen and carbon dioxide in and out of the plant
vascular tissue of leaf
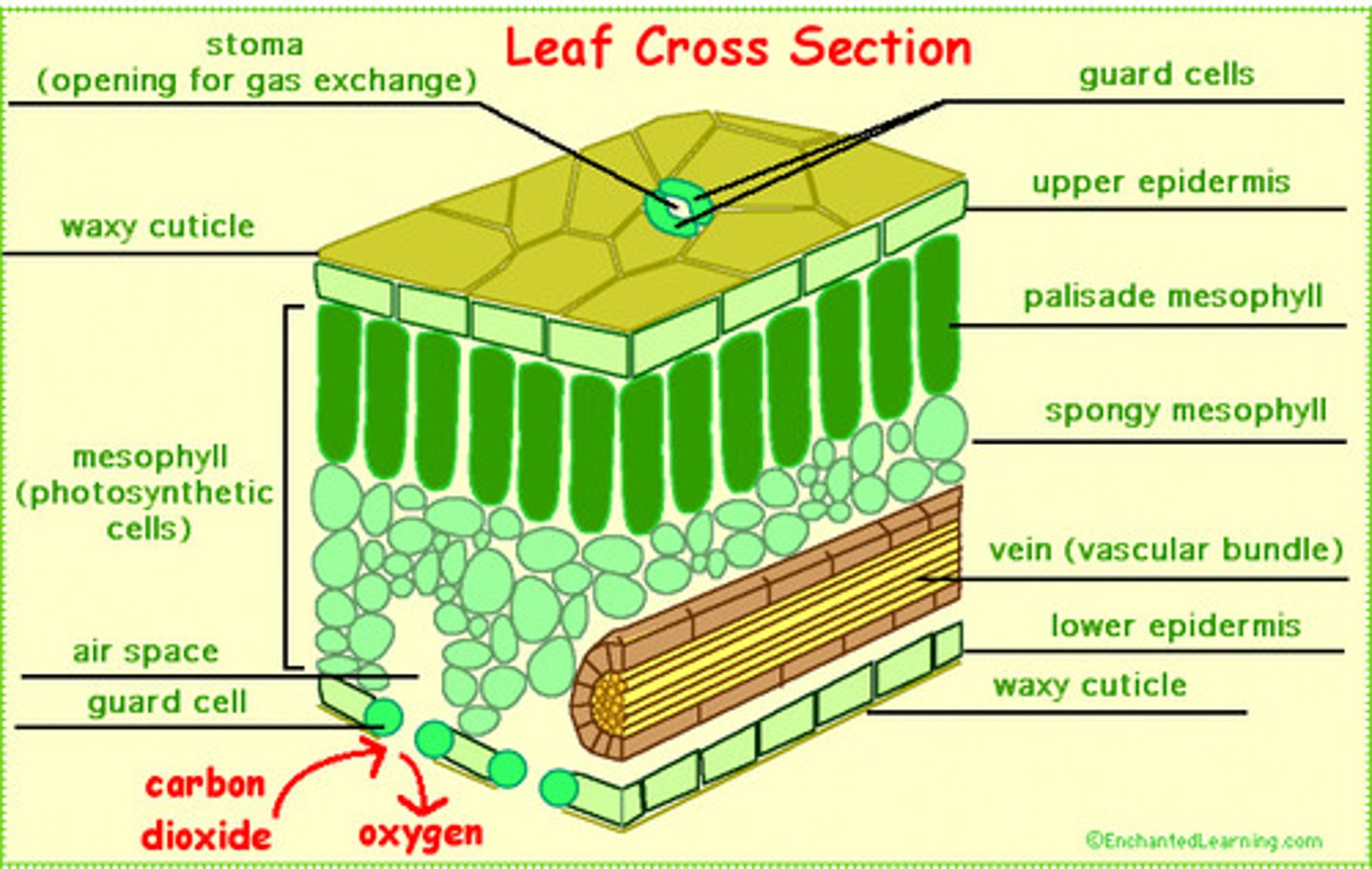
Transpiration
caused by the movement of water upwards through the xylem.
Describe the role of the stomata and vascular tissue in this process
Stomata regulate the exchange of carbon dioxide (moving in) and oxgyen (moving out), as well as the loss of water through transpiration
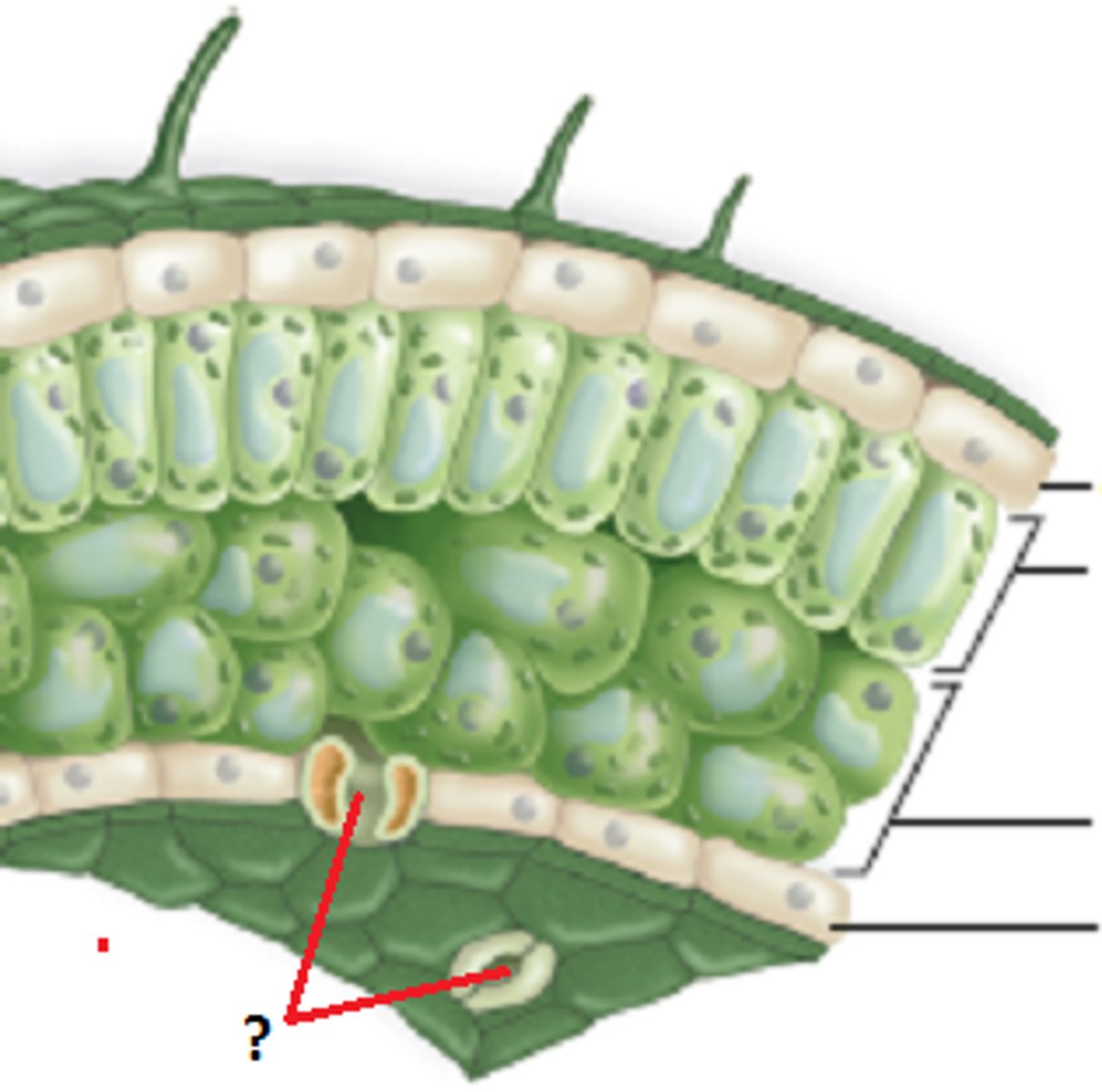
Blade
edge of knife
Petiole
stalk like structure which connects the blade to the stem