Resistors and IV graphs: Electricity: Physics: GCSE (9:1)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Ohm's Law (V = IR)
The current flowing through a device is directly proportional to the potential difference across the it (providing the temperature remains constant)
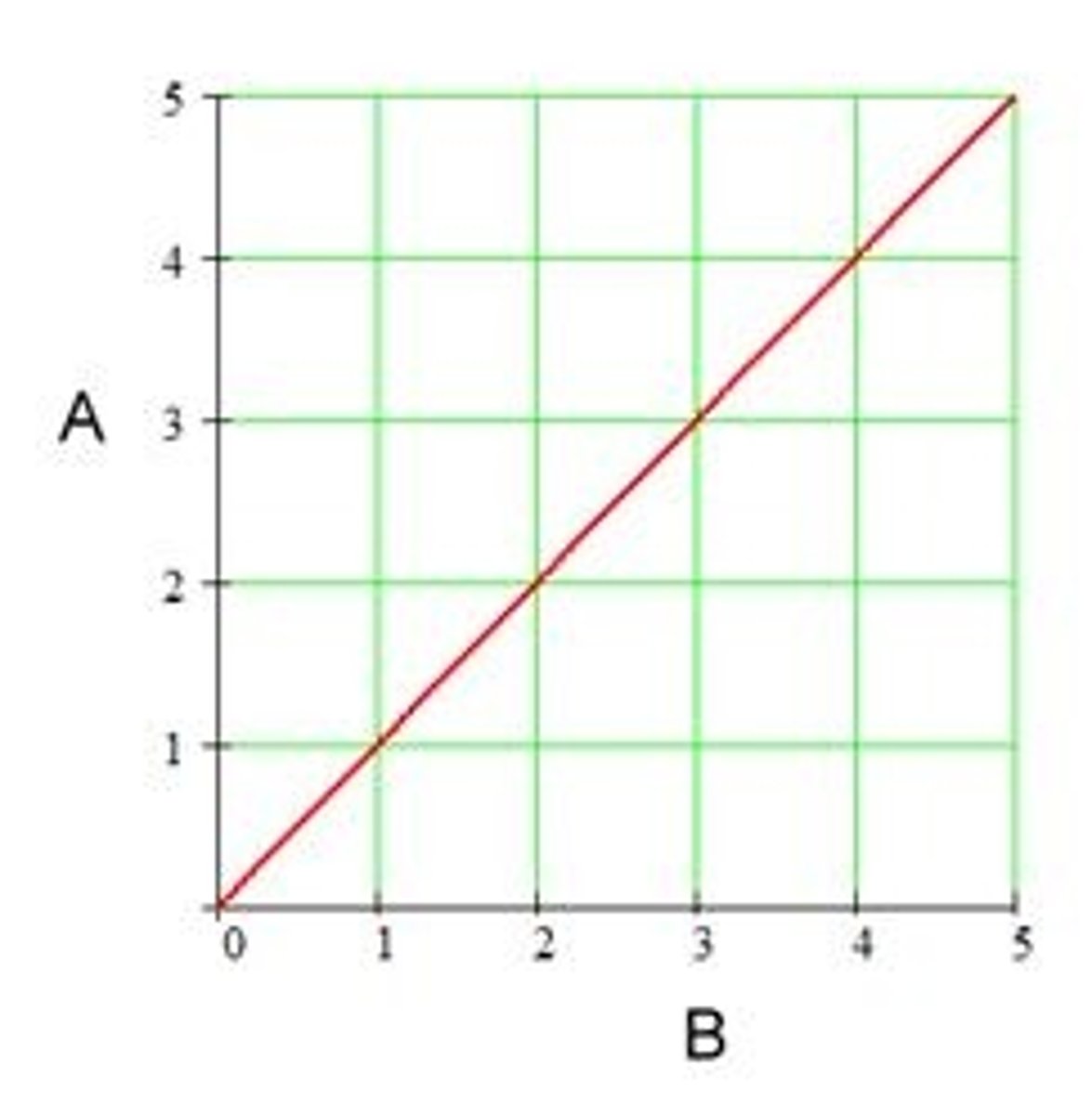
Directly proportional
When a graph of two variables is a straight line that passes through the origin (0,0)
Ohmic conductor
A device that obeys Ohm's Law
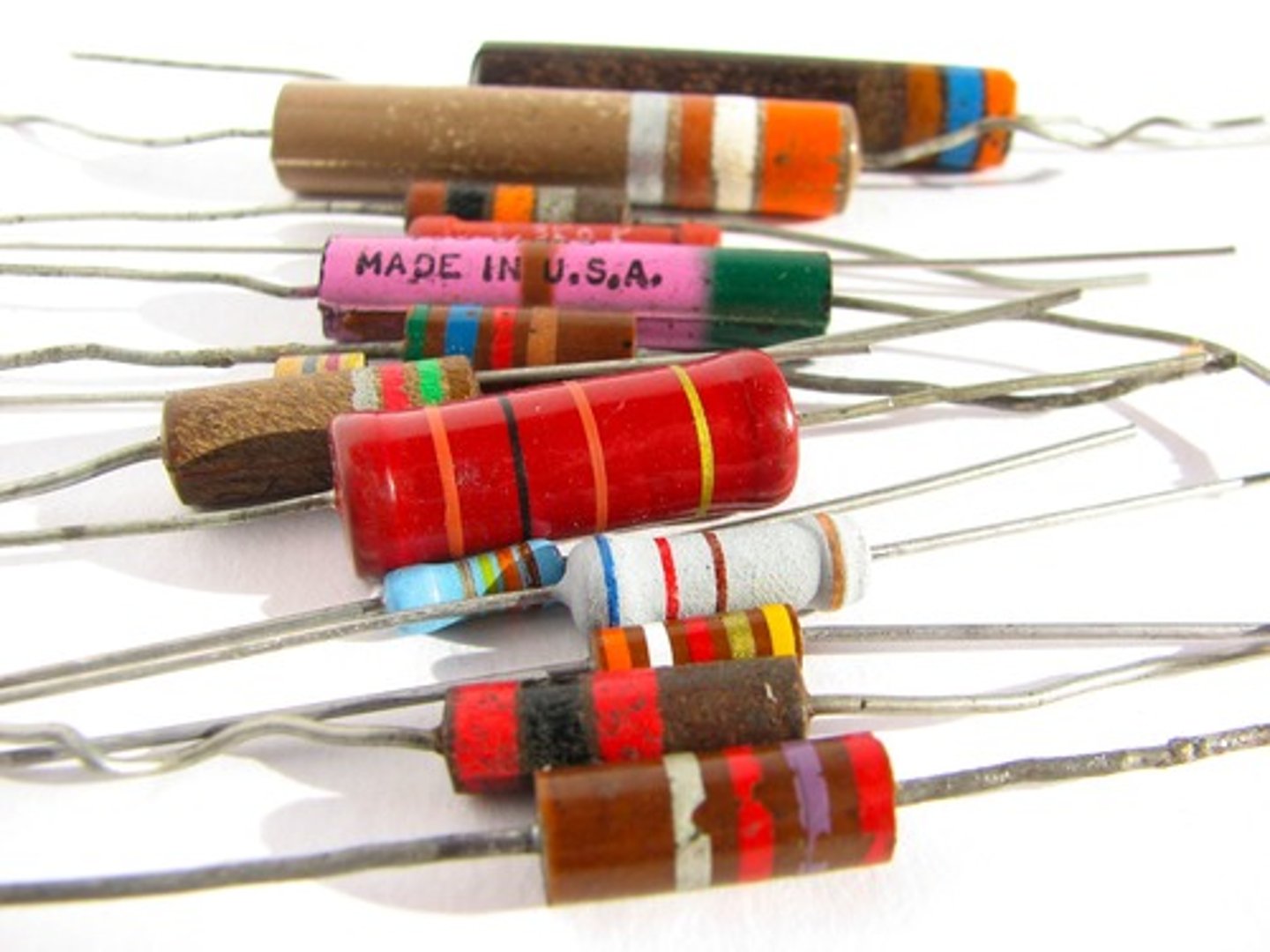
Fixed resistor
An ohmic conductor that obeys Ohm's Law because its resistance is fixed

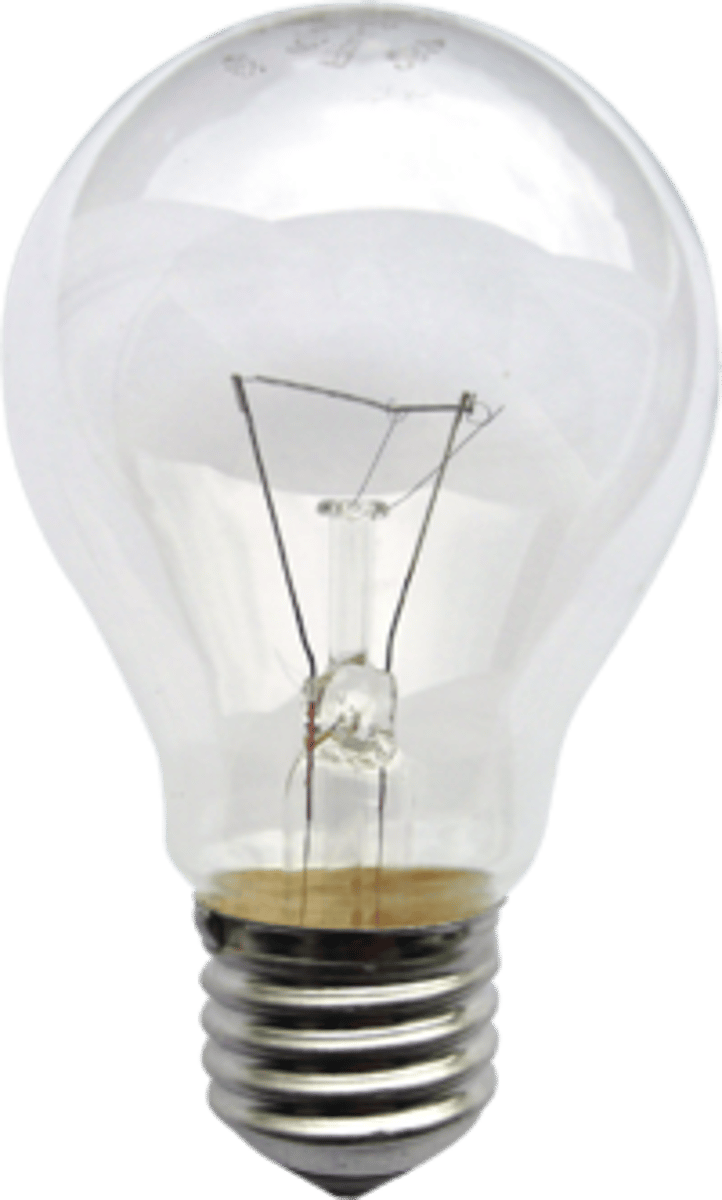
Filament bulb
Not an ohmic conductor because it doesn't obey Ohm's Law

Diode
Not an ohmic conductor because it doesn't obey Ohm's Law
Reason why a filament bulb is not an ohmic conductor
The filament gets hot which causes its resistance to increase
Reason why a diode is not an ohmic conductor
Its resistance changes depending on which direction the current flows through it
IV (current-potential difference) graph
a graph used to show how the current through a component varies as the potential difference across it changes
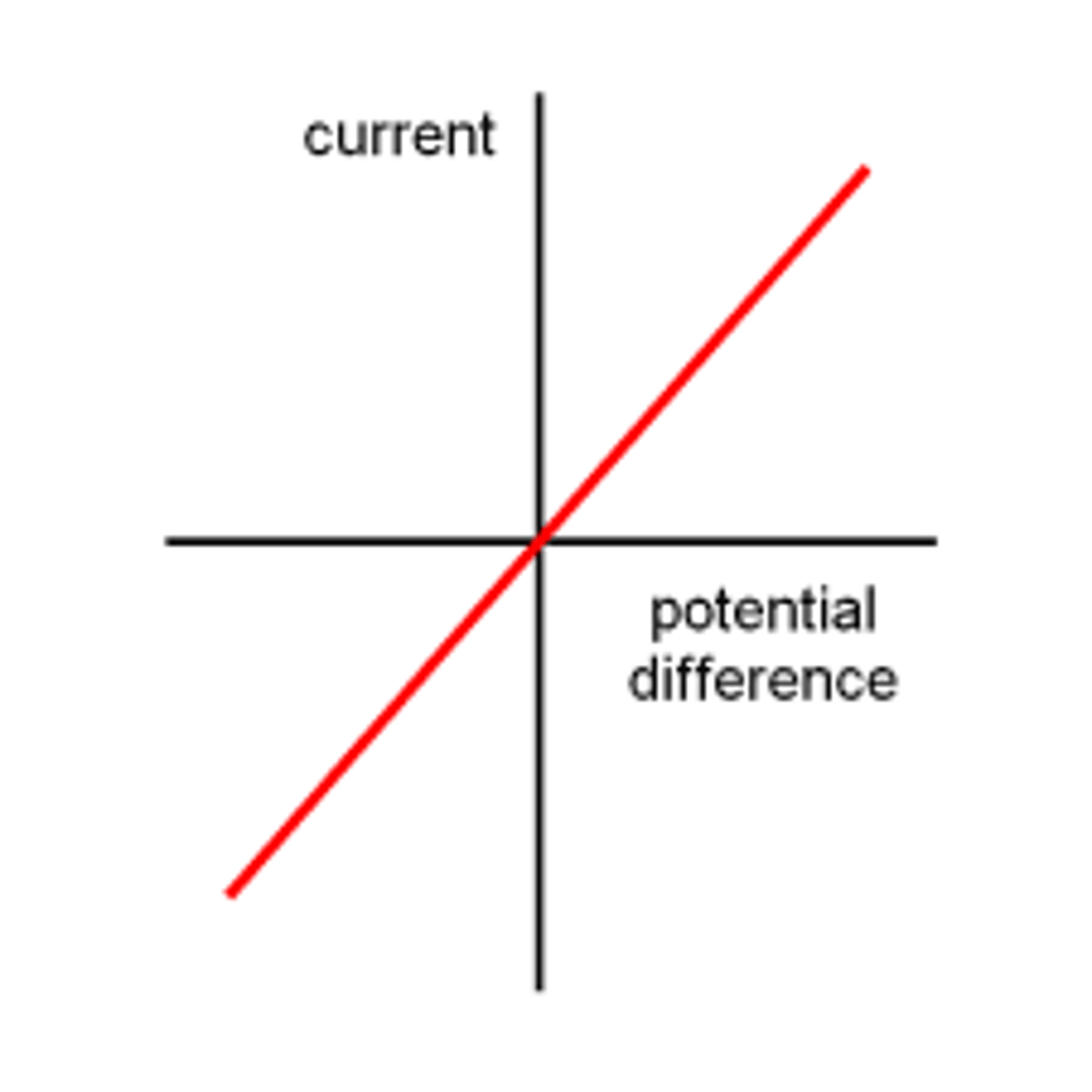
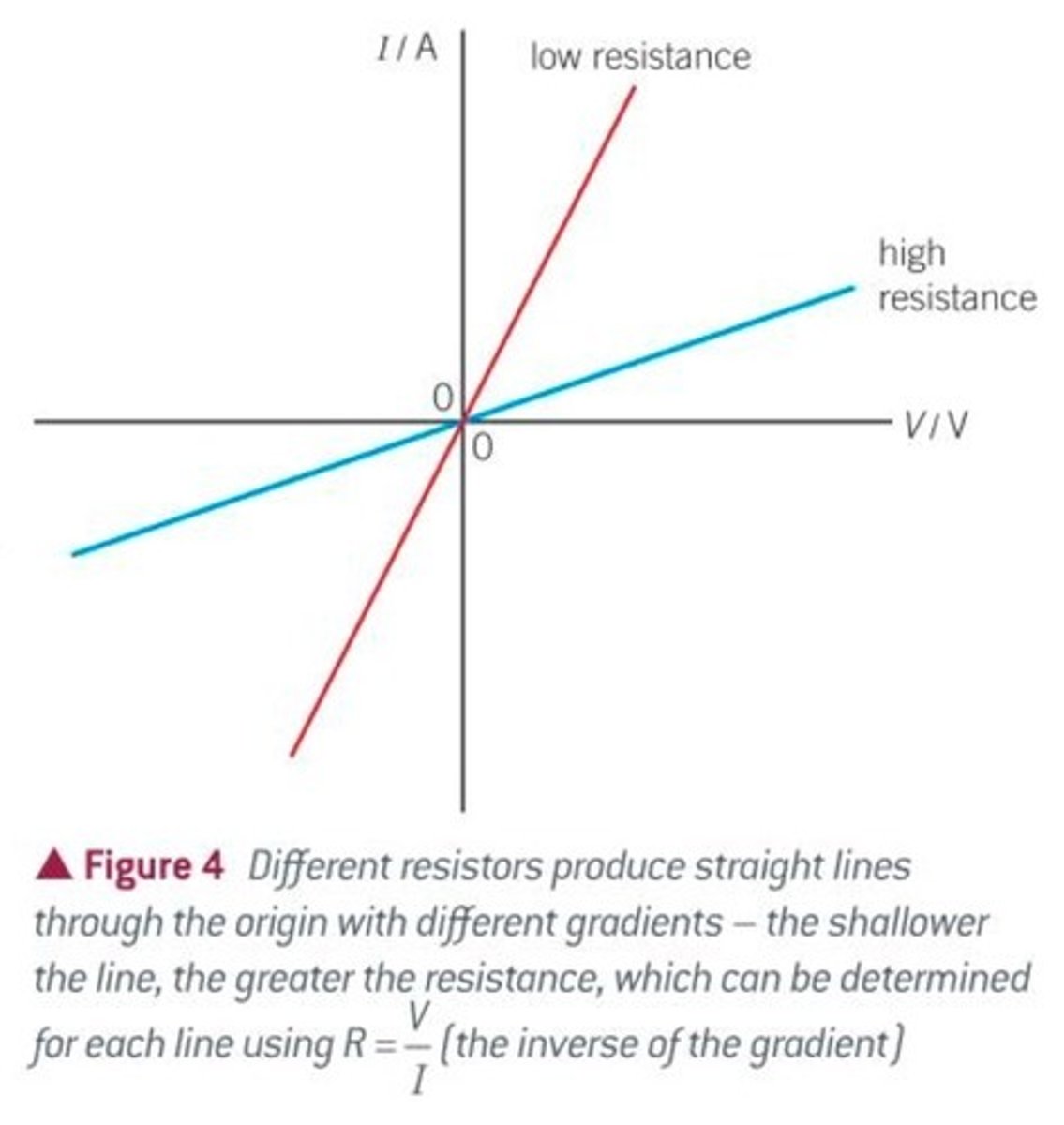
What the gradient of an IV graph represents
The resistance of a component (equal to 1/R)
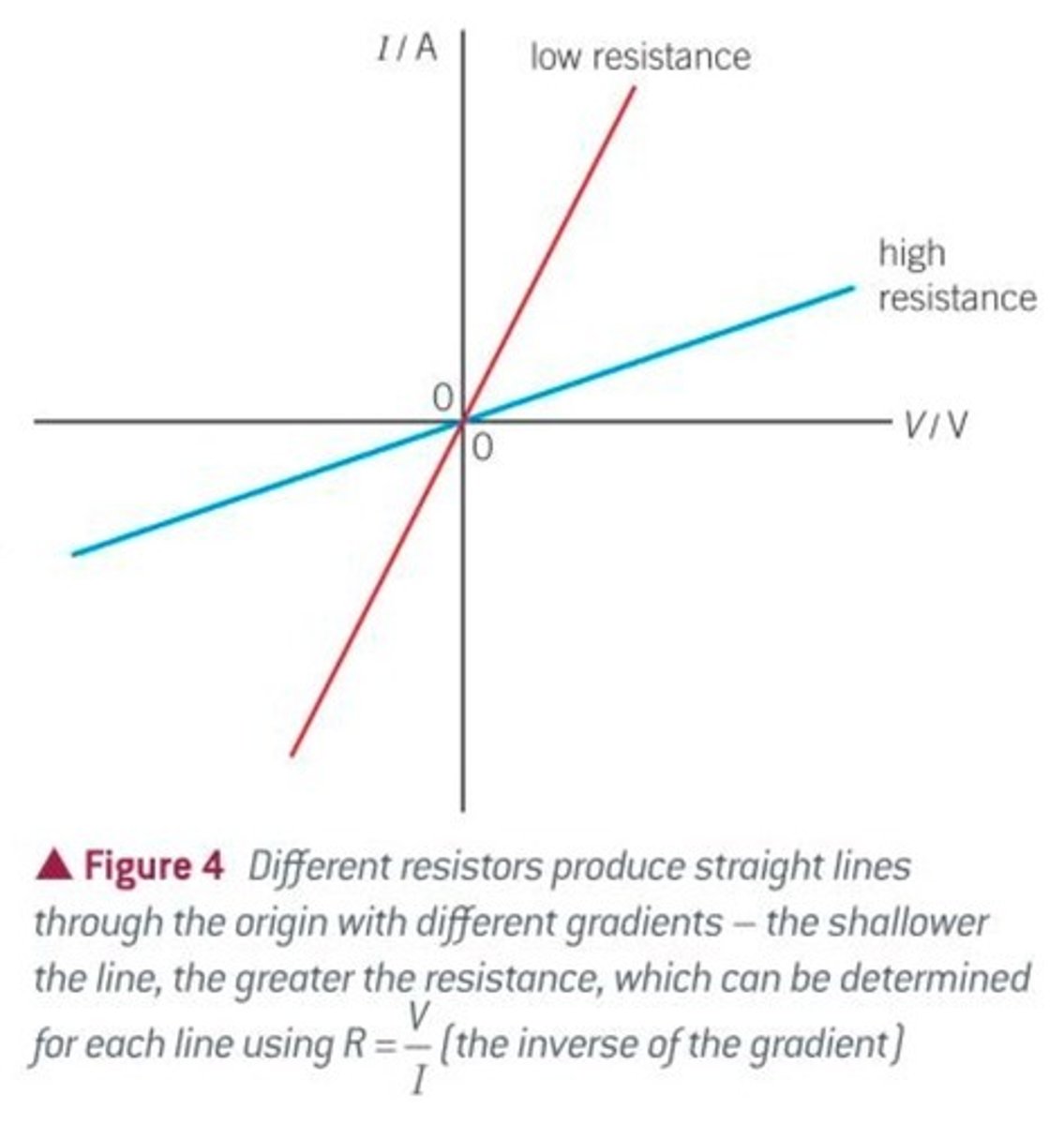
What a steep line on an IV graph represents
A device with a low resistance because increasing the potential difference by a small amount causes a large increase in current
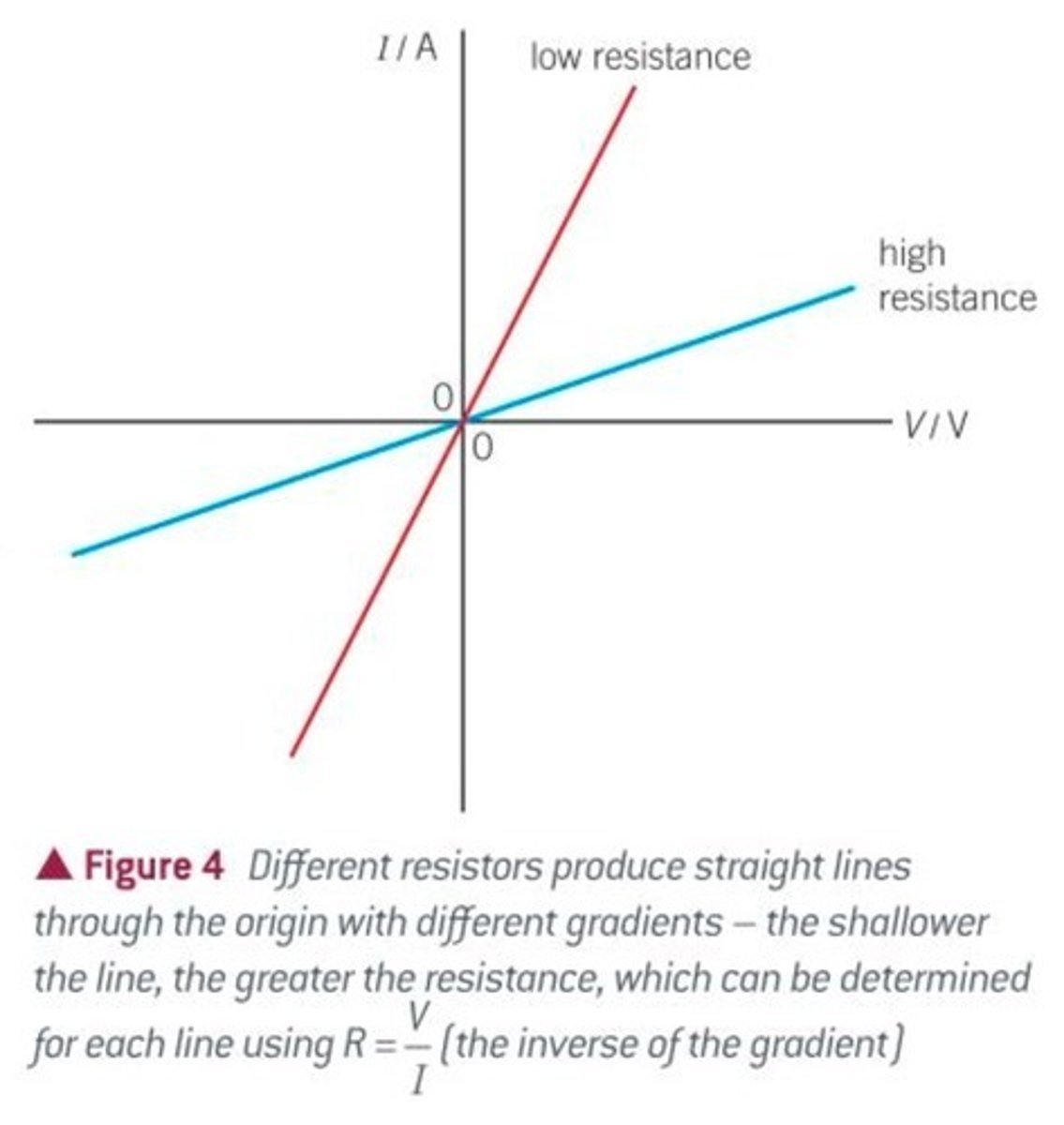
What a shallow line on an IV graph represents
A device with a high resistance because increasing the potential difference by a small amount causes a small increase in current
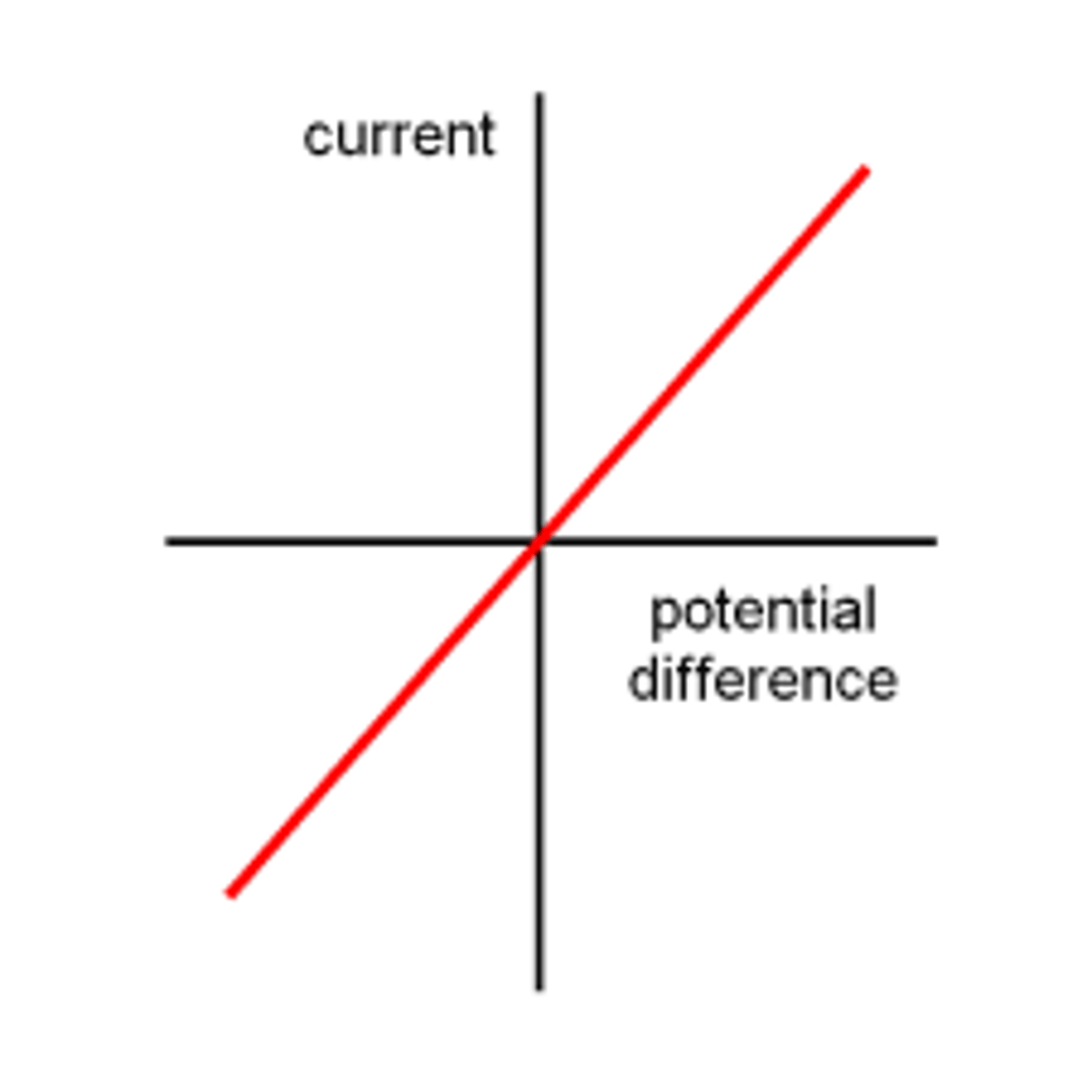
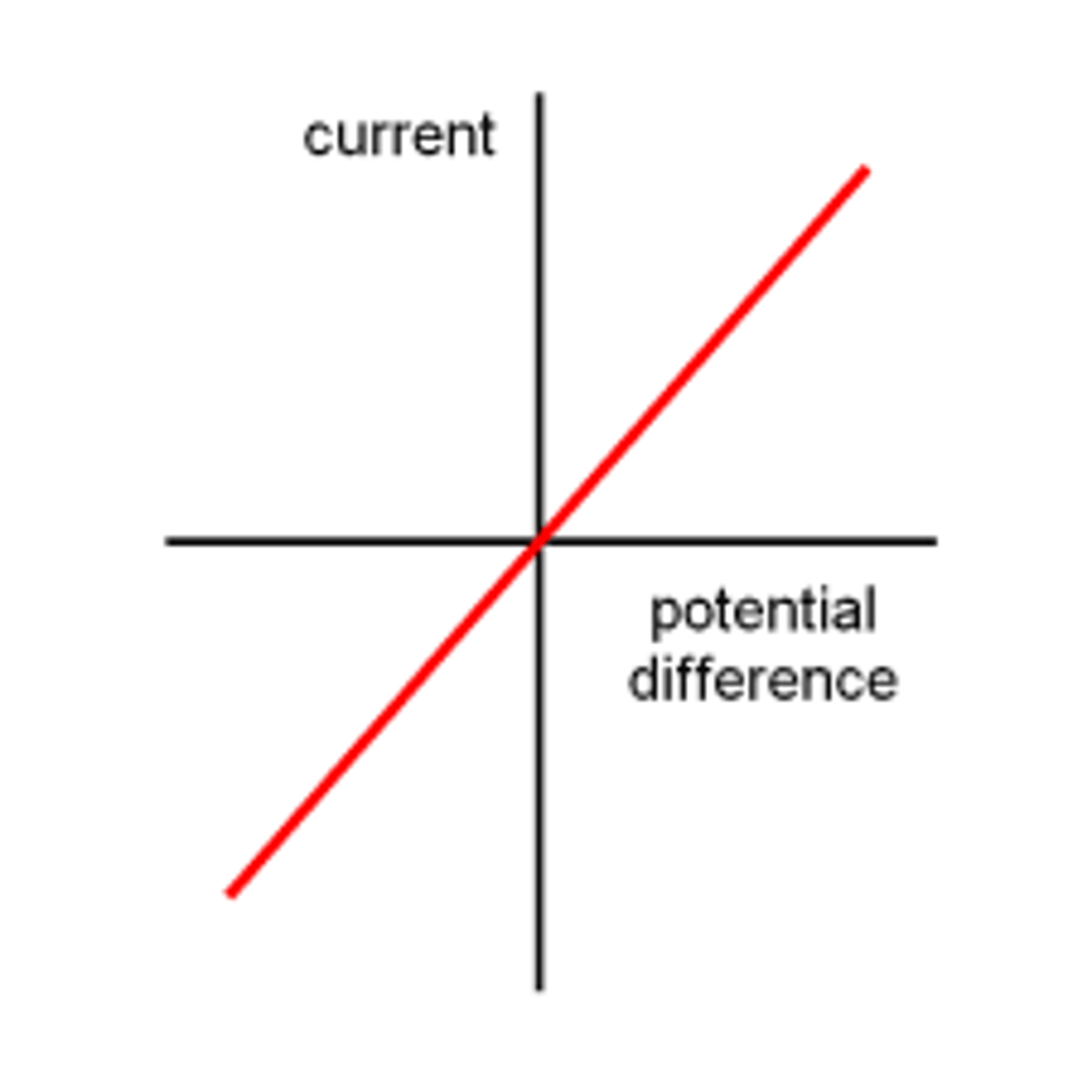
IV graph for a fixed resistor
A straight line which passes through the origin
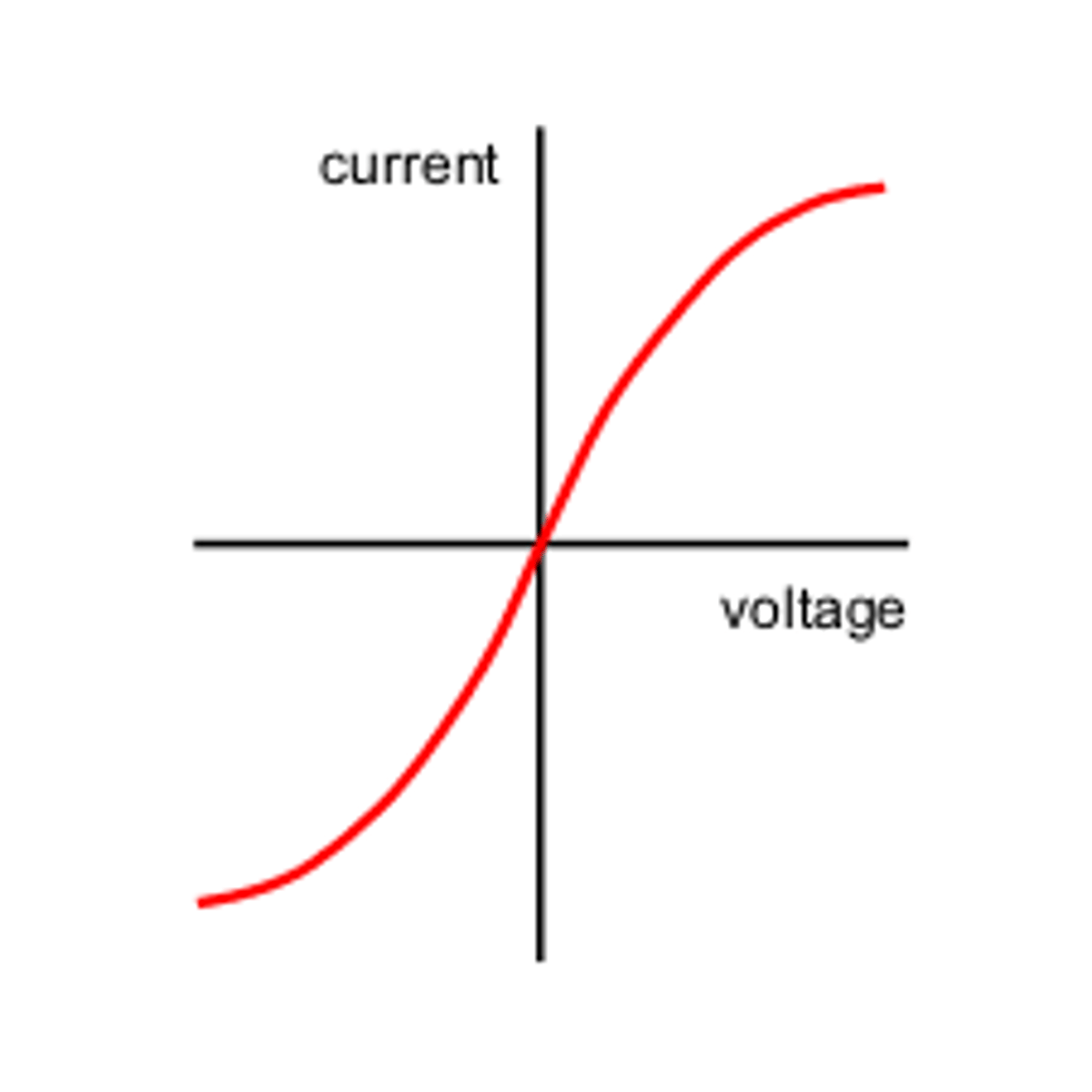
IV graph for a filament lamp
A s-shaped curve which passes through the origin
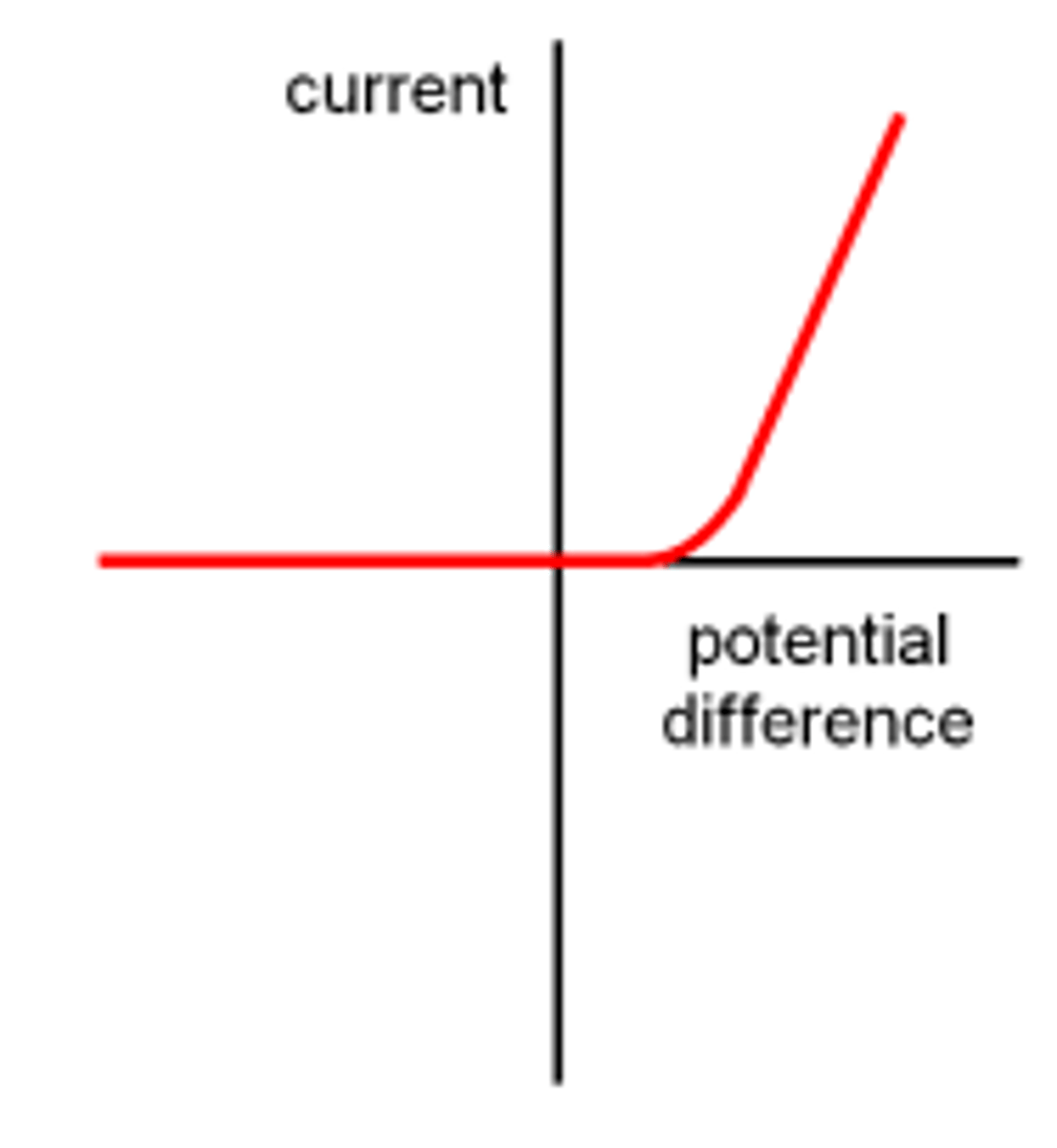
IV graph for a diode
The graph a horizontal line along the x-axis until it reaches around 0.6 V, where it then becomes a straight line with a steep gradient
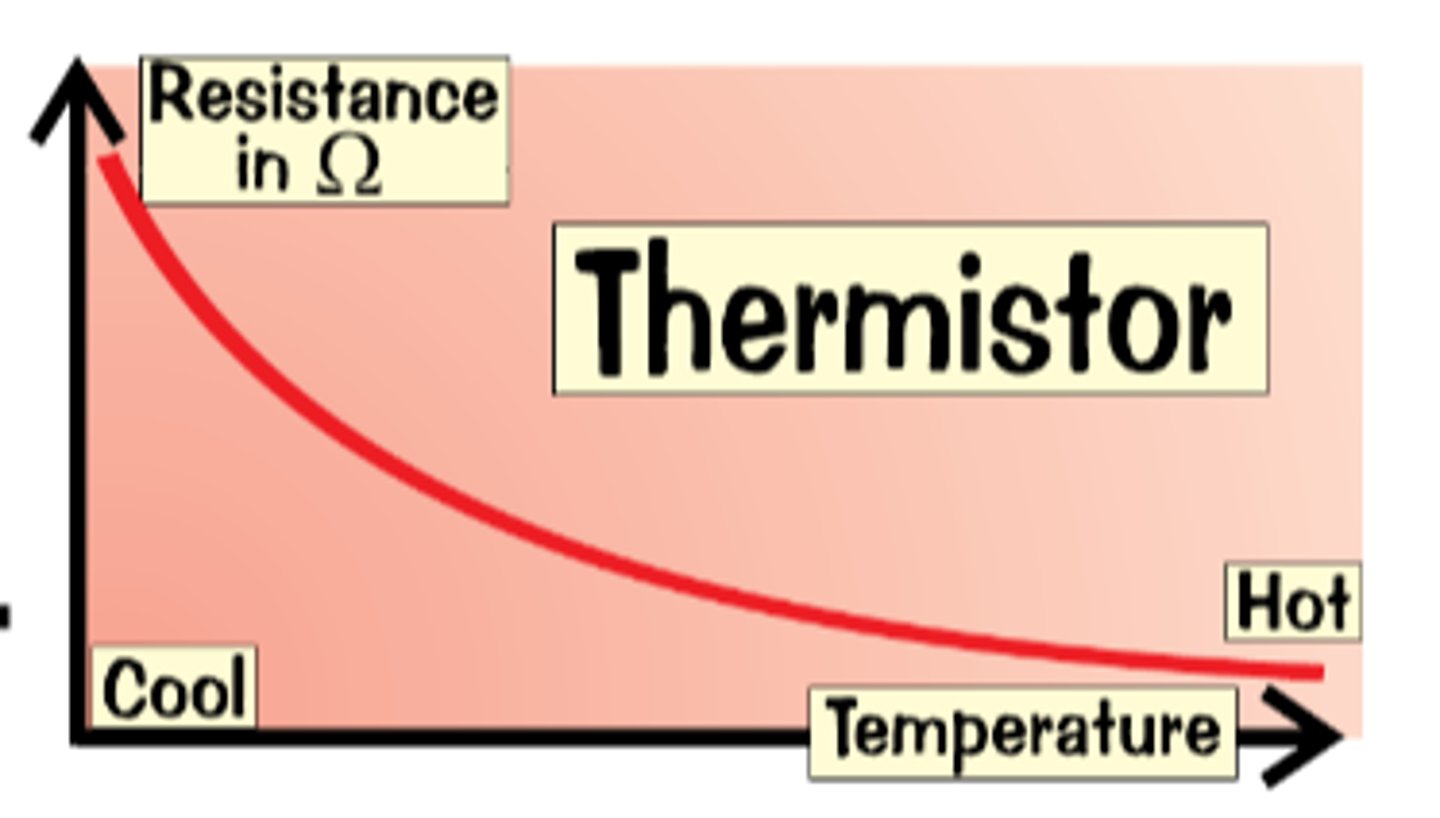
Thermistor
The resistance of a thermistor decreases as the temperature increases
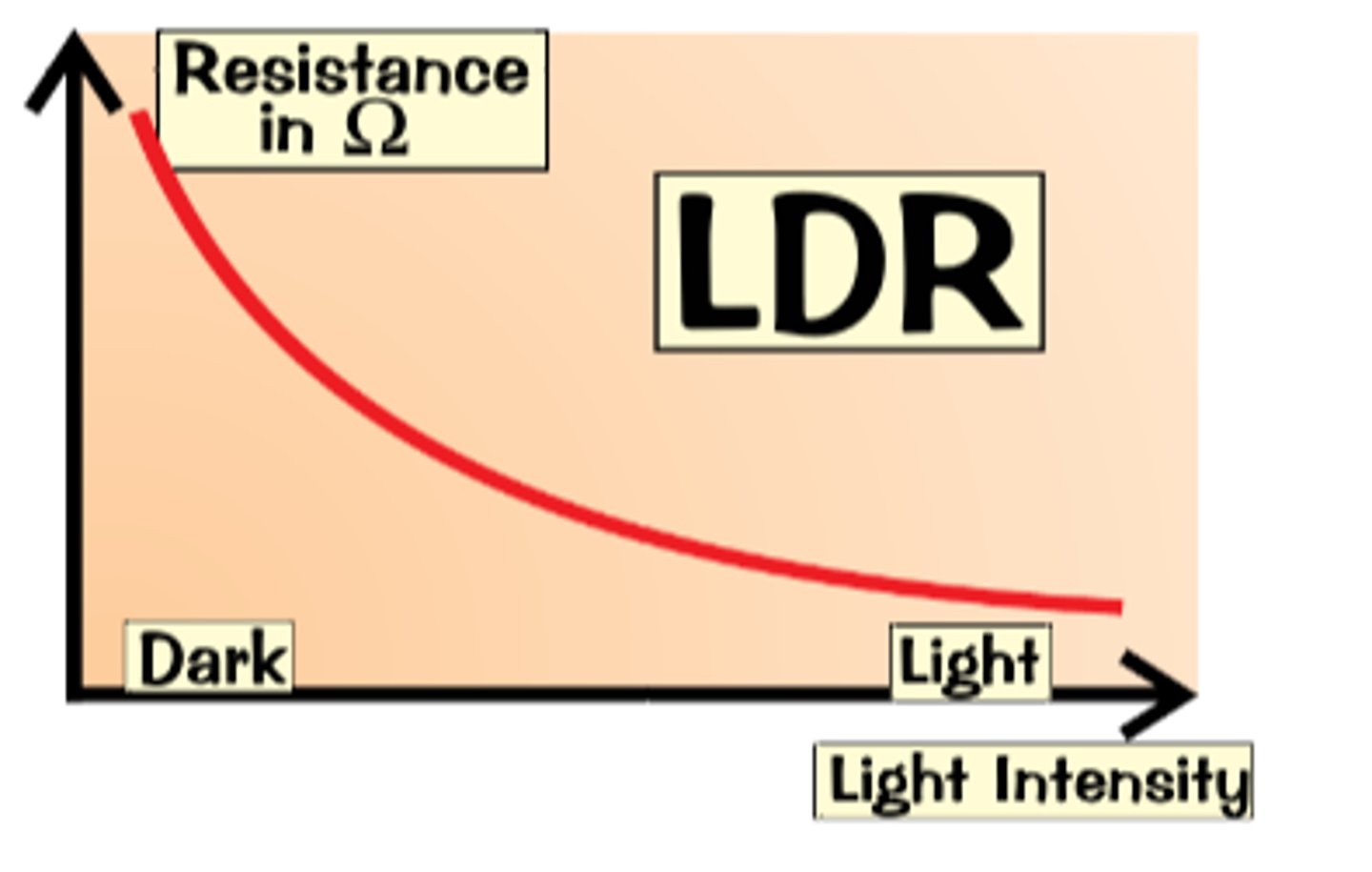
LDR (light dependent resistor)
The resistance of an LDR decreases as light intensity increases