Inequality
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:24 PM on 2/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
What is income?
The flow of money earned over a period of time
2
New cards
How is income earned?
→ Wages/salary
→ Rental income
→ Dividends
→ Rental income
→ Dividends
3
New cards
What is absolute poverty?
When a individual earns less than $1.20
→ Can’t afford essential needs for living
→ Can’t afford essential needs for living
4
New cards
What is relative poverty?
When income is lower than 60% of median household income in a country
5
New cards
What are the causes of income inequality and poverty:
→ Differences in skills and qualifications
→ Unequal holding of wealth
→ Differences in household competition
→ Unemployment
→ Unequal holding of wealth
→ Differences in household competition
→ Unemployment
6
New cards
Differences in skills and qualification:
Low skilled labour → low paid salary → output decreases
High skilled:
→ More bargaining power
→ Capital compliments skilled labour
→ UK specialises in tertiary sector
→ No jobs without qualifications
High skilled:
→ More bargaining power
→ Capital compliments skilled labour
→ UK specialises in tertiary sector
→ No jobs without qualifications
7
New cards
Unequal holding of wealth:
Homeowners can rent out → rental income
→ May have a stock portfolio → Dividend flow
→ Multiple income streams and salaries
→ Depends on tax → Progressive/capital gains
→ May have a stock portfolio → Dividend flow
→ Multiple income streams and salaries
→ Depends on tax → Progressive/capital gains
8
New cards
Differences in household competition:
Single parent → dependents → LIH
→ Cost of childcare high → just on benefits
→ No training → leads to poverty cycle
→ Cost of childcare high → just on benefits
→ No training → leads to poverty cycle
9
New cards
Unemployment:
Little income from benefits → doesn’t rise with inflation
→ If benefits high → people get complacent
→ Poverty trap
→ Stigma of claiming benefits
→ If benefits high → people get complacent
→ Poverty trap
→ Stigma of claiming benefits
10
New cards
What is wealth?
A stock of assets with monetary value
11
New cards
What are the causes of wealth inequality?
→ Income inequality
→ Inheritance
→ Difference in entrepreneurial skills
→ Marriage patterns
→ Inheritance
→ Difference in entrepreneurial skills
→ Marriage patterns
12
New cards
Income inequality:
If on benefits → can’t save → it only covers needs
→ HIH: have a higher MPS → more wealth
→ Multiple income streams → invest in shares
→ Get dividends
→ HIH: have a higher MPS → more wealth
→ Multiple income streams → invest in shares
→ Get dividends
13
New cards
Inheritance:
HIH → assets inherited are large → they give it to children
LIH → may get little to nothing
→ Causing intergenerational income inequality
LIH → may get little to nothing
→ Causing intergenerational income inequality
14
New cards
Difference in entrepreneurial skills:
LIH → don’t take as much risk to start a business
→ Use profits to invest in properties/equities
→ Requires talent
→ Poverty drives entrepreneurship
→ Use profits to invest in properties/equities
→ Requires talent
→ Poverty drives entrepreneurship
15
New cards
Marriage patterns:
People tend to marry of the same class
→ Power couples → causes greater income inequality
→ India → caste system → only marry of the same caste
→ Power couples → causes greater income inequality
→ India → caste system → only marry of the same caste
16
New cards
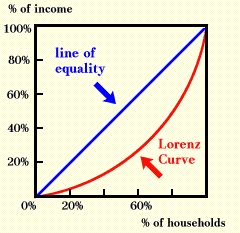
What is the Lorenz Curve?
A line of inequality which implicates progressive taxation
\
The last household income has 100%
Perfect inequality
\
The last household income has 100%
Perfect inequality
17
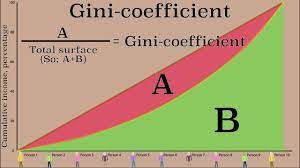
New cards
What is the gini co-efficient?
Perfect equality : Gini co-efficient is 0
18
New cards
What are the consequences of inequality and poverty?
→ Absolute poverty
→ Homelessness
→ Homelessness
19
New cards
Absolute poverty:
Can’t meet basic needs → living standards low
→ Less development → kids in poverty go to work
→ Can’t go to school/college → no skills gained
→ Structurally unemployed → hysteresis
→ Less development → kids in poverty go to work
→ Can’t go to school/college → no skills gained
→ Structurally unemployed → hysteresis
20
New cards
Homelessness:
May not be able to pay rent
→ Can’t setup accounts without proof of address
→ Absolute poverty → OCG formed
→ Government spending increases
→ Resort to payday loans → likely to default
→ Worsens credit store → assets taken
→ Wealth decreases
→ Can’t setup accounts without proof of address
→ Absolute poverty → OCG formed
→ Government spending increases
→ Resort to payday loans → likely to default
→ Worsens credit store → assets taken
→ Wealth decreases
21
New cards
What does the consequences of inequality depend upon?
→ Inequality being a problem
→ Trickle down effect
→ Trickle down effect
22
New cards
Inequality isn’t a problem:
Creates incentive to work hard
→ Less spending on benefits if jobs gained
→ Generated income destroys incentive
→ Low labour productivity
→ Lose output → PPF shifts inwards
→ Depends on the welfare state
→ Could provide free education/healthcare
→ Less spending on benefits if jobs gained
→ Generated income destroys incentive
→ Low labour productivity
→ Lose output → PPF shifts inwards
→ Depends on the welfare state
→ Could provide free education/healthcare
23
New cards
Trickle down effect:
Real high income earners generate the income to setup businesses to employ people
→ They become employed, no benefits
→ They become employed, no benefits
24
New cards
What are policies to reduce inequality and poverty?
→ Tax and Benefits system
→ Improve education and training
→ Increase national living wage
→ Improve social council housing
→ Improve education and training
→ Increase national living wage
→ Improve social council housing
25
New cards
Tax and Benefits system:
Progressive taxation system
→ When income inequality worsens
→ Tax revenue increases
→ Government will hypothecate tax revenue to low earners
→ Means tested benefits
→ Income inequality decreases
→ When income inequality worsens
→ Tax revenue increases
→ Government will hypothecate tax revenue to low earners
→ Means tested benefits
→ Income inequality decreases
26
New cards
Whats a negative of tax and benefits system:
If you cut benefits → WRR lowers → more incentive to work
→ Occupational mobility
\
ARTHUR LAFFER CURVE:
→ Tax rev decreases → human capital flight
→ Take business with them → leaving people unemployed
→ G>T → regressive effects
→ Occupational mobility
\
ARTHUR LAFFER CURVE:
→ Tax rev decreases → human capital flight
→ Take business with them → leaving people unemployed
→ G>T → regressive effects
27
New cards
Improve education and training:
Better skills → occupational mobility increases
→ Productivity increases → bottom decile earn more wages
→ {use same analysis as SSP}
→ Reduces income inequality
→ Productivity increases → bottom decile earn more wages
→ {use same analysis as SSP}
→ Reduces income inequality
28
New cards
Negatives of education and training:
Could be an uneven distribution of good education
→ Regional inequality
→ Graduate unemployment
→ Underemployed → big time lag → expensive
→ Regional inequality
→ Graduate unemployment
→ Underemployed → big time lag → expensive
29
New cards
Increase national living wage:
WRR decreases → Incentive to work increases
→ Develop skills and training
→ Occupational mobility increases
→ Develop skills and training
→ Occupational mobility increases
30
New cards
Negatives of increasing national living wage:
Labour costs increase
→ If salaries increases → people above also demand higher wages to maintain gap in status
→ Maintains incentive to get promoted
→ If salaries increases → people above also demand higher wages to maintain gap in status
→ Maintains incentive to get promoted
31
New cards
Improve social housing:
LIH mostly rent → unable to get a mortgage
→ Better incentive to find work → RDY increases
→ Good QOL → More productive
→ Better incentive to find work → RDY increases
→ Good QOL → More productive
32
New cards
Negatives of improving social housing:
Big opportunity cost
→ PES
→ PES