Sound Beams and Focusing
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
What are the two parts associated with the shape of a beam?
Frequency
Diameter (aperture)
What are the three introductory concepts associated with sound beams and focusing?
Aperture
Diffraction
Huygens’ Principle
What is an aperture?
An opening. The space through which light passes in an optical instrument.
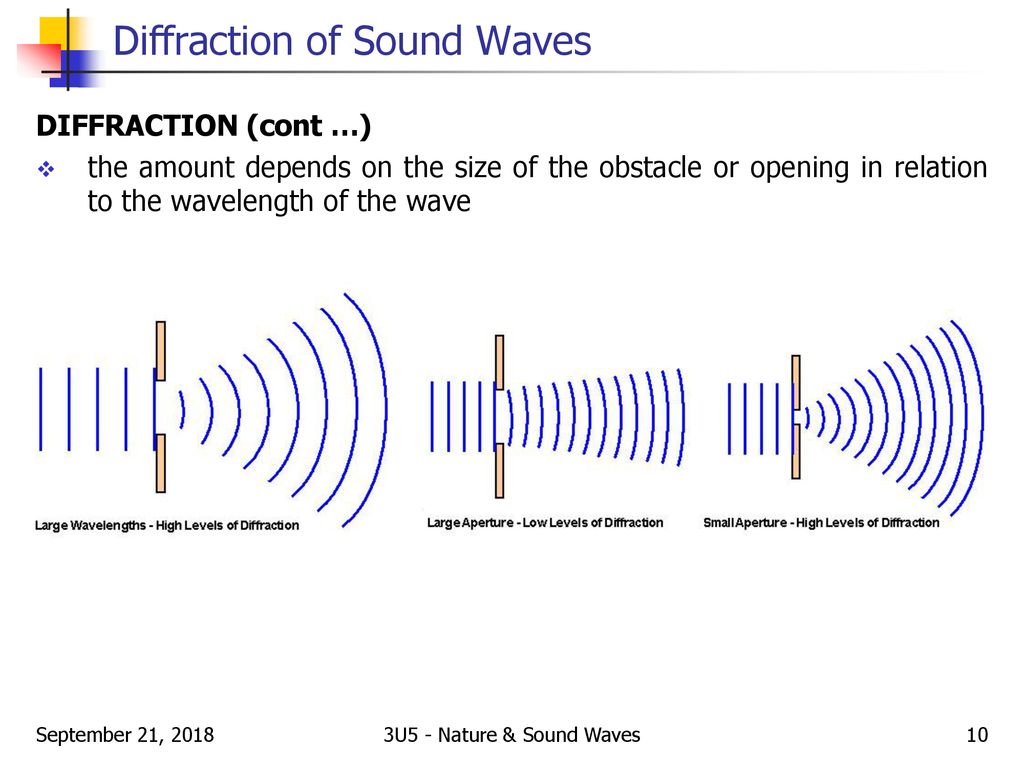
What is an aperture in ultrasound?
The diameter of the source of the sound.
Does the aperture affect the shape of the beam?
Yes.
What is diffraction?
The spreading of wave when emitted from a small aperture (relative to the wavelength).
A large diameter (aperture) source creates what type of beam?
Directional beam.
A small diameter (aperture) source creates what type of beam?
Diverging beam.
The smaller the diameter (aperture) of the source…
the more divergent the wave.
What causes wide spreading of the beam?
A small diameter (aperture).
What causes a more directional beam?
A large diameter (aperture).
What is the Huygens’ Principle?
The theory of wave interaction.
What does the Huygens’ Principle predict? (2)
Location of the wavefront
Shape of the beam (beam profile)
If the speed and frequency are known, the position of the wavefront which results from the interaction of these wavelets can be…
determined.
With large sound sources, tiny wavelets interfere to do what?
Produce a sound beam.
What are the three practical implications of Huygens’ Principle?
Due to wavelet interaction, the sound emitted from a transducer is directional.
The larger the aperture, the more directional the sound field.
The majority of the sound energy is confined to a region close to the beam axis.
Transducers with a single small element creates what type of beam?
A diverging beam.
Transducers with a single large element creates what type of beam?
A directional beam (mechanical transducers).
Transducers with multiple small elements creates what type of beam?
A directional beam - modern array transducer.
What is the sound field?
The region in a medium in which sound eaves are being propagated.
What are the two components of a sound field?
Main beam
Side lobes
What is the main beam?
The area that extends directly in front of the transducer.
True or False: The main beam contains most of sound energy.
True.
The main beam is the beam from which the transducer system expects to receive what?
Echoes.
What are side lobes?
Peripheral side beams surrounding the main beam.
Are side beams very strong or very weak surrounding beams?
Very weak.
Does the system expect to receive echoes from the side lobes?
No.
Why don’t sonographers like side lobes?
Because they cause side lobe artifacts.
Side lobes have high or low intensity?
Low.
What is the clinical importance of side lobes?
May produce artifact if echoes from side lobes are received and displayed.
What are the eight important concepts of an unfocused sound beam?
Beam profile
Near field (near zone)
Far field (far zone)
Transition point
Near field length
Far field beam divergence
Beam diameter
Beam area
What is the beam profile?
The shape of the sound beam.
Unfocused beams have what type of beam profile?
Wide → Narrow → Wider
Sound beam profiles have what type of shape?
An hourglass shape.
The near zone is also known as what?
The Fresnel zone.
Describe the near zone.
Where the beam narrows
Lateral resolution improves
Beam spatial intensity increases
The far zone is also known as what?
The Fraunhofer zone.
Describe the far zone.
Where the beam widens
Lateral resolution degrades
Beam spatial intensity decreases
What is the near zone length?
The distance from the transducer to the transition point.
What is the near zone length (NZL) also known as?
The near field length.
What is the formula for the NZL?
NZL = D²/4 λ
What is the formula for NZL for soft tissue?
NZL ≈ (D² x F)/6
NZL is directly or inversely proportional to frequency?
Directly.
NZL is directly or inversely proportional to D?
Neither! It is proportional to D².
What are the two factors affecting NZL?
Frequency
Crystal diameter
What is far field divergence?
The spreading out of the beam in the far field/
What are the factors affecting far field divergence?
Frequency
Diameter
An increase in frequency does what to far field divergence?
Decrease divergence.
An increase in diameter does what to far field divergence?
Decrease divergence.
High frequency transducers are very directional which does what to divergence?
Decreases divergence.
Large diameter transducers are very directional which does what to divergence?
Decreases divergence.
What is beam diameter?
Transverse diameter of the main beam.
What is the beam diameter measured in?
mm.
What is the clinical importance of beam diameter?
Determines lateral resolution.
Beam width determines what?
Lateral resolution.
What are three important locations of an unfocused beam diameter?
At the transducer, beam diameter equals D
At the transition point, beam diameter equals D/2
At 2 NZL, the beam diameter equals D
Is a beam diameter 2D or 3D?
3D.
What is beam area?
The cross-sectional area of the main beam.
What is the beam area measured in?
mm² or cm²
Beam area is important for what?
Intensity.
Intensity is equal to what?
I = P/A
Does the beam area vary along the beam?
Yes.
Where is the smallest beam area?
At the transition point.
The smallest beam area has the greatest…
intensity.
What is focusing?
Deliberate reduction in beam width in order to improve lateral resolution.
Lateral resolution depends on what?
Beam width.
What is the advantage of focusing?
It improves lateral resolution in the focal zone.
What are the disadvantages of focusing? (2)
Can only be applied to the near field.
Degrades lateral resolution in the far field (increases divergence in the far field).
What are the three focusing terms?
Focal point
Focal length
Focal zone
What is the focal point?
The narrowest part of the beam with on a focused beam.
What type of resolution where it is best is found at the focal point?
Lateral resolution.
The focal point has what type of beam area?
A small beam area; the smallest beam area.
What is the focal length?
The distance from the transducer to the focal point.
What is the focal length measured in?
mm or cm
A rule of thumb, the focal length is never larger that what?
NZL (near zone length).
What is the focal zone?
The region of the beam around the focal point.
What are the two focusing methods?
Mechanical focusing
Electronic focusing
What is mechanical focusing?
Where there is a fixed focus on the specific transducer used. There is no way to change the focus.
Today, what is used to achieve mechanical focusing?
A lens at the front of the transducer (think of it as eyeglasses directing light to the retina).
What is the order of materials found in a typical array transducer from the back to the face (or footprint)? (4)
Damping block
Crystal
Matching layers
Lens
What is electronic focusing?
Gives you the ability to change the focus with single or multiple areas.
Electronic focusing is found in what type of transducers>
Array transducers.
What is a standoff pad?
A layer of gel-like material used to improve imaging of superficial layers.
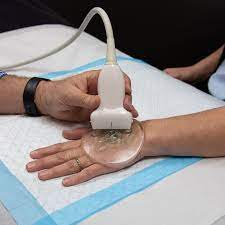
What is the construction of a standoff pad?
Low attenuating
Homogeneous
Speed of sound within it is made to be at 1540 m/s
Typically used with a single crystal fixed focus transducer
What is the use of a standoff pad?
It puts superficial structures into the focal zone. Without it, these structures would be scrunched up to the top of the display.
What can you do if your department does not have a standoff pad?
Fill a glove with water.
Use ALOT of gel, but be sure not to press against the skin. You want to hover your transducer so there is a thick layer of gel in between the footprint of the transducer and the skin.