Mechanisms of Drug Acition, Dose, Response Curves
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Pharmacology
Scientific study of the effects of drugs and chemicals on living organisms where a drug can be broadly defined as any chemical substance, natural or synthetic, which affects a biologic system
Pharmacodynamics
Study of a drug’s molecular, biochemical, cellular, and physiologic effects or actions.
“Pharmakon”: drug
“Dynamikos”: power
Pharmacokinetics
Study of how the body interacts with administered medication for the entire duration of exposure
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
Molecular target (drug target)
macromolecule or cellular or tissue structures that a drug interacts with (binds to) resulting in a change in their function that elicit a desired pharmacological effect. The vast majority of targets are proteins with some drugs targeting DNA, lipids and carbohydrates.
Receptors (Pharmacologic)
Target molecule for an endogenous or exogenous ligand.
With few exceptions, drug actions are mediated through the effects of drug ligand molecules on drug receptors in the body.
Most receptors are large regulatory molecules that influence important biochemical processes (eg, enzymes involved in glucose metabolism) or physiologic processes (eg, ion channel receptors, neurotransmitter reuptake transporters, and ion transporters).
Receptors (biochemical)
Proteins that bind to external messengers to create a series of downstream effects that mediate a specific response in the cell
Have a ligand-binding domain that recognizes the specific ligand and the effector domain that undergoes conformational changes to produce a downstream event.
Antacids
Combination of various compounds with various salts of calcium, magnesium, and aluminum as active ingredients.
Act by neutralizing the acid in the stomach and by inhibiting pepsin, which is a proteolytic enzyme
Chelating agents
Used to reduce blood and tissue levels of injurious heavy metals
Classified based upon target heavy metal (iron, copper, mercury, and lead)
Some have high degree of specificity for target metal, while others chelate multiple agents
Mannitol
Increases osmolality of blood plasma
Used to lower pressure in head and increased pressure in eye
Can treat brain swelling
2-Mercaptoethane sulfonate (Mesna)
Sulfhydryl compound used to reduce incidence of hemorrhagic cystitis (inflammation of bladder) associated with certain chemo agents
converted to free thiol compound in kidney —> binds and inactivates acrolein + other urotixic metabolites of ifosfamide and cyclophosphamide —> reducing toxic effects on urinary effects on urinary tract during excretion
Bile acid sequestrants (Cholestyramine)
Bile acids, metabolites of cholesterol, normally reabsorbed in jejunum + ileum
Excretion increased tenfold when given —> enhanced conversion of cholesterol to bile acids in the liver via 7α-hydroxylation normally controlled by negative feedback by bile acids
Lowers cholesterol by excretion —> body is forced to create instead of recycle
What are receptors responsible for?
Molecular size, shape, and electrical charge
Agonist
Drug/substance that binds to a receptor inside a cell or on its surface —> causes same action as the substance that normally binds to the receptor
Antagonist
Drug/substance that reduces the action or effect of another substance (can also block)
Receptors
Protein inside/surface of cell that binds to a specific substance (ligand)—> causes specific effect in the cell
Main classes: GPCR, tyrosine kinase, ion channel receptors, hormone receptors
Enzymes
Biologic catalyst and is almost always a protein
Speeds up rate of a specific chemical reaction in the cell
Not destroyed during the reaction (recycled)
Transport proteins
Transfers polar solutes across cell membranes
Occur in many forms and in all types of biologic membranes
Each protein transports a particular class of molecule and often only certain molecular species of the class
Structural Proteins
Maintain cell shape
Compose structural elements within cells/connective tissue
E.g. tubulin
Non-covalent forces governing ligand-receptor interactions
Ionic Interactions
H-bonds
Van der Waals Forces
Hydrophobic Interactions
Small molecule/micromolecule
Low molecular weight (< 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate biological process
Size on the order of 1 nm
Dalton
A unit of mass for expressing masses of atoms, molecules, or nuclear particles equal to ¹/₁₂ of the atomic mass of the most abundant carbon isotope C-12: atomic mass unit
Biologics
Pharmaceutical compounds synthesized/extracted from a biologic source
Highly complex structures
Divided into: monoclonal antibodies, receptor modulators, replacement/modulators of enzymes
Manufacturing process of biologics
Involves living systems and complex processes
Level of constitutive activity of a receptor for cells is dependent on
Allosteric transition state (L)
Receptor density
Effector concentration and activity
Receptor-effector coupling efficiency
Type of conformation that the receptor adopt in the absence of ligand
Effector
Small molecule that selectively binds to a protein to regulate its biological activity
Act as ligands that can increase/decrease enzyme activity, gene expression, influence cell signaling, other protein functions
Cellular response to a specified concentration of a drug is composed of:
Drug dependent properties (affinity and intrinsic efficacy)
System-dependent properties (target density and efficiency of target-effector coupling)
Magnitude of response that a drug produces is determined by the:
Affinity and intrinsic efficacy of drug
Fraction of the target population occupied by the drug (defined by concentration of drug and drug’s affinity value)
Total target density
Efficiency with which the drug causes active conformation (multiple may exist) and converts activated targets into a response (coupling efficiency)
Effector(s) concentration and activity
EC50
Dose or concentration at which effect is half-maximal
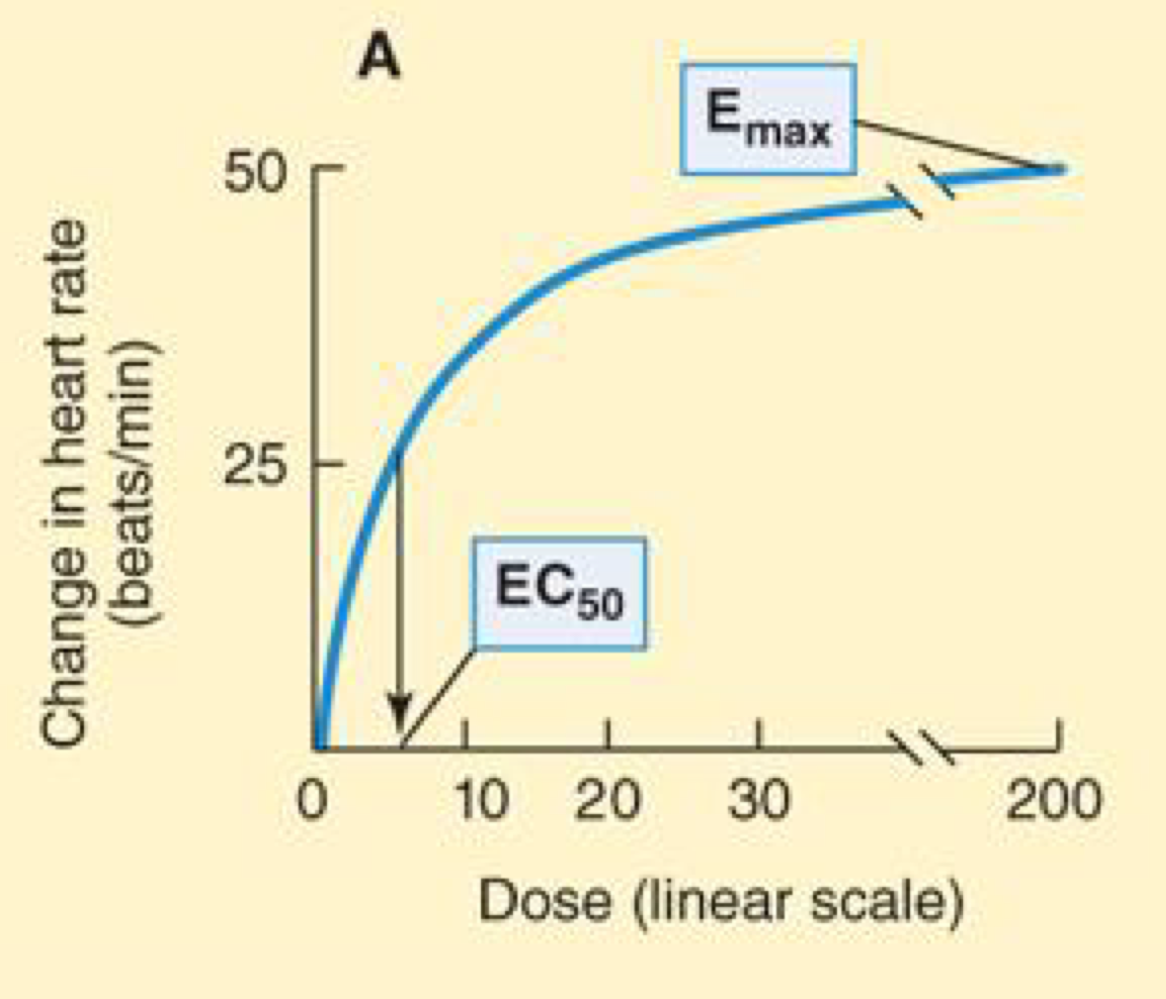
Relation between drug dose or concentration (X-axis) and drug effect (Y-axis)
Dose axis linear —> hyperbolic curve
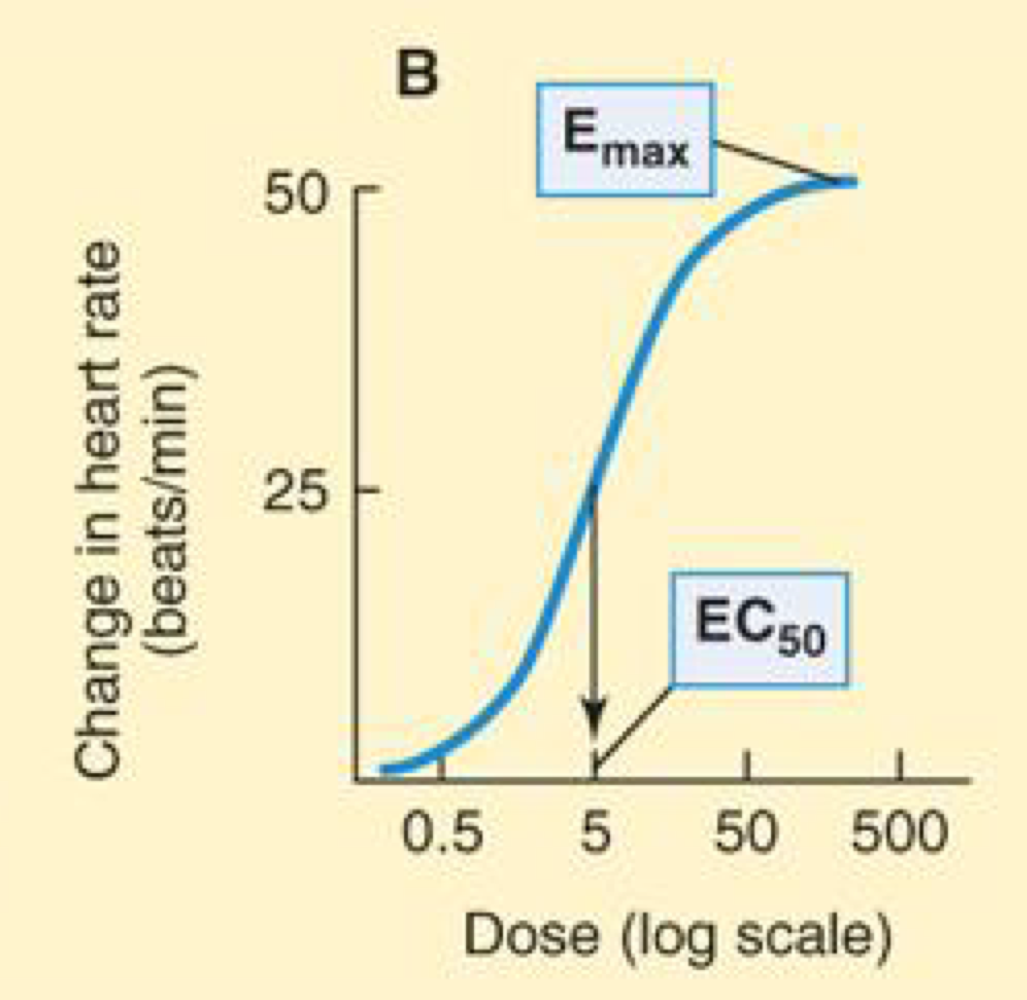
Logarithmic dose axis
The dose or concentration at which effect is half-maximal is denoted EC50, whereas the maximal effect is Emax
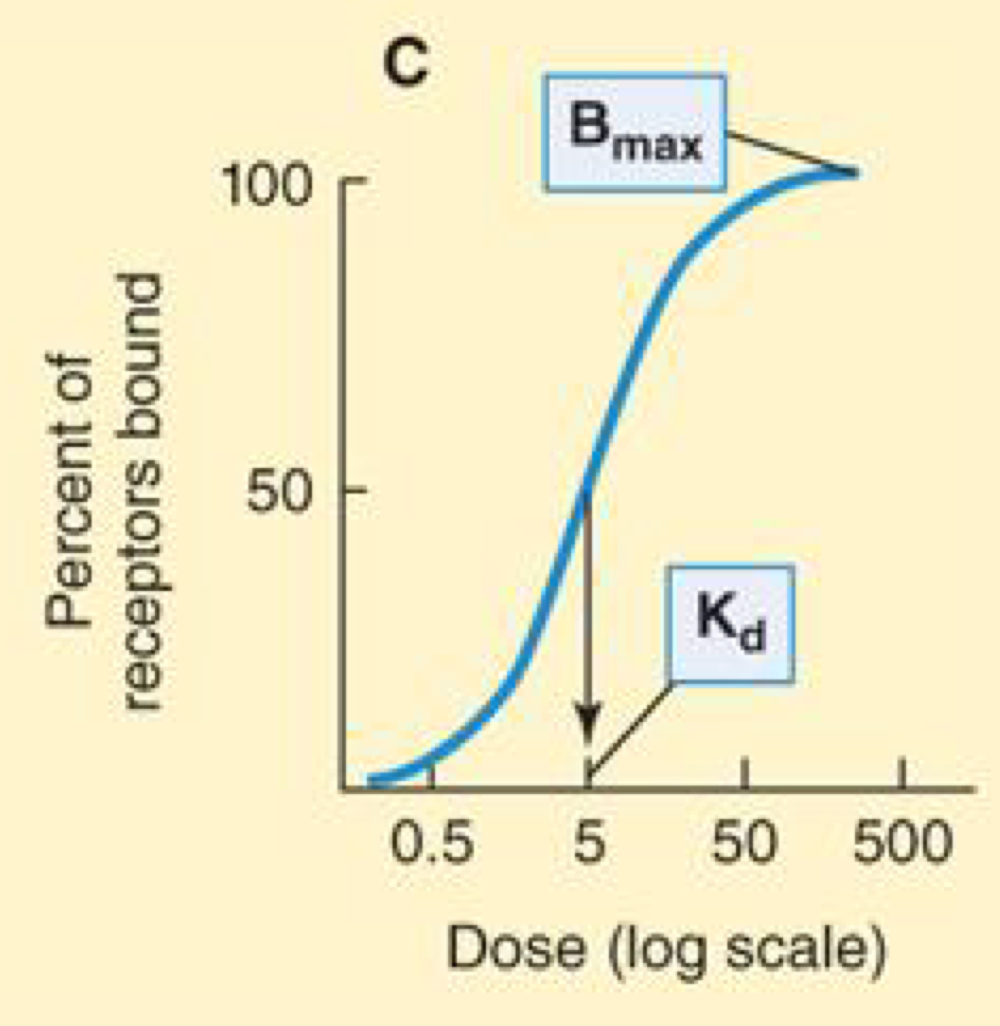
If the percentage of receptors that bind drug is plotted against drug concentration, a similar curve is obtained like in B
Concentration at which 50% of the receptors are bound is denoted Kd, and the maximal number of receptors bound is termed Bmax
Potency
Amount of a drug that is needed to produce a given effect
E.g. EC50 (or ED50) is the concentration or dose of drug that causes 50% of maximum effect
Efficacy
Maximum effect that a drug can produce regardless of dose (Emax)
If you have two drugs and drug A has a higher potency than drug B, does that mean that drug A will also have a higher efficacy?
No, not really