TCP/IP
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Commands used to gather information aout nodes on a network. These commands will be executed on both windows and Linux environments.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
CAT
a Linux utility that concatenates and lists files such as : -A, -b, -e, -E, -n, -s, -T, -v
MAN PAGES
Manual Page, a form of software documentation found on Linux machines used to provide help with concepts such as programs or command syntax
DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical system that translates user-friendly domain names into IP addresses, enabling browsers to load Internet resources. It primarily operates using the UDP protocol on port 53 for query responses.
FQDN
Fully Qualified Domain Name is the complete domain name for a specific host on the Internet, consisting of the hostname and the domain name that uniquely identifies it within the DNS hierarchy.
Authoritative DNS Server
A DNS server that holds the complete database of records for a specific domain and provides responses to queries about that domain's names.
Nonauthoritative DNS Server
A DNS server that does not have the complete database of records for a domain and relies on other DNS servers for query responses, typically caching results for efficiency.
Alias
A secondary name assigned to a host within the DNS system that points to the same IP address or resource, allowing multiple names to refer to a single entity.
in-addra.arpa
the reverse lookup zone used by IPv4 to map IP addresses to DNS names.
Socket
the combination of an IP address and a TCP or UDP port number separated by a colon (ex. 192.168.12.10:53)
ICMP
Internet Control Message Protocol: a protocol within the TCP/IP suite that resides at the OSI Network Layer (Layer 3) used to send query or error messages to network nodes.
TTL
Time to Live: a mechanism to specify the lifetime of data on a network
ARP
Address Resolution Protocol : a protocol within the TCP/IP suite that resides at the OSI Network Layer (Layer 3) used to resolve network layer addresses (IP addresses)
MAC Address
Media Access Control Address : the physical address burned into the ROM of an Ethernet network card: used by switches at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model to move information between nodes on the same network.
Wireshark
Is a network protocol analyzer. It lets you capture and interactively browse the the traffic running on a computer.
TCP/IP Networking Model
4 layers : application, transport, network, and data link layers.
Application Layer
This is the first TCP/IP layer.
FTP, telnet, HTTP, ect.
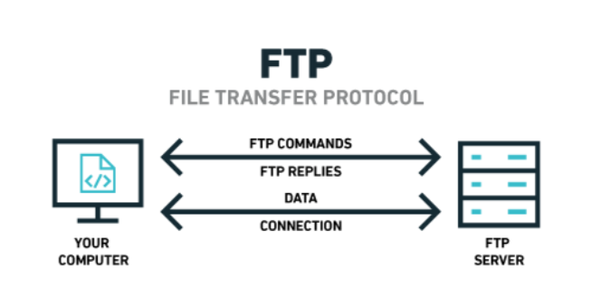
FTP
File Transfer Protocol : a network protocol that allows for the transfer of files between a client and a server over a TCP/IP connection
Port : 21
HTTP / HTTPS
Hyper Transport Protocol / Secure : the foundation of the World Wide Web, used to transfer data between we servers and clients (like web browsers).
It is an application-layer protocol and builds on top of other network protocols like TCP/IP.
Telnet
A network protocol and an application that enables users to connect to and communicate with remote computers over a TCP/IP network. It is the remote control for the internet allowing you to physically interact within the internet.
Transport Application
The second TCP/IP layer.
TCP/UDP
Network LAyer
The third layer TCP/IP layer.
IP addresses
Network Access Layer
Also known as the Link Layer, this layer deals with the physical transmission of data across the network, including framing, addressing, and physical media.
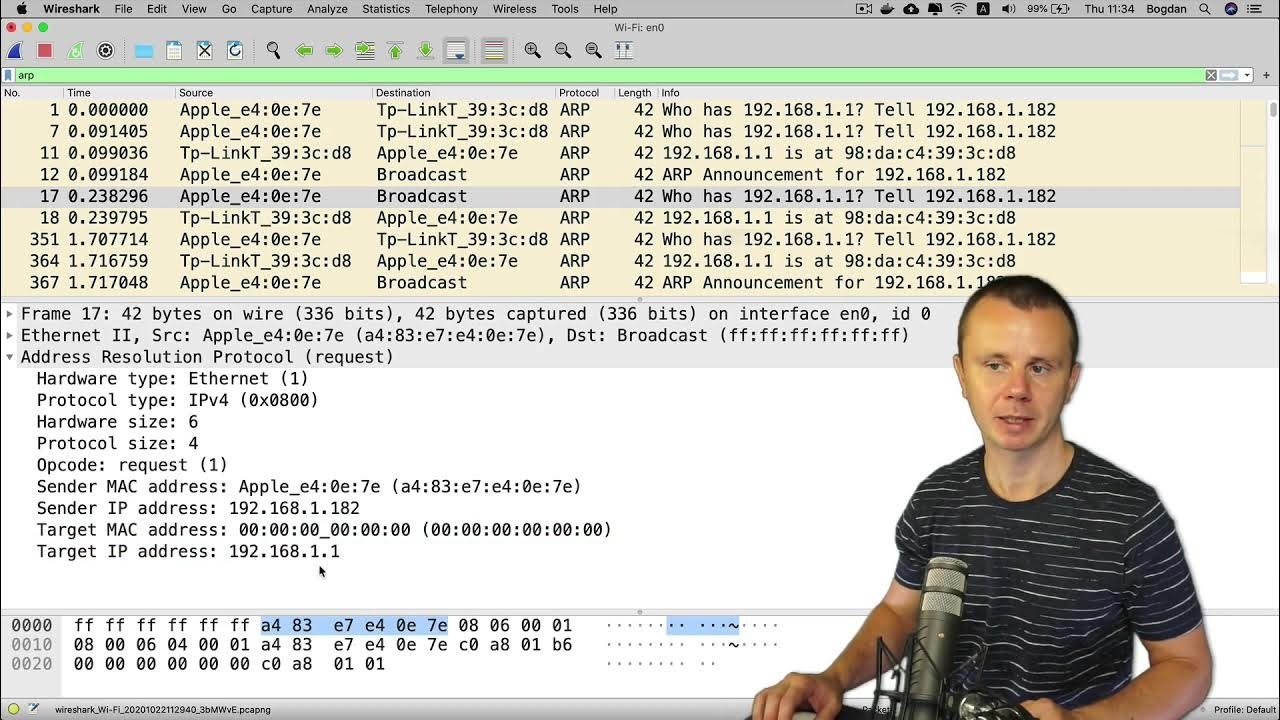
ARP Map
ARP Cache is stored in the map and can be manipulated with the ARP command.

IPv6
It is an upgrade to IPv4 to allow for more addressing. Allows for 128-bit address space which is displayed in hexadecimal notation.
IP (IPv4)
A connectionless network layer protocol that transmits packets from a source host to a destination host. Uses 32 bit address space (ex; 192.153.10.1)
TCP
A protocol that sits at the transport layer of the TCP/IP stack. Its job is to make sure that a connection is created between the source and the destination host and reliably send packets over the network. TCP works in three stages: connection setup, data transmission, and connection termination.