Pages 1-11
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Retinal disparity
Binocular cue
eyes view things differently due to 2.5 inches apart
Convergence
Binocular cue
things far away, eyes are relaxed
tings close to use, eyes contract
Weber’s law definition
Made the term “just noticeable difference”
threshold at which you will feel a change in any sensation
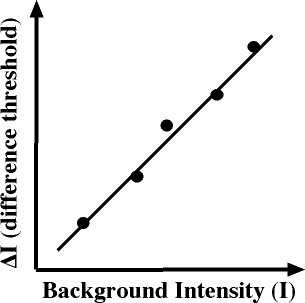
Weber’s law equation
ΔI / I = K
ΔI is the JND, I is the original stimulus intensity, and K is a constant specific to the sensory modality (like weight, sound, or light)
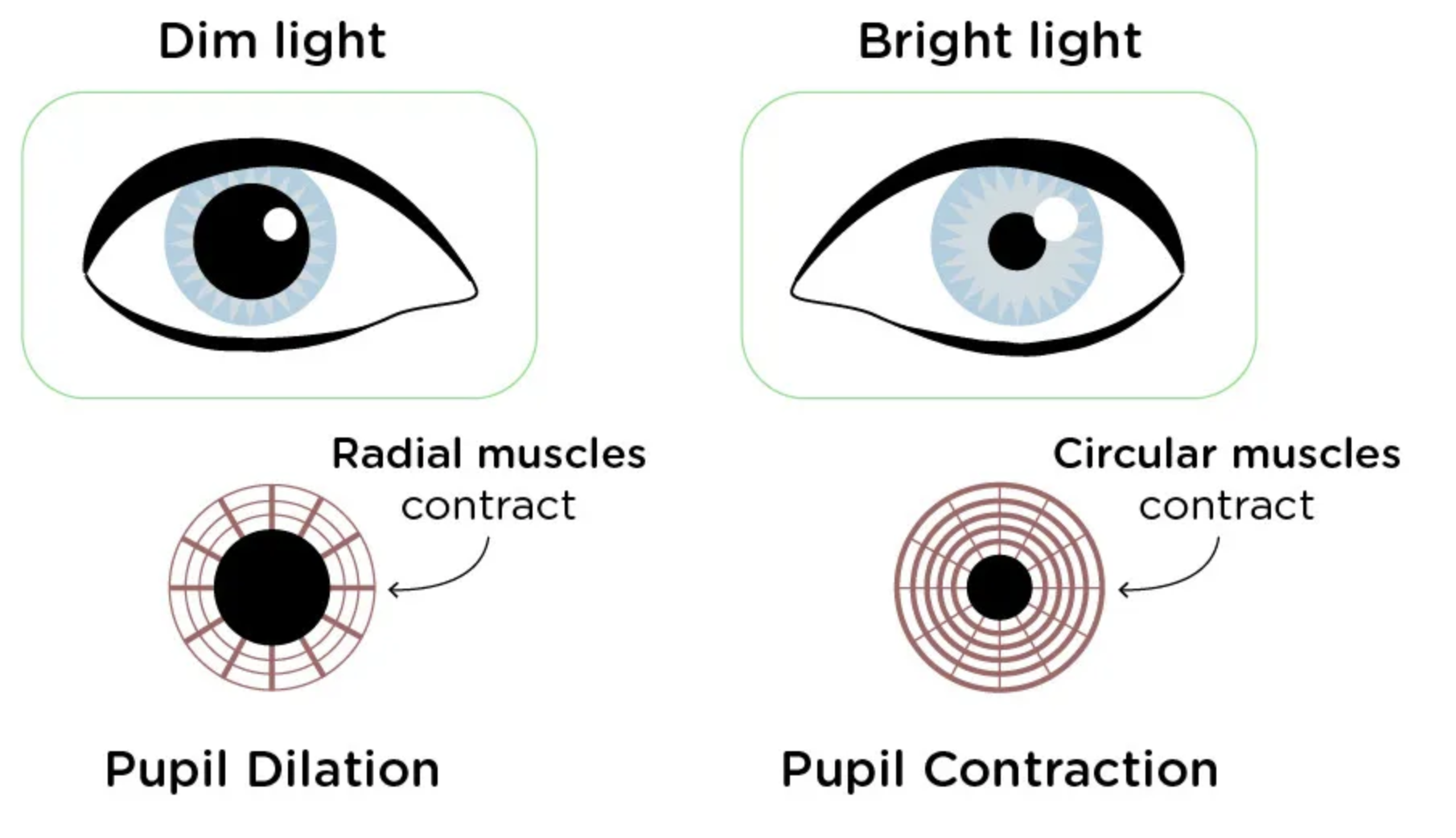
Absolute threshold of sensation
Minimum intensity of stimulus needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time
Signal detection theory
How we make a decision under conditions of uncertainty—discerning between important stimuli and unimportant “noise”
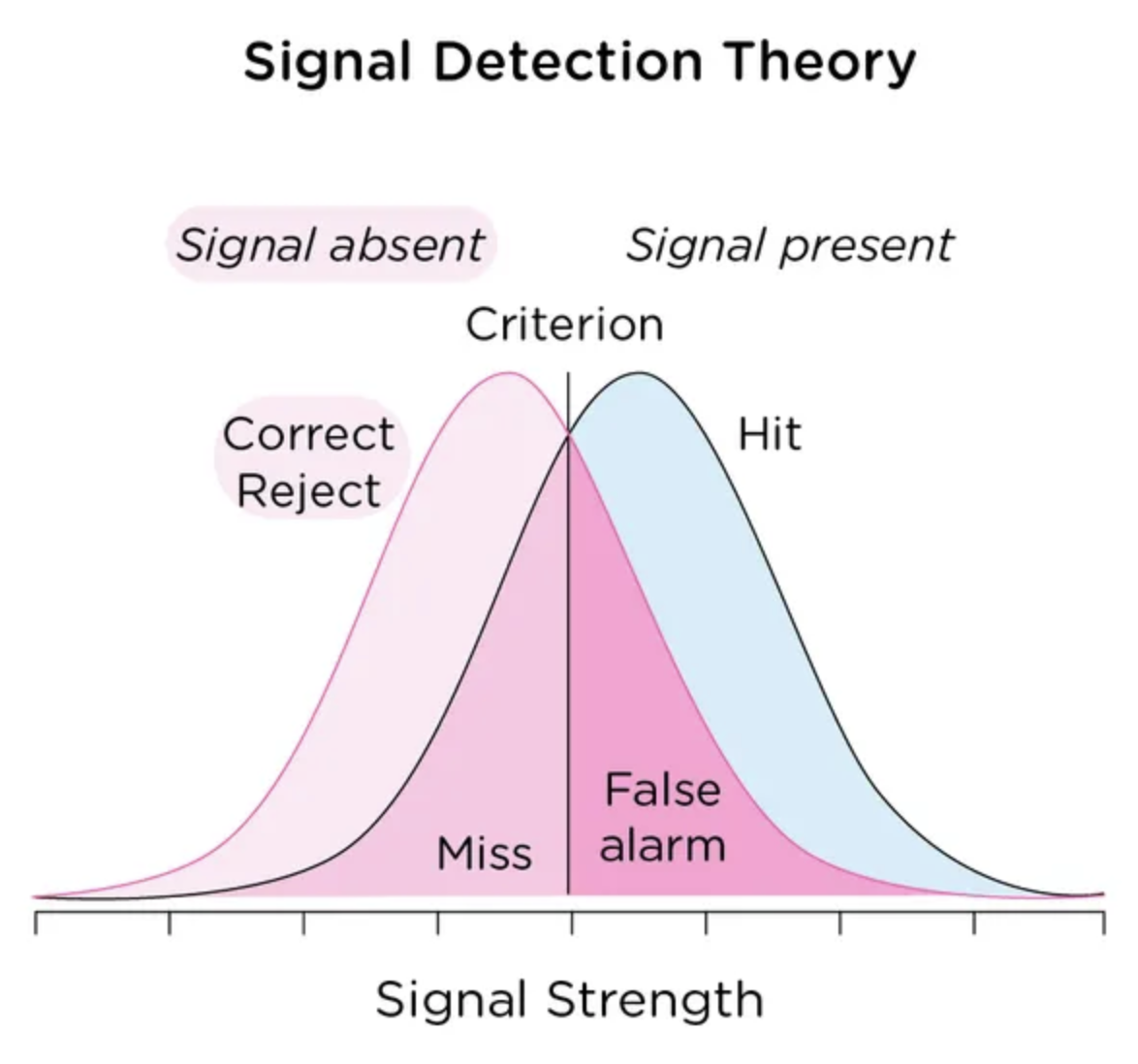
Strength of a signal using d’ and c
d’: hit>miss (strong), miss>hit (weak)
Big d’ is strong signal
c: conservative (no unless 100% signal is present), or liberal (always say yes, even if false alarms)
Bottom-up processing
Stimulus influences our perception
Processing sensory information
Top-down processing
Background knowledge influences perception
Driven by cognition
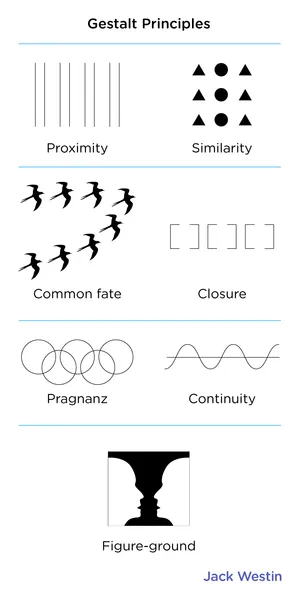
Similarity
items similar to each other are grouped together
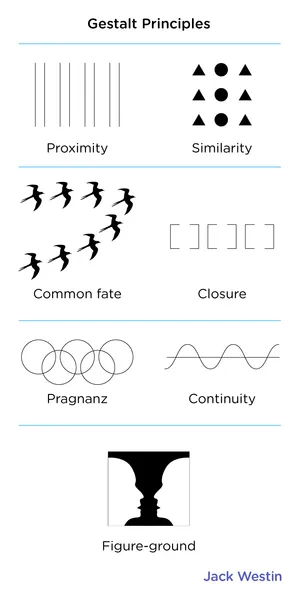
Pragnanz
reality is organized and reduced to the simplest form possible (ex. 5 circles become olympic rings)
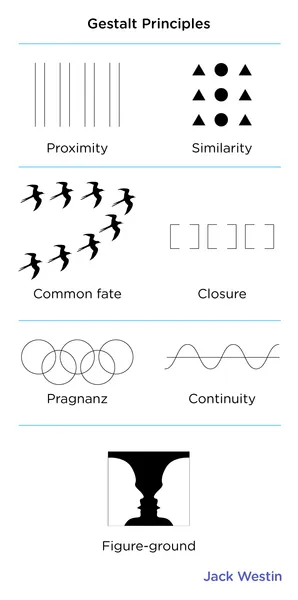
Proximity
objects that are close are grouped together
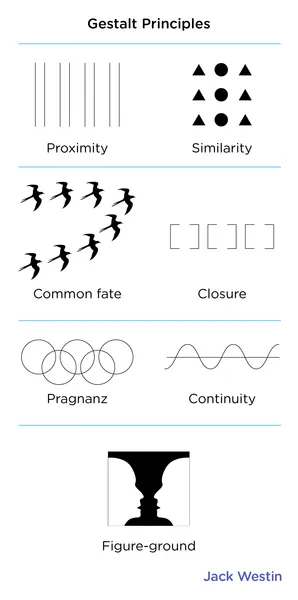
Continuity
lines are seen as following the smoothest path

Closure
objects grouped together are seen as a whole
What are rods? How many do we have?
Night vision (found in the periphery)
120M
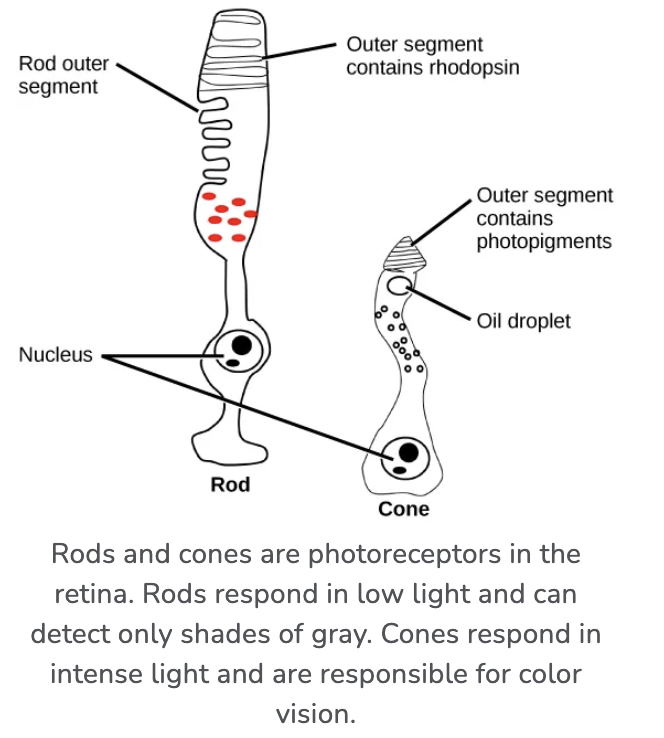
What are cones? How many do we have?
Color vision: red, green, blue (centered in fovea)
6-7M
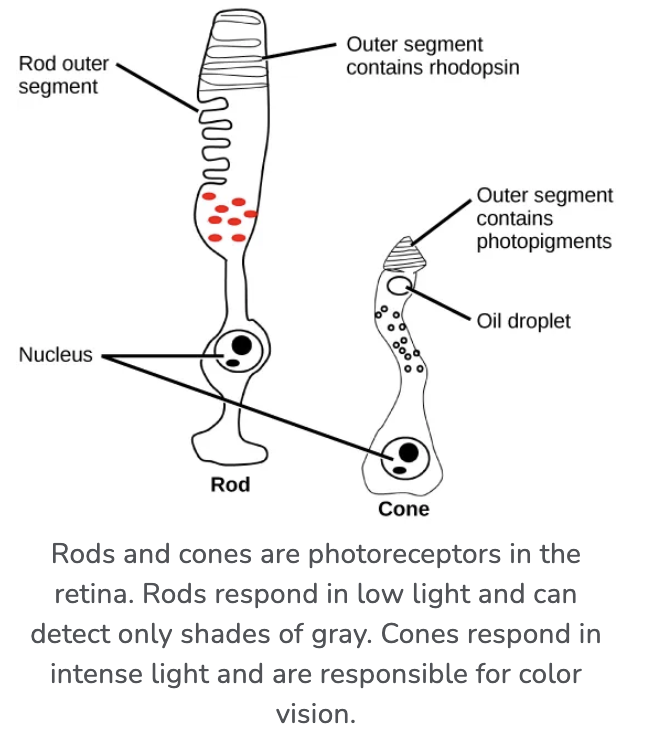
What is the mechanism in rods vs. cones
Both:
Phototransduction cascade initiates if light hits rhodopsin
Rods: 1000x more sensitive, but slow recovery time
Cones: fast recovery time
Parallel processing
Using multiple pathways to process incoming stimuli that differs in quality
What is the function of the cribriform plate?
Separate olfactory epithelium from the brain, creating a space for the olfactory bulb, a bundle of nerves with specific receptors at each end.
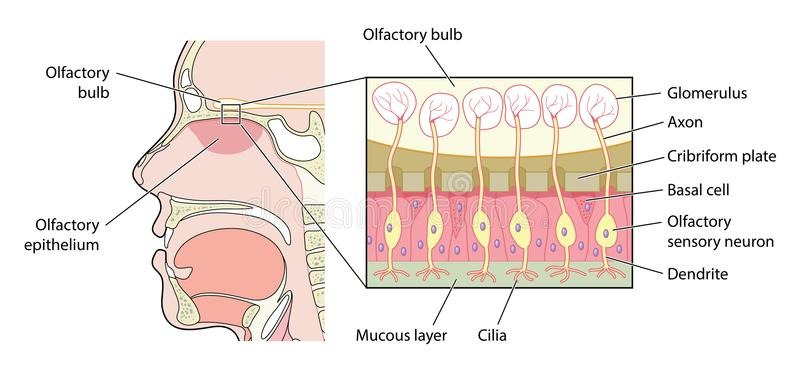
Mechanism for smell
Molecule binds receptor → Glomerulus → Synapses with Mitral/Tufted cell → Brain → GPCR → AP
Pheremone
Chemical signal that induces innate response that leads to mating, fighting, and communication
Vomeronasal system
Basal and apical cells have receptors
Basal cell sends signal to amygdala
What is the two different types of gustation mechanisms?
GPCR, G protein dissociates, ion channel, cell depolarize and AP
Sweet, umami, bitter
Binds directly to ion channel → AP
Sour (H+), salty (Na+)
What is the sequence for stages of sleep?
N1 → N2 → N3 → N2 → REM
Describe the first stage of sleep:
N1:
Theta waves are dominant
Hypnic Jerks
Tetris effect
Hypnagonic hallucinations
Describe the Tetris effect
If you play tetris before bed, you might see blocks
Characteristic of N1 Sleep
Describe the second stage of sleep:
N2:
People are harder to awaken
MORE Theta waves present
Sleep spindles
K-complexes
What is the purpose of sleep spindles?
To inhibit certain perceptions to maintain a tranquil state during sleep allowing us to sleep through loud noises
What the purpose of K-complexes
The suppress cortical arousal while you sleep
Memory consolidation
Moving somebody makes them show up.
Describe the third stage of sleep:
N3:
Delta waves present
Slow wave sleep
Sleep walking and talking
What is REM sleep for
Most important for memory consolidation
Most dreams happen here
Body is paralyzed but mind is active
Waking up during REM prevents dream memory
What controls the Circadian rhythms?
Melatonin produced in the pineal gland across 24 hours
What is an indicator of a person dreaming?
Rapid eye movement
Prefrontal cortex activity is blocked (no logic)
What was Freud’s analysis on dreams
Unconscious thoughts and desires that must be interpreted
Manifest content (what happens-monster killed you)
Latent content (hidden meaning-got fired)
Can help us resolve hidden conflict
What is the evolutionary principle behind dreaming?
Threat simulation
Activation synthesis hypothesis
Humans construct dream stories as soon as they wake up in an attempt to decode electrical brain impulses
What is the reasoning behind hypnosis?
What are the two theories
To retrieve memories and alter them
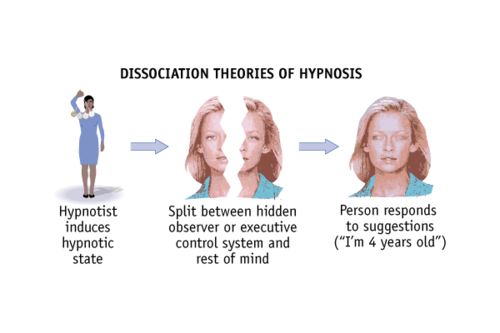
Dissociation theory
Social influence theory
Dissociation theory:
Hypnotism is an extreme form of divided consciousness
Social influence theory
People do and report what is expected of them
What is the purpose of meditation?
Increased attention control
More alpha waves than a regular relaxed state
More theta waves in deep meditation
Depressants
Reduce body’s function, think slowly, disrupt REM sleep
Alchohol
GABA receptor
Barbiturates
Induce sleep and reduce anxiety
Depresses the CNS
Reduces memory, judgement, and concentration
GABA receptor
Benzodiazapines
Suppressant, opens GABA Cl- channels
Short and Intermediate for sleep aids
Long for anti-anxiety
Opiates
Used to treat pain and anxiety
Act at endorphin receptor
Lead to euphoria