Above ground: stems and leaves
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
stem tuber
modified stem used to store food underground (ex/potato)
bulb
(onion), short, flattened stem bearing fleshy, food-storing leaves
rhizome
underground, horizontal stem
Shoot system
mostly above ground
-stems, leaves, reproductive organs
-origin in plume of embryo
stem functions
support, conduction, photosynthesis, food storage
orient towards sun (support)
tropisms
food storage in stems
Modified stems can serve as food storage (mainly starches)
Plant stems characterized by presence of ___
nodes: points of attachments of leaves, spaced at regular intervals
internode
region of the stem - the area between two nodes - elongates early in its development to ensure separation of leaves
axillary bud
usually found in the axil - area between a leaf and the stem.
• It can give rise to a new shoot (axillary shoot) - with its own apical meristem
Identifying ___ can help you figure out where a leaf starts
the axillary bud
Apical meristem produces 3 types of primary meristematic tissue
protoderm: rise to epidermis
ground meristem: gives rise to ground tissue (photosynthetic, storage, support)
procambium: rise to vascular tissue (transport)
secondary growth
increase in thickness or girth of stem caused by division of secondary meristem
secondary (lateral) meristem consists of
vascular cambium and cork cambium
secondary tissue
periderm and wood and tertiary tissue (bark)
vascular cambium divides into
secondary xylem (inside) and secondary phloem (outside)
cork cambium produces
periderm tissue
secondary growth-periderm
replaces the epidermis in shoots at the end of the first year of growth
• It is mostly not permeable due to waxy suberin
-New layers of periderm are produced inside the older layers
gas exchange happens via
lenticels- elevated regions with large intercellular space
rhytidome
older layers of periderm, die and are pushed out - cracking and producing typical texture of bark
secondary growth-bark
all tissue external to the vascular cambium.
-inner bark: secondary phloem. The cortex, and the phelloderm
-outer bark: cork cambium and everything outside (periderm, cork, etc).
-protects plant against physical damage and prevents water loss
older layers of secondary phloem are ____
lost/crushed, makes bark thick
Secondary growth-wood
consists of the original pith, primary xylem and secondary xylem
vascular cambium divides in 2 directions
secondary phloem (outside) and secondary xylem(inside).
• Older (dead) layers of secondary xylem are retained - adding layers of wood
• As new layers of xylem are created, the pith tissue at the center may be destroyed
heartwood
the oldest (inner most) layers of secondary xylem which NO longer conduct water
• Darker in color• Tylosesvessel elements prevent water flow
sapwood
water-conducting xylem in the periphery of heartwood.
• Lighter in color
branching
Lateral (or axial) buds can give rise to branching -new stems.
2 types of branching
monopodial: buds do NOT degrade, and all shoots continue to grow
sympodial: terminal buds degrade, and lateral buds closest to the apex become the new terminal shoot
Plant growth forms
vines: climbing woody and herbaceous
trees: woody plants with one main long-lived trunk
shrubs: woody plants with multiple main long-lived trunks/stems
herbs: herbaceous plants (no secondary xylem), rosette, erect, mat
leaves arise from shoot apical meristem through _____
leaf primordia
most leaves have ____ growth
determinate
true leaves subtend an ____ at their base and are ____
axillary bud, lateral
blade
(lamina) - flat, usually widest, part of leaf
petiole
stem-like part of the leaf, collecting the blade to the stem
petiolate leaves
leaves containing visible petiole (usually attached to margin)
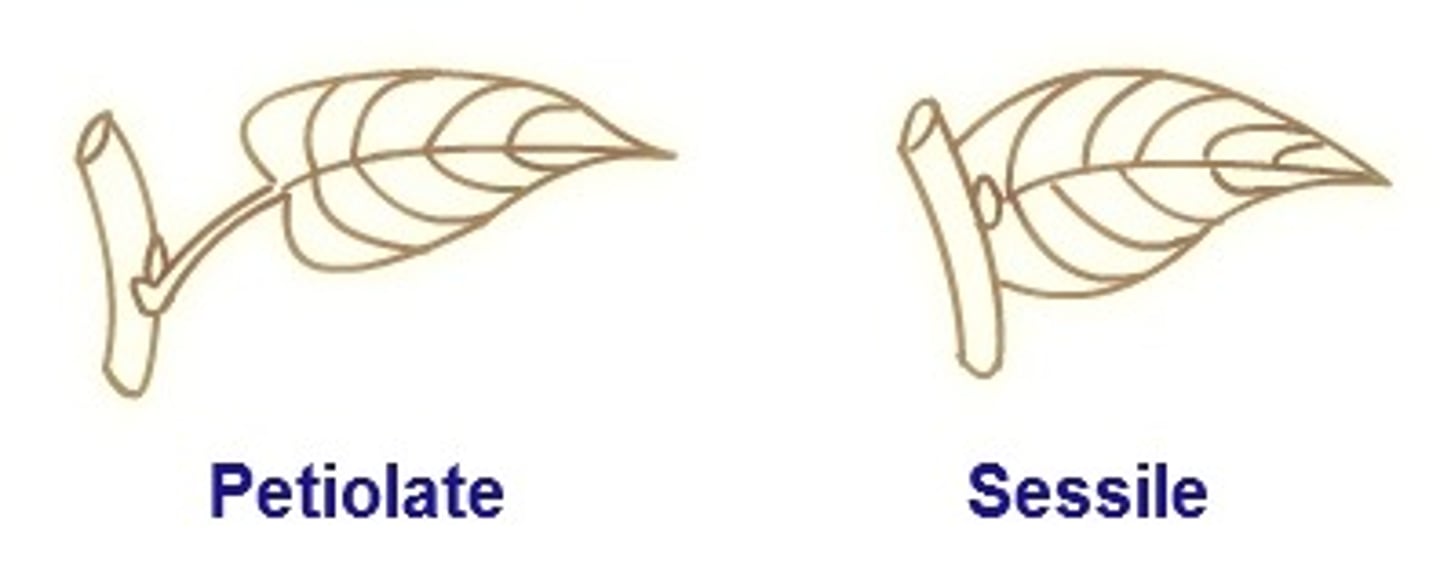

sessile leaves
leaves without visible petiole
midrib
contains main vein
peltate leaves
special type of petiolate leaves in which the petiole attaches underneath the blade (instead of margin)
perfoliate leaves
special type of sessile leaves in which the stems passes through the center of the blade
phyllotaxy
Is the arrangement of leaves on the stem.
• Number and arrangement of leaves is species dependent
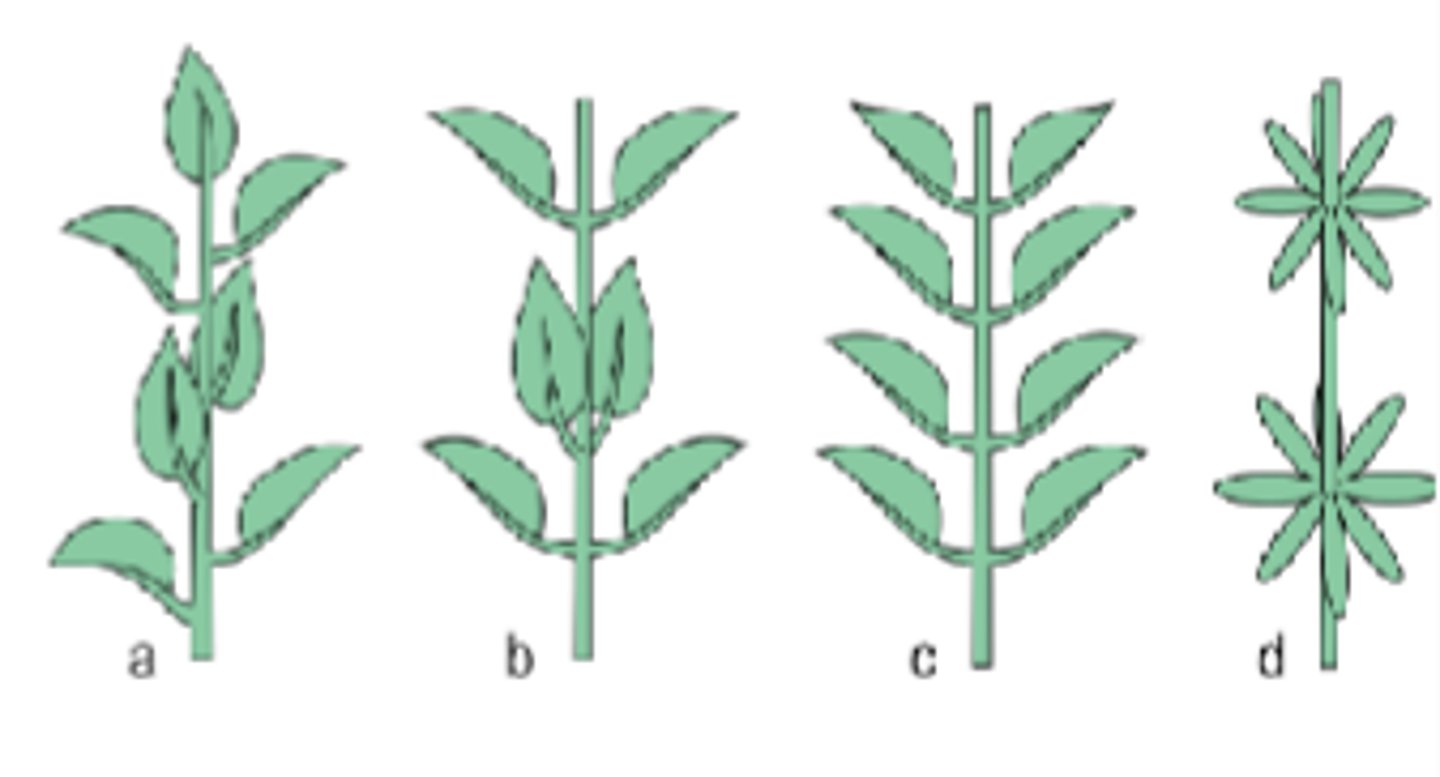
3 main types of leaves phyllotaxy
1)Alternate: one leaf per node
2)Opposite (deccusate): pair of opposite leaves per node, each pair rotated 90 degrees
3)Opposite(distichous): pair of opposite leaves per node, all pairs in same plane
4)whorled: 3 or more leaves per node
simple leaf
blade is undivided
compound leaf
blade is completely divided into leaflets. Notice position of axillary buds!
palmately compound
leaflets arise from a common point (resembles palm of hand)
pinnately compound
leaves originate from the midrib (feather-like)
doubly compound
rachis (stem-like structure)originate from midrib, and then divide into leaflets.
leaf veins are ____ coming from the stem
vascular bundles
-main vein (usually midrib)
-secondary veins branch from main vein
-tertiary veins branch from secondary
3 main arrangements of veins
a) Parallel venation – runs longitudinally
b) Pinnate venation – branch from main vein
c) Palmate venation – arise from a single point at base of leaf
reticulate vs percurrent venation
reticulate: netlike pattern, percurrent: ladderlike pattern
Leaf margins
entire: smooth margin
undulate: wavy margin
palmately lobate: lobes outlining palmate venation
pinnately lobate: lobes outline pinnate venation
toothed leaves
Serrate = sharp teeth pointing forward
• Dentate = sharp, symmetrical teeth
• Crennate = teeth are rounded
leaf shapes
• Ovate - are widest towards the base
• Obovate - are widest towards the apex
• Elliptic - single wide middle portion
• Oblong - longer wide middle portion
• Linear - long and thin
• Lanceolate - lance shaped (intermediate between ovate and linear)
leaf shape-tips and bases
• Rounded
• Acute - less than 90o angle
• Obtuse - greater than 90o angle
• Attenuate - tappering to a point
• Acuminate - curving inward to a point
• Cuneate - wedge-shaped (only base)
• Cordate - upside-down heart(only base)
hetrophylly
Some plants might have more than one type of leaf -juvenile vs adult, aquatic vs aerial, sun vs shade .For instance, in the common ivy, young leaves are palmately lobate, and older leaves are entire