Cellular Signals
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1 - 8 Basics 9 - 15 How it Works 16 - 19 Signalling Molecules 20 - 25 Animal Hormones 26 - 33 Plant Hormones 34 - 44 Endocrine Glands 45 - 48 Nerve Cells 49 - 52 Pheromones 53 - 54 Immune system
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Cellular Signals
Sources/transmission of signalling molecules to target cells
Apoptosis
Regulatory process of cell death to prevent malfunction
Cell Communication
Cells receive/send signals from other cells/the environment
Hydrophobic molecules
Don’t dissolve in water/blood, transported in a vesicle
Hydrophilic molecules
Dissolve and transported by water/blood
Homeostasis
The ability to maintain internal stability
Negative Feedback
Loop producing hormones, adrenaline stops after threat
Positive Feedback
Continues to produce hormones, prolactin when feeding a baby
Stimulus Response Model
The three step process of signal transduction
Reception
Protein molecules bind to chemical signals
Intracellular Receptors
In cytoplasm, binds to hydrophobic molecules
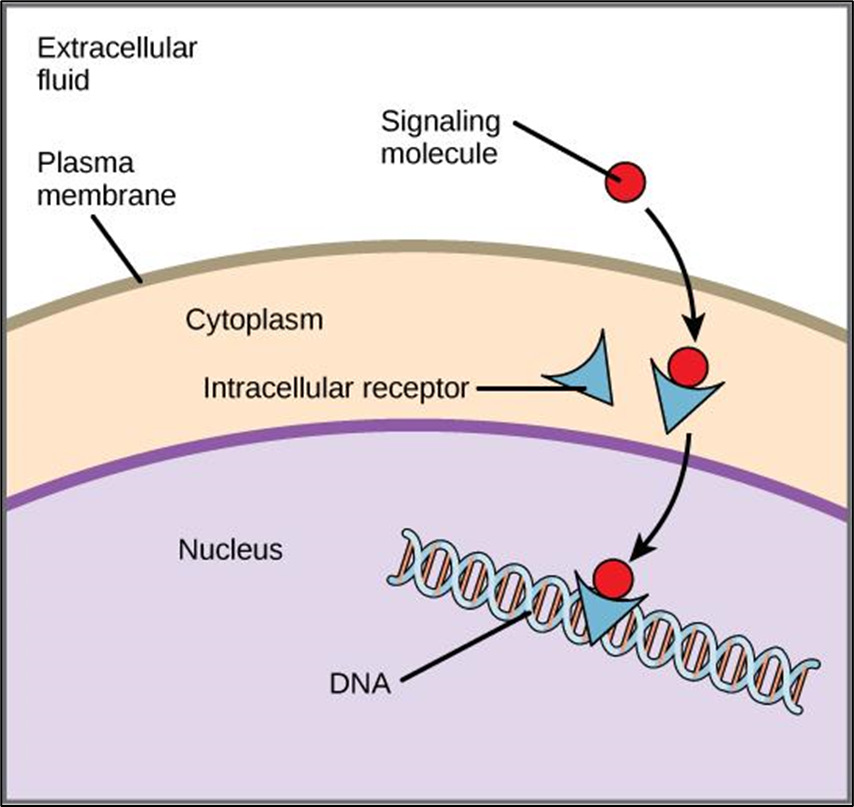
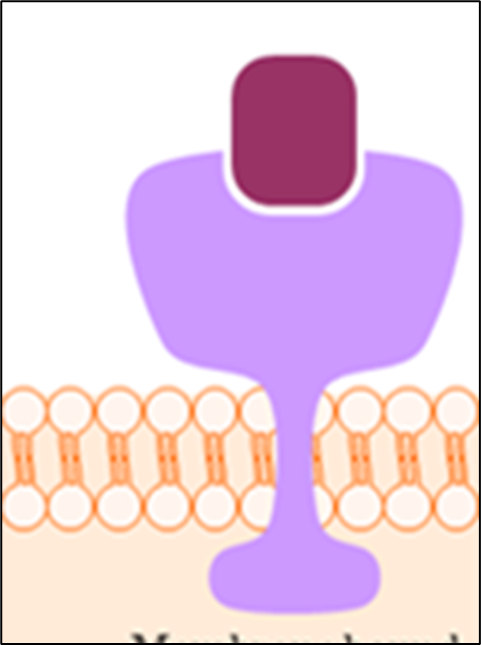
Intercellular Receptors
On cytoplasm, binds to hydrophilic molecules
Transduction
Amplifies and converts the signal into a cellular response
Cellular Response
Changes in gene activity/effector proteins for specific jobs
Effector protein jobs
Cell migration, Metabolism changes, Cell division and Apoptosis
Signal Molecules
Classified by effect distance, bind to receptor on target cell
Endocrine signalling
Long distances, transported by blood, hormones
Paracrine signalling
Short distances by diffusion, neurotransmitters
Autocrine signalling
Cells produce/react to their own signals, growth/immune system
Animal hormones
Made in endocrine glands, transported by blood, long lasting
Amino-Acid derived hormones
Hydrophilic, thyroxine and adrenaline
Lipid derived hormones
Hydrophobic, testosterone and cortisol
Peptides
Hydrophilic short hormones, insulin
Proteins
Hydrophilic and long, growth hormones
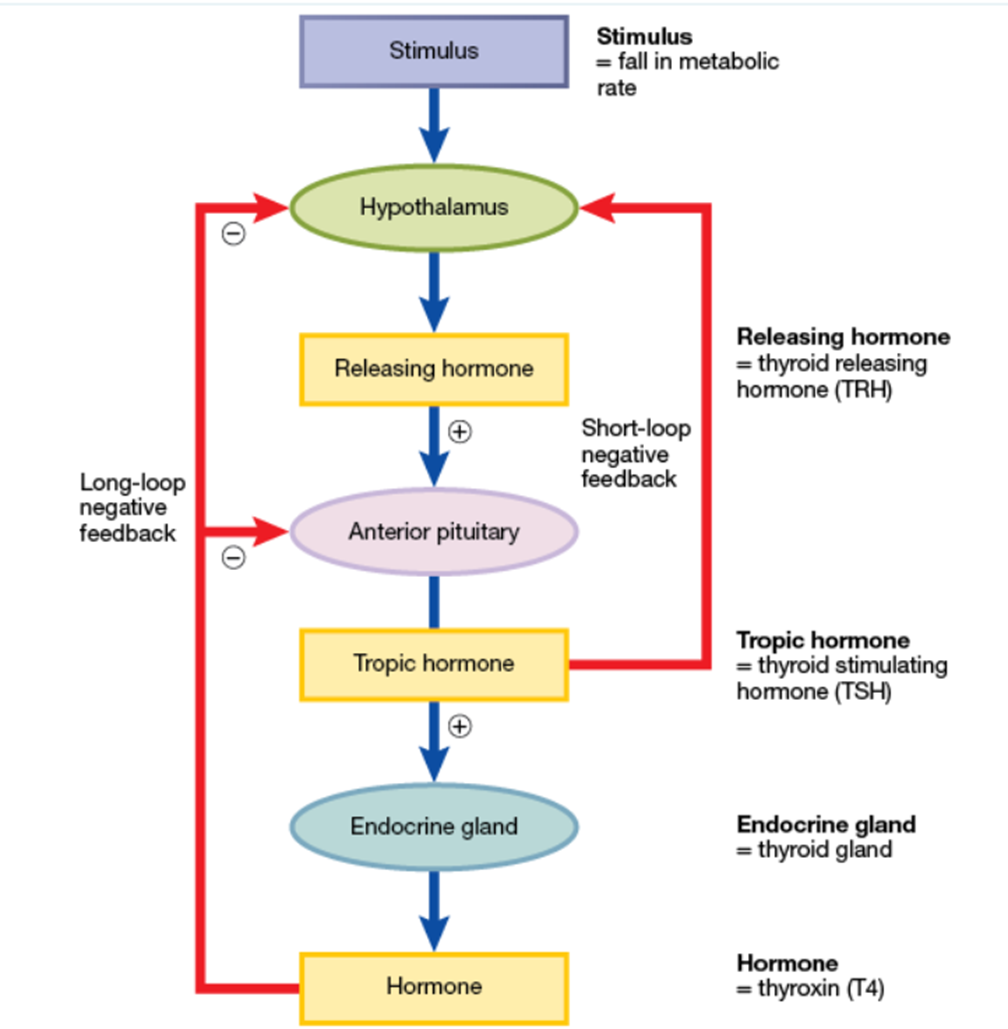
Hormone regulation
Plant hormones
Made in growing areas of the plant, transported by phloem vessels
Phloem tissue
Made of cells with holes, water and food, two way, transports hormones
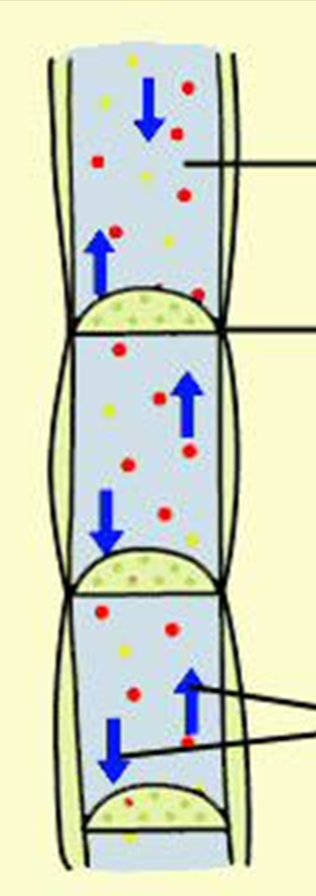
Xylem vessel
Thick walls, water and minerals, one way
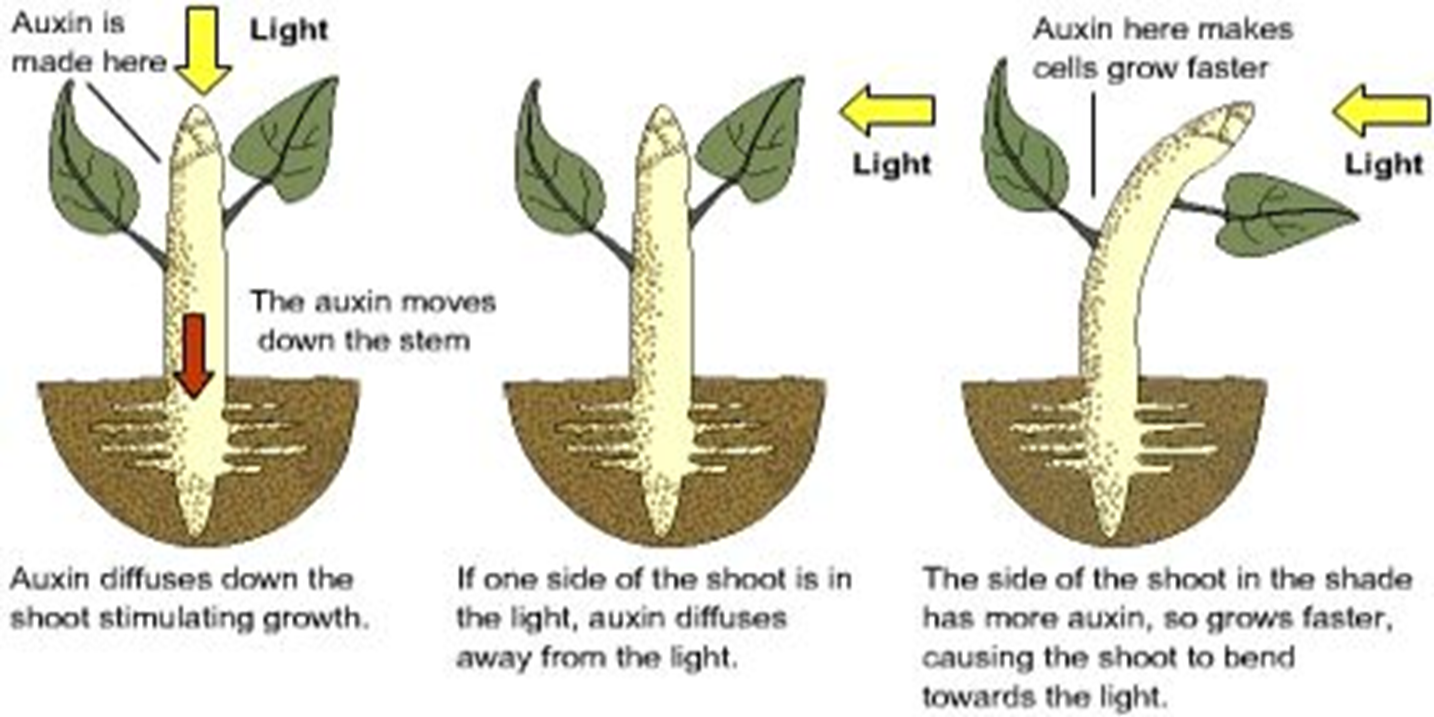
Auxins
Bends plants towards life by growing shaded areas
Cytokinin
Promote cell reproduction in shoots, roots and fruits
Gibberellins
Stem/fruit growth, no seed dormancy, seedless fruit development
Abscisic acid
Closes stomata and induces dormancy, in winter
Ethylene
Influences the lifecycle of the plant, ripens fruit, drops leaves
Pineal gland
Secretes melatonin for the circadian cycle
Thalamus
The body’s information relay system
Hypothalamus
Makes releasing/inhibiting hormones to direct the Pituitary gland
Pituitary gland
Directs the thyroid, adrenal glands, and reproductive organs
Thymus
Produces/matures immune cells
Thyroid gland
Regulates metabolism, growth and development
Parathyroid glands
Regulates calcium, phosphorus and magnesium in bones/blood
Adrenal glands
Regulates metabolism, immune system, blood pressure, fight/flight
Pancreas
Makes insulin to control blood sugar levels
Uterus/Ovaries
Makes estrogen/progesterone for girlie stuff
Testes
Makes testosterone and sperm
Neurons act on
Acts on nerve or muscle cells
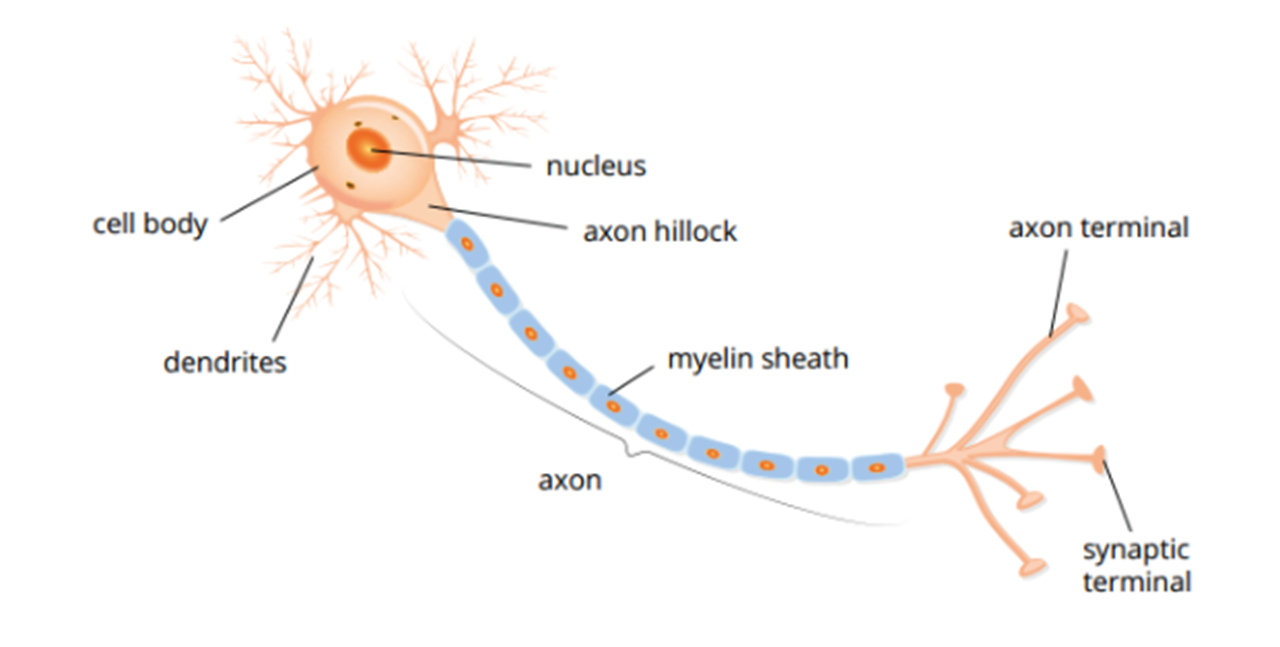
Action potentials
Electrical signals made by the movement of sodium/potassium ions moving in/out of the neuron
Neuron Communication
Uses action potentials to transmit a nerve impulse along the axon
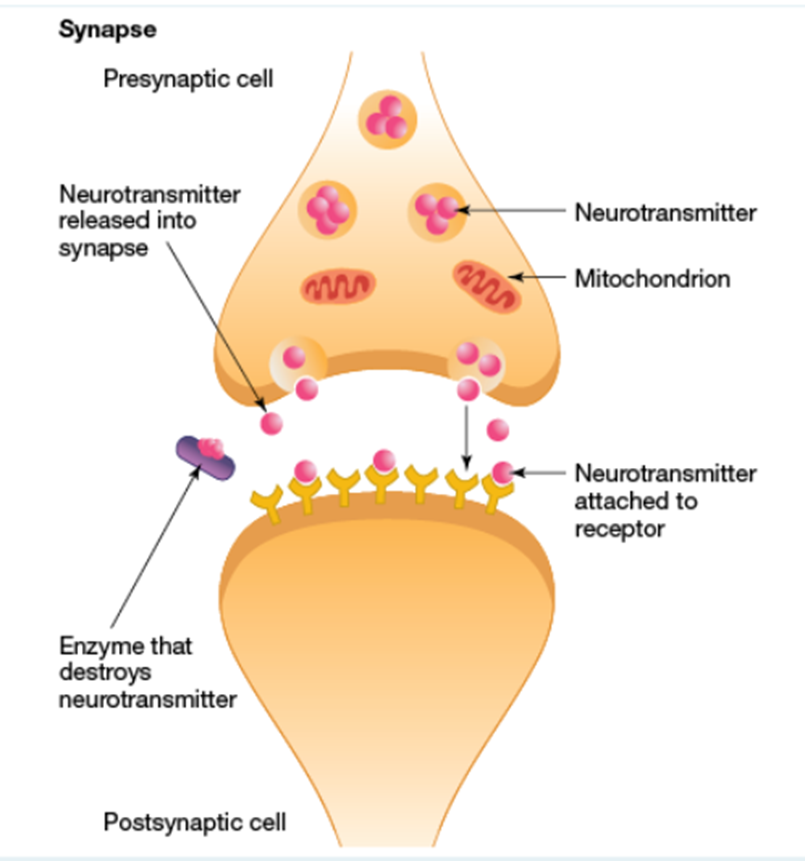
Neurotransmitters
Diffuse across the synaptic cleft between neurons/muscle cells
Pheromones
Chemical signals released/received by animals of the same species
Pheromone messages
Warnings, food trails, territory, mating
Volatile pheromones
Disperse rapidly by air, insect sex pheromones
Localised pheromone
Disperse slowly, marking territory
Cytokines
Peptide signals made by immune cells to move towards inflammation, infection and trauma
Modulators
Molecules that directly influence other molecules