Genetic Processes: DNA and meiosis
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U Lesson #1 (Secours)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid
DNA is coded to create ______
proteins
3 components of DNA
Sugar (pentose)
Phosphate Group (phosphoric acid)
Nitrogenous base (four types)
Purine nitrogenous bases
Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidine nitrogenous bases
Thymine and Cytosine
Purines vs Pyrimidines
Purines are double ring, while pyrimidines are single ring
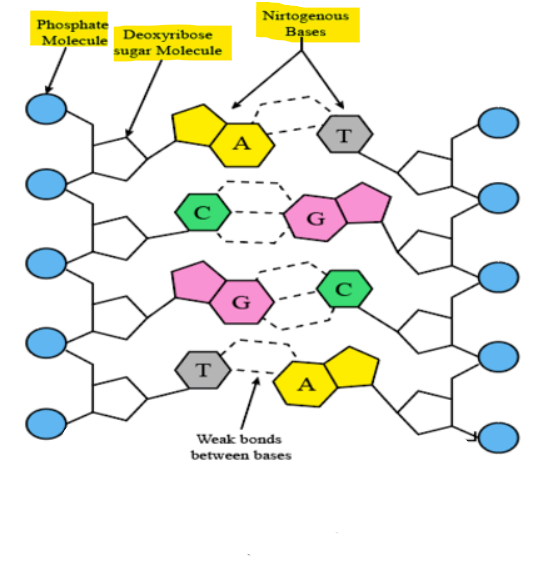
Complementary Bases + their # of Hydrogen Bonds
A = T (two hydrogen bonds)
C ≡ G (3 hydrogen bonds)
Hershey & Chase
discovered that genetic info was carried in the DNA, not the proteins (radioactive dye)
Chargaff
Chargaff’s Ratios: unviersal rule stating that regardless of species, the ratio of A and T is equal, as is the ratio of C and G
Rosalind Franklin
used x-ray crystallography to take Photo 51 and determine the double helix structure
Watson & Crick
Used Franklin’s photo to determine that strands align in opposite direction, creating a double helix
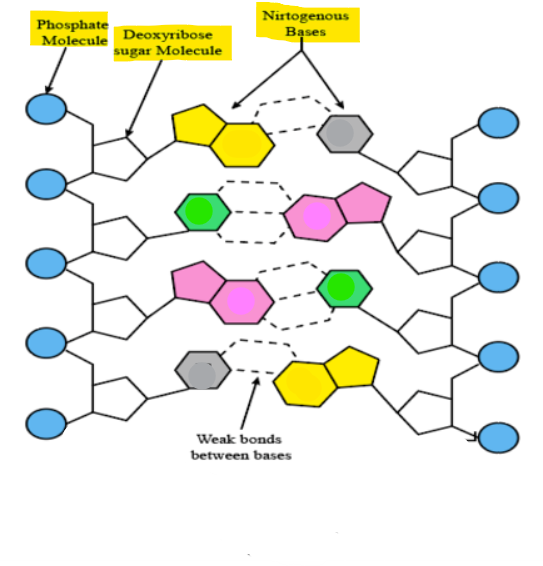
Identify the Complementary Bases
Mitosis takes place in ______ cells
Somatic
Meiosis takes place in ______ cells to create ______ cells
Somatic, sex/germ
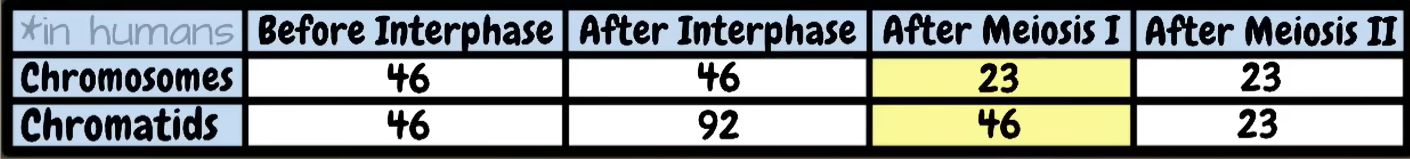
Human somatic cells contain
46 chromosomes
Gametes (sex cells) contain
23 chromosomes
Diploids
Somatic cell
Formed by mitosis
2 sets of chromosomes (2n)
Haploids
germ/sex cells
formed by meiosis
single set of chromosomes (n)
Each sperm or egg cell contains
22 autosomes and 1 sex chromosome (X or Y)
Autosomes
chromosomes unrelated to determining offspring’s sex
Genome
complete set of DNA in an organism
Gene
basic unit of heredity, a segment of DNA
Sex of offspring is determined by
the sex chromosome provided by the father
Karyotype
visual representation of homologous pairs
Purpose of meiosis
Reduce the number of chromosomes (fertilization will regenerate a regular number)
Genetic variation (ensures variation among population and increases survival chances for the species)
Homologous Pairs
chromosomes that are similar in shape, length, and arrangement of genes
Synapsis
physical pairing of the homologuous pairs, occurs during prophase I
Prophase I
CROSSING OVER: maternal and paternal chromosomes exchange genetic material
plus usual steps (spindle fibers form, nuclear membrane dissolves…)
Metaphase I
chromosomes line up as TETRADS in the center
the tetrads are oriented randomly, RANDOM ASSORTMENT
Anaphase I
chromosomes pulled to opposite ends of the cell by spindle fibers (homologous pairs are separated)
Telophase I + Cytokinesis
nuclear membranes reform
cleavage furrow, cytoplasm splits, two new cells are formed
Meiosis II
essentially mitosis
⤷ in metaphase II, chromosomes line up single file, and the chromatids are pulled apart
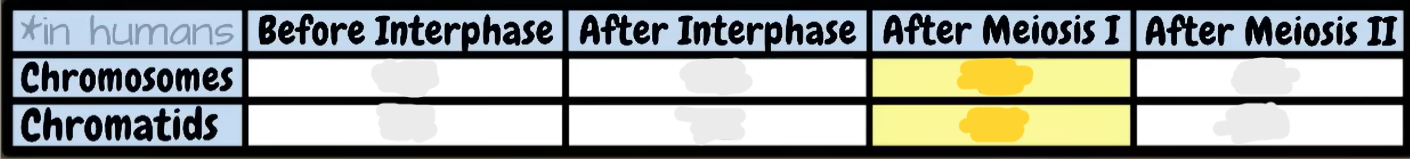
fill in the table:
What causes genetic variation?
Crossing Over: prophase I
Random Assortment: metaphase I
Fertilization: random encounter btn sperm and egg
Non-disjunction
poor separation of chromosomes
takes place during meiosis
causes addition of deletrion of one or more chromosomes from a gamete
Trisomy
occurs when a gamete with an extra chromosome is fertilized
all cells that develop from the zygote will have an extra chromosome
Trisomy-21
Down Syndrome (extra chromosome 21)
Monosomy
Occurs when there is a chromosome missing (lethal)
Turner's syndrome
monosomy XO
Klinefelter's syndrome
trisomy XXY
Super female syndrome
trisomy XXX
Triploid
occurs when chromosomes don’t separate during meiosis 1
the resulting gamete is diploid
if fertilized with a normal haploid, the zygote will contain 3 SETS of chromosomes (3n)
Polyploid
organisms that have more than two sets of chromosomes
Zygote
The fertilized egg; this cell has a comination of DNA from the parents
Fertilization
formation of a zygote
Spermatogenesis
production of sperm cells (same size) in the testes
starts at puberty and continues for life
Oogenesis
production of the large egg cell (ovum) and polar bodies in the ovaries
begins before birth and is properly completed at puberty (when ovulation starts)
Gametogenesis
Production of gametes