MT 37 (LEC): GRAM-POSITIVE COCCI 2
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
182 Terms
Fill in the blank: MRSA is resistant to antibiotics such as ________, ______, and ______.
methicillin, nafcillin, and oxacillin
True or False: MRSA can be acquired through nasal secretions, prolonged hospital stay, and broad-spectrum antibiotic use.
True.
Three (3) types Of METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS (MRSA)
HA-MRSA, CA-MRSA, HACO-MRSA
MRSA acquired during dialysis, indwelling devices (catheter), long term hospitalization
Healthcare-associated MRSA (HA-MRSA)
MRSA that is common in athletes, children, inmates, recipients of tattoo
Community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA)
MRSA acquired in hospitals but symptoms only occur discharge and the patient goes home
Hospital-associated Community Onset MRSA (HACO-MRSA)
Identify the gene that encodes the altered penicillin-binding protein PBP2a in MRSA.
mecA gene
How does the mecA gene protect S. Aureus from penicillin?
inhibits the binding of the penicillin to S. aureus
True or False: MRSA infections are only hospital-acquired.
False.
Fill in the blank: The altered penicillin-binding protein in MRSA is known as ________.
PBP2a or PBP2’.
METHODS FOR THE DETECTION OF MRSA BY ANTIMICROBIAL TESTING
Vancomycin agar screen plate, Oxacillin screen plate, Cefoxitin disk diffusion, Double-disk diffusion test (D-zone test)
Identify the screening method for MRSA using 6 µg/mL vancomycin in Blood heart Infusion Agar (BHIA).
Vancomycin agar screen plate.
How many ug/mL of vancomycin is need for the Vancomycin agar screen plate?
6 ug/mL
True or False: Any growth on a vancomycin agar screen plate indicates MRSA resistance or a significant result.
True.
Identify the screening method that uses Mueller Hinton Agar (MHA) with 4% NaCl and 6 ug/mL of antibiotic
Oxacillin screen plate.
Components Needed in the Mueller-Hinton Agar (MHA) for oxacillin screen plate
4% NaCl and 6 ug/mL oxacillin
True or False: The oxacillin screen plate can reliably detect oxacillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNs)
False.
True or False: Oxacillin screen plate is suitable for detecting BORSA in clinical specimens
True
Fill in the blank: BORSA stands for ________.
Borderline oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
If staphylococcus is resistant to oxacillin, it is ruled out that it is also resistant to _____?
B-lactam drugs
What antimicrobial disk is preferred for detecting oxacillin resistance in both S. aureus and S. lugdunensis?
Cefoxitin disk (30 µg).
True or False: Oxacillin induces the expression of PBP2’ in mecA-containing strains of staphylococci
False, Cefoxitin
Fill in the blank: The test used to detect inducible clindamycin resistance is called the ________.
Double-disk diffusion test or D-zone test
Identify the antibiotic disks used in the D-zone test.
Erythromycin and clindamycin.
When is D-zone test performed?
When the results of the macrolides (erythromycin and clindamycin) are opposite with one another.
For instance, resistant to erythro and susceptible to clinda
Antibiotic disks used in the Double-Disk diffusion test (D-zone test)
15 ug erythromycin and 2 ug clindamycin
15 mm to 26 mm
A 15-ug erythromycin disk and a 2-ug clindamycin disk are placed ___ to ___ mm apart on MHA or BAP with the isolate to be tested and incubated overnight
Agar used for the Double-disk diffusion test (D-zone test)
Mueller-Hinton Agar (MHA), Blood Agar Plate (BAP)
True or False: A positive D-zone indicates inducible resistance to clindamycin.
True.
True or False: A negative D-zone is when the ZOI of the clindamycin disk is flattened or blunted near the erythromycin disk
True
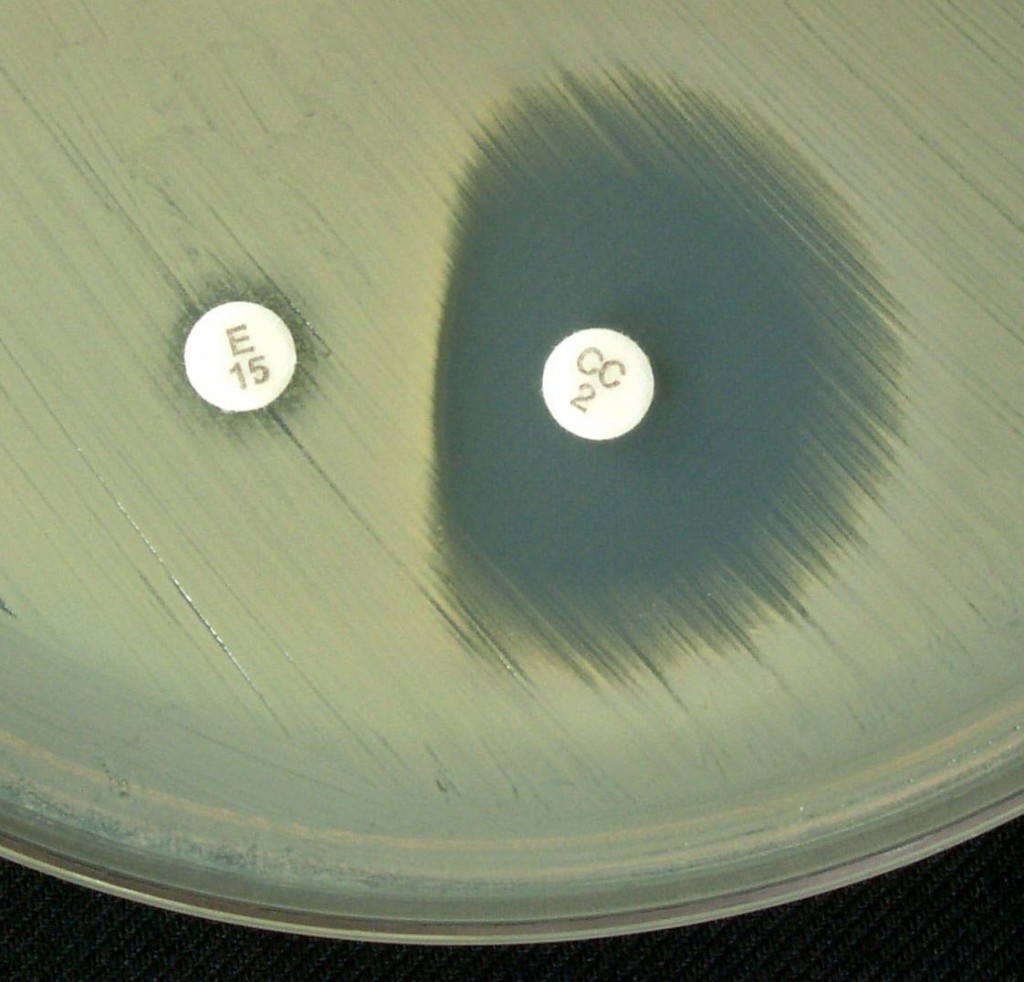
What is the first test used FOR THE IDENTIFICATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL SPECIES and the result it must indicate?
Gram stain (+)
What is the second test used FOR THE IDENTIFICATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL SPECIES and the result it must indicate?
Catalase test (+)
What is the third test used FOR THE IDENTIFICATION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL SPECIES?
Coagulase (+) means S. Aureus
coagulase (-) means CoNs or Micrococci
What test is performed for differentiating CoNs and Micrococci?
Oxidase or Bacitracin susceptibility
a positive result in the Oxidase or Bacitracin susceptibility indicates?
Micrococcus sp.
a negative result in the Oxidase or Bacitracin susceptibility indicates?
Coagulse-negative Staphylococcus sp. (CoNs)
Novobiocin susceptibility differentiates ____ and ____?
CoNs and S. saprophyticus
Fill in the blank: The best specimen for staphylococcal recovery is ________.
Aspirate.
True or False: A single swab is the best method for culture and smear.
False.
True or False: 3 swab must be requested for Gram stain and culture
False, only 2
Spherical; singly, in pairs, or clusters
Staphylococcus: Gram-positive ____ cells that appear ____, in ____, or ____ (grape-like)
Identification: an enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) to water and oxygen
Catalase
Reagent used in the Catalase test for staphylococcus
3% H2O2
Reagent used in the Catalase test for neisseria
15% H2O2
What indicates a positive result in the catalase test?
bubble formation or effervescence in seconds
BAP
Colonies to be used for the Catalase test must not be taken from ____
Identify the confirmatory method for a positive slide coagulase test.
Tube coagulase test.
True or False: Coagulase test uses rabbit plasma and Heparin as anticoagulant.
False, EDTA as anticoagulant.
Best single criterion of pathogenicity of S. aureus
Coagulase test
What does a positive coagulase test result look like?
Clot or coagulum formation within 30 seconds
2 methods of coagulase test
Slide method, Tube method
Detects cell-bound coagulase or clumping factor on the surface of the cell wall which reacts with fibrinogen in the plasma
Slide method
What are the Other slide coag-positive staph:
S. lugdunensis, S. schleiferi
Considered a sensitive but definitive method for coagulase testing
Tube method
Fill in the blanks: Tube method coagulase testing has a positive result of Clot or coagulum formation after ____ of incubation at ___ degrees celsius
1-4 hours, 35 degrees celsius
True or False: for Tube method coagulase test, If no clot appears after 4 hours of incubation, the tube should be left at room temperature for an additional 24 hours of incubation
False, only 20 hours
What are Other tube coag-positive staph?
S. hyicus, S. intermedius, S. lutrae, S. delphini, and S. schleiferi subsp. coagulans
What test is Used to differentiate the pathogenic staphylococci from nonpathogenic ones?
Mannitol fermentation test
What is the culture medium for Mannitol fermentation test?
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
Fill in the blank: Mannitol fermentation test uses ________ as pH indicator.
Phenol red.
True or False: S. aureus ferments mannitol, resulting in yellow colonies.
True.
What ferments mannitol that results in red/colorless colonies?
S. saprophyticus, S. epidermidis, Micrococcus sp.
S. aureus comes out as resistant to what test?
Polymyxin Sensitivity Test
This is For the presumptive identification of S. saprophyticus using a 5-ug novobiocin disk
Novobiocin Susceptibility Test
True or False: If the bacteria is resistant to an antibiotic, you will record 6 mm or the size of the disk since there is no ZOI to be measure
True
Identify the coagulase-negative staphylococcus that shows resistance to novobiocin.
Staphylococcus saprophyticus.
True or False: S. epidermidis and other CoNs are novobiocin-resistant.
False, only S. saprophyticus
Fill in the blank: S. aureus colonies appear ________ on Tellurite Glycine Agar.
Jet black.
True or False: The DNase test is used to identify pathogenic Staphylococcus species that produce DNAse.
True.
What does a positive DNase test show?
Clear/colorless zone around colony.
Identify the culture medium used in the DNase test.
DNA-methyl green agar.
This test Differentiates S. aureus (VP +) from S. intermedius (VP -)
Voges-Proskauer (VP) test
Fill in the blank: The Voges-Proskauer test detects ________ production.
Acetoin.
True or False: S. aureus is VP negative.
False, VP positive.
What is the (+) Result of the Voges-Proskauer (VP) test show?
Pink color acetoin
True or False: Vogues-Proskauer test is used to differentiate the bacteria in the enterobacteriaceae
True
Identify the culture medium used for routine staphylococcal isolation.
5% Sheep Blood Agar.
Culture for purulent exudates and appropriate isolation of staph
Colistin-Nalidixic Agar (CNA)
Culture with enriched with 5% sheep blood
Phenylethyl Alcohol (PEA) Agar
Fill in the blank: Phenylethyl Alcohol (PEA) Agar: selective for _______
Gram-positive bacteria
What culture is used for heavily contaminated specimens?
MSA and PEA
Fill in the blank: The CHROM agar is a medium selective for ________.
MRSA.
Rapid Methods for Identification
Test Kits, Molecular methods, Mass Spectrometry
What type of test kits are used for differentiating S. aureus from CONS?
Agglutination test kits
True or False: Latex agglutination tests detect both clumping factor and Protein A in the cell wall of S. aureus
True.
Fill in the blank: Test kits have Higher specificity and sensitivity and are particularly useful for the identification of ___
MRSA
Fill in the blank: MALDI-TOF stands for ________.
Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Time-of-Flight.
A mass spectrometry method that identifies the protein profile of MRSA and other microorganisms including the presence of mecA gene
MALDI-TOF
True or False: RT-PCR can only be used to detect MSSA.
False, it is for both MRSA and MSSA.
This molecular method involves for rapid identification of staph from blood culture smears
Qualitative nucleic acid hybridization assay
Identify the coagulase-negative staphylococcus common in prosthetic valve endocarditis.
Staphylococcus epidermidis.
Contaminant of medical instruments, catheters (indwelling and IV), CSF shunts, and prosthetic heart valve implants
Staphylococcus epidermidis
True or False: S. epidermidis is commonly found in the skin microbiota.
True.
Fill in the blank: PGA stands for ________ and provides adherence in S. epidermidis.
Poly-γ-DL-glutamic acid.
Fill in the blanks: S. epidermidis has Colonies on BAP that appear ____, opaque, _____ sized pin-heads, and ______
white, small to medium, non-hemolytic
what is the coagulase result of S. epidermidis?
Coagulase (-)
Fill in the blanks: Staphylococcus epidermidis is Susceptible to _____
5-ug Novobiocin
Measuring tool for determining the ZOI size for Antimicrobial test
Vernier caliper
Identify the CoNS that causes UTI and cystitis in young, sexually active females.
Staphylococcus saprophyticus.