701: Larynx, thyroid, and parathyroid glands
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
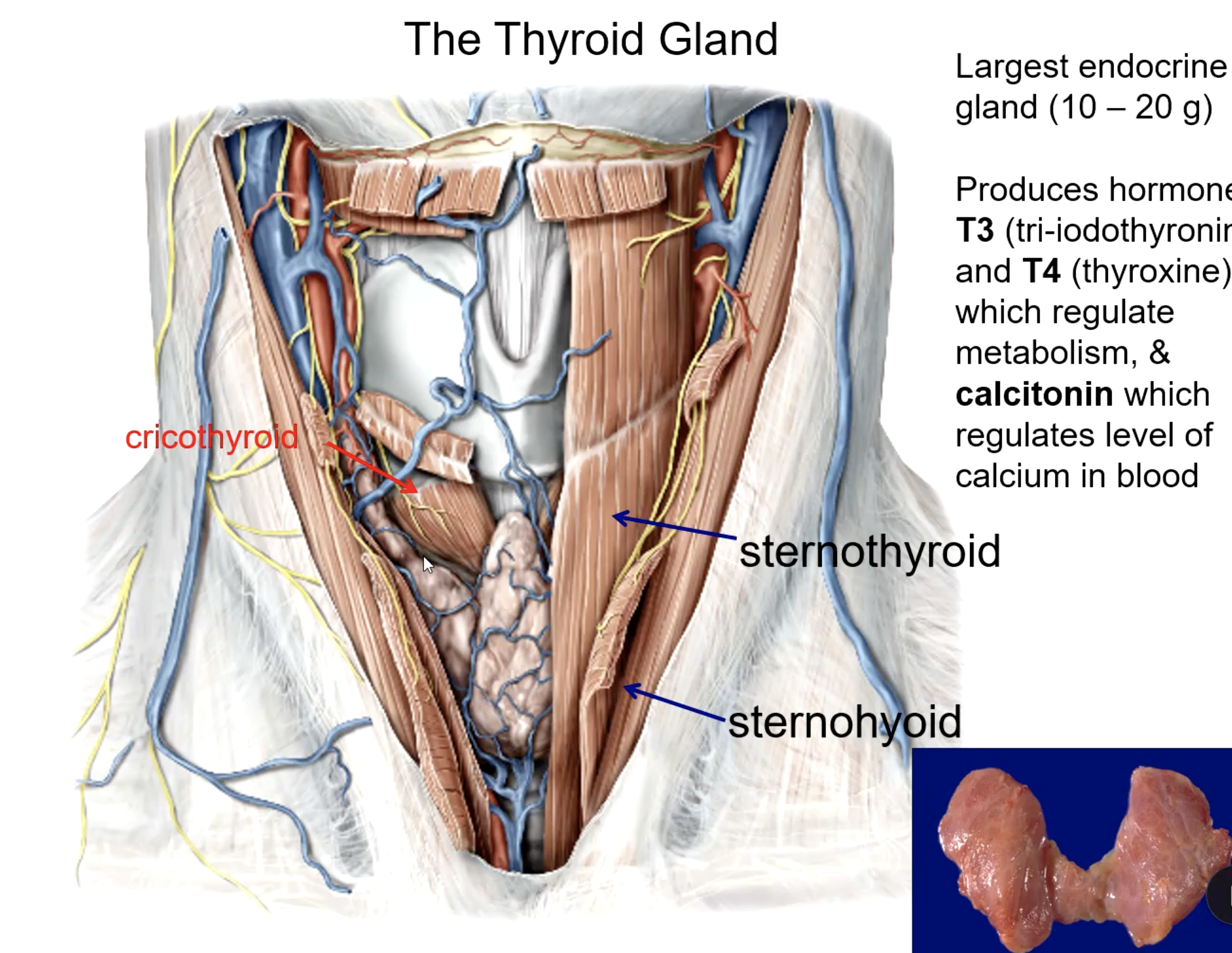
thyroid gland
what is the largest endocrine gland in the body?
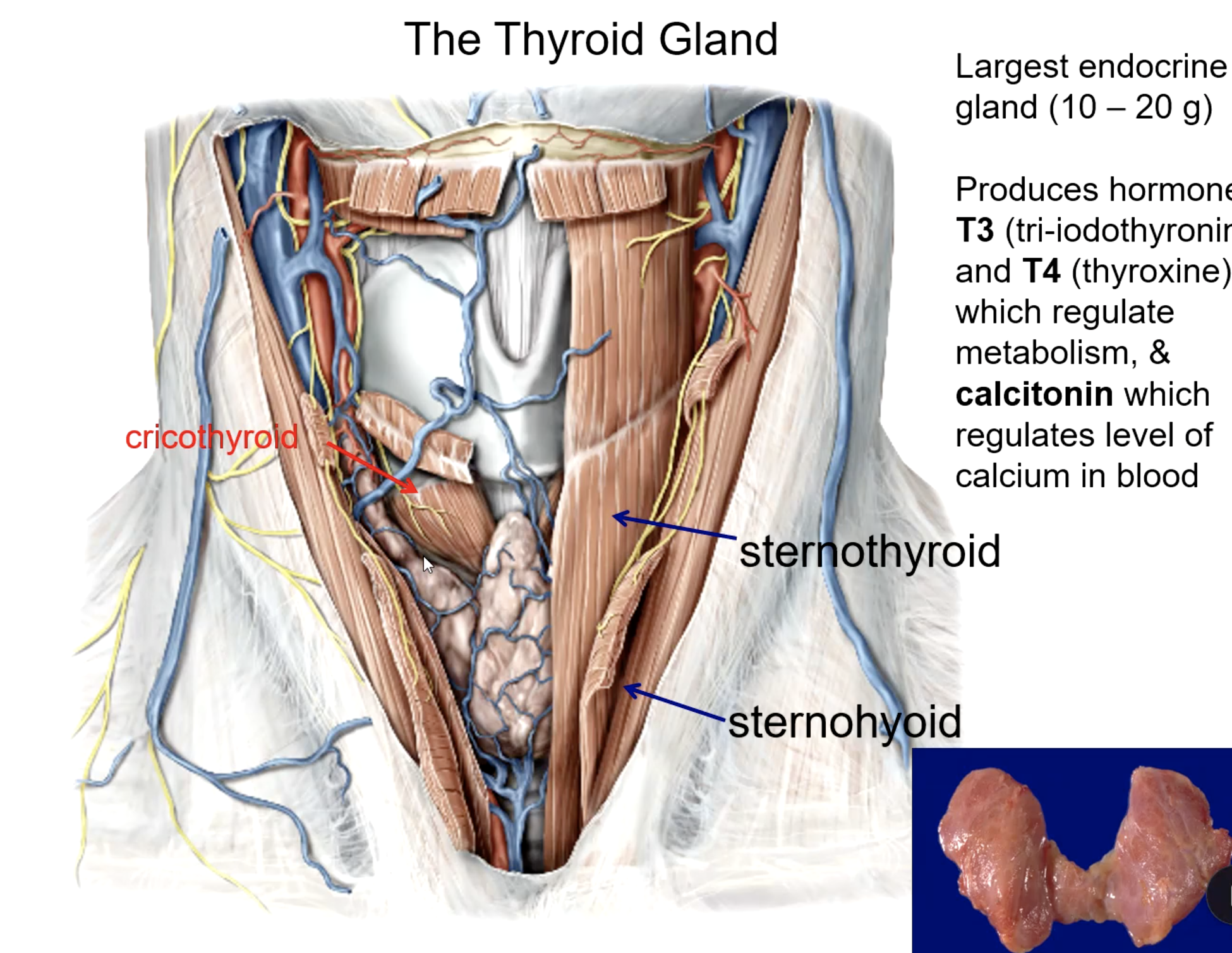
platysma m.
sternothyroid m.
sternohyoid m.
what 3 muscles must be reflected to view the thyroid gland?
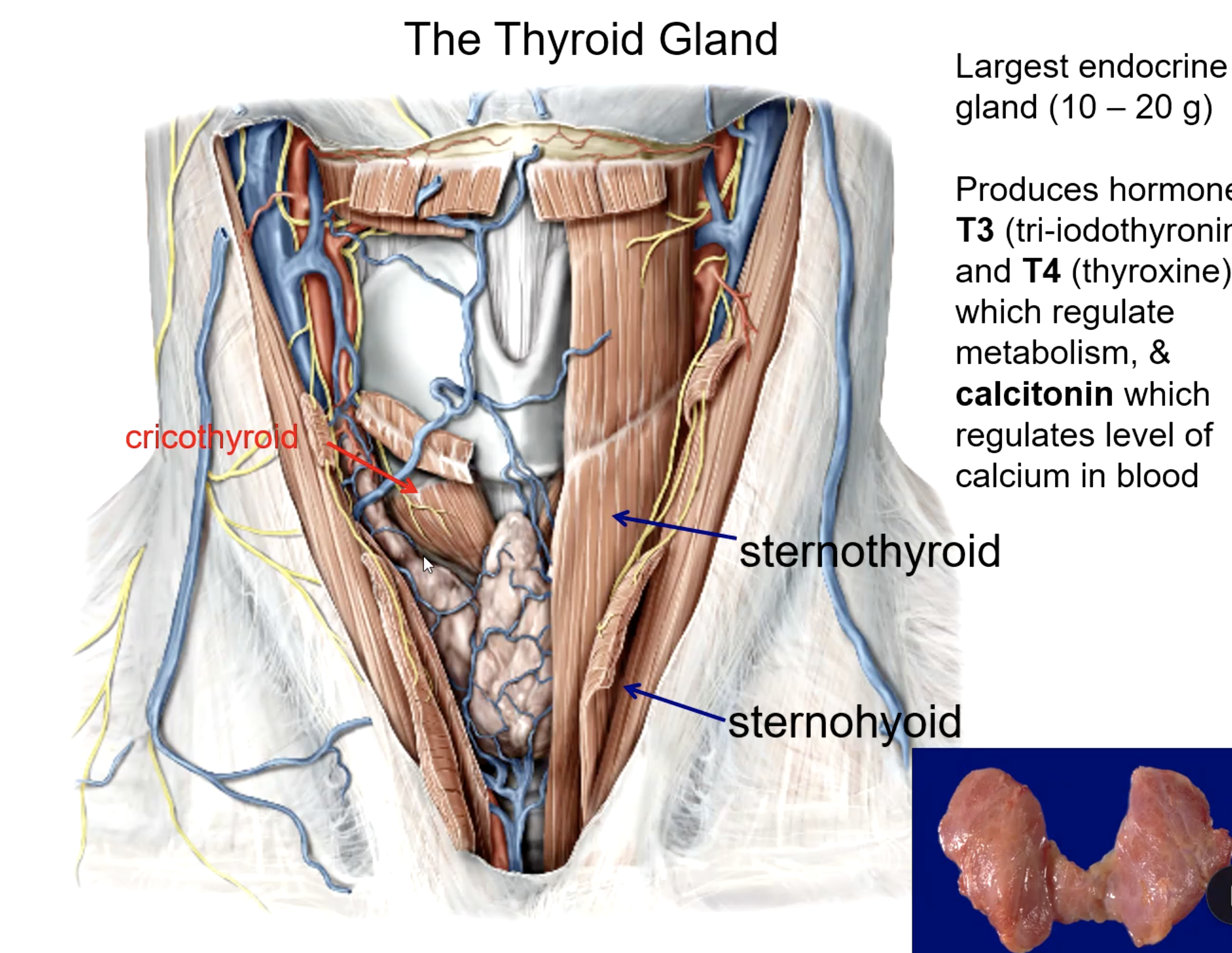
cricothyroid m.
the thyroid gland lies posterior to all these muscles except:
-platysma m.
-cricothyroid m.
-sternothyroid m.
-sternohyoid m.
T3 (tri-iodothyronine)
T4 (thyroxine)
calcitonin
what hormones do the thyroid gland produce?
T3, T4
hormone that regulates metabolism:
calcitonin
hormone that regulates calcium levels:
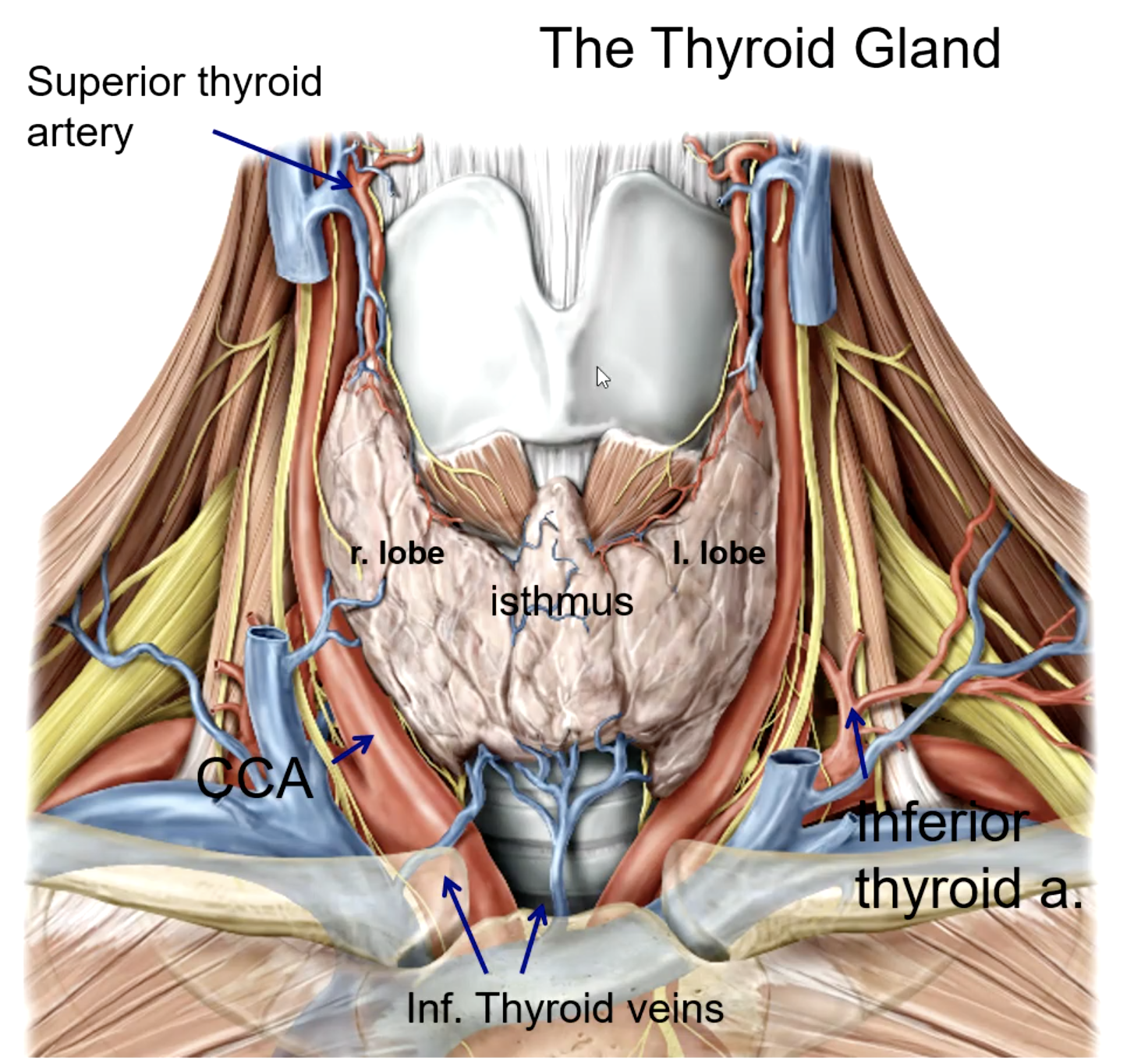
carotid sheath containing common carotid a, internal jugular v, and vagus n.
the thyroid lies medial to what structure?
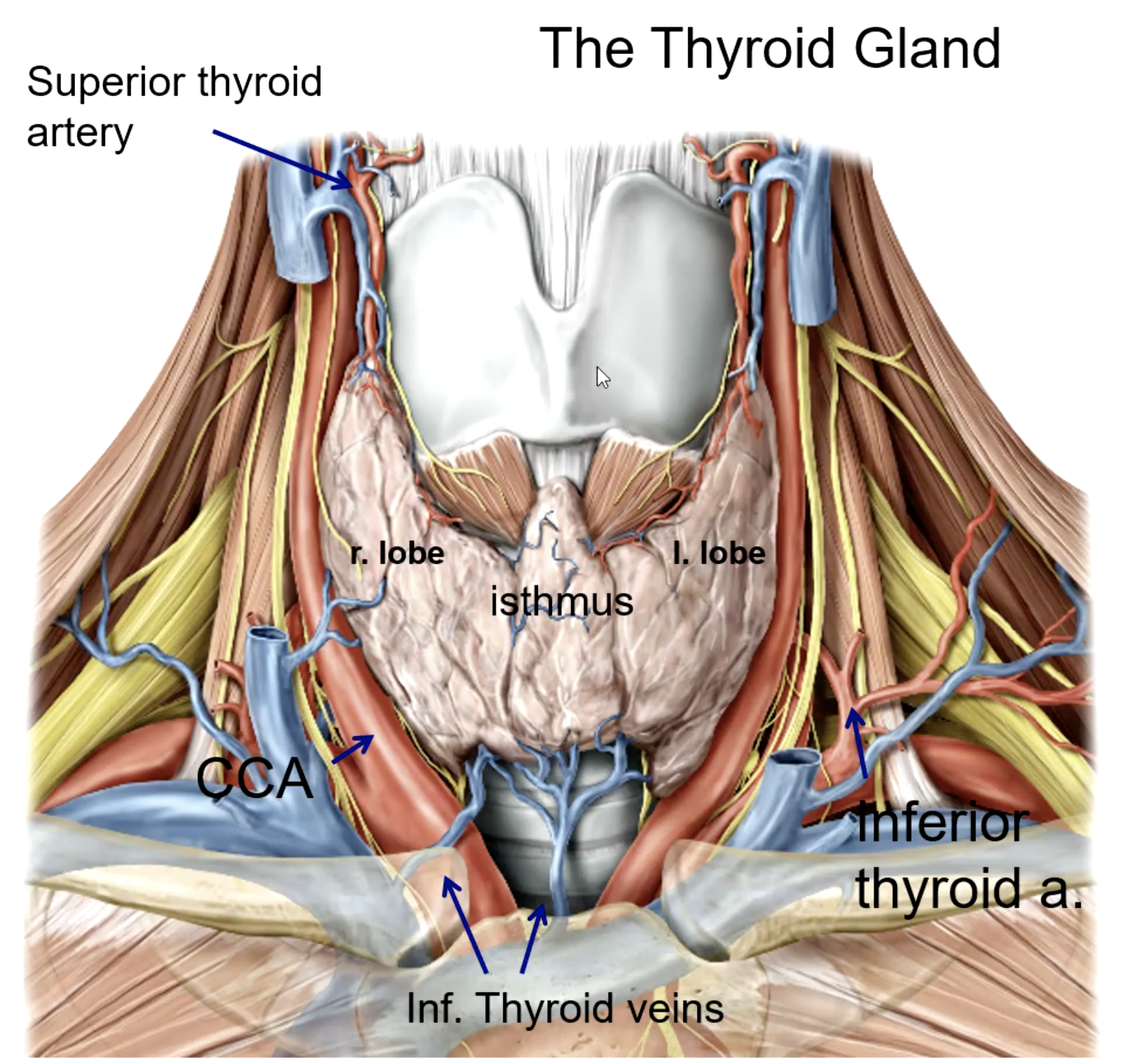
isthmus
the right and left lobes of the thyroid gland is connected by
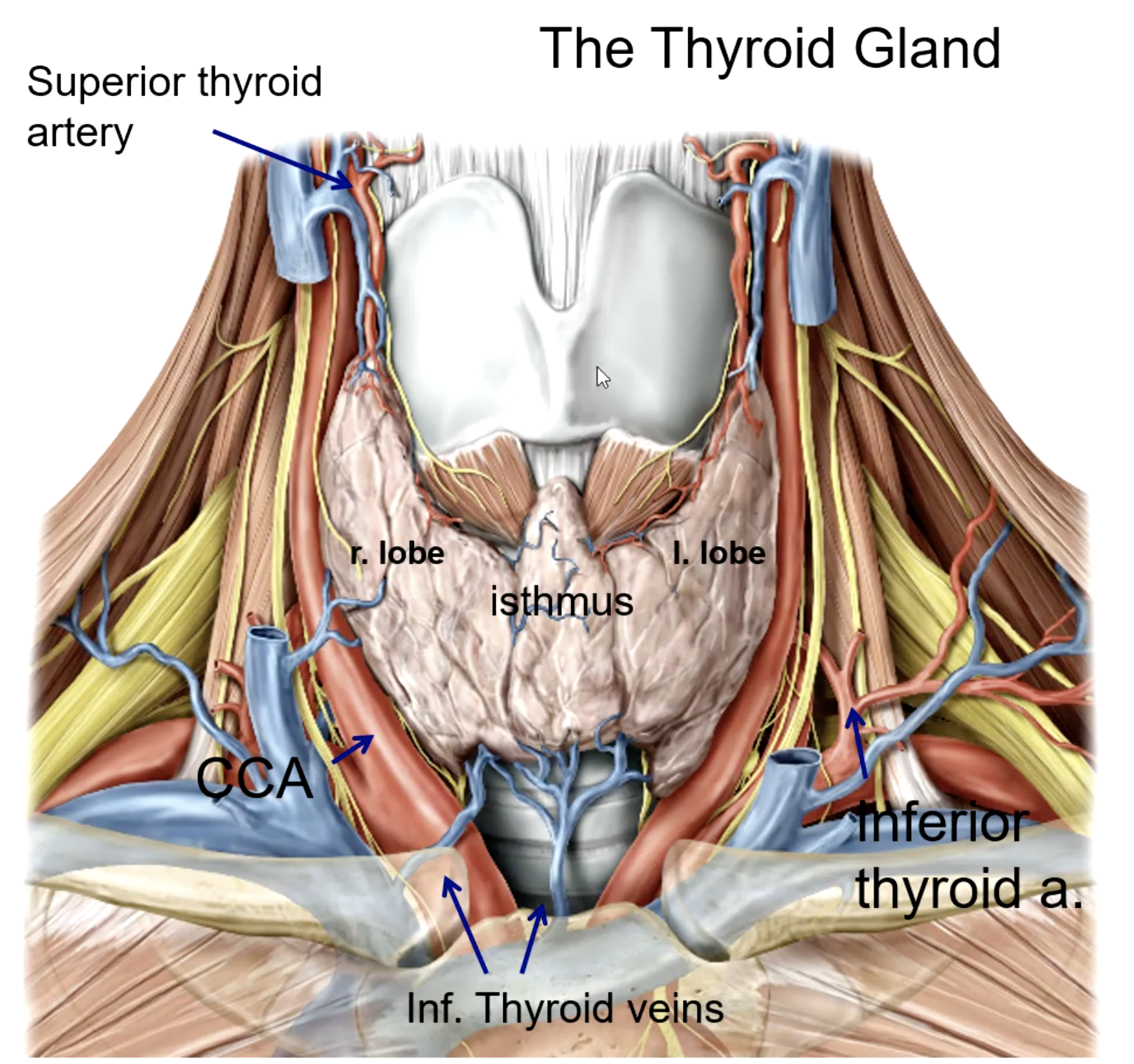
trachea and esophagus
the thyroid gland is anterior and lateral to what structures?
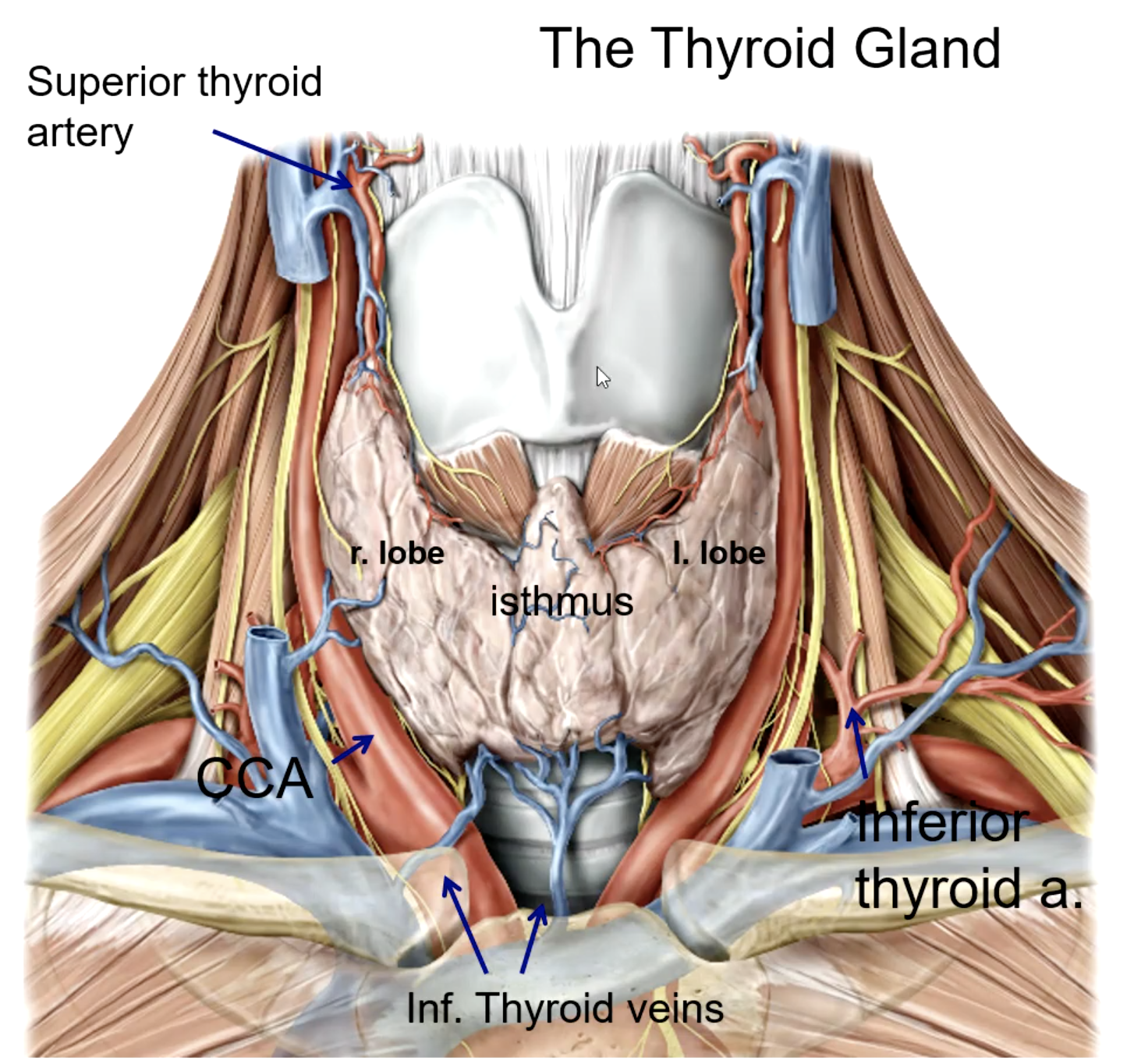
external carotid a.
the superior thyroid artery is the 1st branch of the:
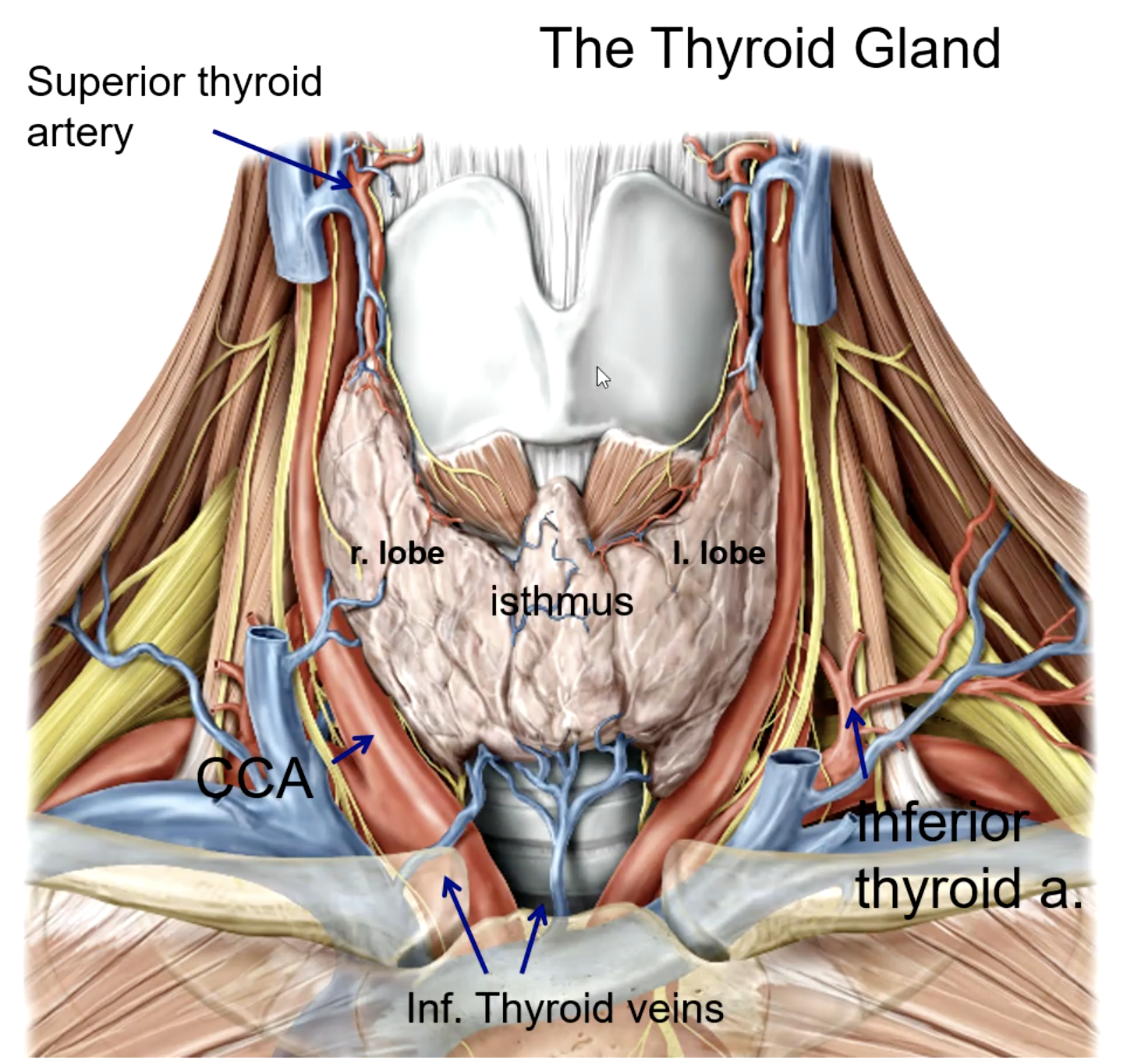
thyrocervical trunk (subclavian a.)
the inferior thyroid artery is a branch of the:
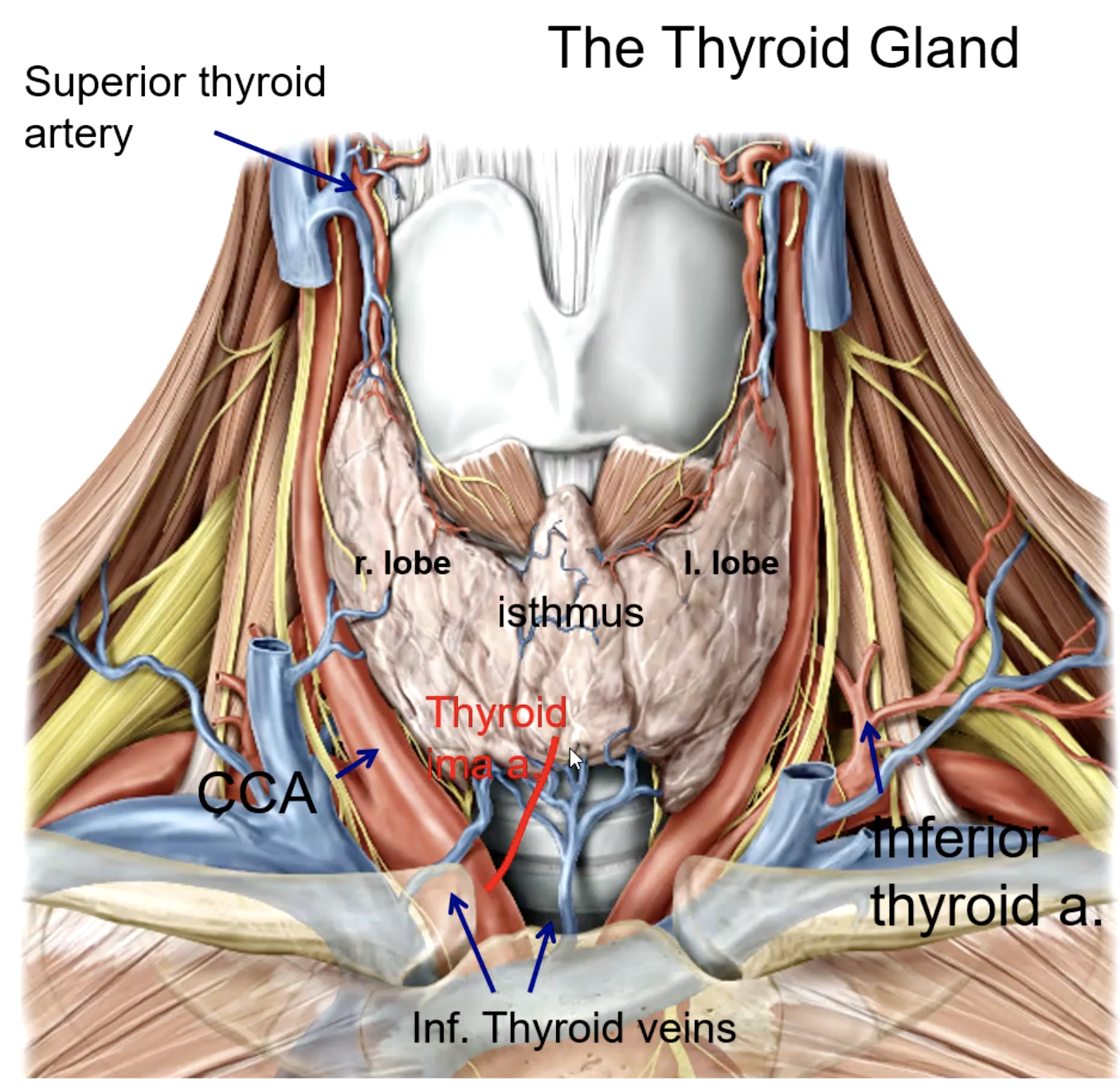
brachiocephalic trunk
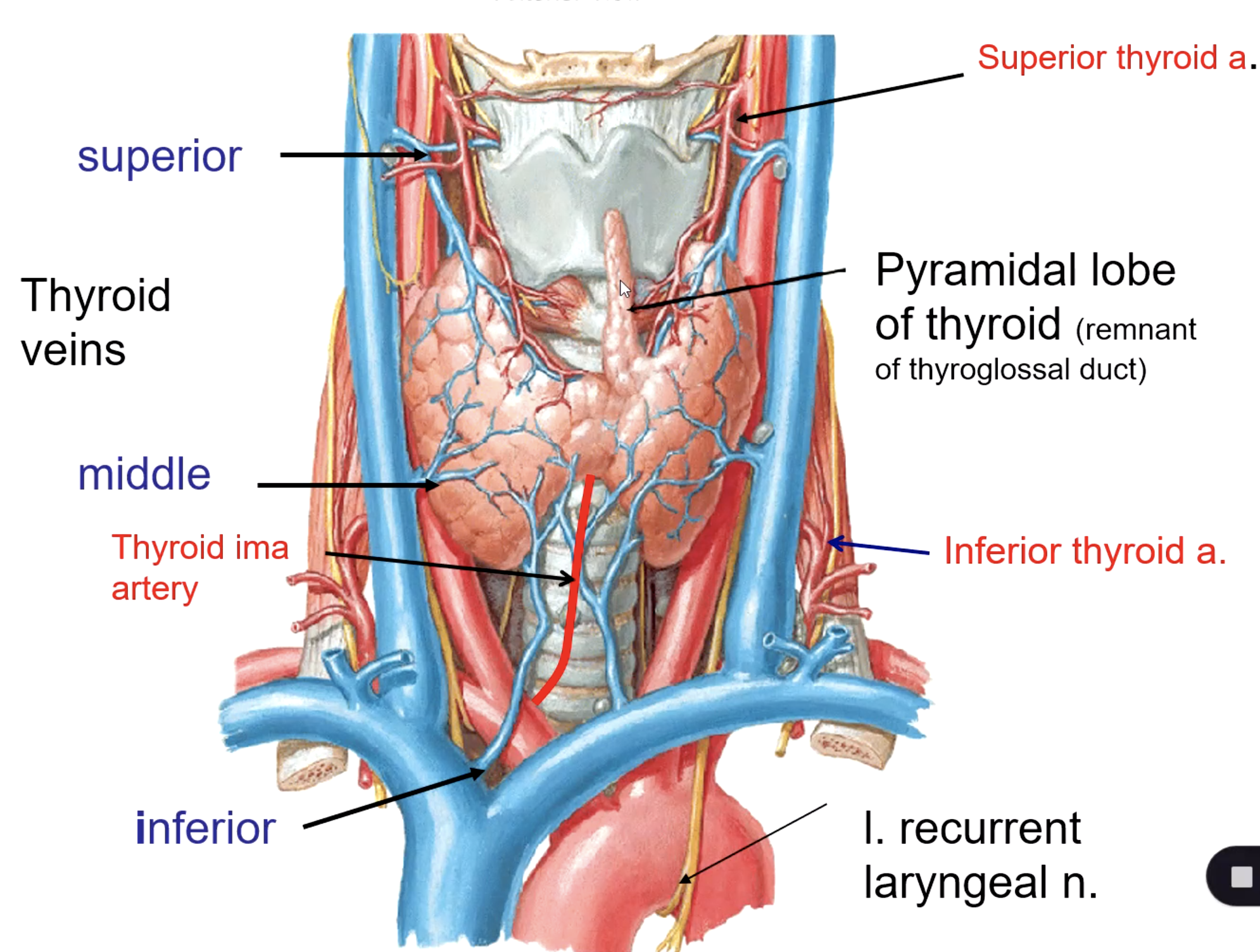
the thyroid ima artery is a branch of the:
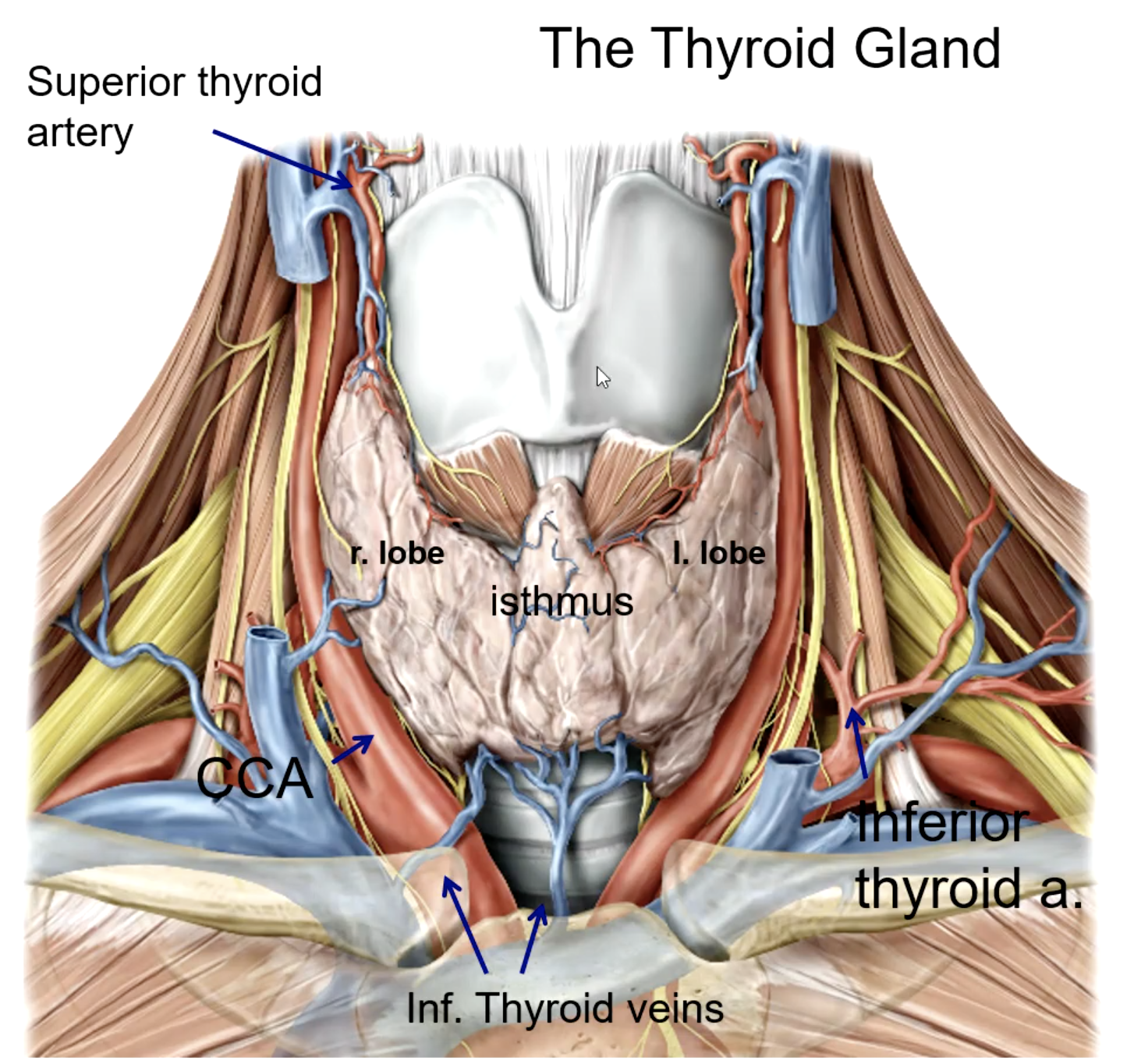
isthmus
the thyroid ima artery supplies the _______
trachea
what large structure lies directly posterior to the thyroid gland?
superior thyroid a.
inferior thyroid a.
thyroid ima a. (not in every patient)
what is the main blood supply to the thyroid gland?
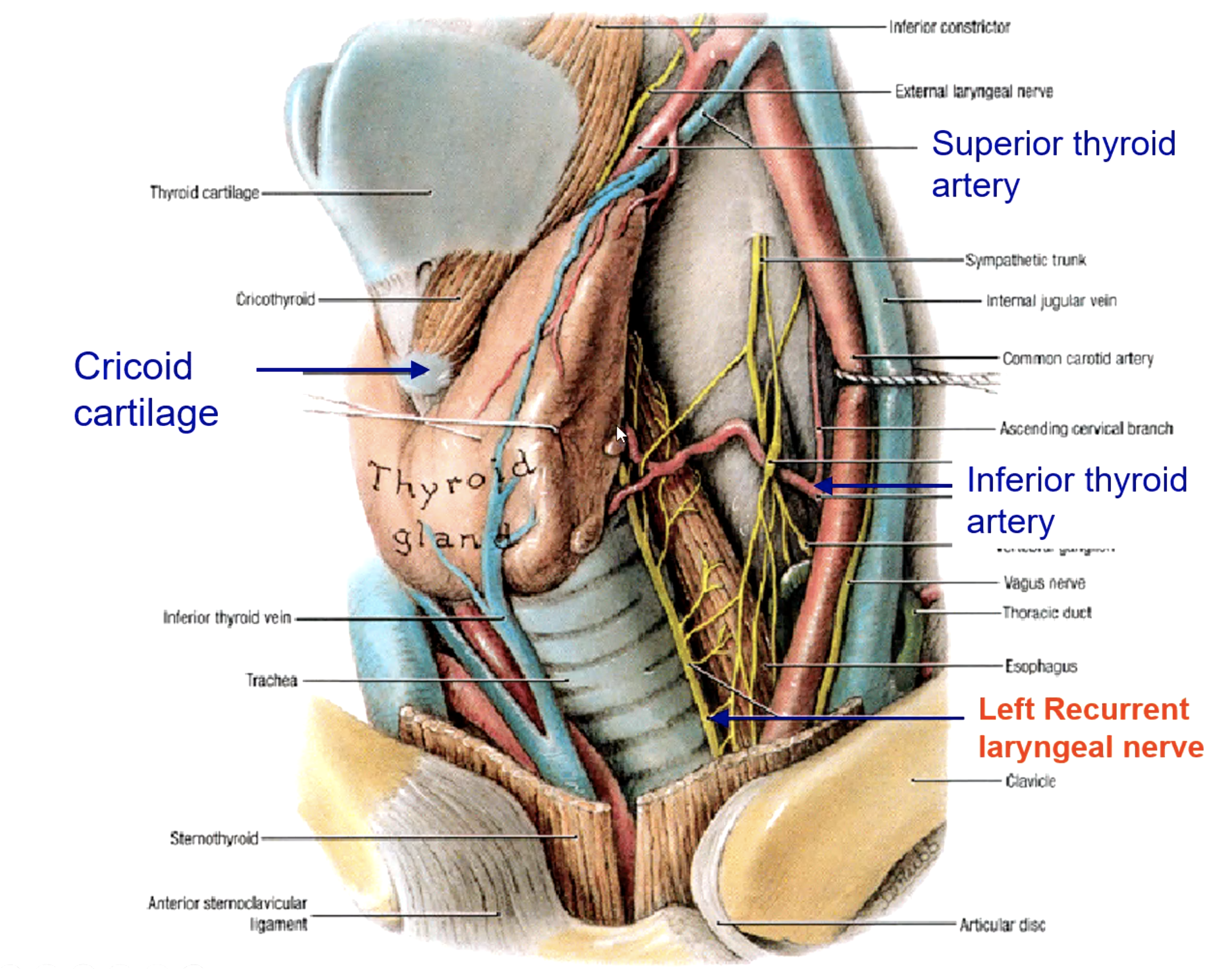
recurrent laryngeal n.
what structure runs in the groove between the trachea and the esophagus?
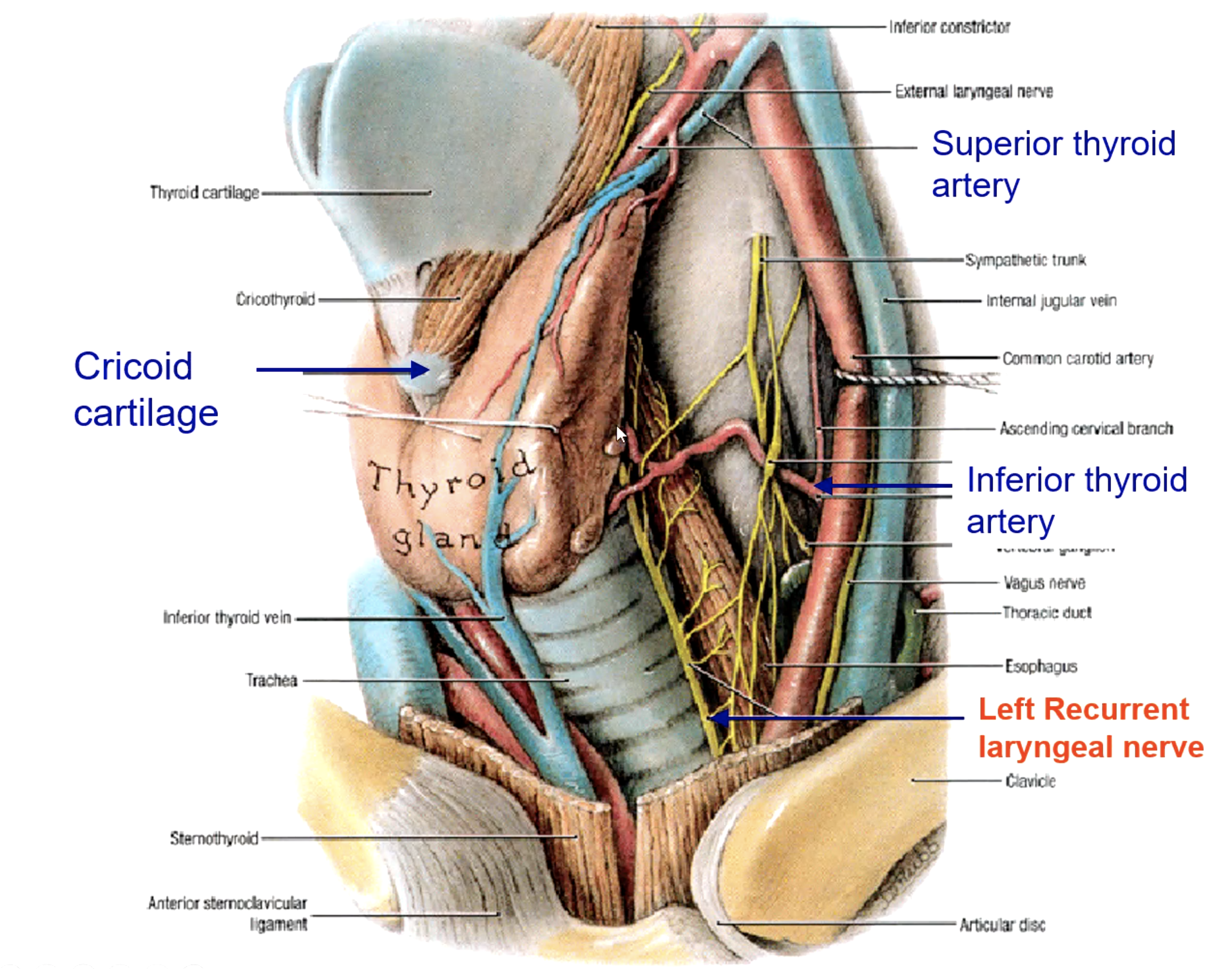
inferior thyroid a.
patient presents with the inability to speak after a thyroid removal surgery. You know that the surgeon must have nicked the recurrent laryngeal n. What artery was the surgeon ligating when he cut the recurrent laryngeal n.?
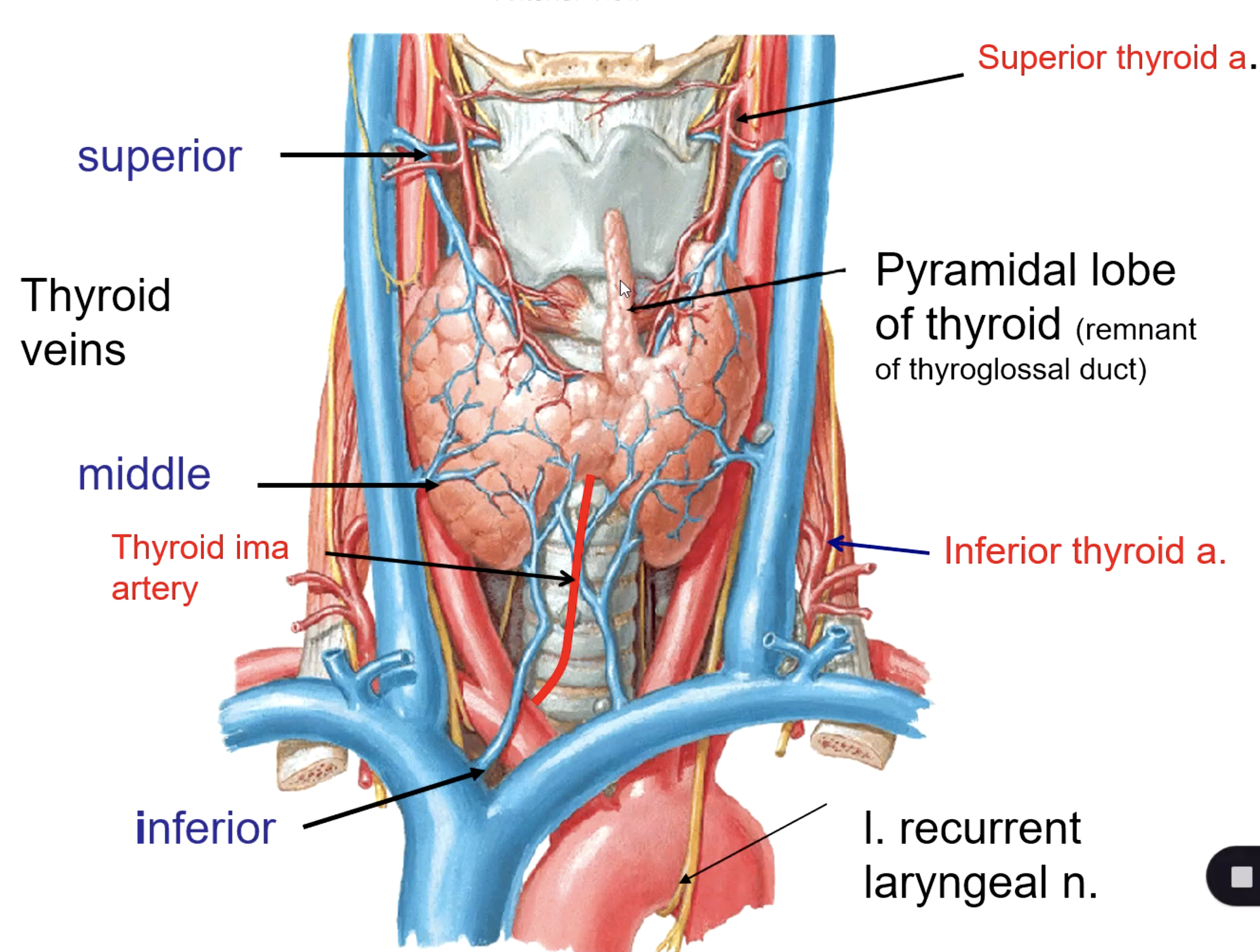
superior thyroid v.
middle thyroid v.
inferior thyroid v.
what veins drain the thyroid gland?
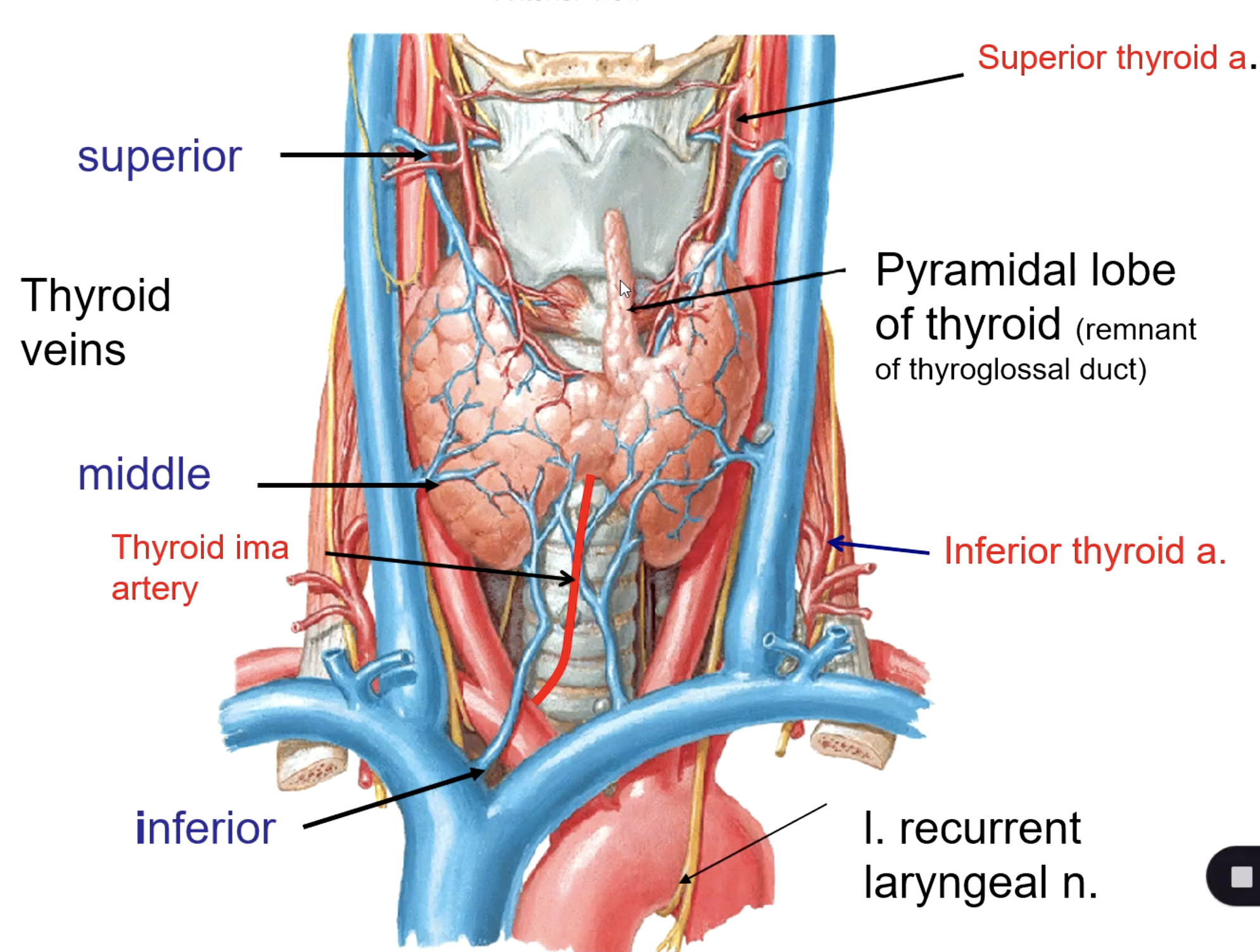
internal jugular v.
the superior thyroid vein drains into the:
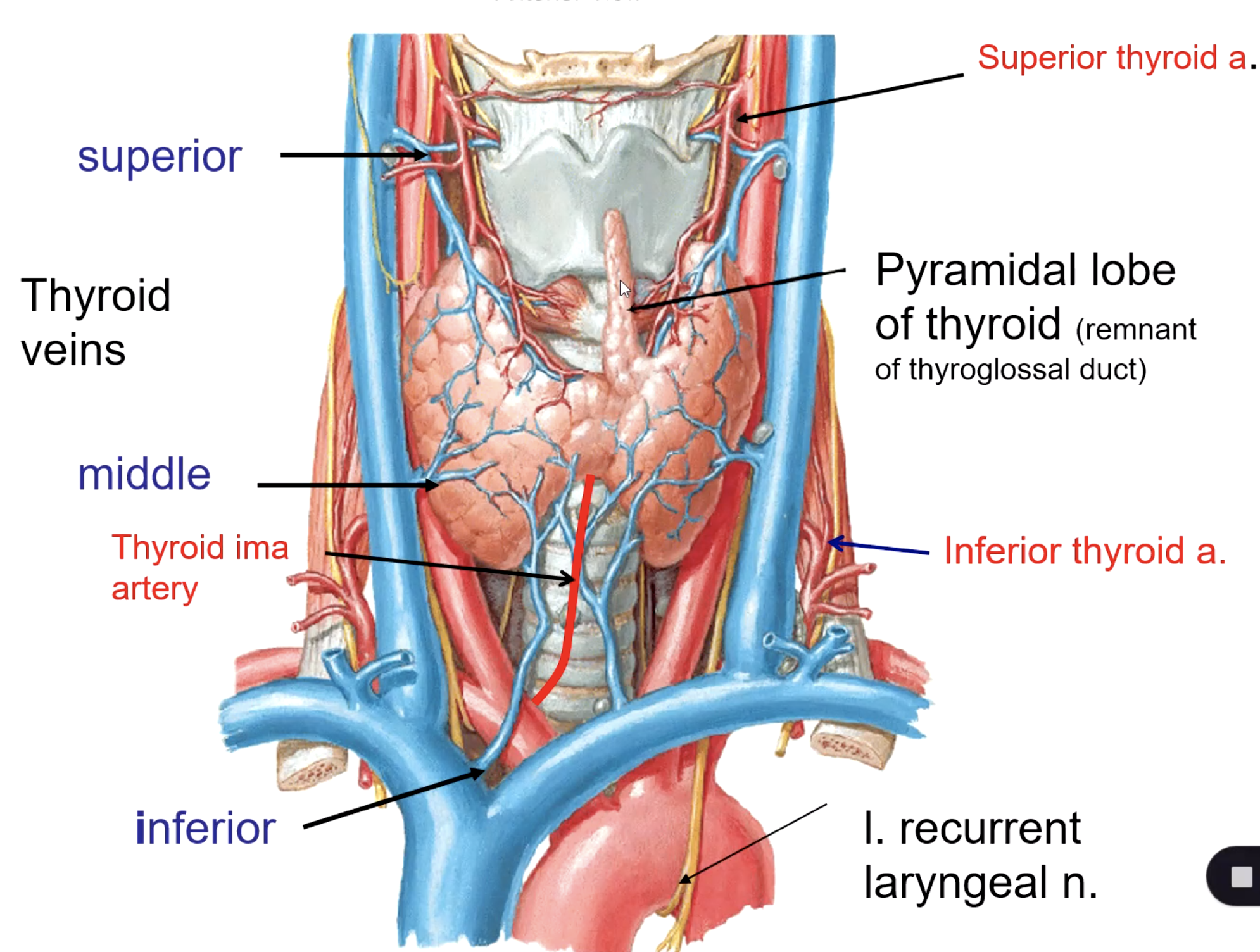
internal jugular v.
the middle thyroid vein drains into the:
brachiocephalic v.
the inferior thyroid vein drains into the:
thyroglossal duct (not all people still have this lobe)
the pyramidal lobe of thyroid is a remnant of
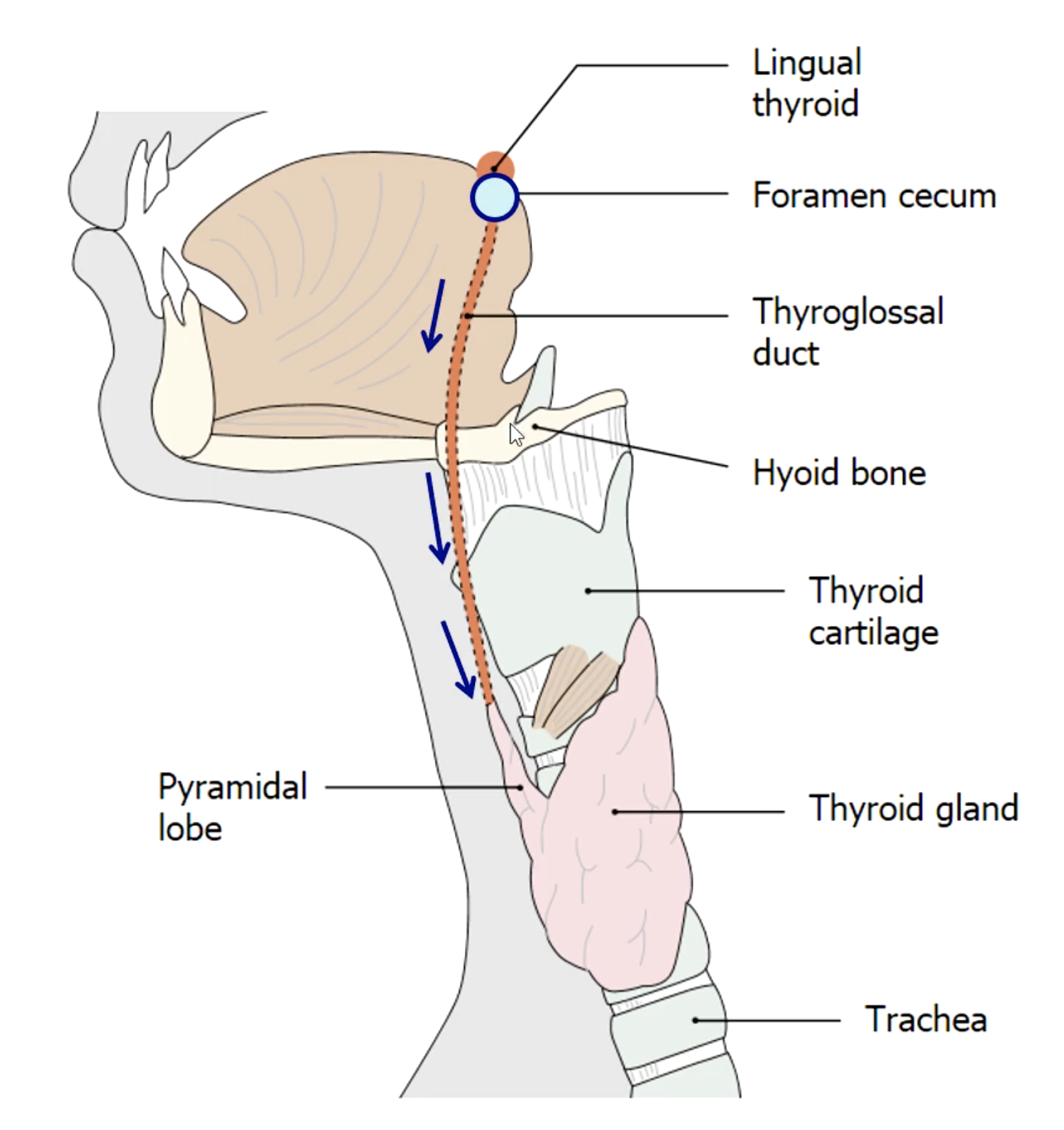
base of the tongue (foramen cecum)
that’s why some people have a pyramidal lobe of thyroid
the thyroid gland developed at the:
thyroglossal duct cyst
presents as a painless swelling in the midline near hyoid bone that moves when swallowing. What is the diagnosis?
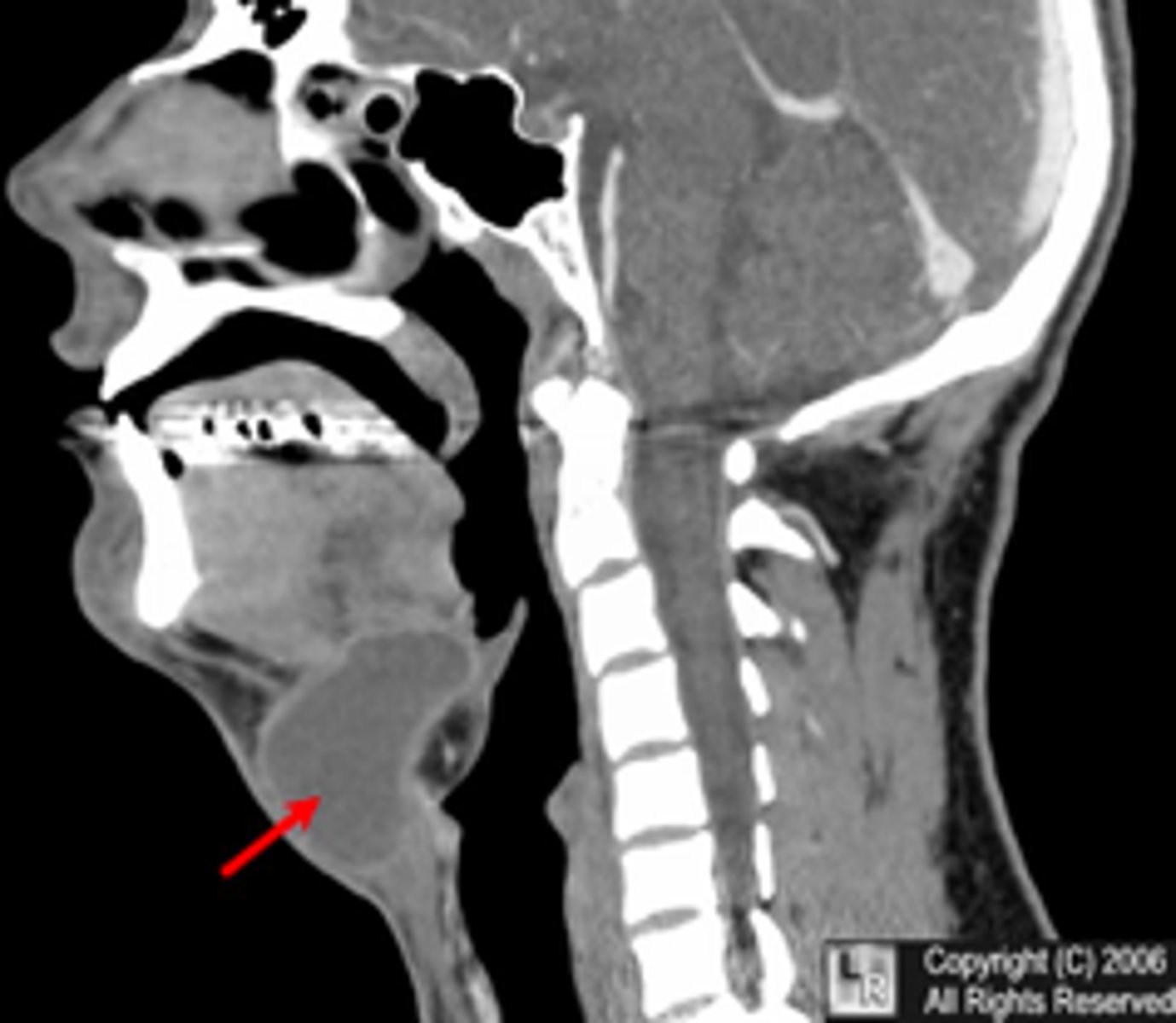
thyroglossal duct cyst
what is the diagnosis?
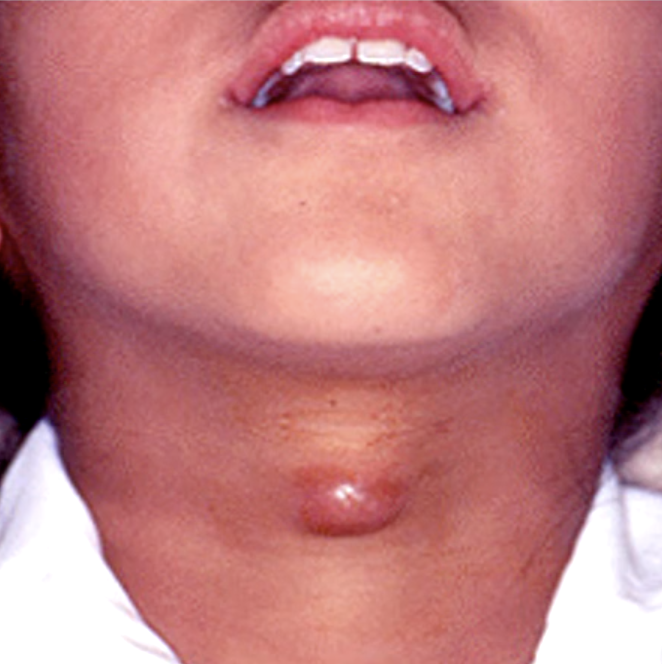
Sistrunk procedure (surgical resection of duct to base of tongue including body of hyoid bone to ensure complete removal of duct)
what is the treatment for thyroglossal duct cyst?
goiter
patient presents with abnormal enlargement of the neck. Patient experiences feeling of tightness in the throat area and hoarseness. Blood screening shows a normal calcium levels and low iodine levels. What is the diagnosis?
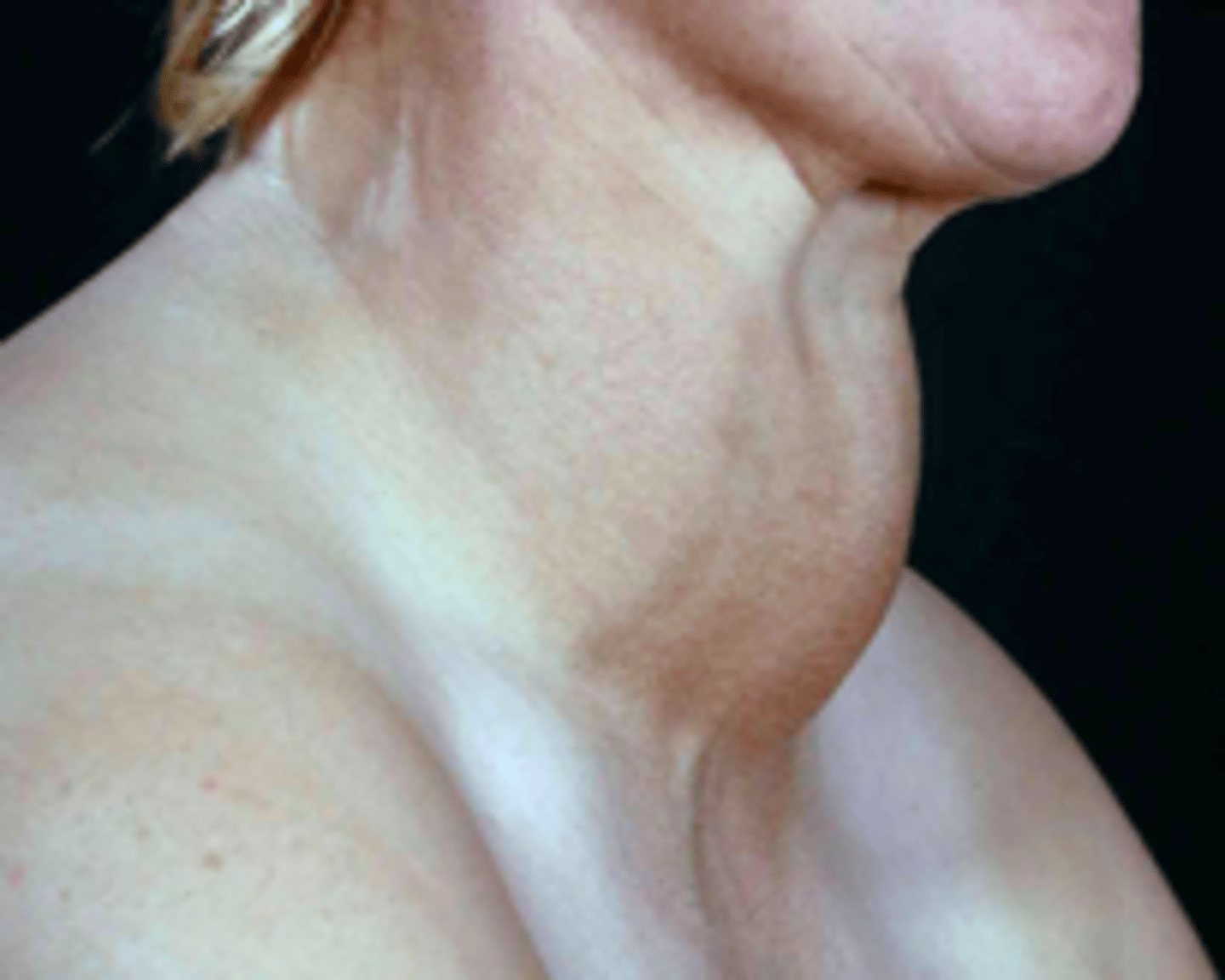
low iodine (main)
Graves Disease, thyroiditis, thyroid cancer
what is the main cause of goiter? what are some other causes?
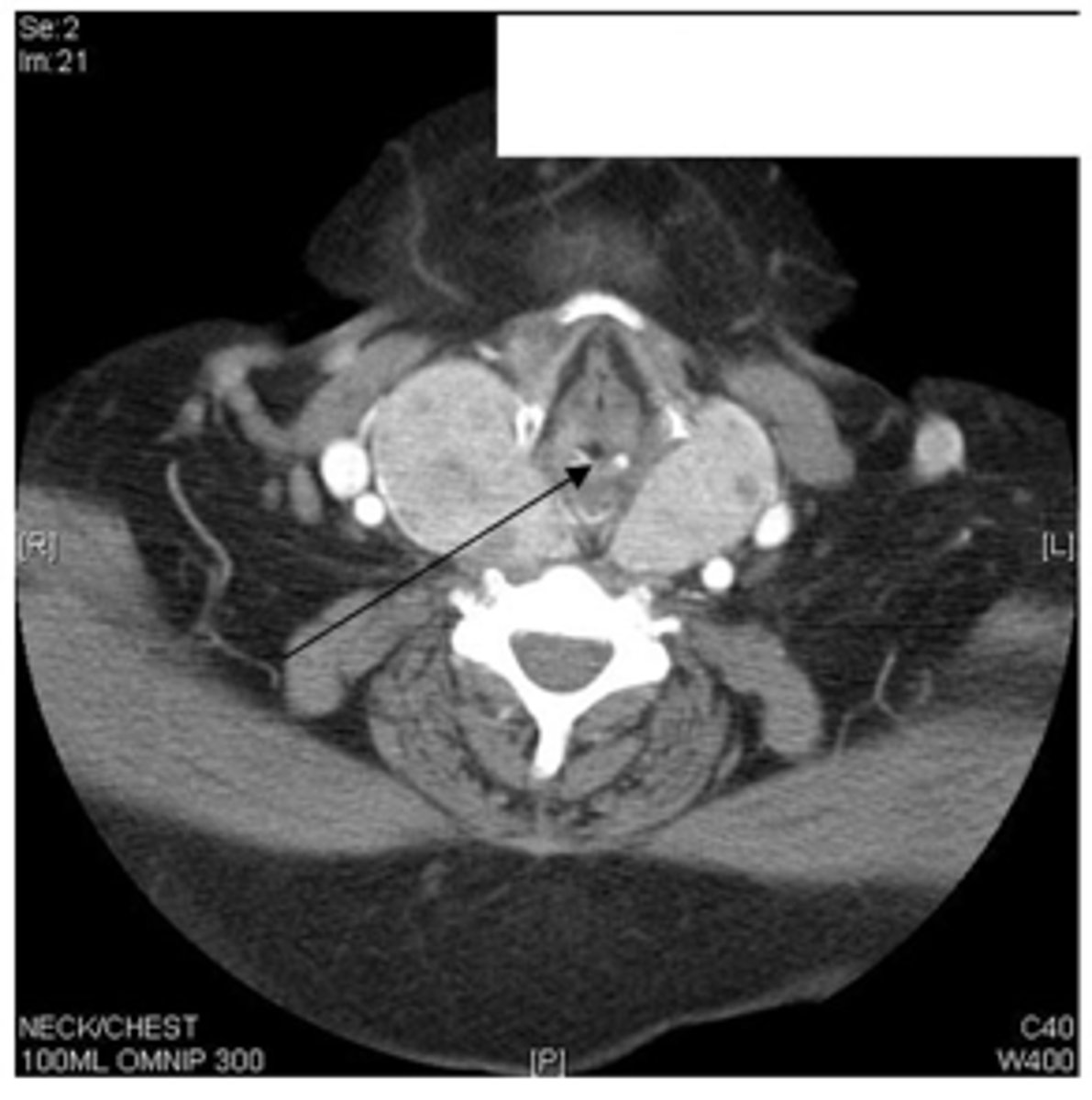
goiter (affects larynx)
patient presents with the following CT. What is the diagnosis?
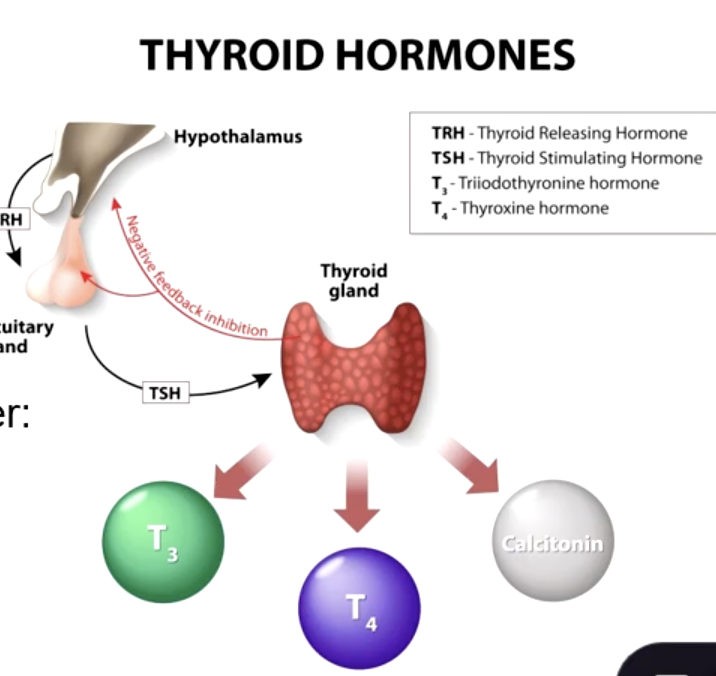
T3 and T4 cannot be produced without iodine so thyroid releasing hormone (TRH) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) become overactive causing cells in thyroid gland to hypertrophy
why does low iodine cause goiter?
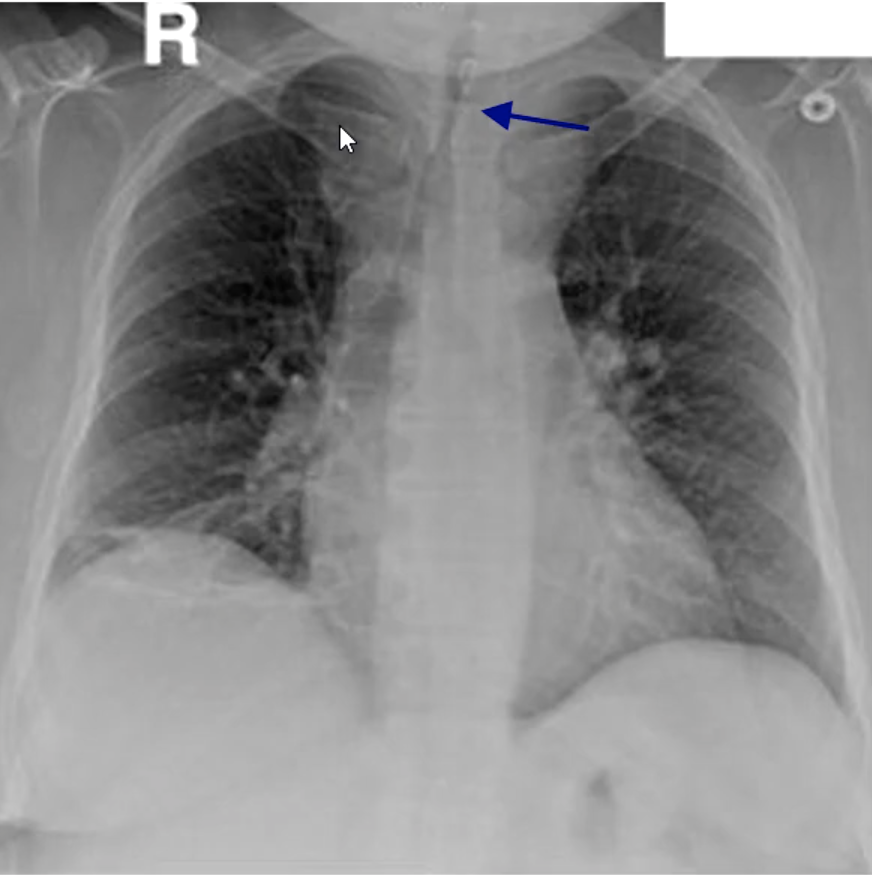
goiter causing severe tracheal compression pushed to the right (breathing problems)
patient presents with the following radiograph. What is the diagnosis?
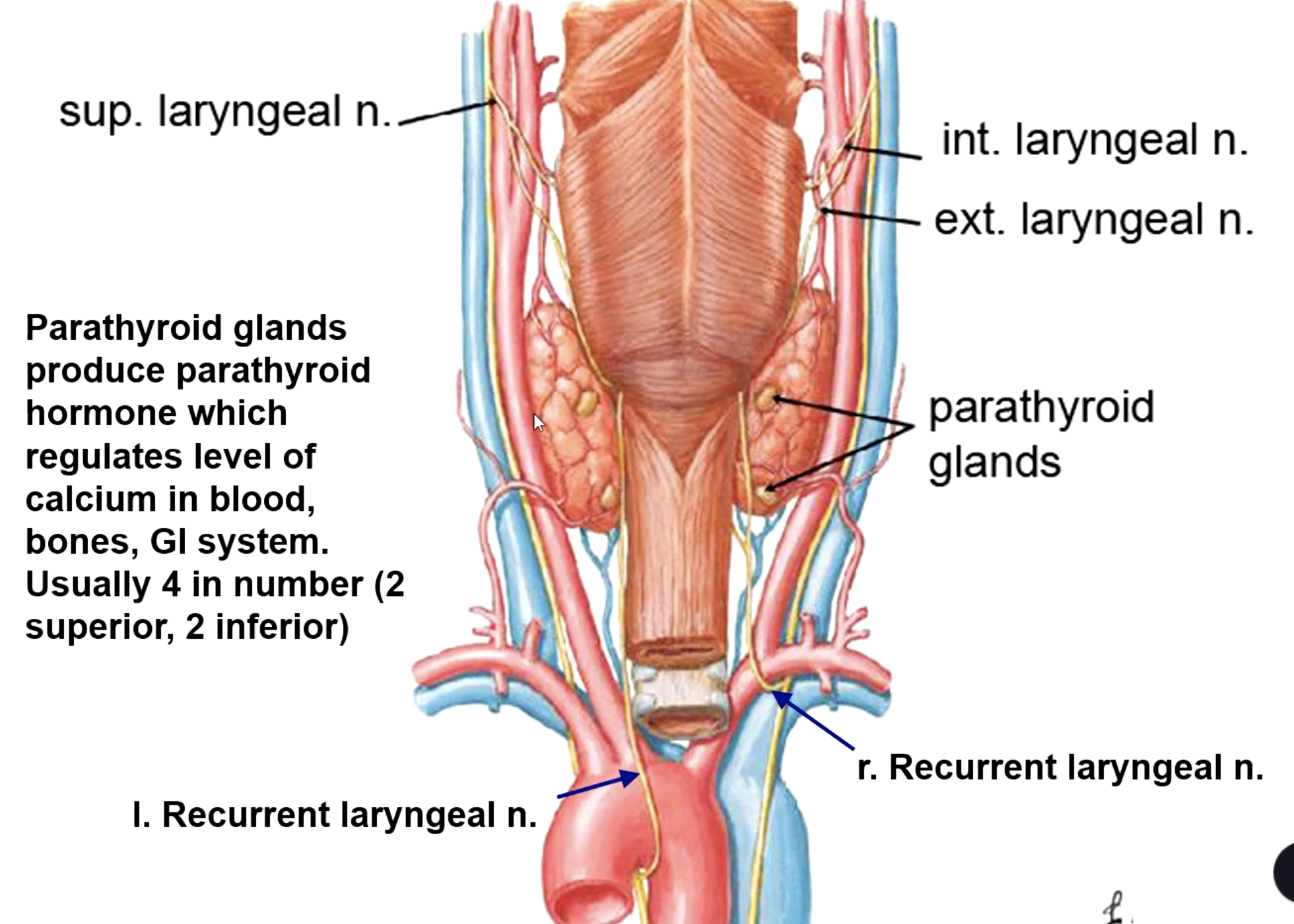
parathyroid hormone
hormones that regulates level of calcium in blood, bones, GI system
posterior
the parathyroid glands lie on the _______ aspect of the thyroid gland
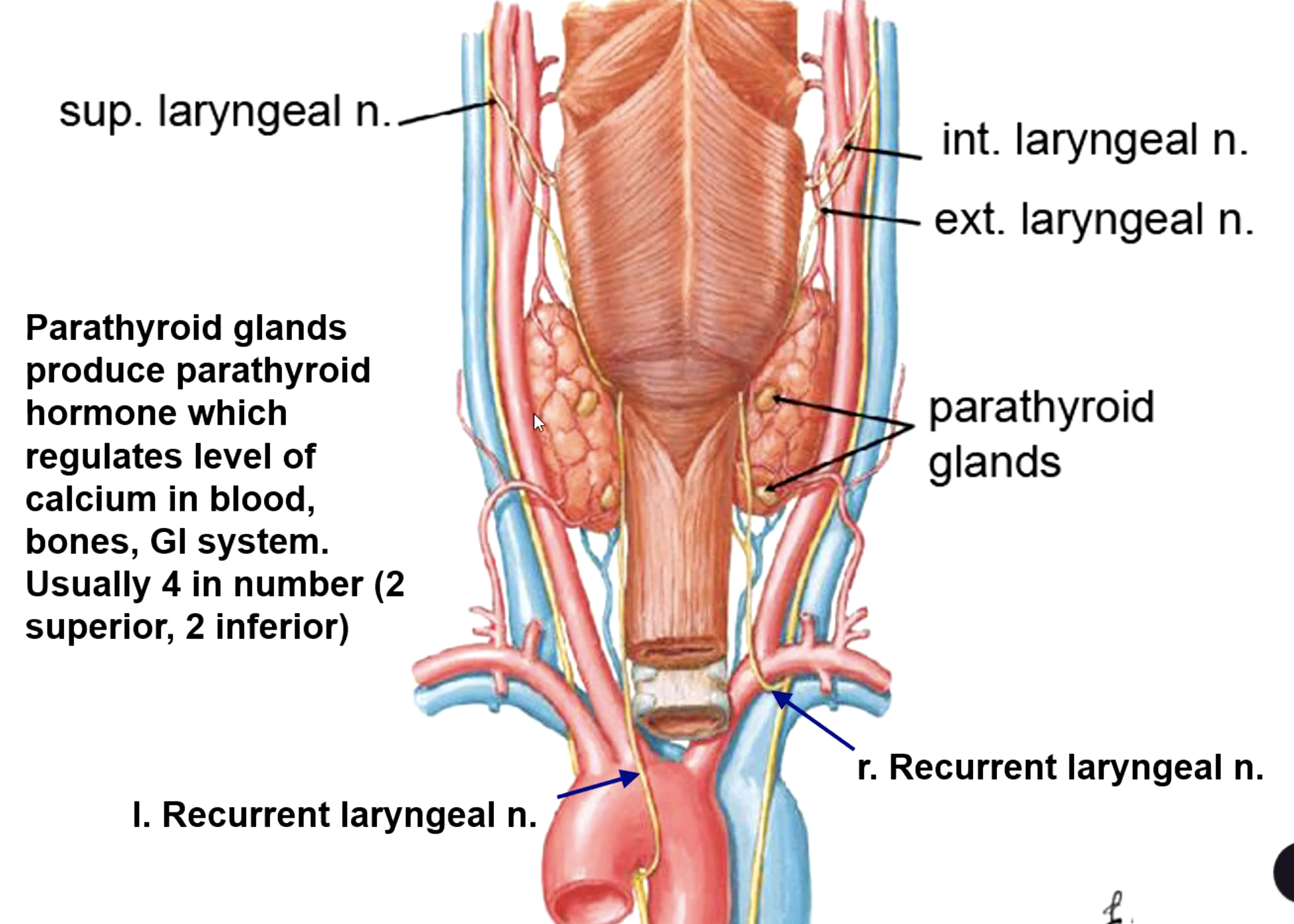
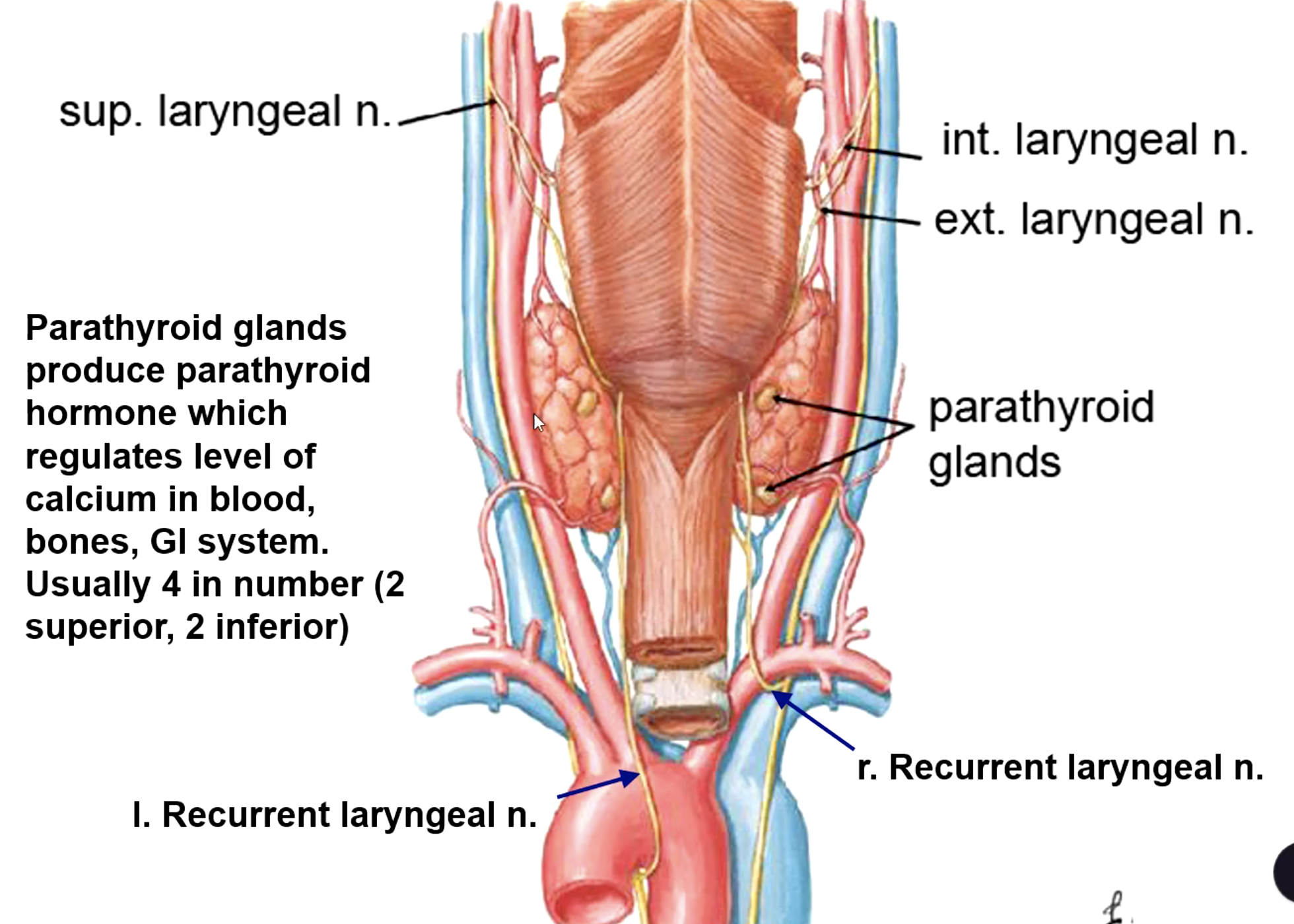
4 total
2 superior, 2 inferior
how many parathyroid glands are there usually?
too much calcium in blood (kidney stones)
cancer in parathyroid glands can cause
weak muscles
removal of parathyroid glands can cause
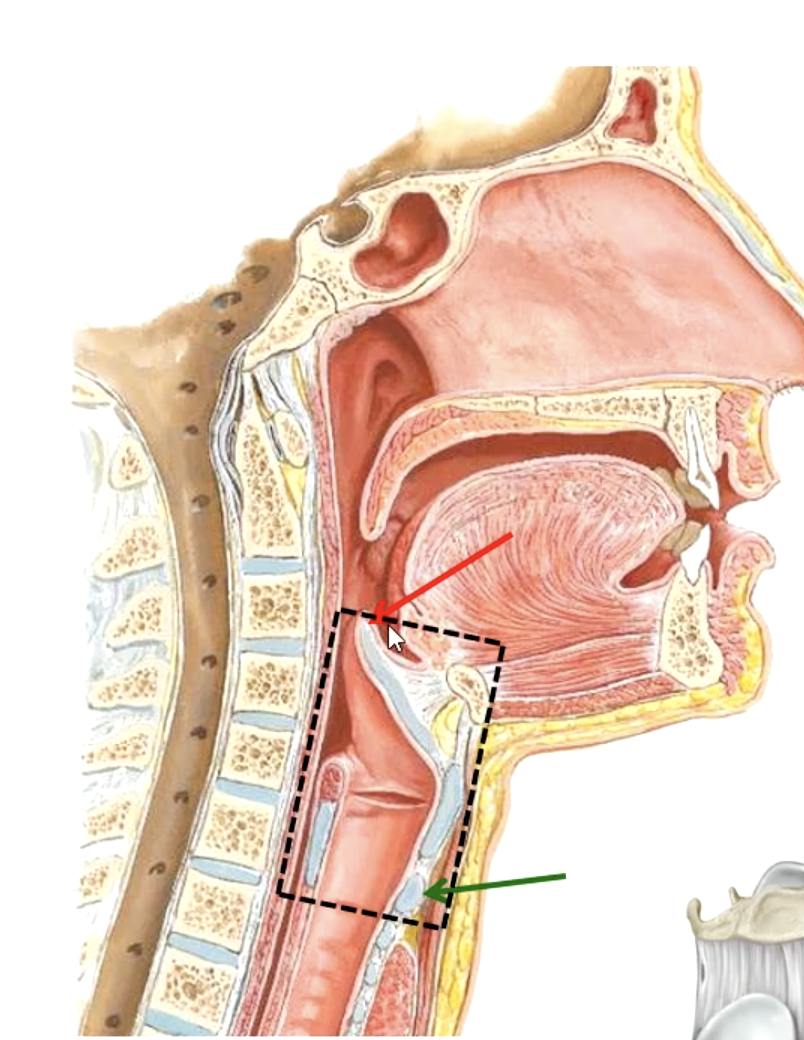
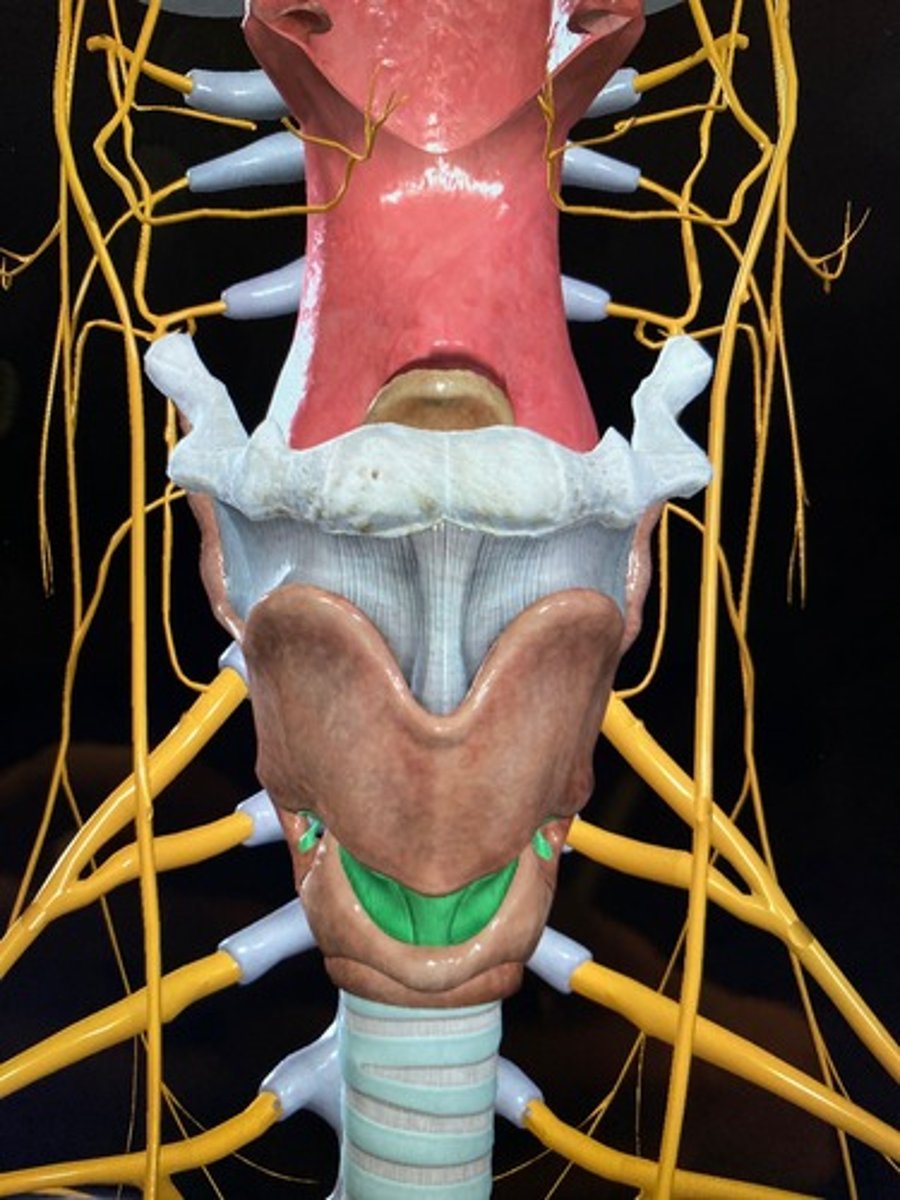
larynx
what part of the respiratory system contains the vocal cords?
phonation (production of sound)
sphincter for respiratory system
swallowing (acts w muscles of oral cavity, oral pharynx)
functions of larynx
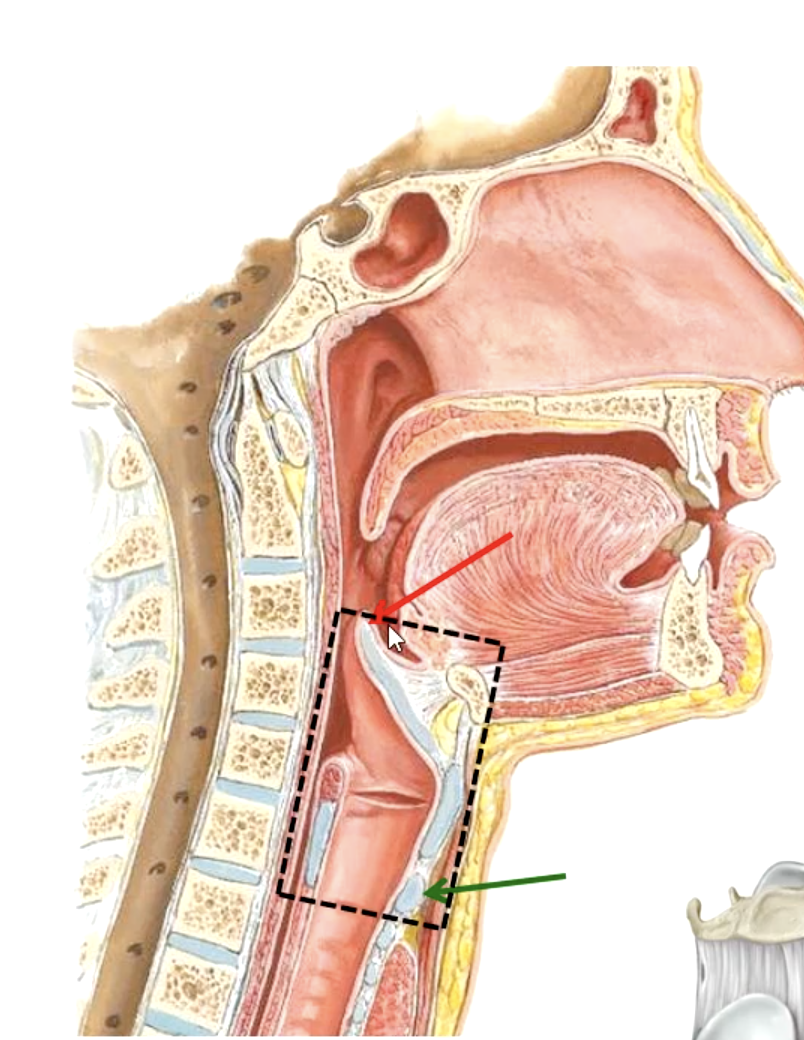
tip of epiglottis
upper boundary of the larynx:
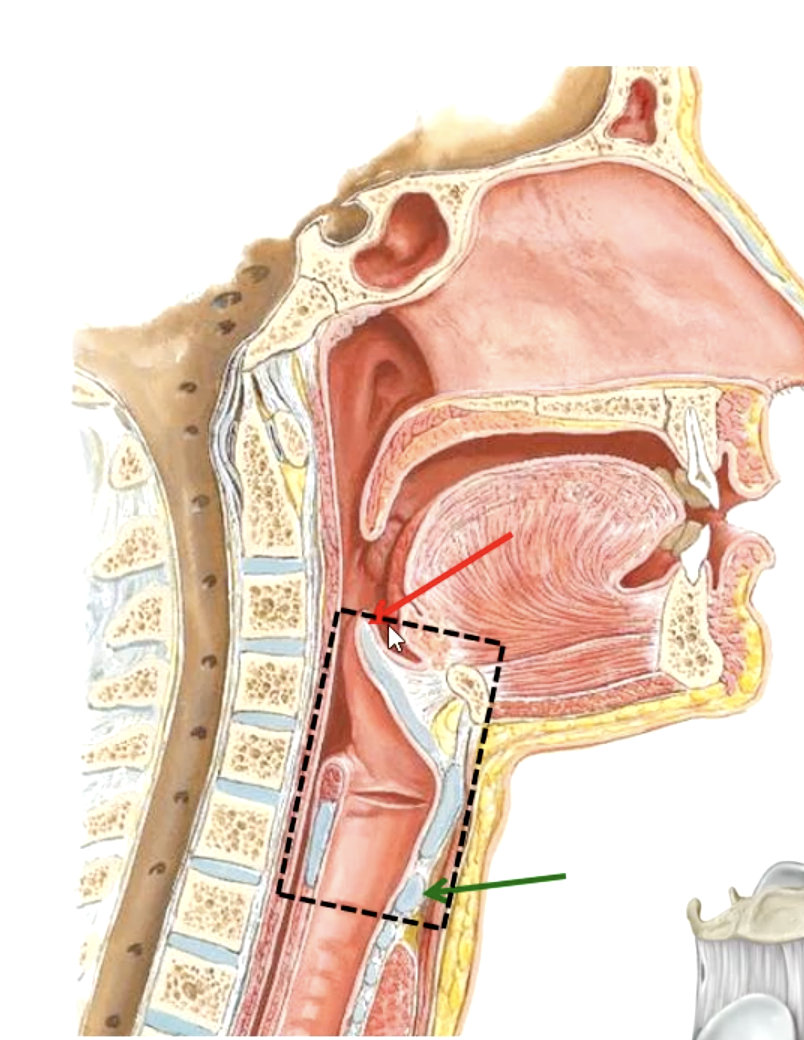
lower level of cricoid cartilage
lower boundary of the larynx:
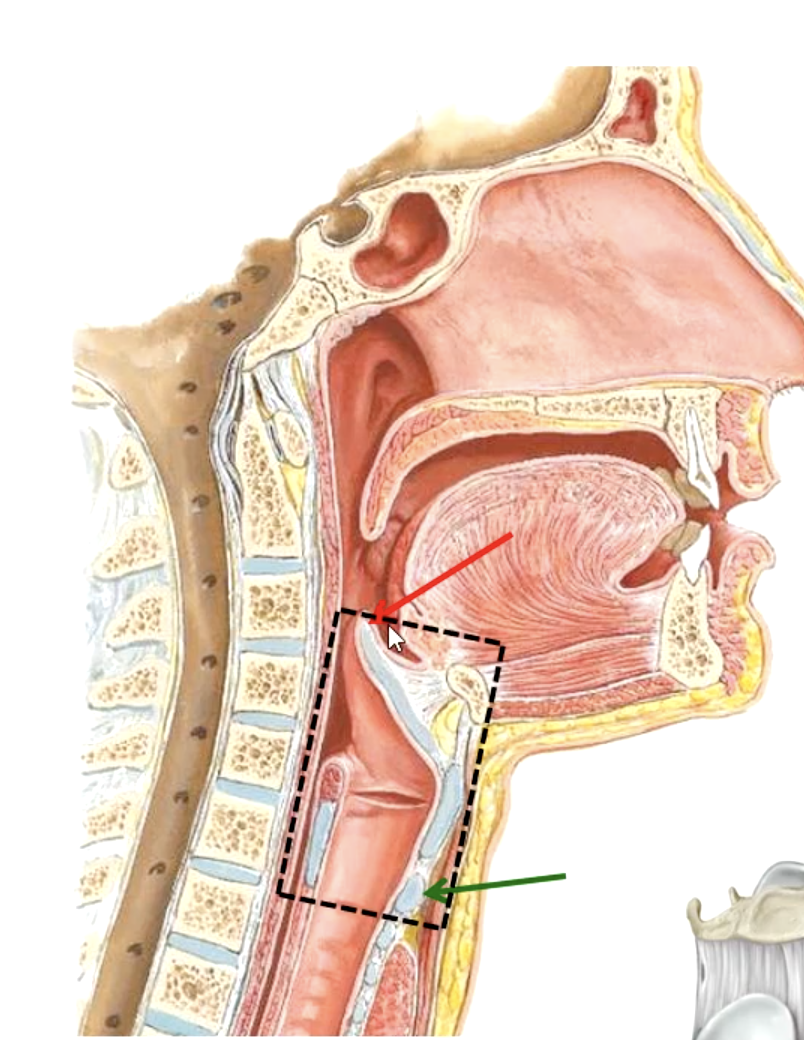
C3-C4
the epiglottis lies at what vertebral level?
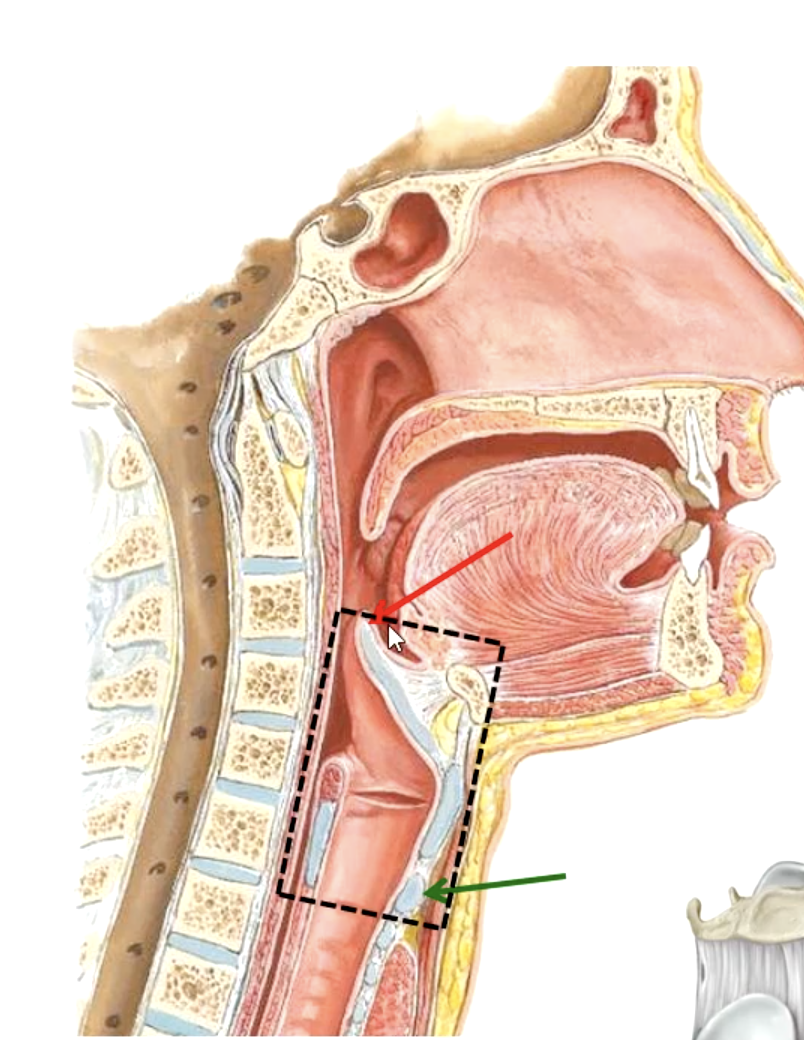
C6
the cricoid cartilage lies at what vertebral level?
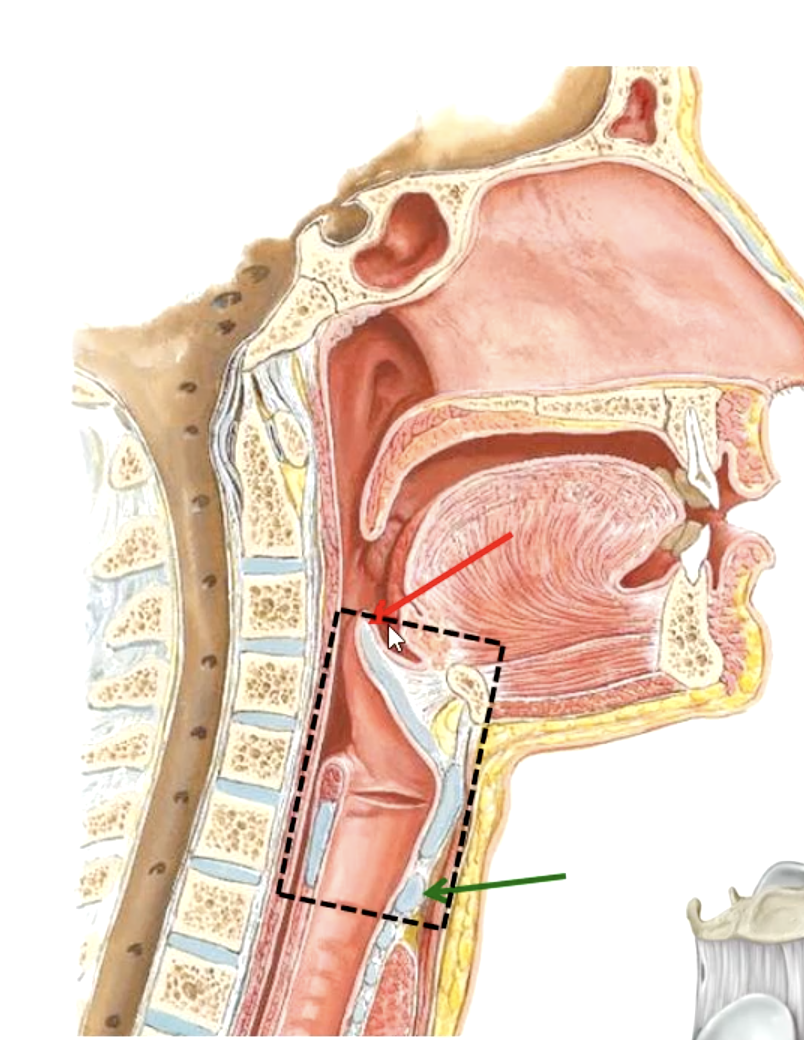
5-7 cm
how long is the larynx?
inferior
the larynx is located _______ to the hyoid bone
superior
the larynx is located _______ to the thyroid gland
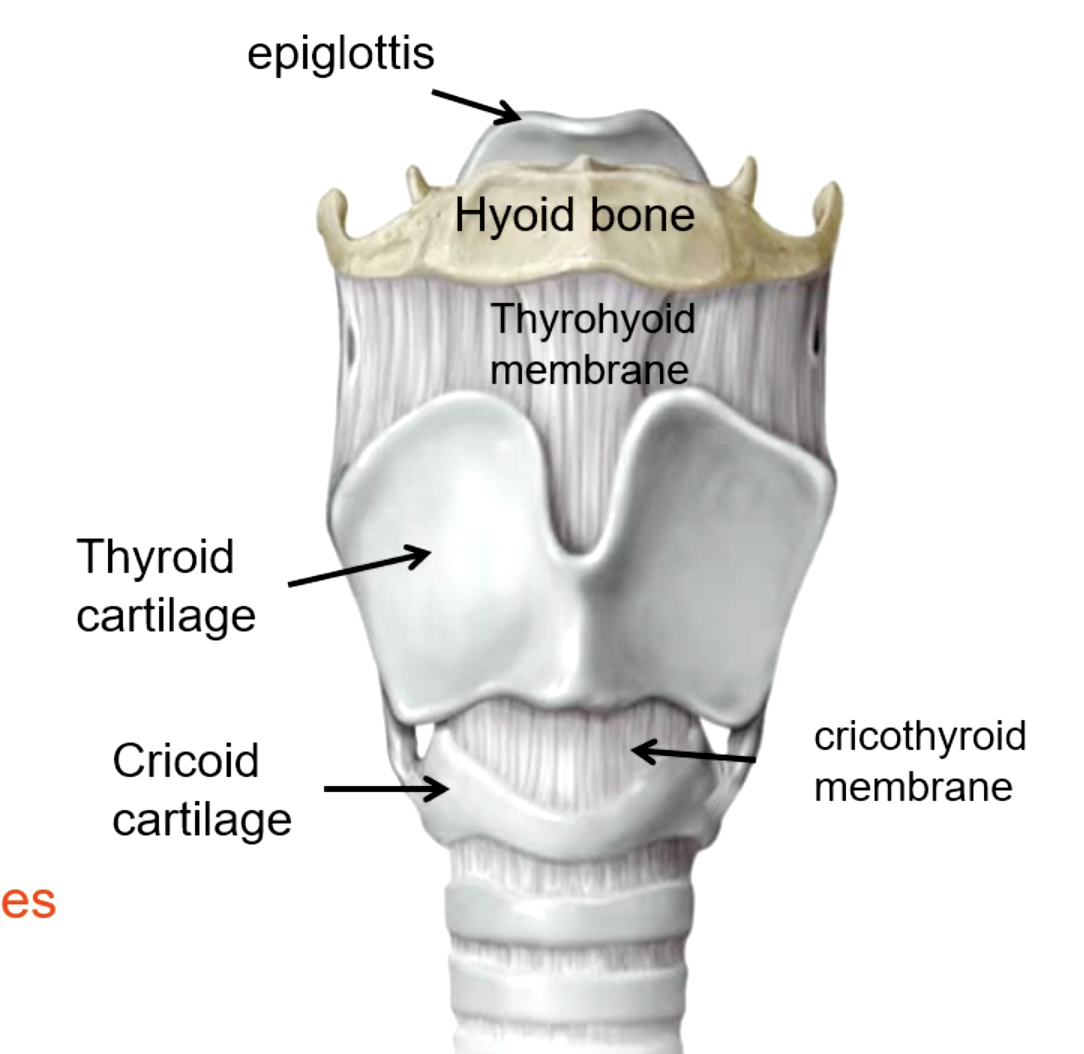
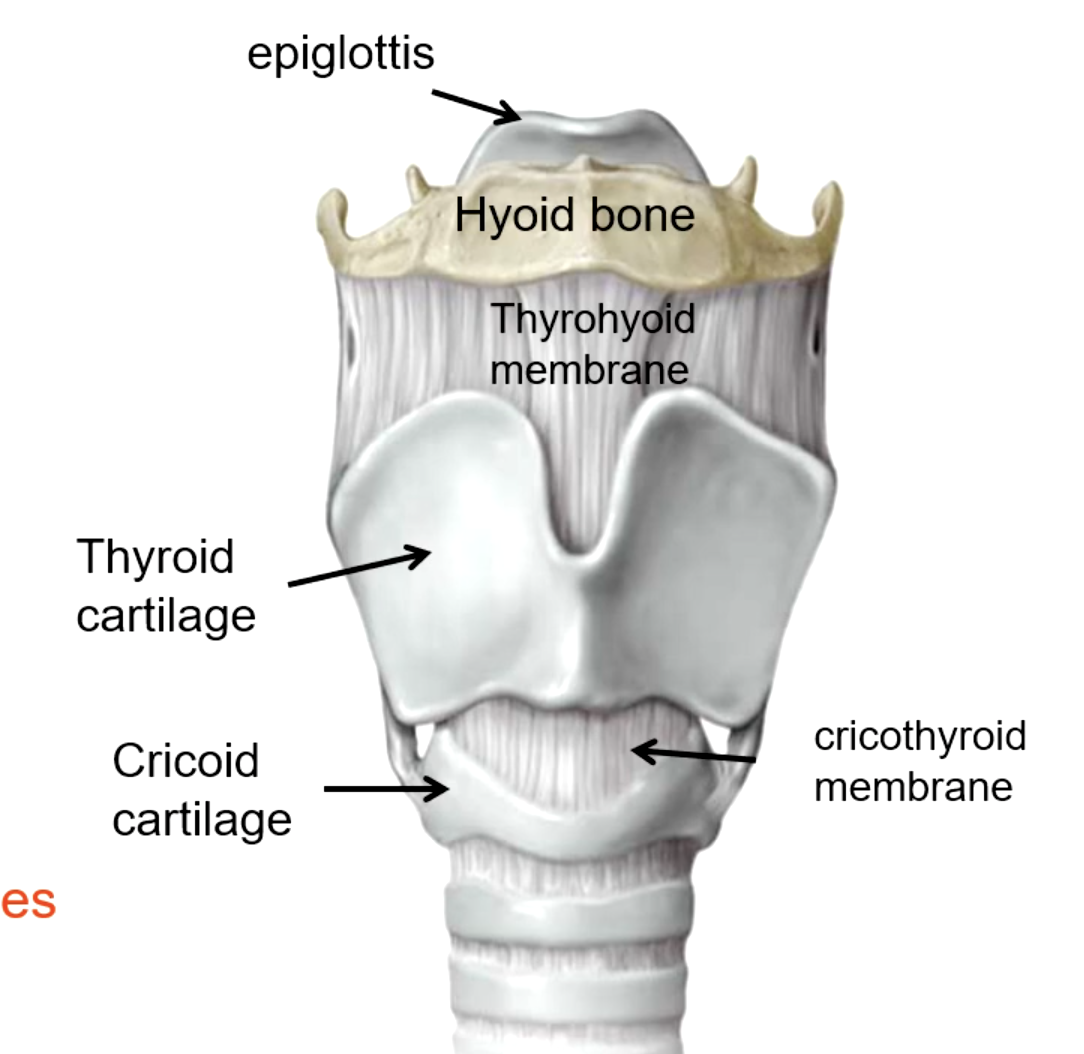
epiglottis
thyroid cartilage
cricoid cartilage
what are the unpaired cartilages of the larynx?
arytenoid
corniculate
cuneiform
what are the paired cartilages of the larynx?
6 total
3 paired, 3 unpaired
how many cartilages make up the skeleton of the larynx?
connected by joints, membranes, ligaments
moved by muscles
the larynx cartilages are connected by…? but moved by…?
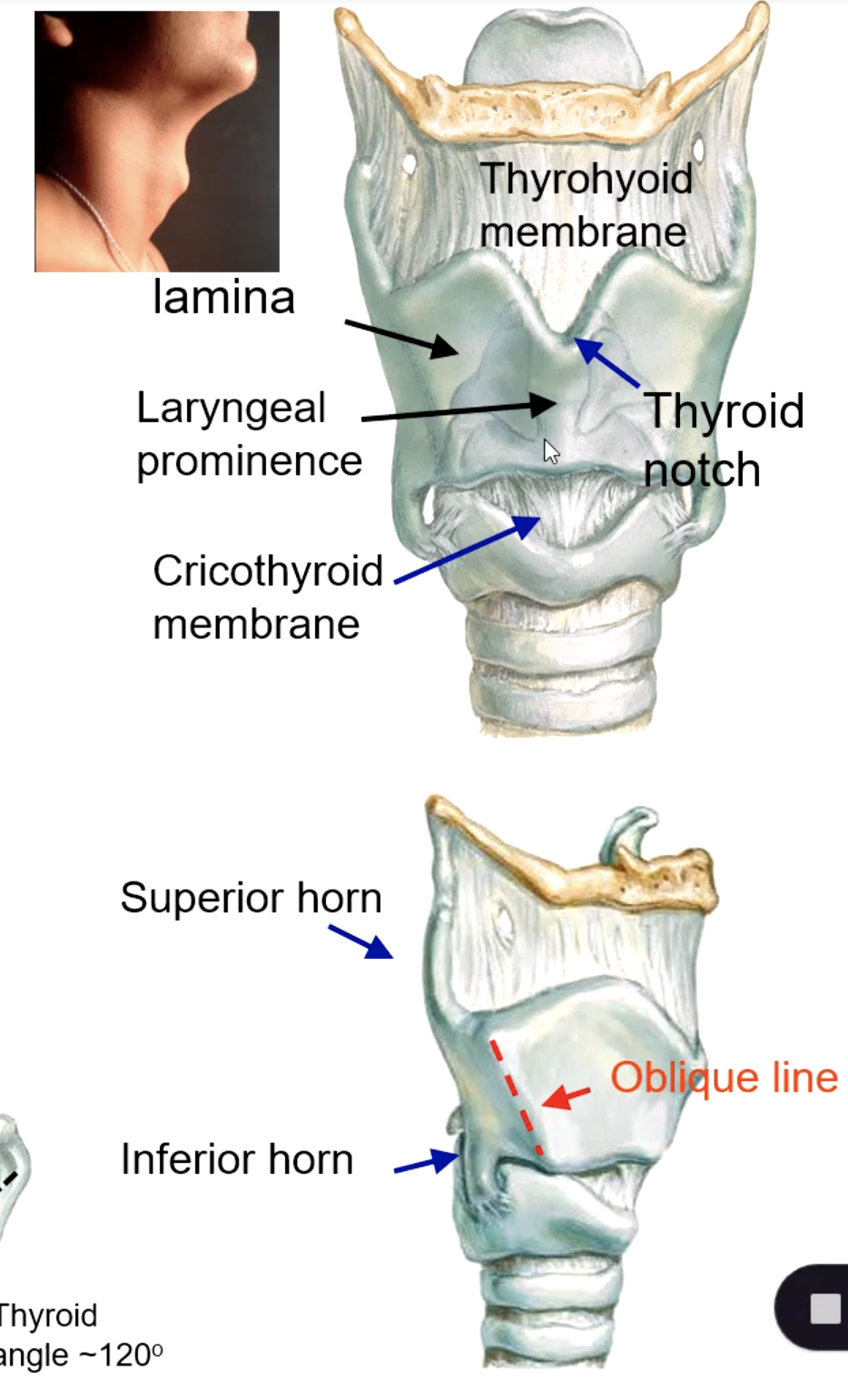
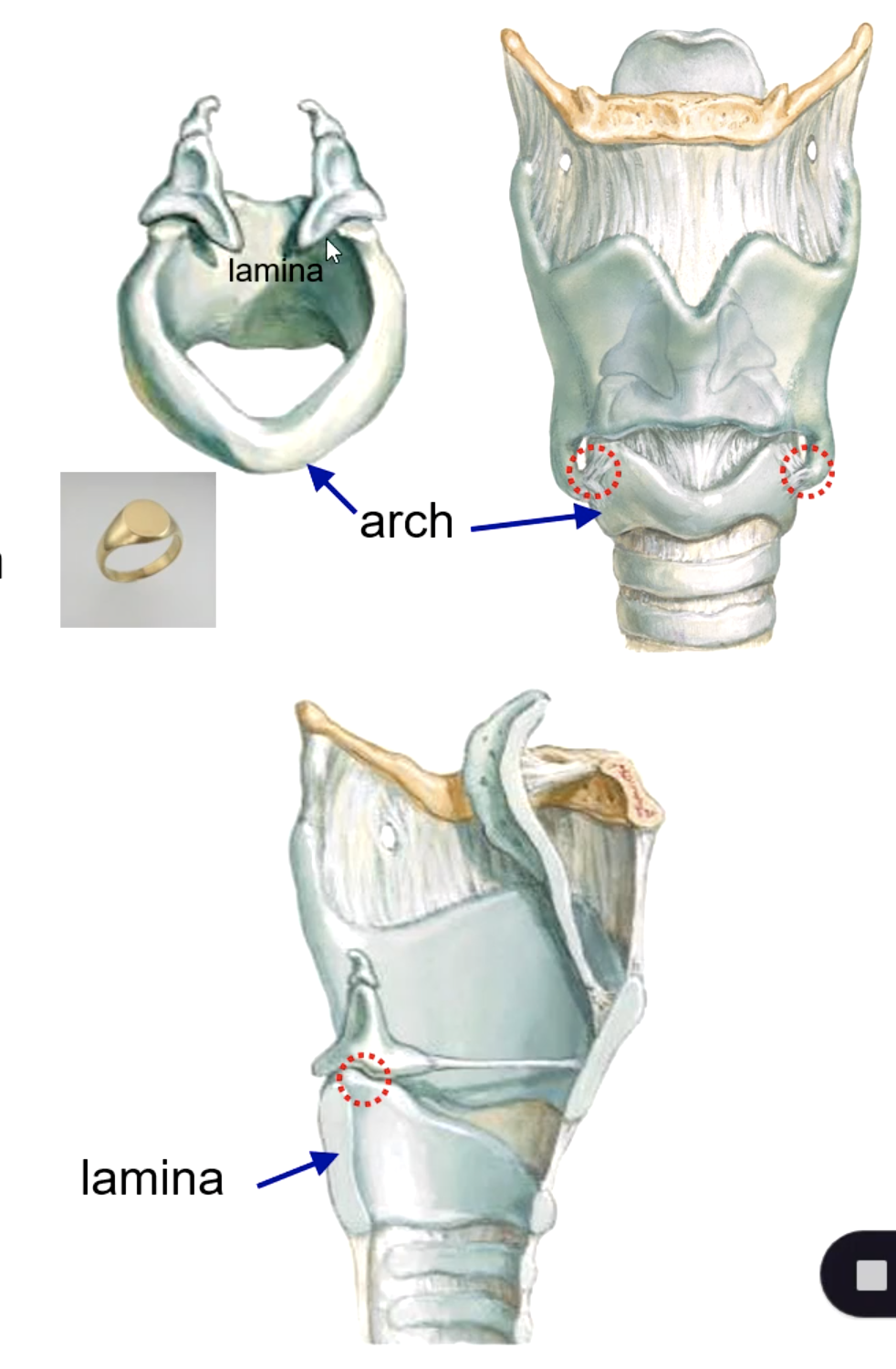
thyroid cartilage
what structure is the largest larynx cartilage and forms the Adam's apple?
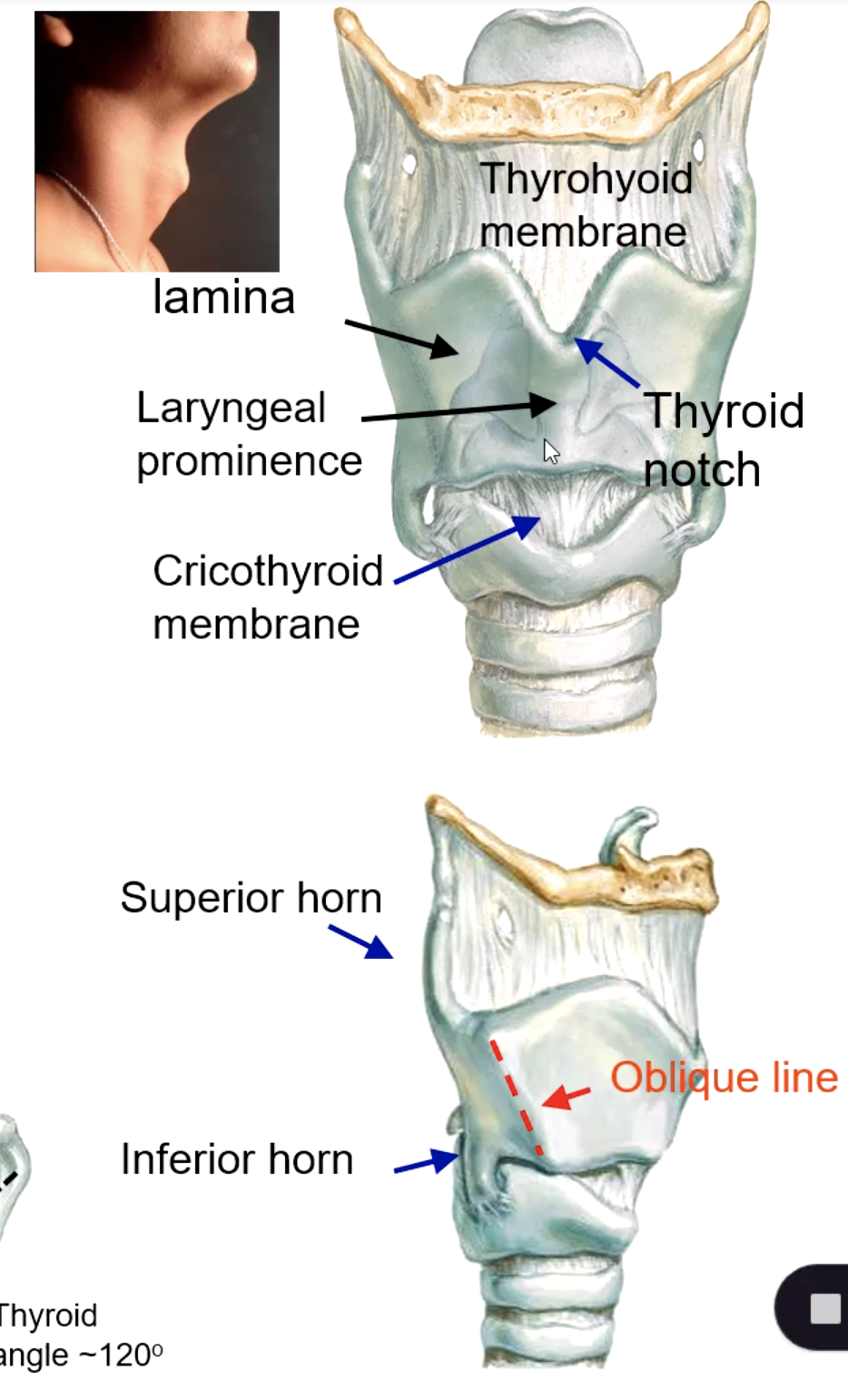
thyroid cartilage
the laryngeal prominence (“Adam’s apple”) is located on which cartilage?
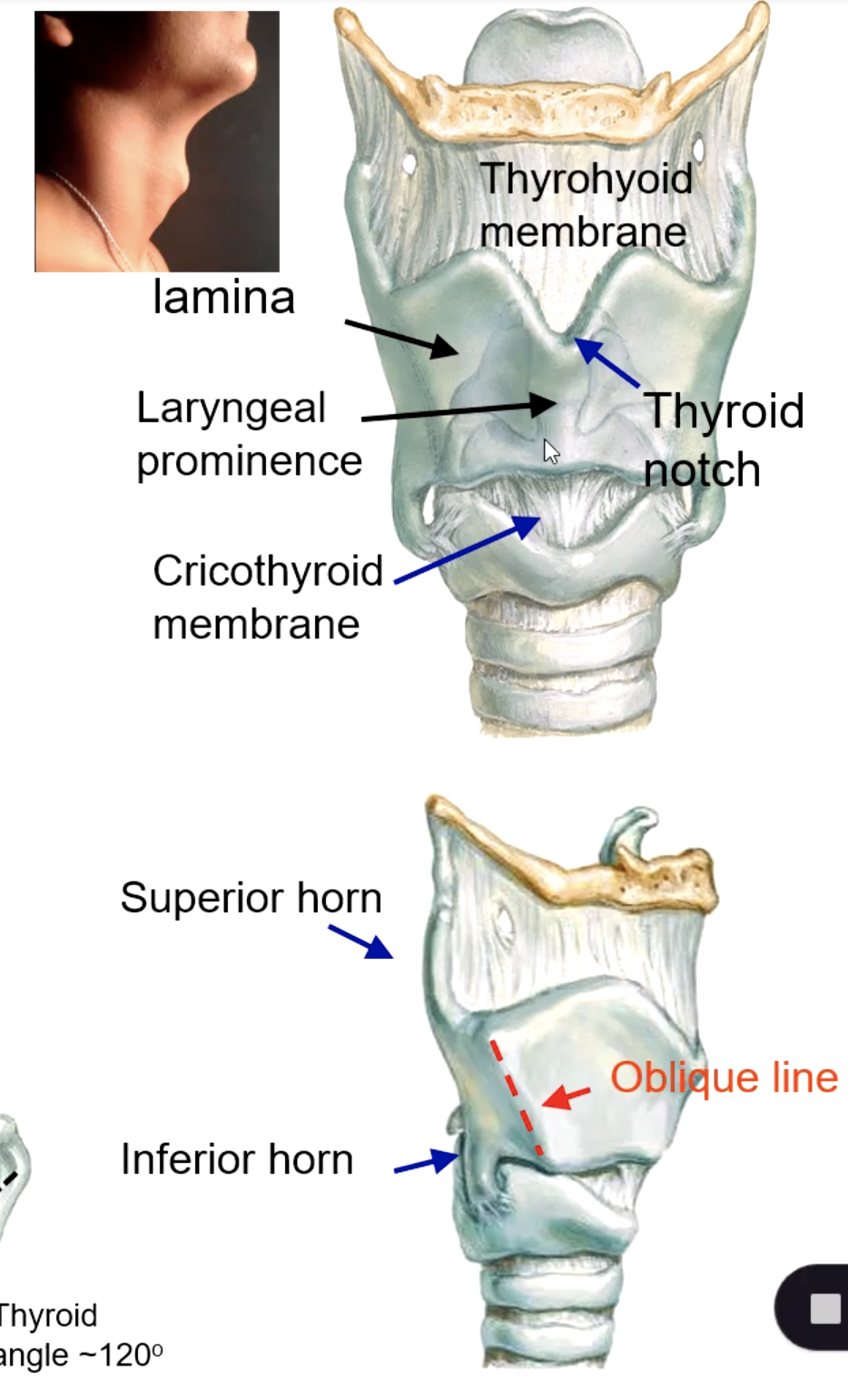
thyroid laminae
identify the structure:
laryngeal prominence
identify the structure:
superior thyroid notch
identify the structure:
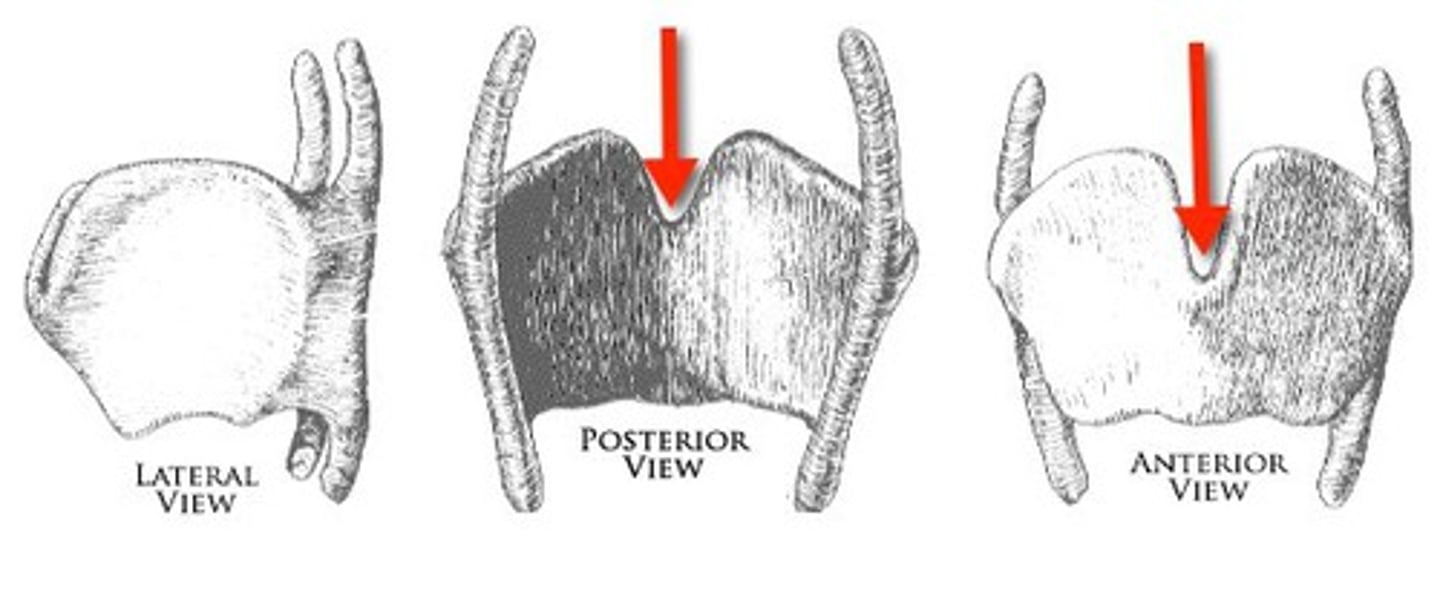
superior horn of thyroid cartilage
identify the structure:
inferior horn of thyroid cartilage
identify the structure:
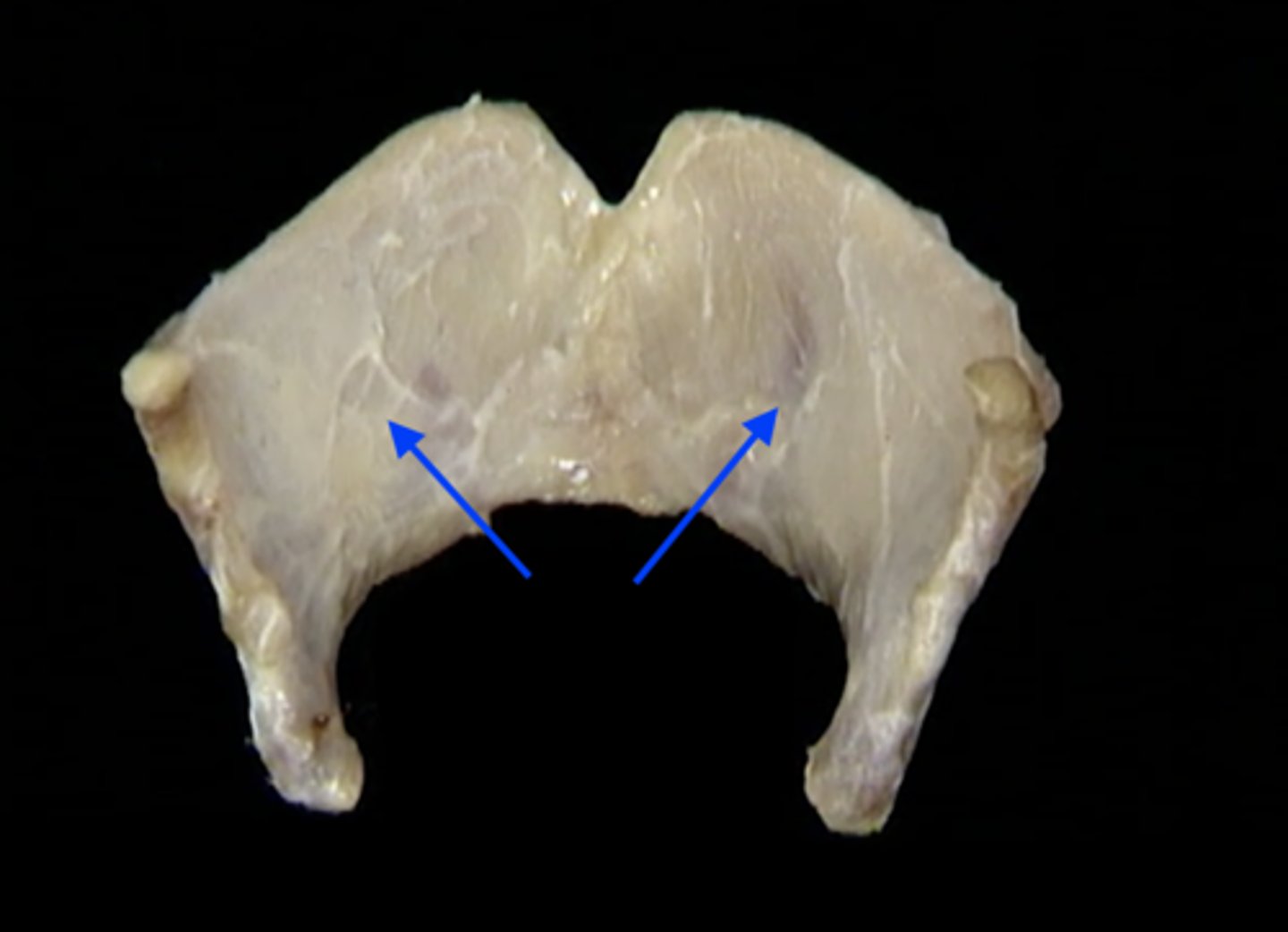
oblique line of thyroid cartilage
identify the structure:

thyrohyoid membrane
identify the structure:
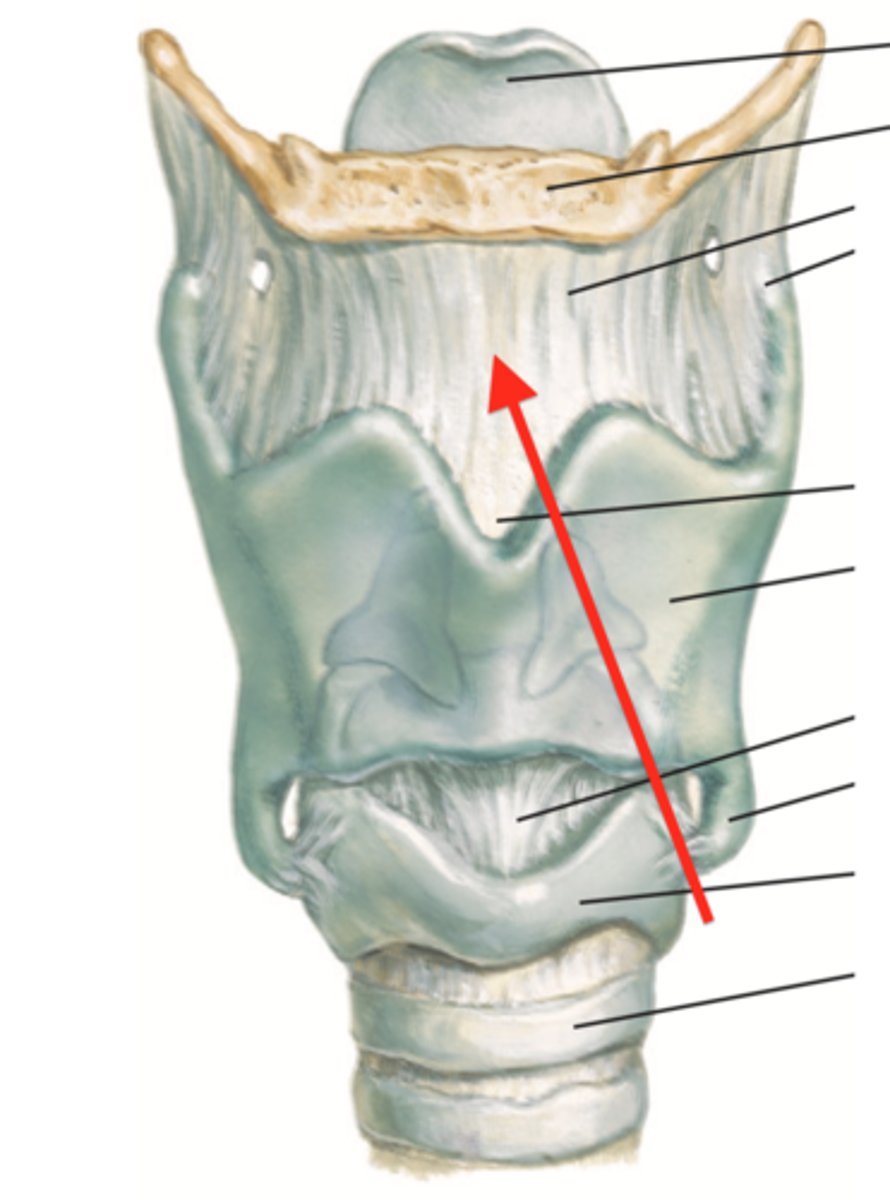
cricoid membrane
identify the structure:
thyrohyoid m.
sternothyroid m.
inferior constrictor of pharynx m.
what 3 muscles attach to the oblique line of thyroid cartilage?
inferior horn of thyroid cartilage (synovial joint)
the lateral surface of the cricoid cartilage articulates with the:
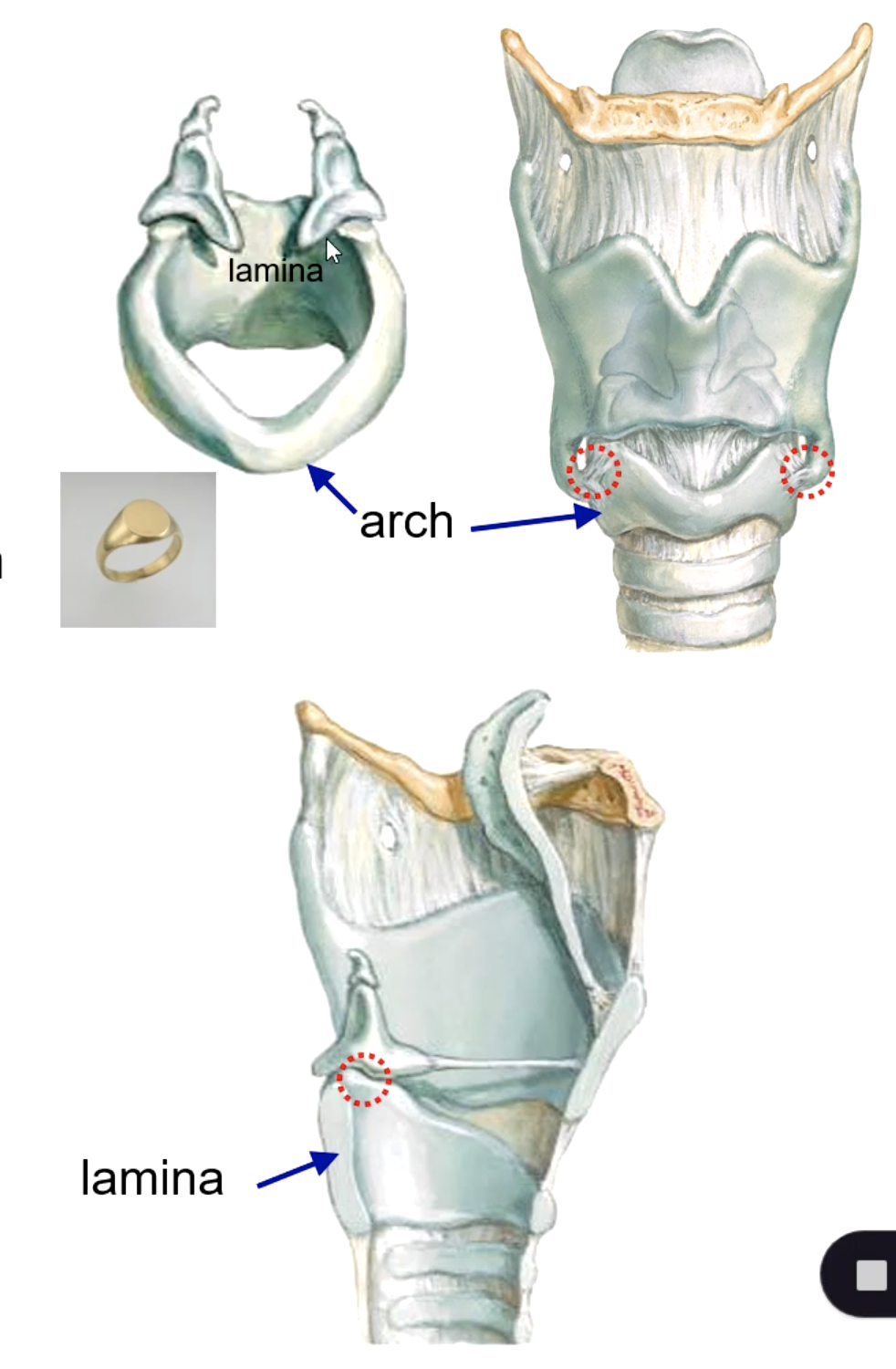
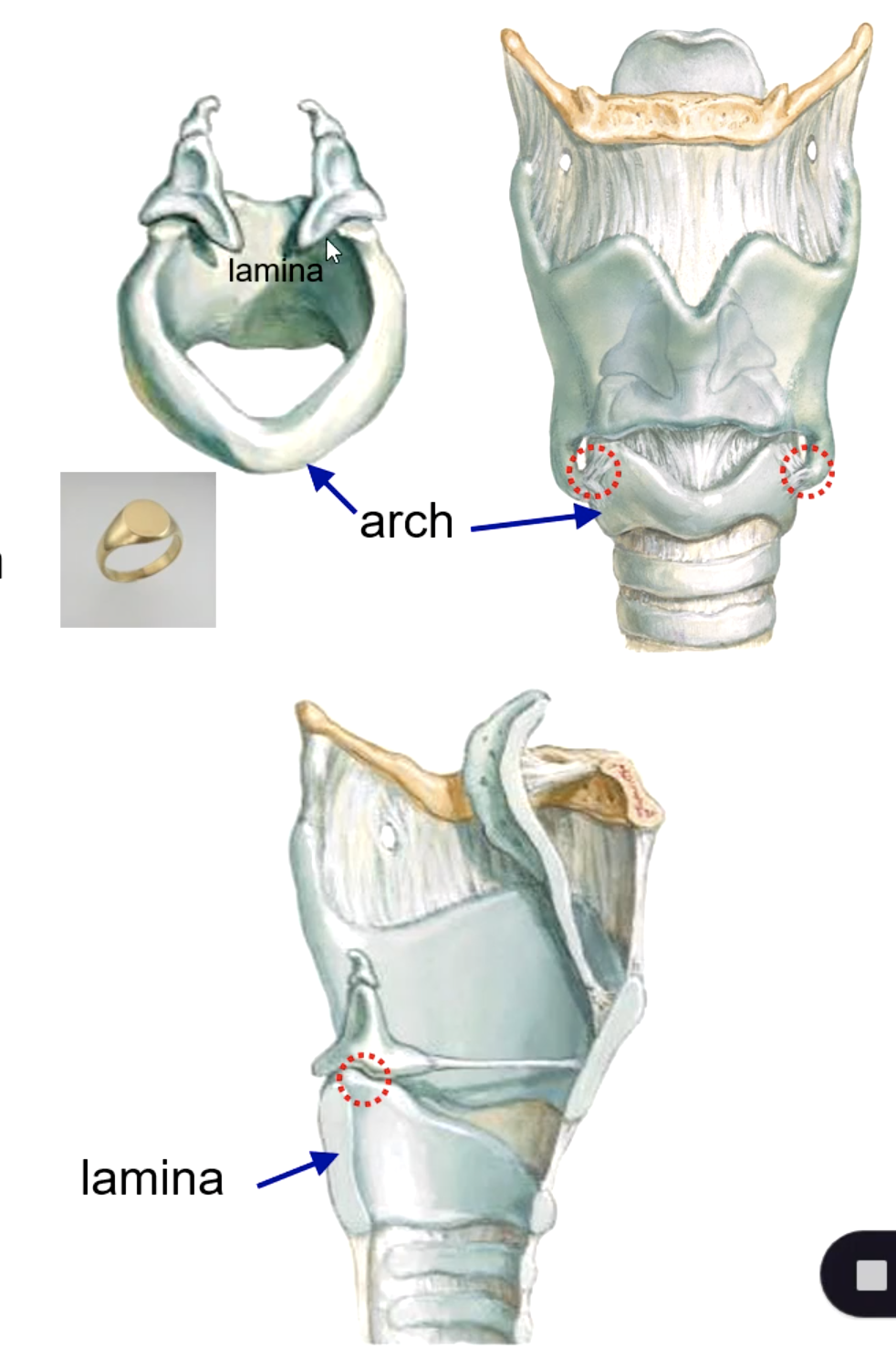
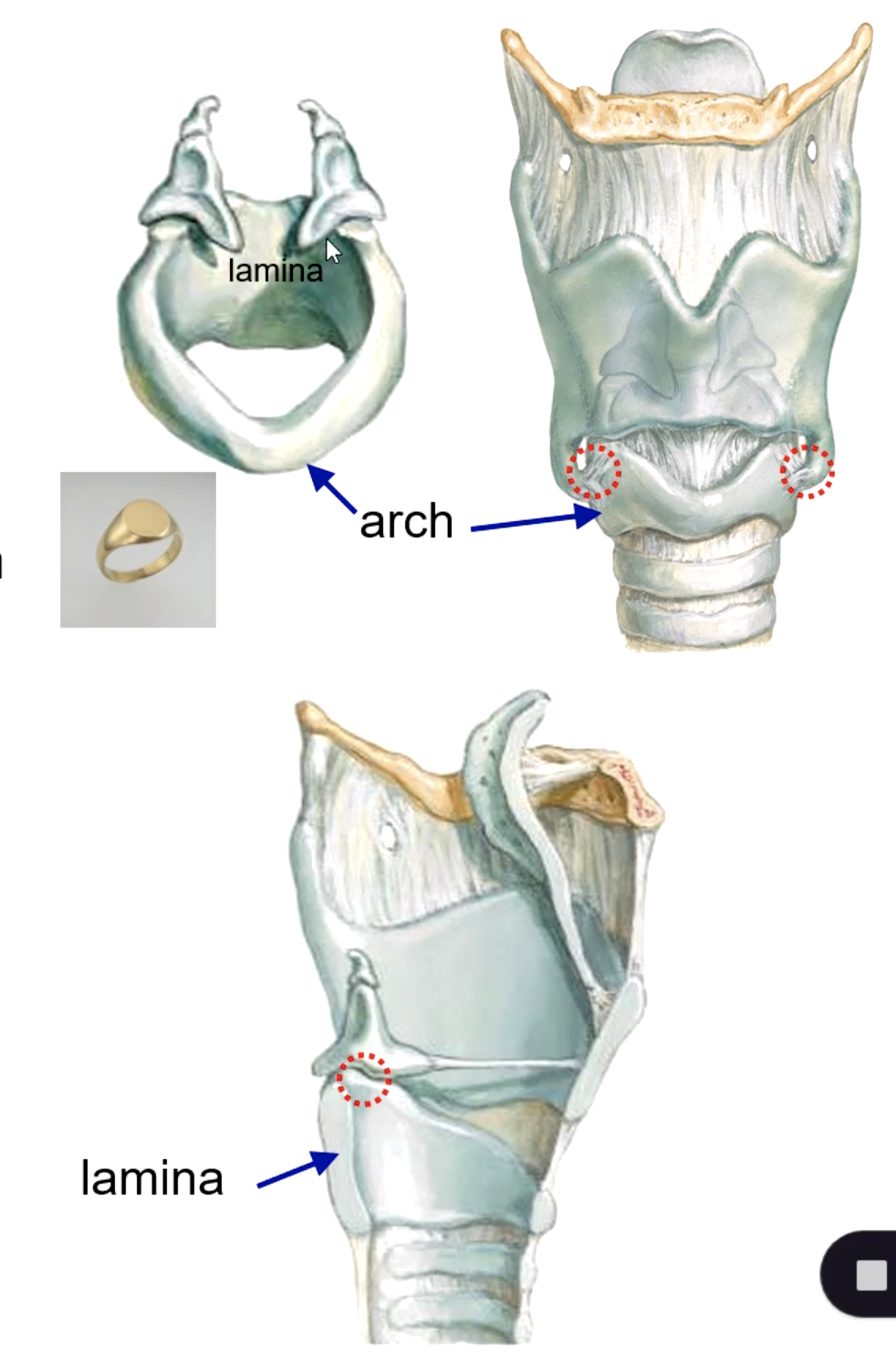
cricoid cartilage
which cartilage is the 1st and only complete tracheal ring?
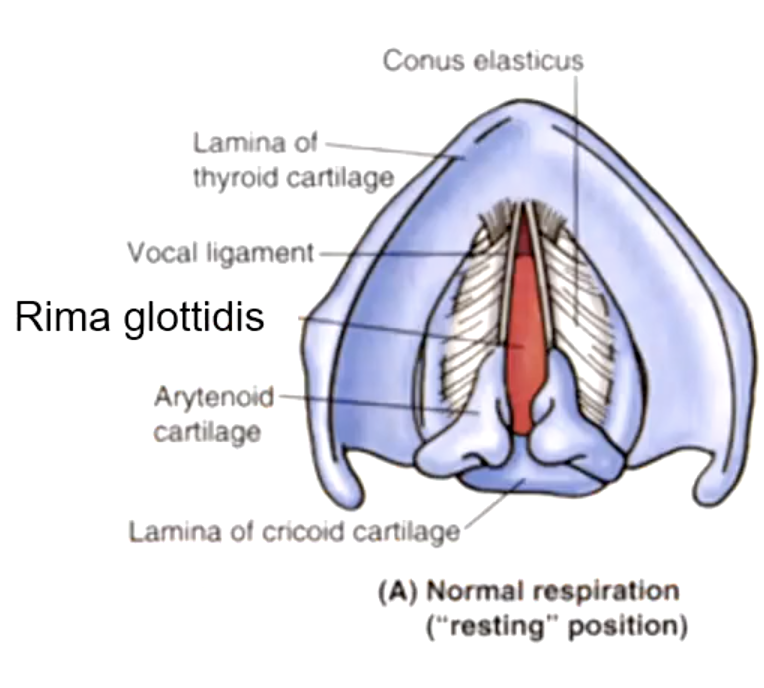
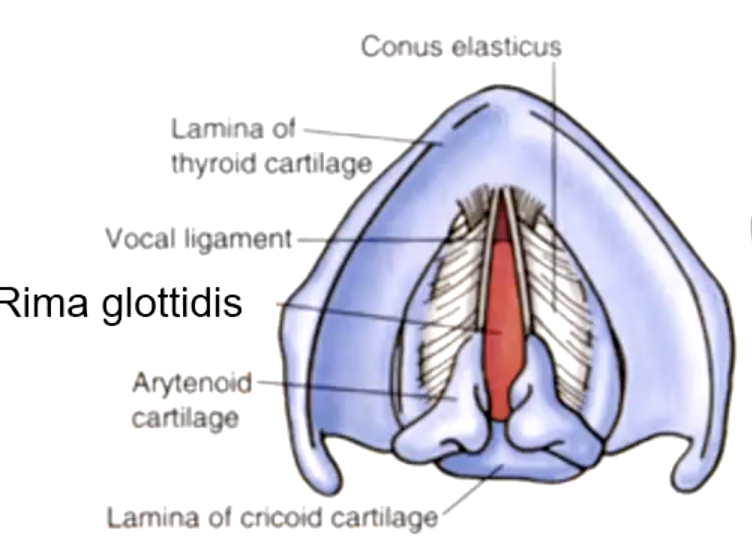
arytenoid cartilage (synovial joint)
the upper border of the cricoid cartilage articulates with the:
cricoid cartilage
identify the structure:
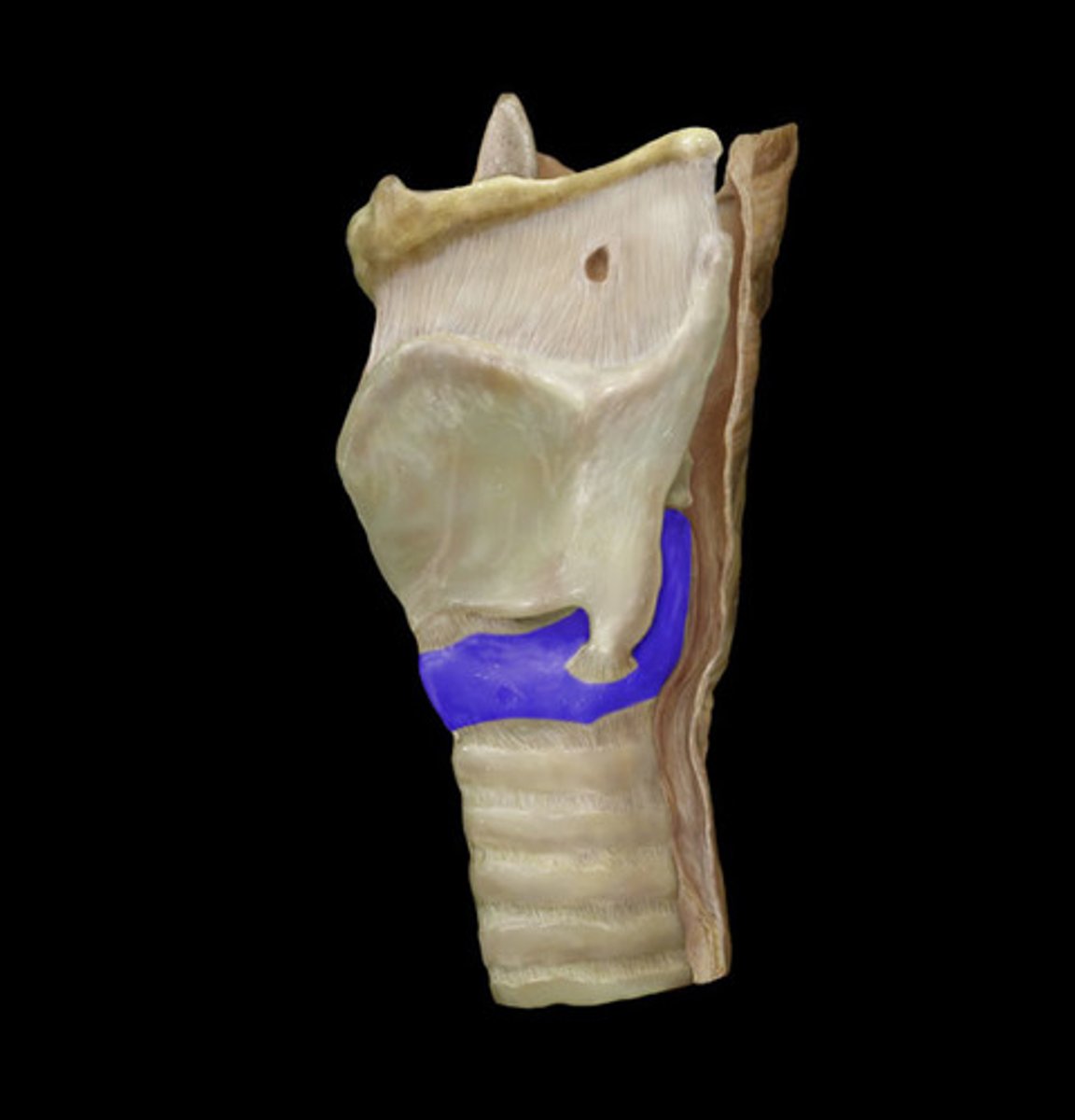
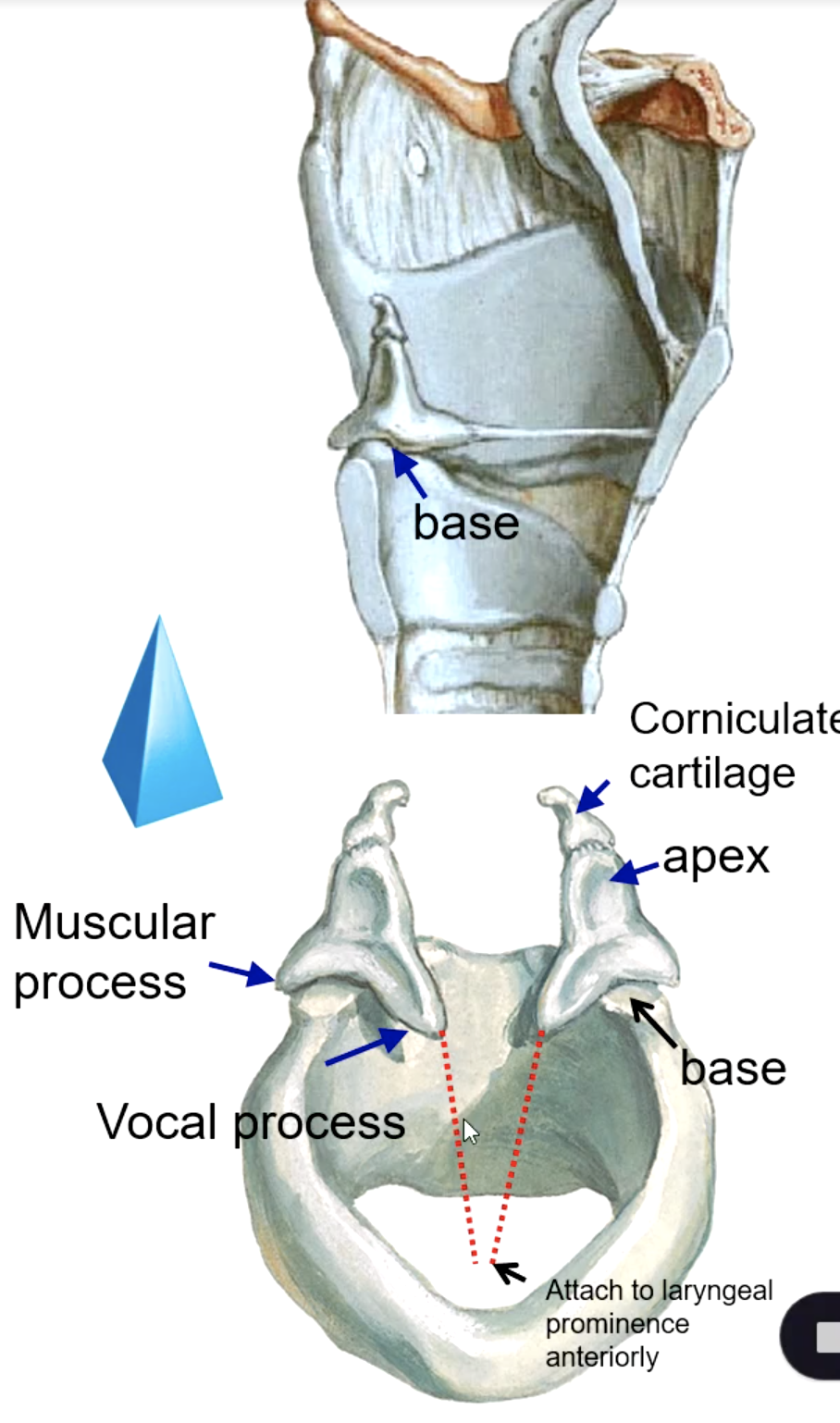
arytenoid cartilage
identify the structure:
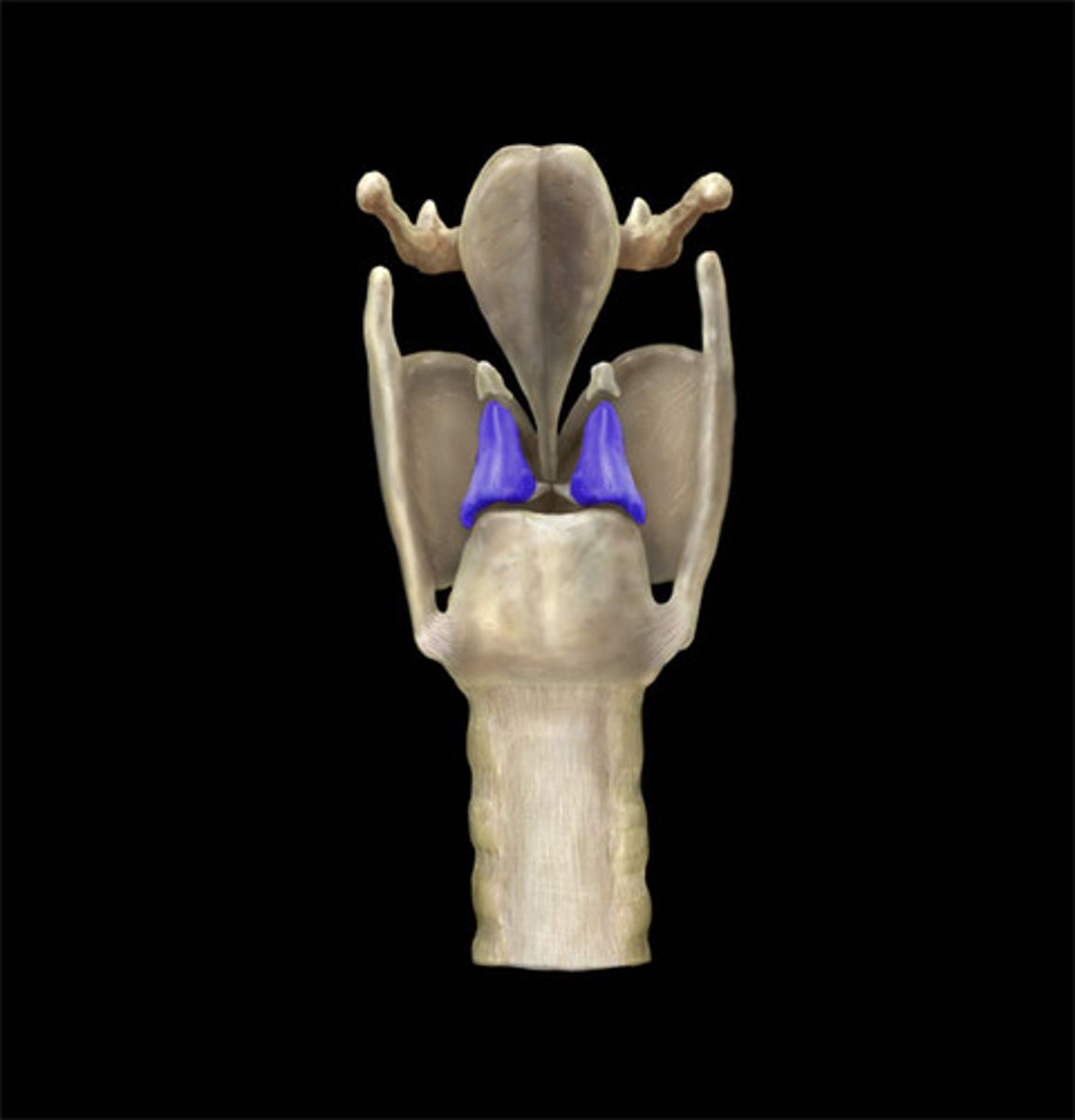
cricoid cartilage
the arytenoid cartilages sit on the posterior aspect of the:
cricoid cartilage
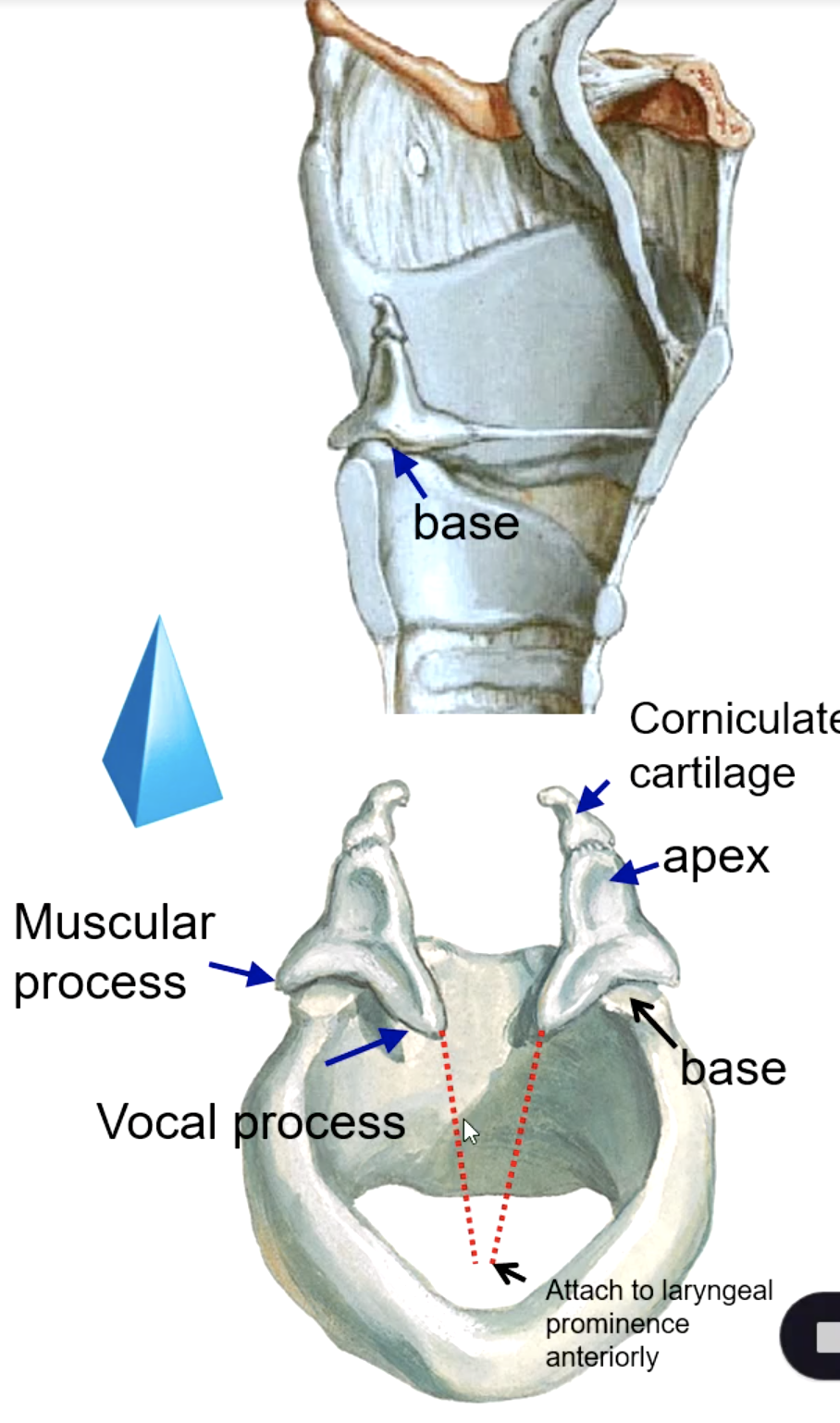
the base of the arytenoid cartilage articulates with what structure?
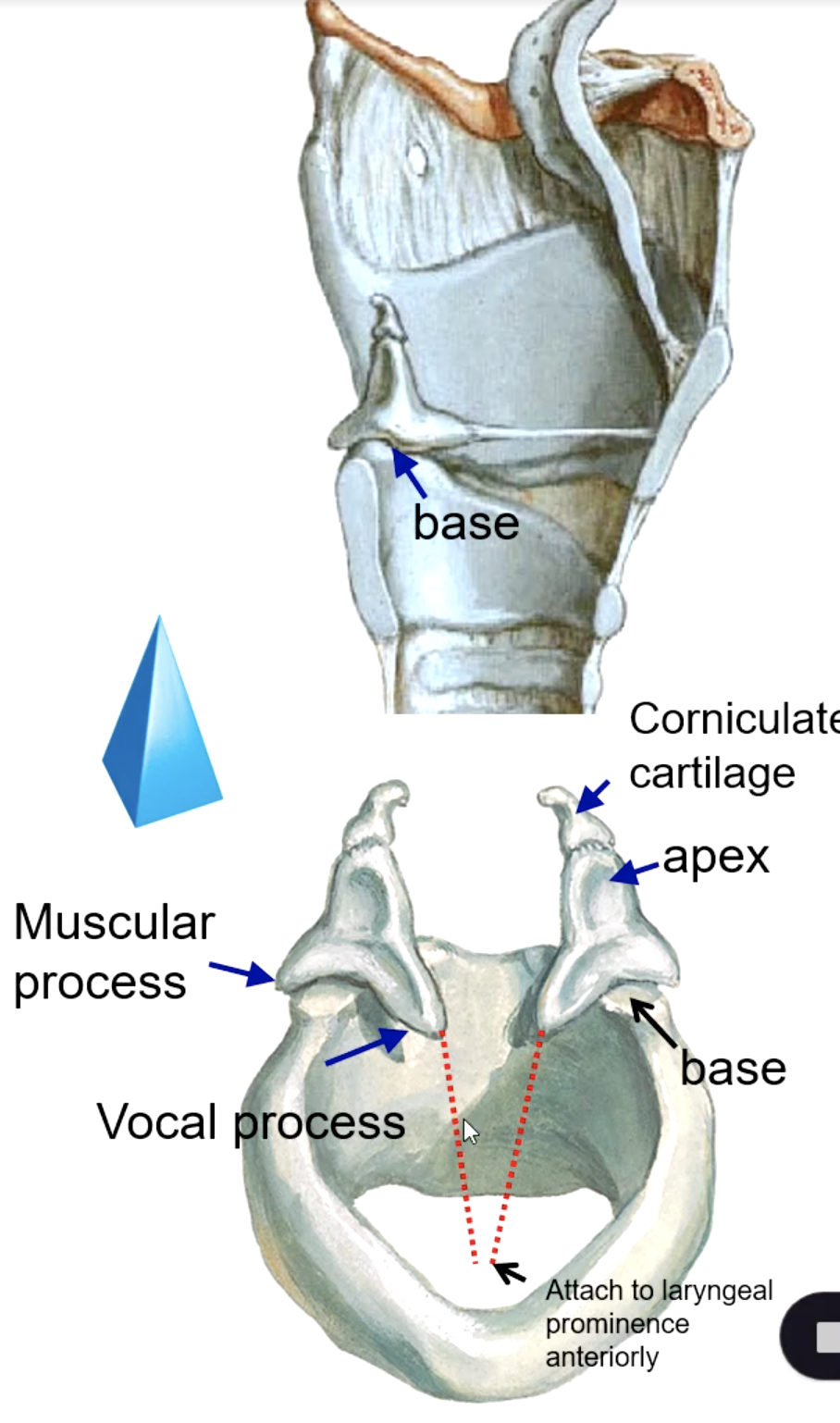
corniculate cartilage
what structure sits on the apex of the arytenoid cartilages?
corniculate cartilage
identify the structure:
vocal process
the base of the arytenoid cartilage that give attachment to the vocal ligaments medially:
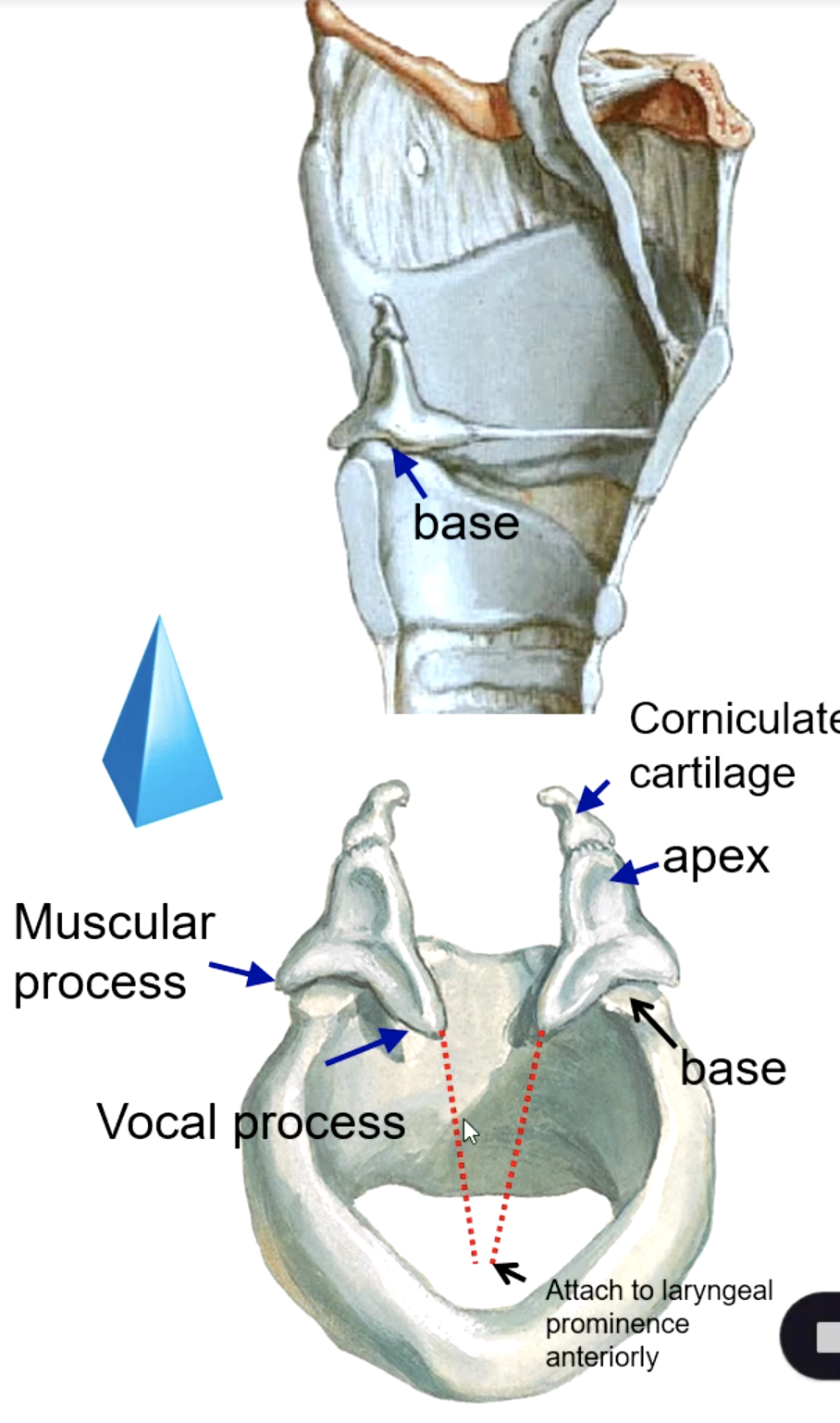
muscular process
the base of the arytenoid cartilage that give attachment to muscles laterally:
lateral cricoarytenoid m.
what muscle attaches to the muscular process of the arytenoid cartilage?
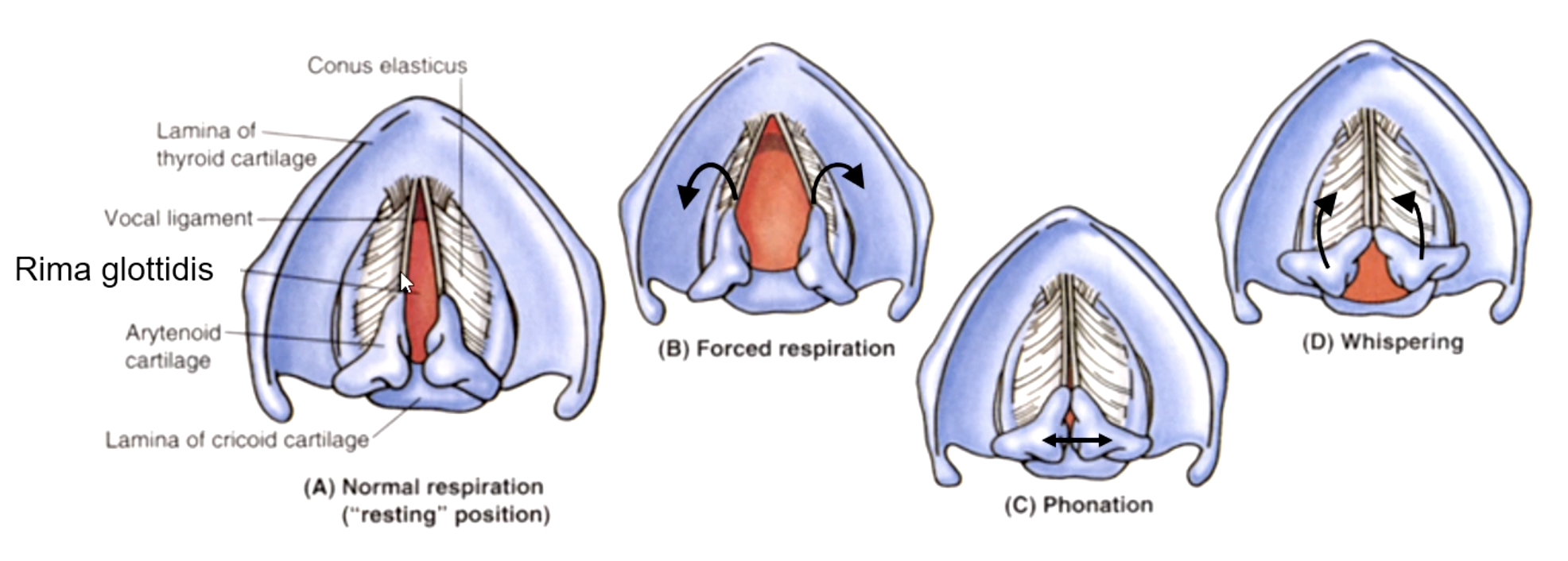
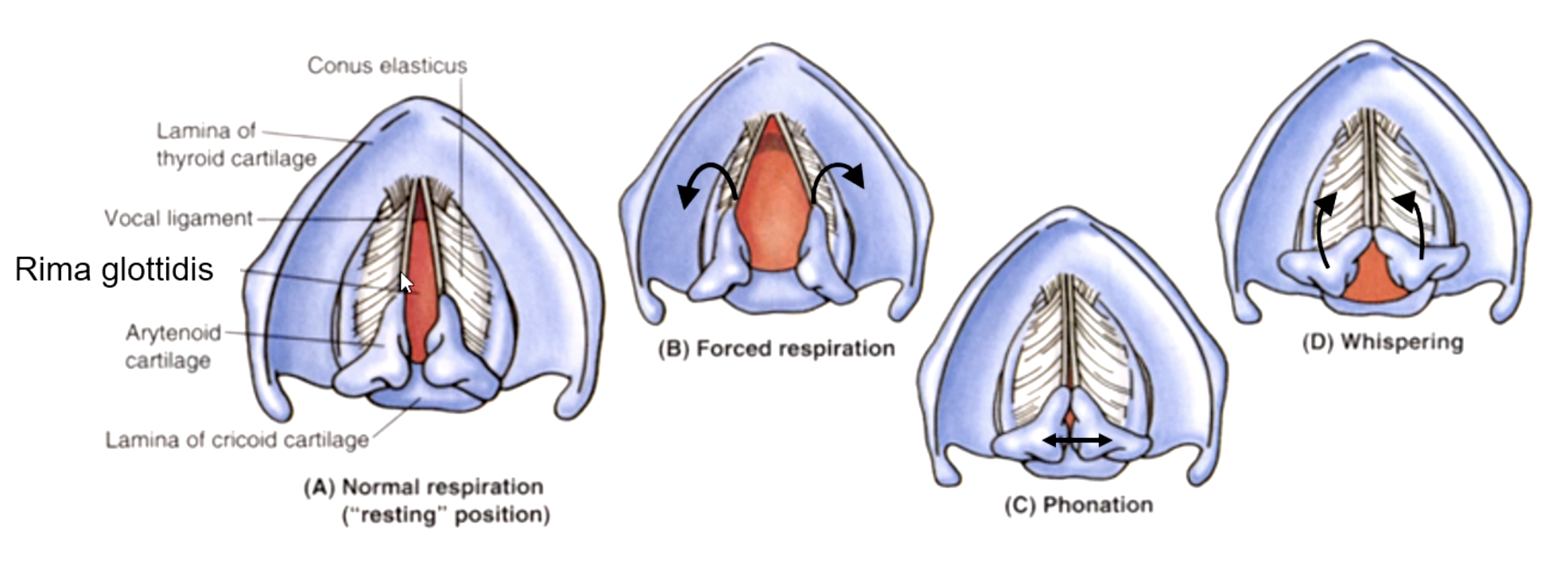
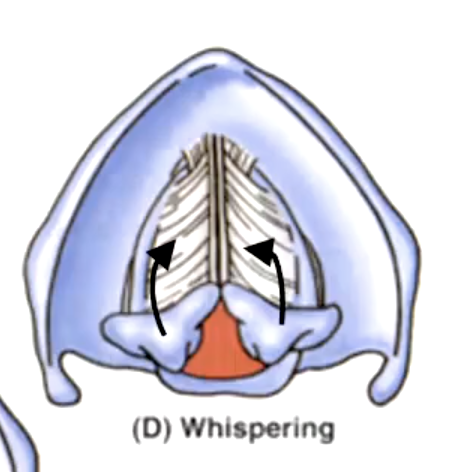
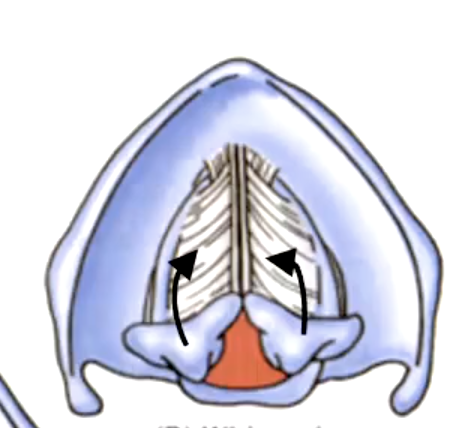
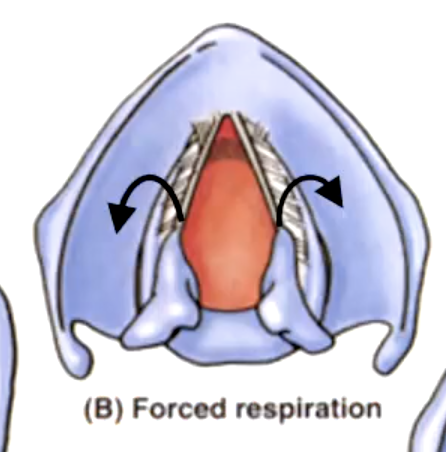
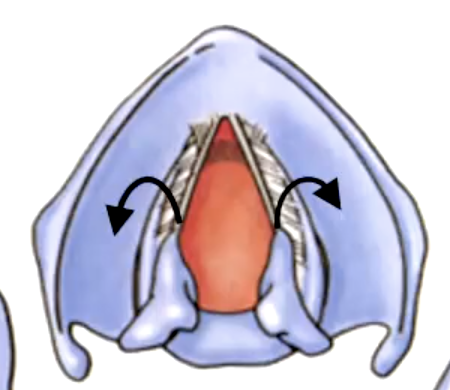
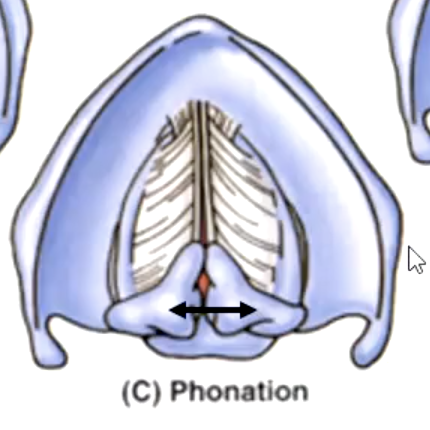
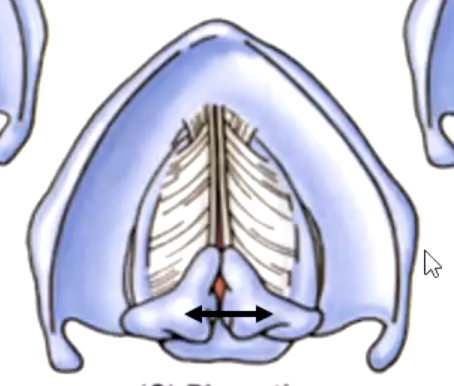
rima glottidis
the space between the vocal cords:
arytenoid cartilage
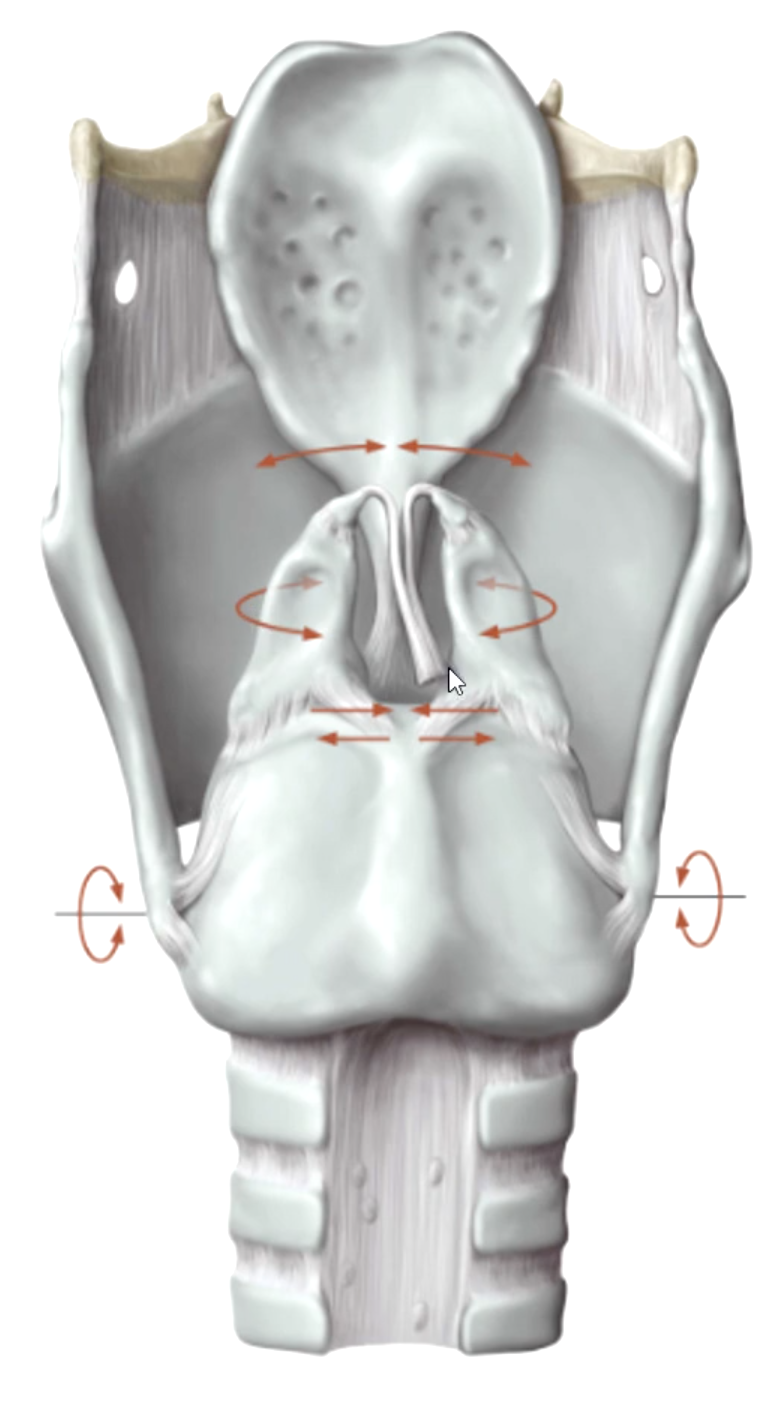
variation of the rima glottidis depends on the position of the:
False. they can slide toward/away, tilt anteriorly/posteriorly, rotate laterally/medially to bring vocal cords into abduction/adduction or to tense/relax the vocal cords$
T/F: the arytenoid cartilages are fixed on the posterior lamina.
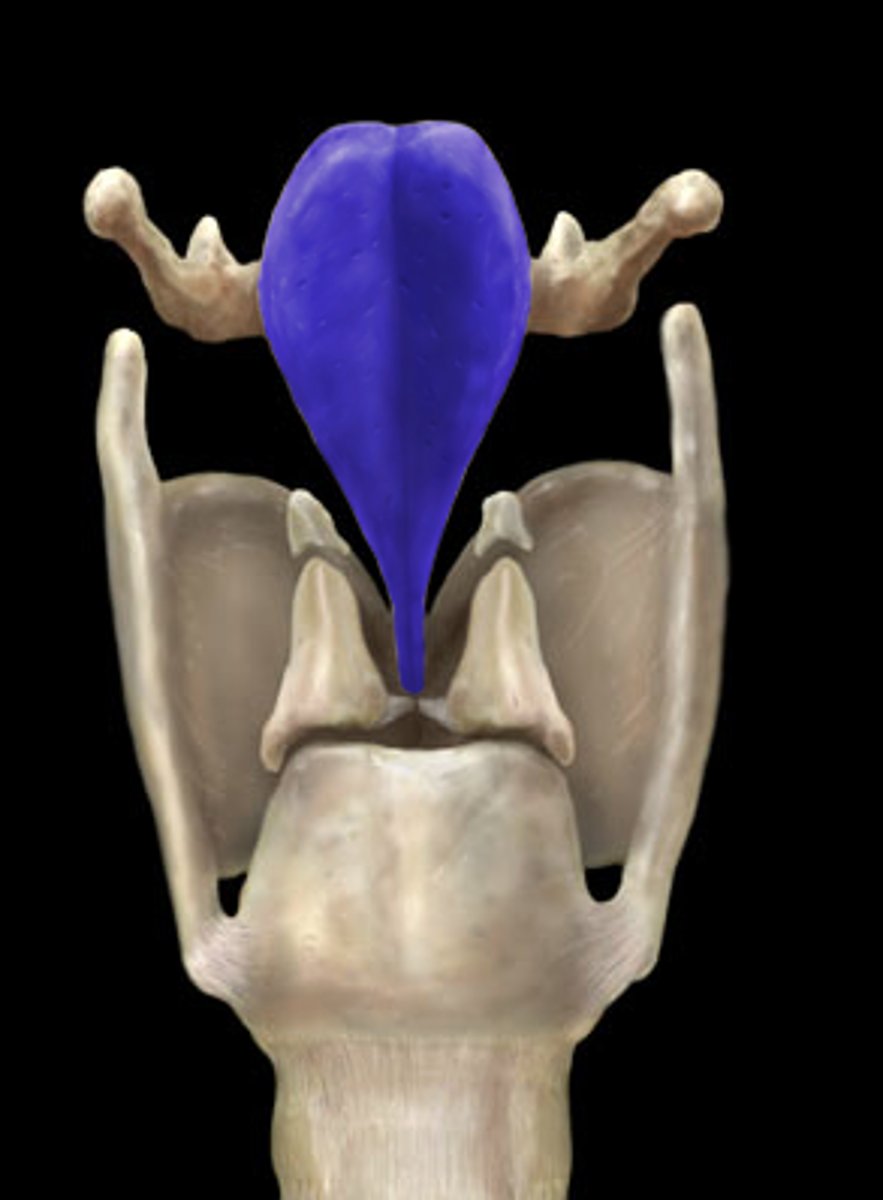
epiglottis
identify the structure:
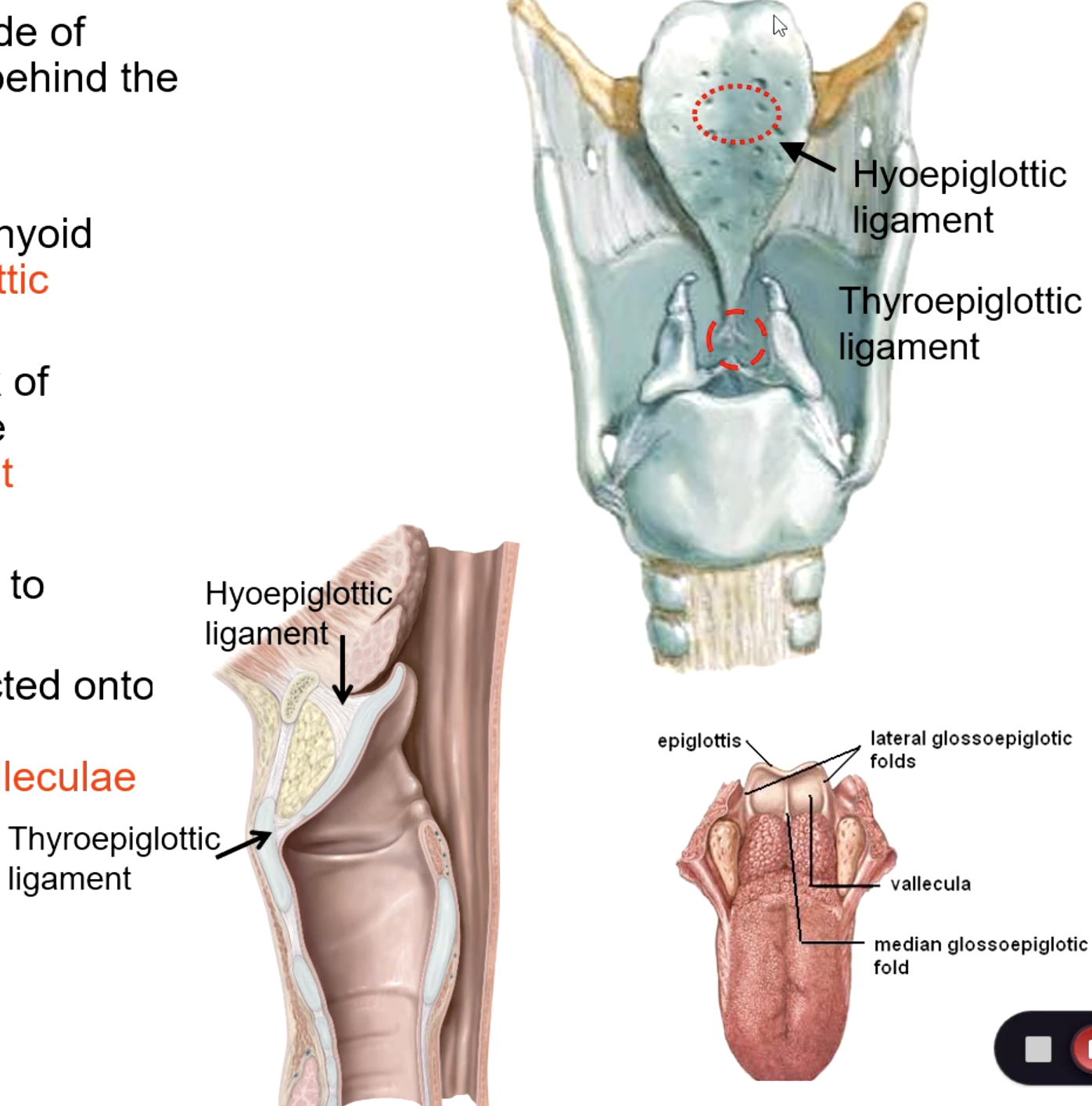
hyoepiglottic ligament
what connects the epiglottis to the hyoid bone:
thyroepiglottic ligament
what connects epiglottis to thyroid cartilage
vallecula
space between posterior portion of tongue and epiglottis
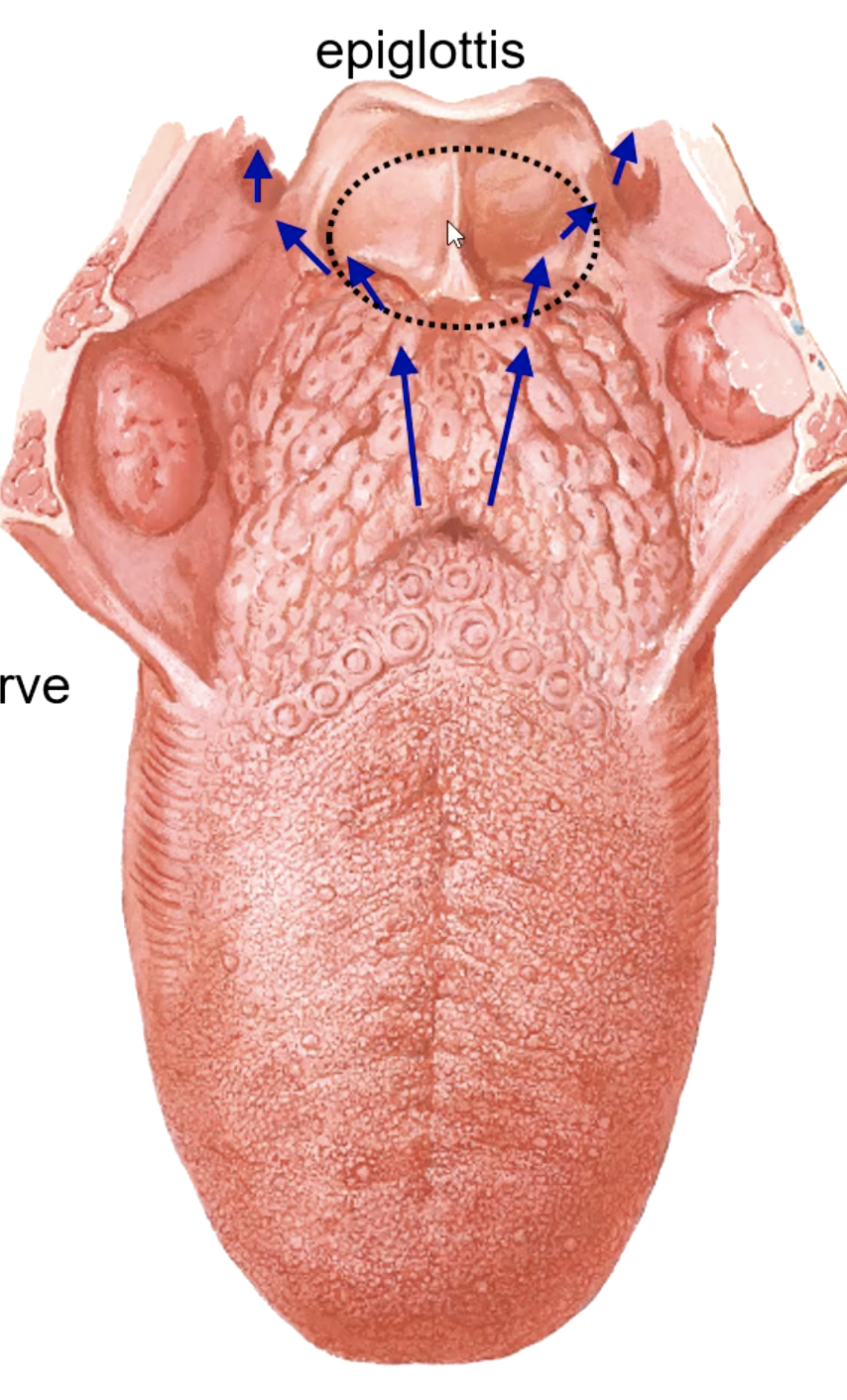
CN X
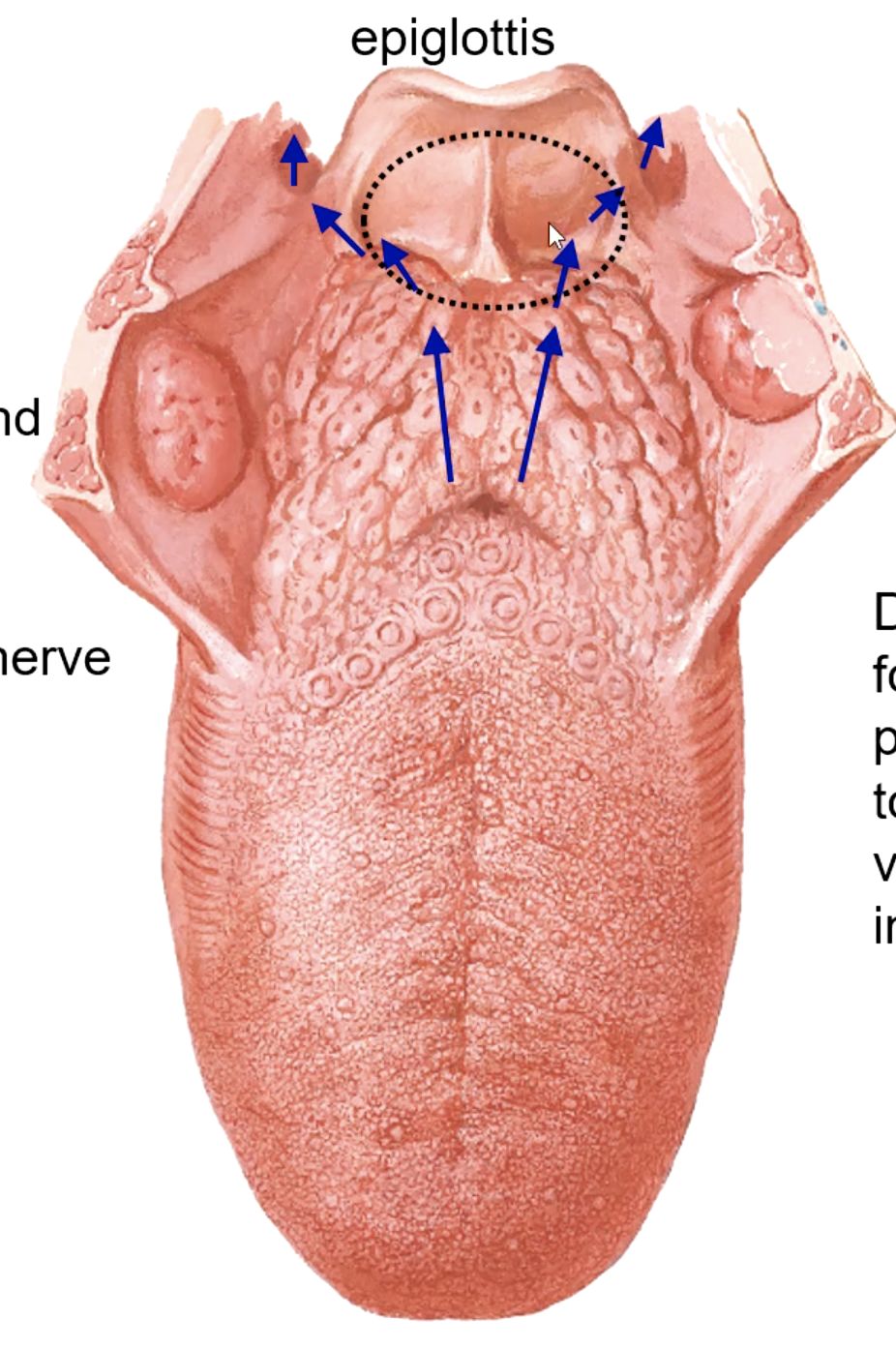
the taste buds located on the epiglottis are innervated by the:
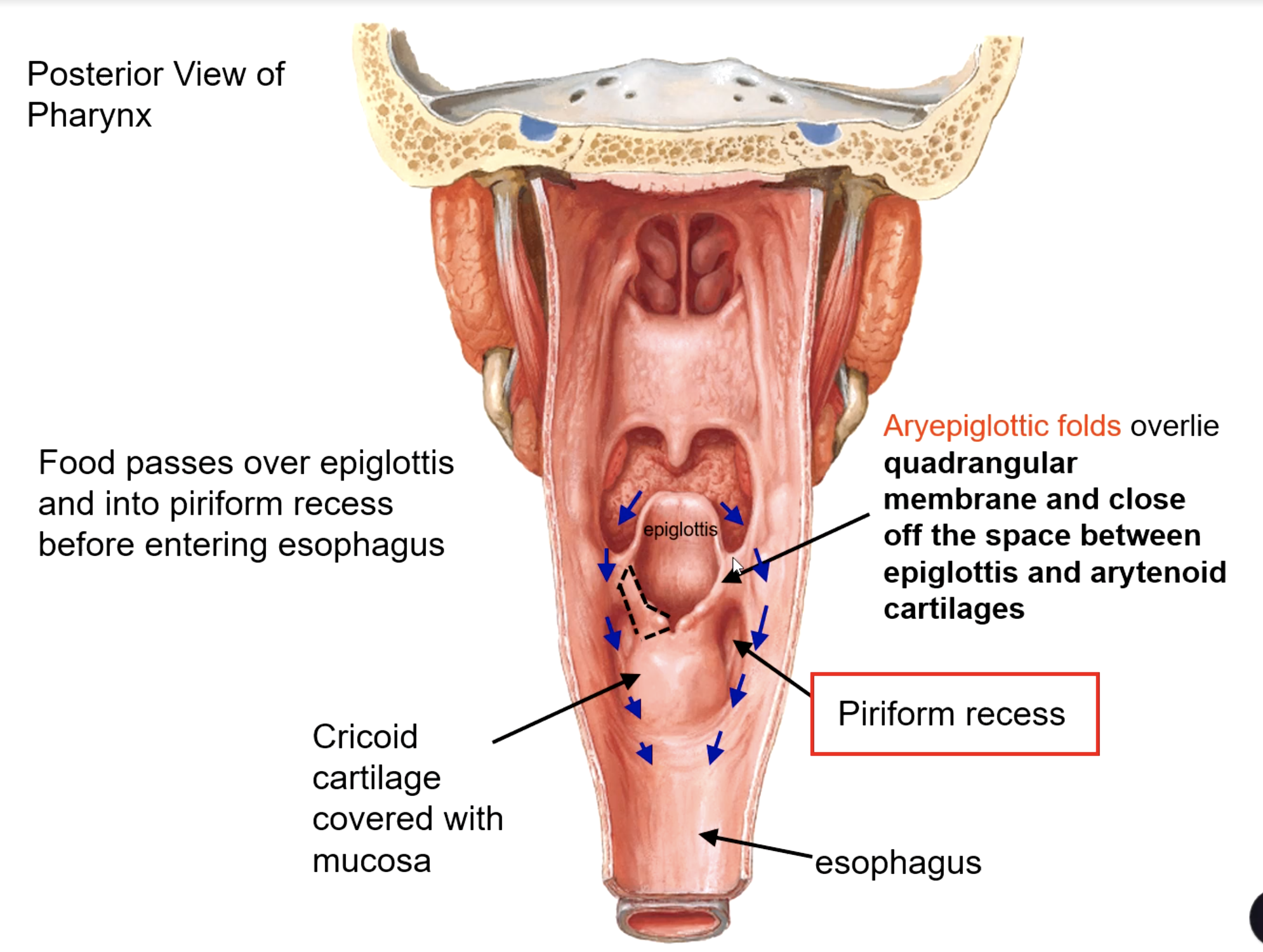
piriform recess
Food passes over epiglottis and into the _______ before entering esophagus
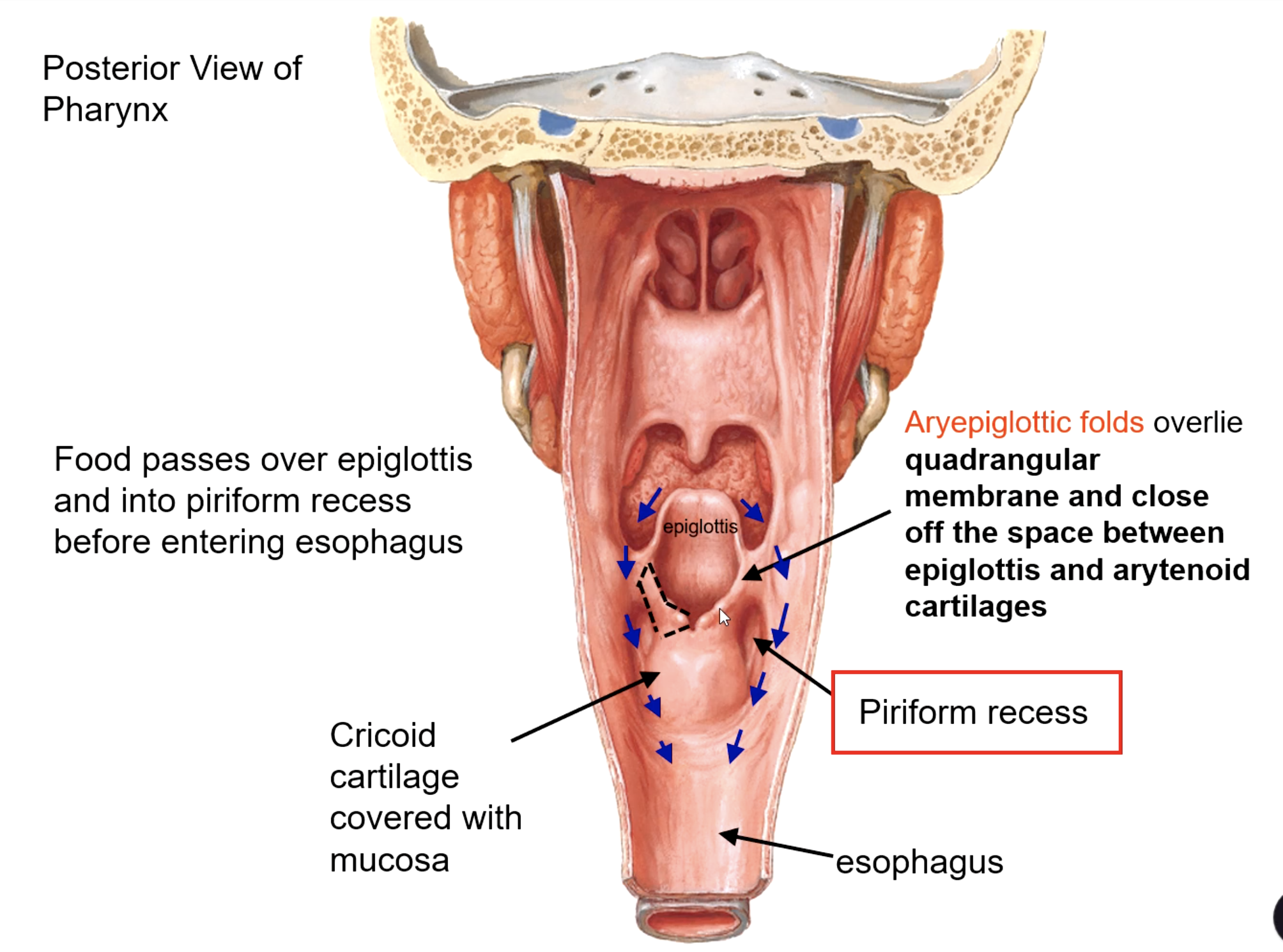
aryepiglottic folds
this structure overlies quadrangular membrane and close off the space between epiglottis and arytenoid cartilages
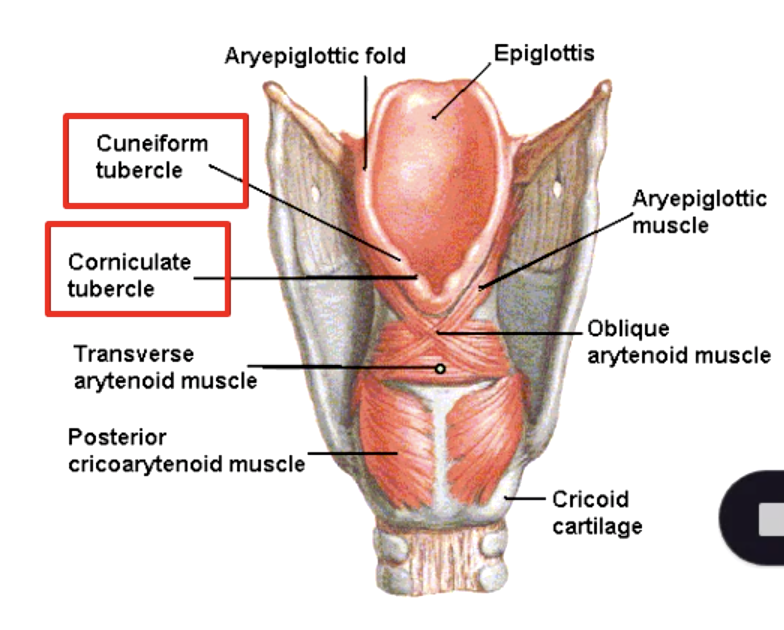
cuneiform cartilage
which cartilage does not articulate with any other cartilage?
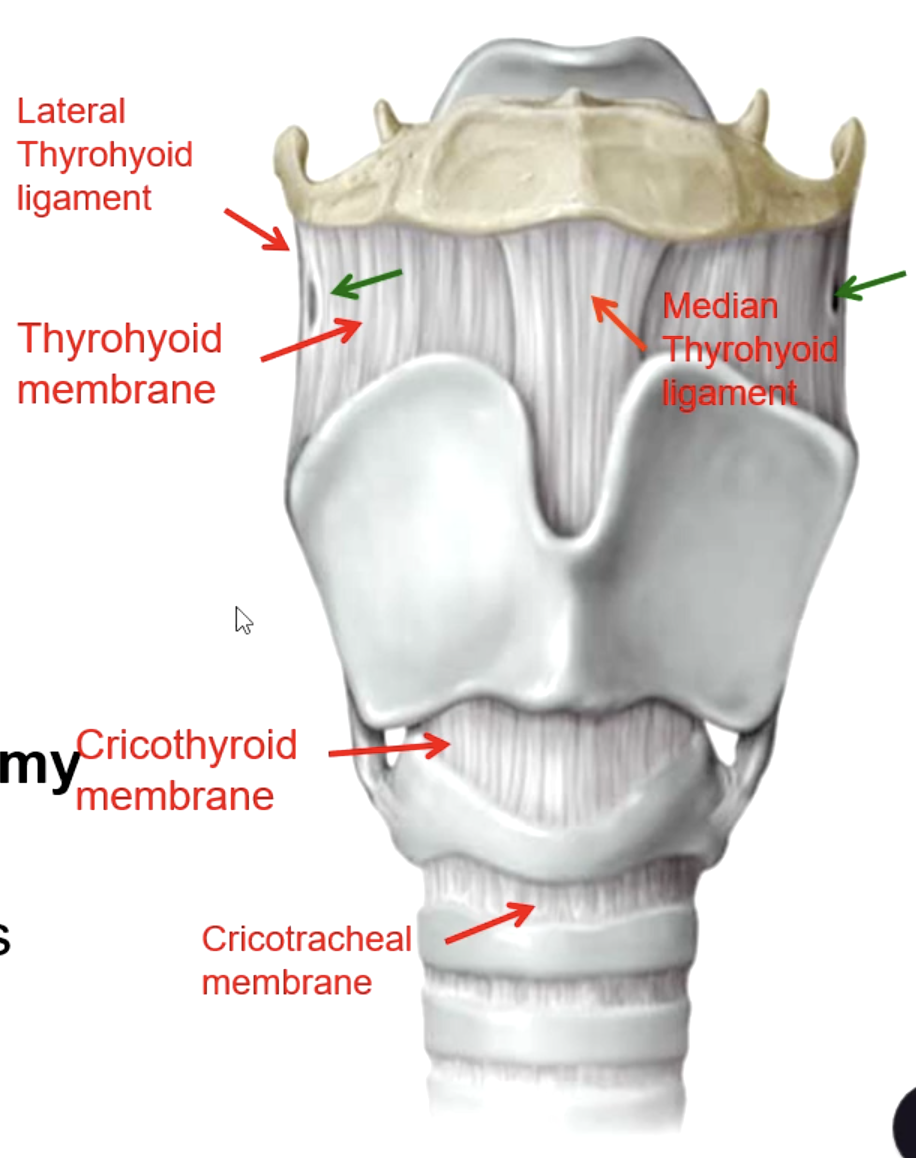
cricothyroid membrane
patient presents with the inability to breath. Everything else has been unsuccessful, but you do know the obstruction is near the vocal cords. What structure must be pierced to perform a cricothyroidotomy?
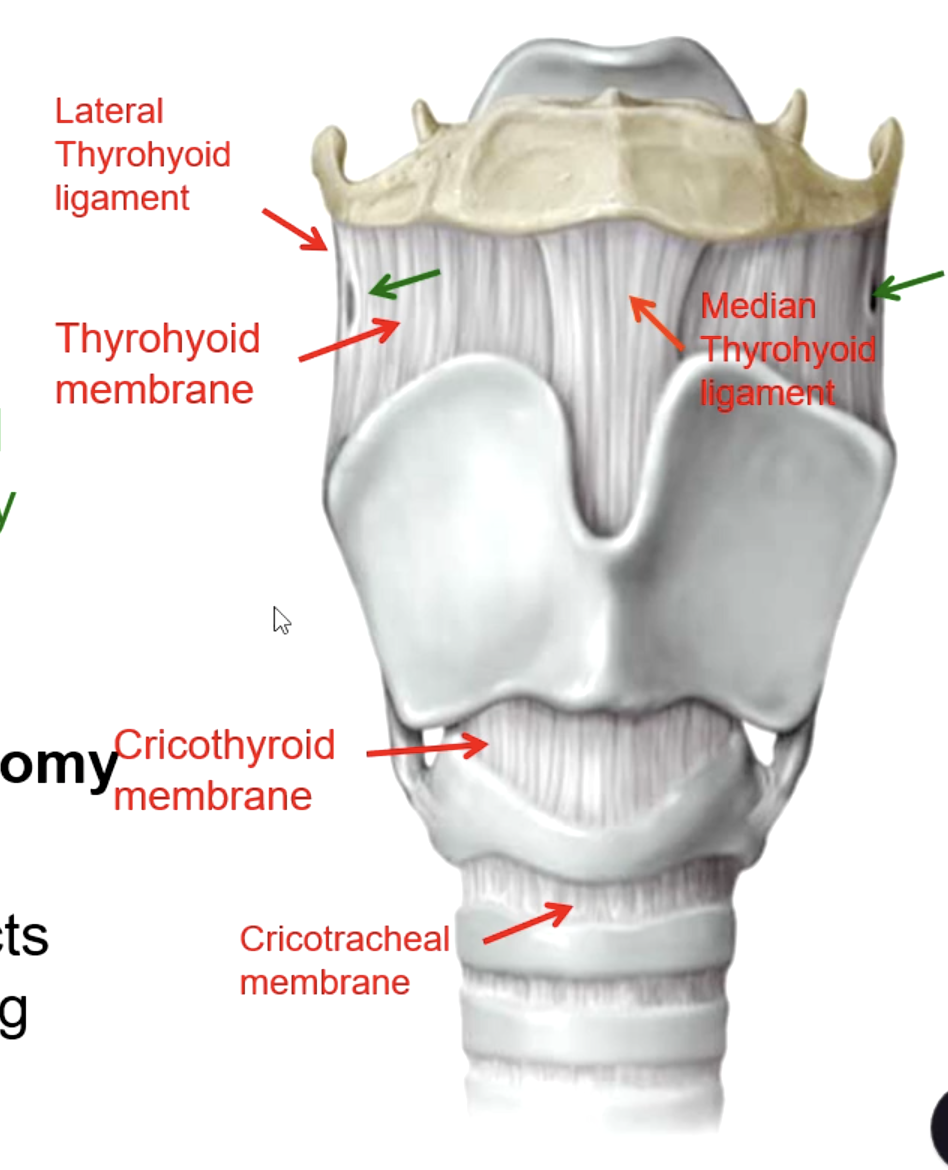
cricotracheal membrane
if you needed to perform a tracheotomy, what structure must you pierce?
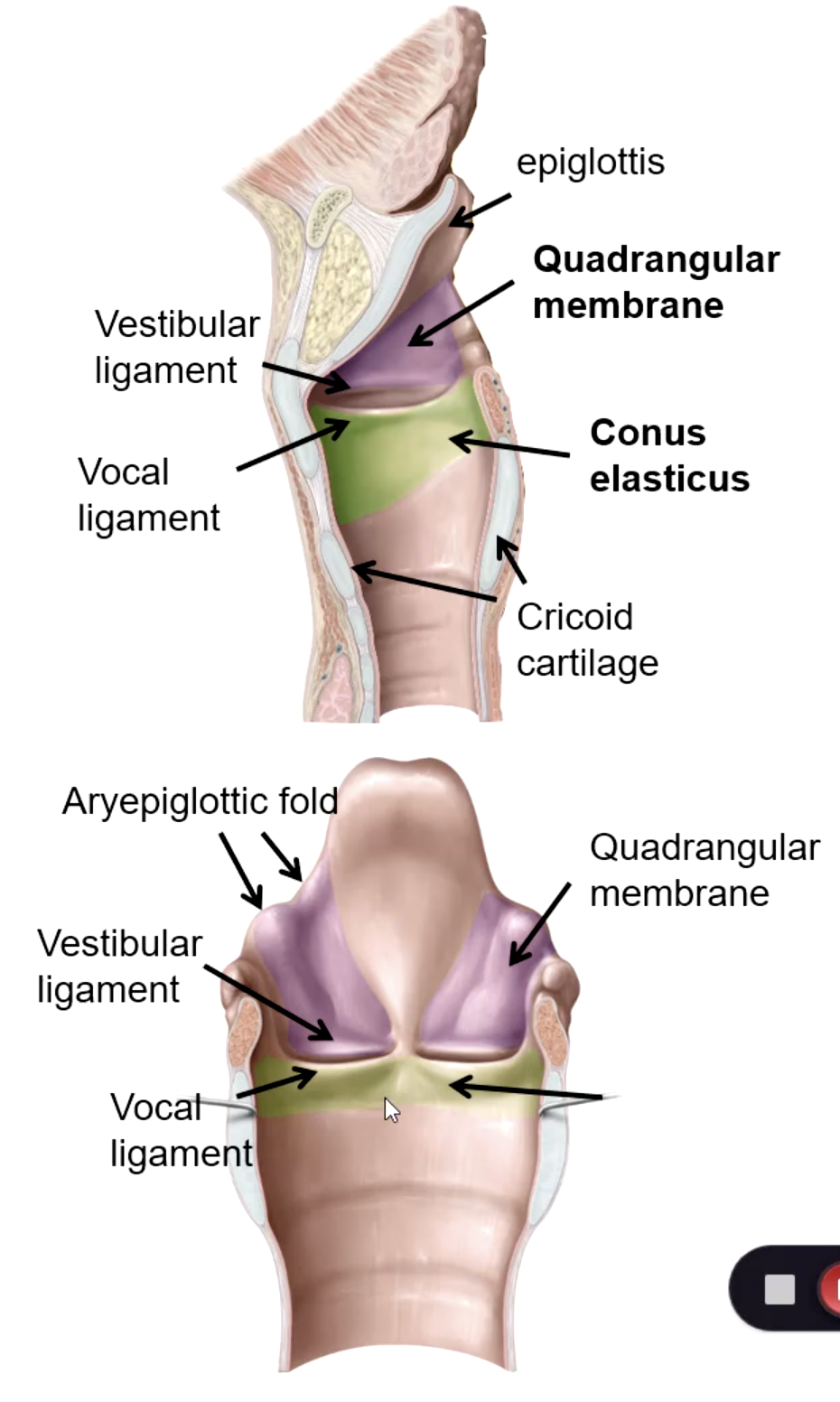
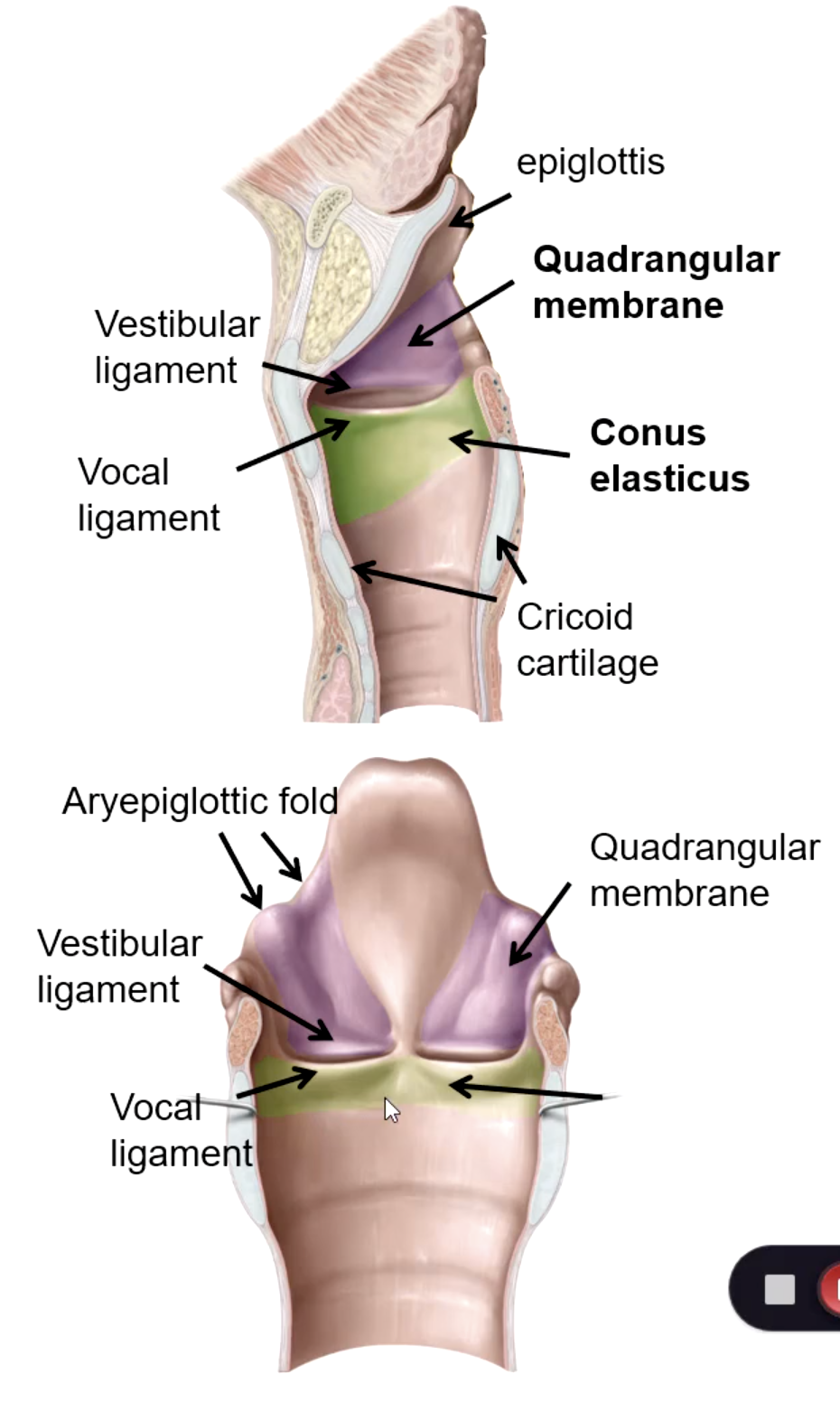
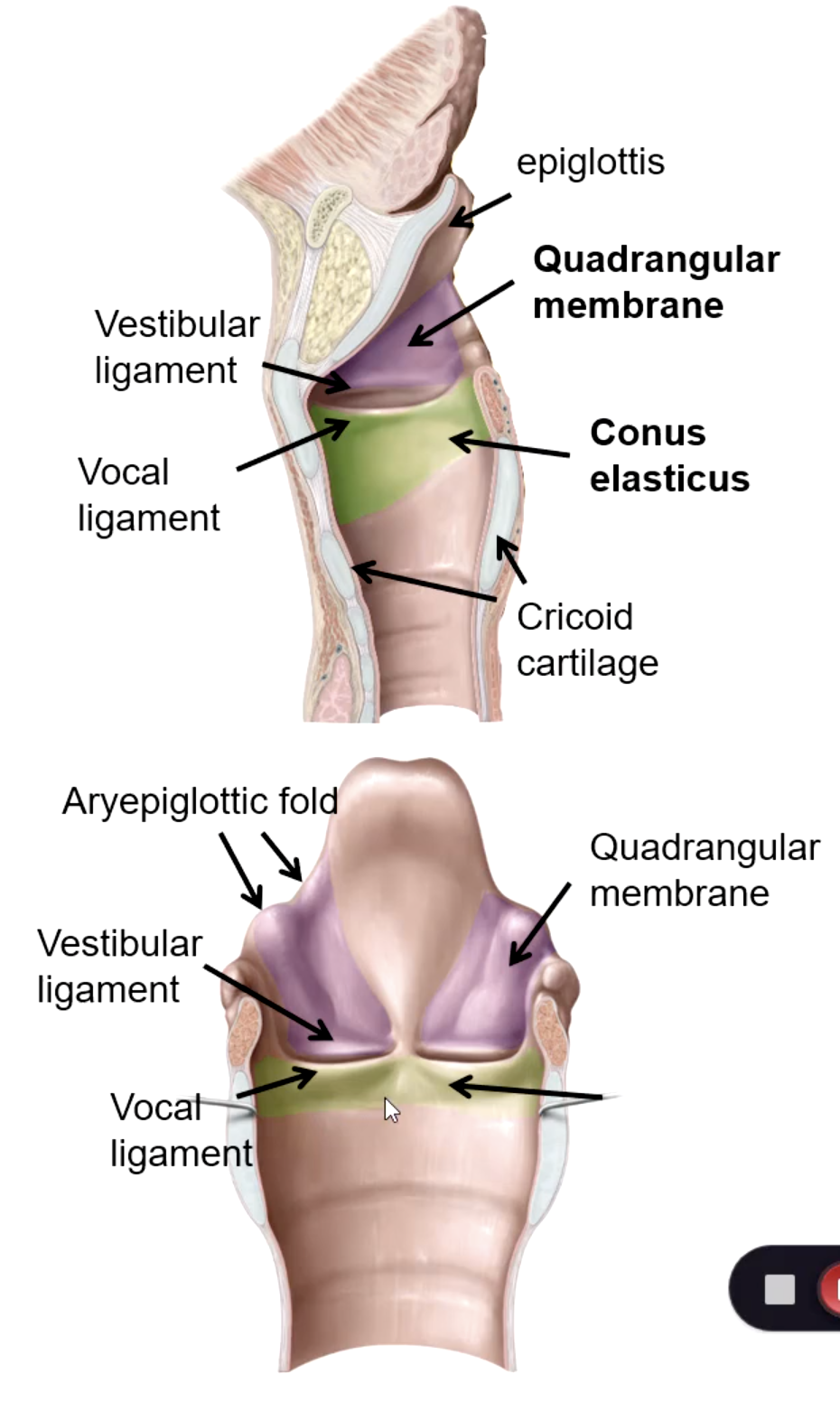
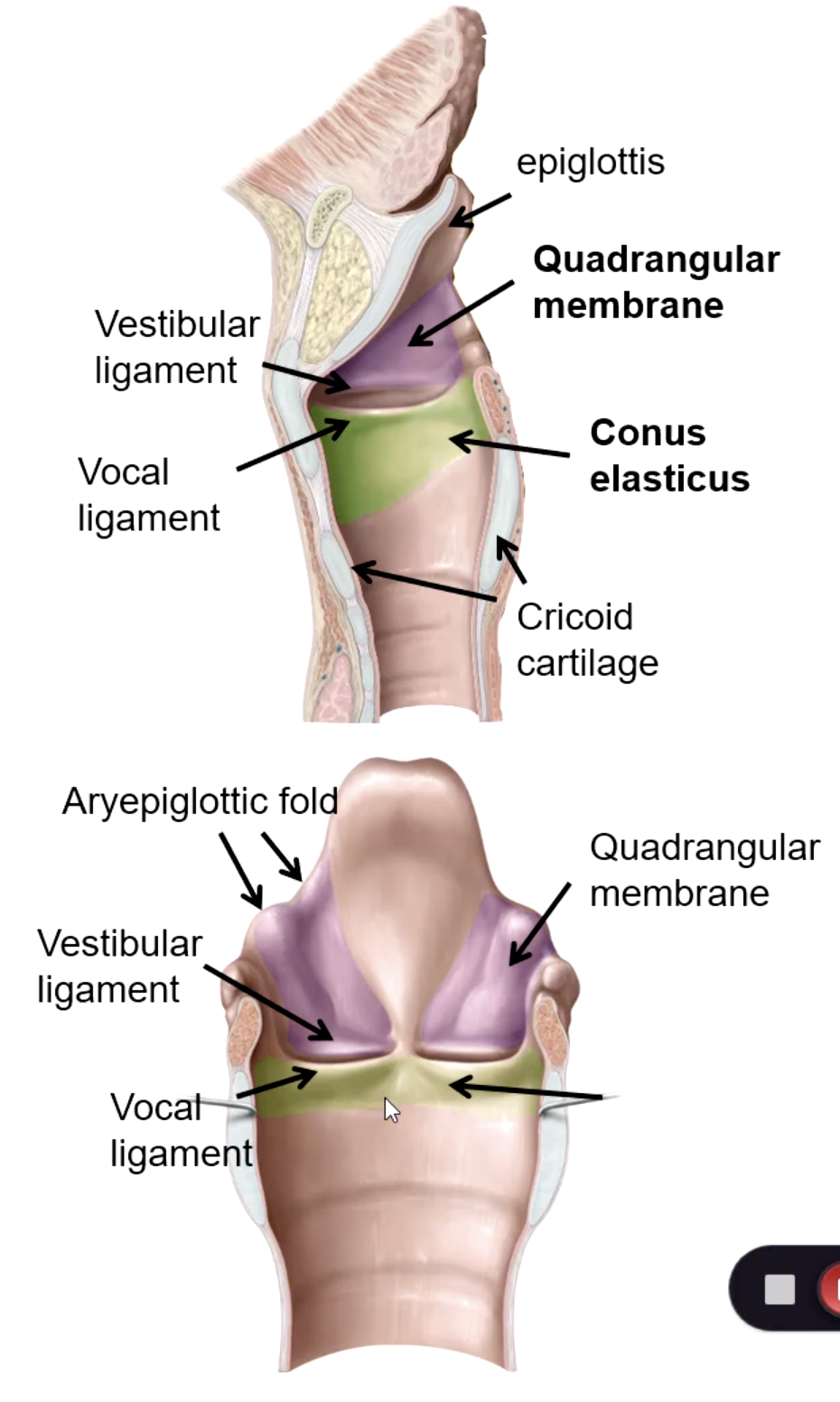
quadrangular membrane
Extends between the epiglottis and the arytenoid cartilages. Its lower free edge forms the vestibular ligament
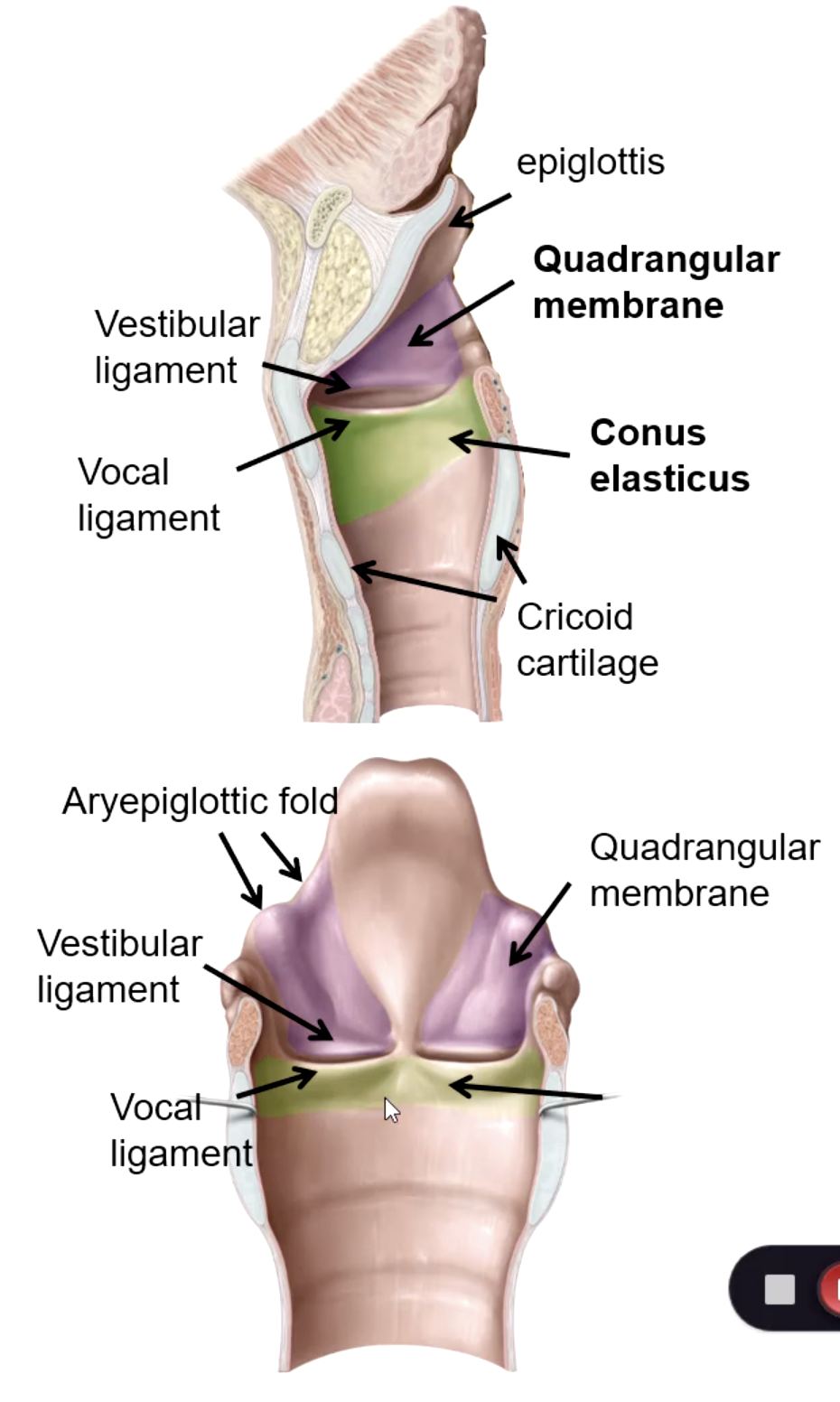
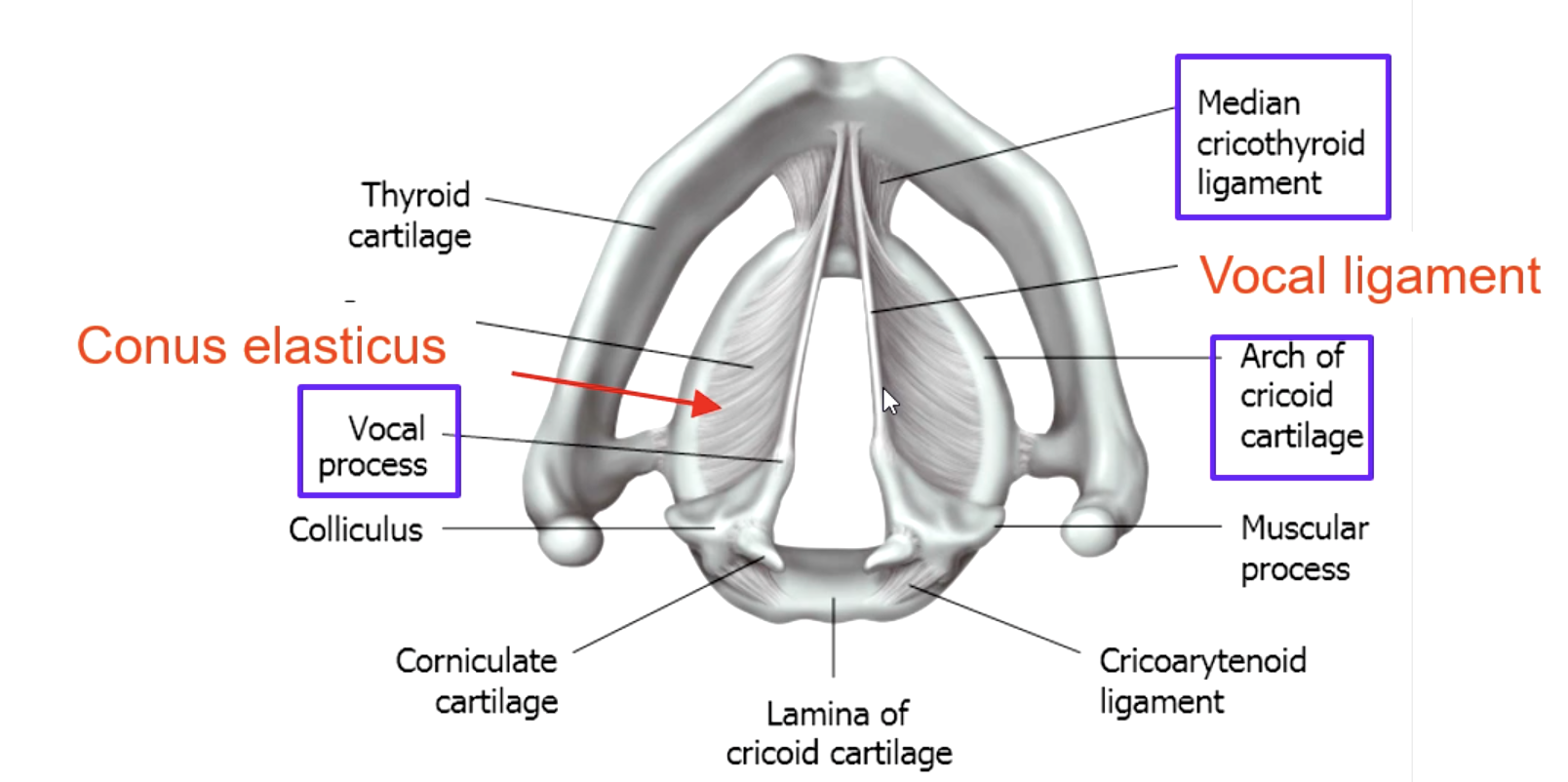
conus elasticus
Lower edge is attached to upper border of cricoid cartilage. Upper free edge forms vocal ligament
sound production
closed rima glottidis stops outflow of air
what are the functions of conus elasticus?
false vocal cords
the vestibular folds are considered the _________
true vocal cords
the vocal ligament is considered the ________
ventricle
area between true and false vocal folds
thyroarytenoid m.
vocalis m.
what two muscles form the vocal cords?
epiglottis
anterior boarder of the laryngeal inlet:
aryepiglottic folds
lateral boarder of the laryngeal inlet:
arytenoid cartilage
posterior boarder of the laryngeal inlet:
rima vestibuli
Narrow in the region of the vestibular (false) folds: