Decision Making in Marketing Lecture 2, Chapter 12/13/14 - Cultural Characteristics
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Culture
Characteristics and knowledge of particular group of people. Encompassing language, religion, cuisine, social habits, music and arts.
Adopted through socialization
What does culture shape?
Norms = Collective decision about what is appropriate behavior
(Core) Values = What is good and bad?
Behavior = Words and actions which are apparent to the casual observer
Interpretations = How we feel the core values should be reflected in situations in daily life
What is step of Consumer Decision-Making Process is affected by culture?
Need-Recognition: The consumer realizes they have a need or problem.
How does culture influence marketing? Ethnic Targeting
Marketers group people based on demographics, throwing them all in the same pot —> Simplification to cluster people around those demographics
More specific measures need Value Questionnaires —> Targeting sub-groups is costly and might sometimes harm your brand
Social Class
A status hierarchy in which individuals and groups are classified on the basis of prestige acquired through economic succes and wealth.
Objective indicators: Income, ownership, job
Subjective indicators: Own opinion (how you like the way someone speaks)
Social Class - Marketing
Social class is a natural form of segmenting consumers
Social classes differ in terms of
Distributional channels and promotional efforts that can reach them
Product attributes they care about/benefits they seek out
Norms and values
—> Need to match marketing mix to social class
Social Mobility
The degree to which social status can change within a culture
Upward social mobility = People rise in status
Downward social mobility = People fall in social status
Horizontal social mobility = Change in social situation that does not affect status
Expressed social status vs Actual social status
Expressed and actual social status is not the same
There are people who have high status need + high income who show off their money
There are also people who have low status need + high income who consume premium goods but quietly without showing off
And there are skeere people who have high status need + low income that buy counterfeits (nep merk) to show off.
Conformity
The tendency to behave as the group behaves
Brand-choice congruence
The likelihood that consumers will buy what others in their group buy
Compliance
Doing what someone explicitly asks you to do
Reactence
Doing the opposite of what the group wants us to do
Foot-in-the-door technique
Technique designed to induce compliance by getting an individual to agree first to a small favor, then to a larger one, etc.
Door-in-the-face technique
Technique designed to induce compliance by first asking an individual to comply with a very large request, then a smaller more reasonable request
Even-a-penny-will-help technique
Technique designed to induce compliance by asking individuals to do a very small favor (so small that it almost does not qualify as a favor)
Informational influence
The extent to which sources influence consumers simply by providing information
Consumer socialization
The process by which we learn to become consumers (value of money, spending vs saving)
Valence
Whether information about something is good or bad
Positive valence = good
Negative valence = bad
Viral marketing
Rapid spread of brand information among a population of people stimulated by brands, goal is to go viral. (Tiktok)
Tie-strength
The extent to which a close, intimate relationship connects people
Generational Cohort Theory
Theory that specifies that independent of age and period, generations share similar defining life events, and therefore long-lasting values and patterns of behavior.
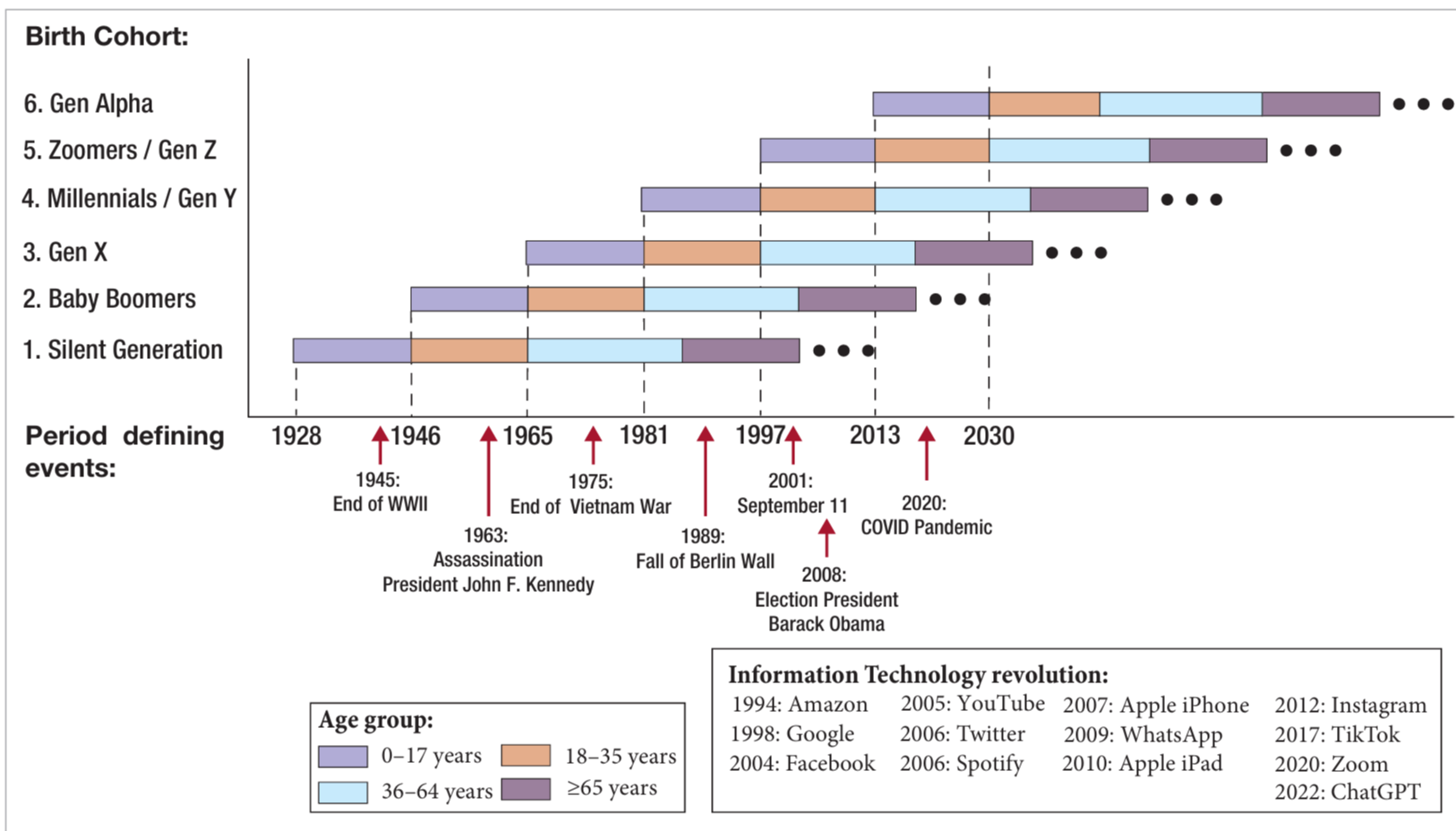
Gender
Behaviors that a given culture associates with a person’s biological sex
Sex
A person’s biological sex at birth
Gender identity
A person’s physchological sense of their gender
Communal goals
Goals that emphasize affiliation and fostering harmonious relations with others
Sexual orientation
Hetero, gay, non-binair etc.
Clustering
A statistical technique that groups consumers based on their common characteristics, such as demographics
Acculturation
Process of change in values, beliefs, behaviors, and identities of cultural groups
Bicultural consumers
These consumers identify with their cultural heritage and with their host culture (Chinees en NL)
Multicultural marketing
Marketing tactics that appeal to a variety of cultural groups at the same time
Accomodation
The more effort a source puts into communicating with a group, the greater the response by members an the more positive feelings
Trickle-down consumption
When products consumed by upper classes are adopted by lower classes
Trickle-up consumption
When products consumed by lower classes are adopted by upper classes
Trick-across consumption
When products are adopted by all social classes
Socioeconomics status SES
A consumer’s status in society compared and measured with others’
Subjective social status SSS
A consumer’s perceived relative social status in society
Conspicuous consumption
Buying and displaying services and products to show off their high status
Conspicuous compassion
Publicly donating to charity to signal one’s virtue (high moral)
Conspicuous waste
Visibly buying products and services that one never uses
Parody display
When status symbols start in the lower social classes and move upward.
Fraudulent symbol
Products/brands that become so widely adopted that they lose their status.
Compensatory consumption
Buying products to compensate frustrations or difficulties in life.
Psychographics
Description of consumers based on their psychological and behavioral characteristics, specifically, their personal values, personality traits, and lifestyles. Values, personality, and lifestyles
Value conflict
When a particular behavior is consistent with one or more of their core values but inconsistent with one or more of their other core values.
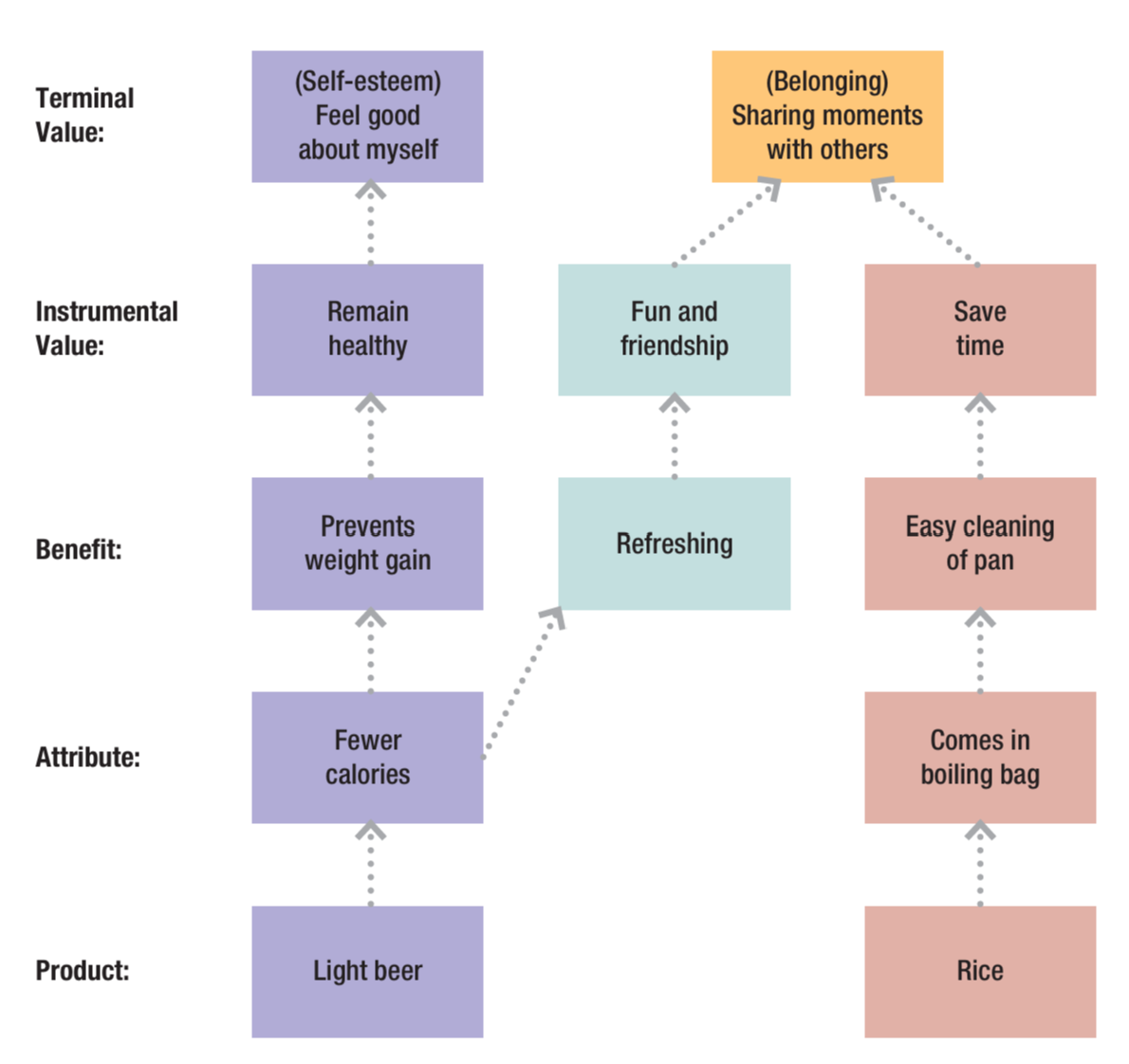
Terminal values
The desired end states such as equality and pleasure.
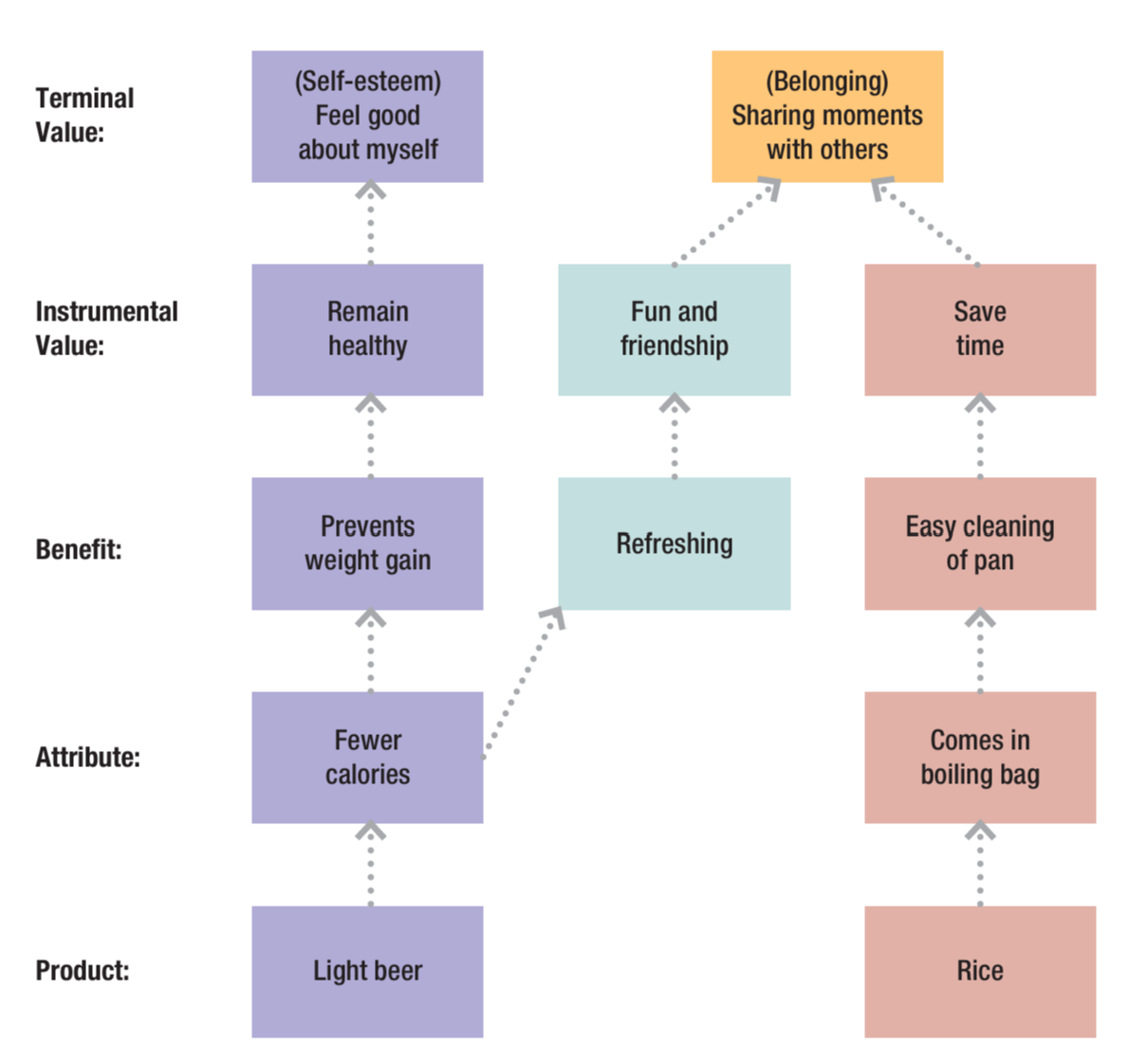
Instrumental values
Values that are needed to attain the desired end states.
Hedonism
The principle of pleasure seeking. Searching for gooods, services, experiences that make life enjoyable.
Value segmentation
Grouping consumers by their shared values and customizing marketing offeres based on these values
Means-end chain analysis
Describes how attributes of products and services link to the values of consumers
Rokeach Value Surves RVS
Survey that measures instrumental and terminal values proposed by psychologist Milton Rokeach
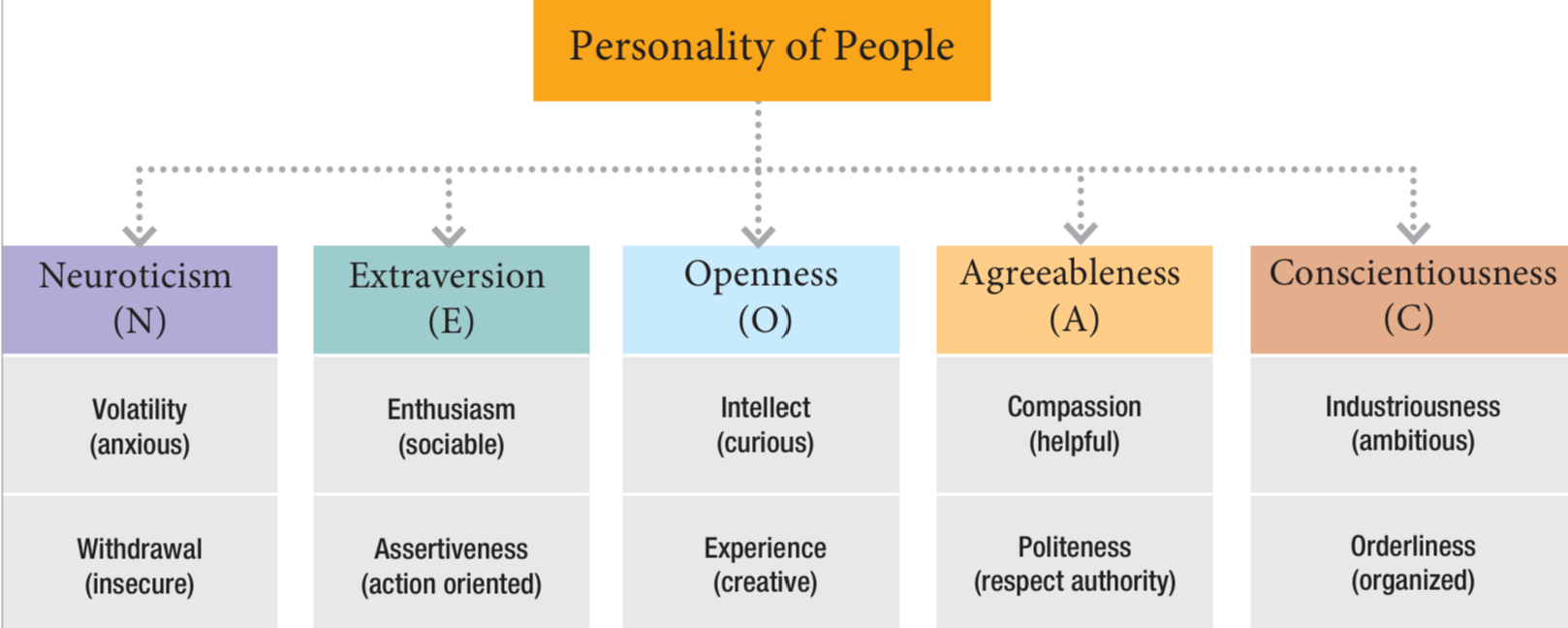
Big Five personality traits
Personality = Thinking and behavior that differentiate people from each other
Locus of control
How much control a person believes they have over the events in their life.
Political orientation
Set of beliefs that people have about the proper order of society and how it can be achieved