Genomes and DNA Replication
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
DNA polymerase are off to the races! - BI301
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is a Genome?
the entire compliment of an organism’s genes, but it’s limitation is that it won’t tell us what genes are being expressed at a given time; lets us look at genetic potential, organism’s relationships, virulence factors, antimicrobial targets
First genome sequence that was discovered? First genome from living organism?
RNA Virus MS2 (3569 bp); Haemophilus influenza (1.8 Mbp)
What does a genome sequence tell us?
Outlines the genetic potential for organisms, functions are assigned to genes (38.1% of e.coli has unknown functions)
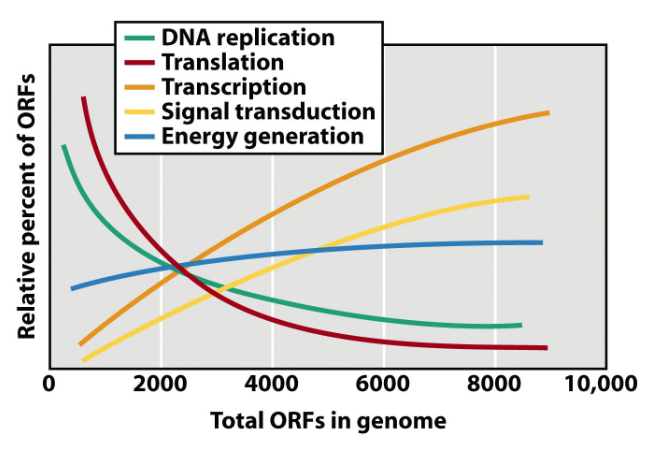
ORFs (“Open reading frames”)
gene sequence predicted to code for a protein; note the positive/negative correlations (ex. more genes = more signalling necessary in the complex organism)
Characteristic of Bcaterial Chromosomes
Most are circular and covalently closed, cells are haploid (one copy of each gene), DNA is in nucleoid, one origin of replication, Most of DNA sequence codes for proteins
Flow of Biological Information
DNA→mRNA→Protein (aka. gene expression or Central Dogma)
Topoisomerases
Cause DNA packaging and condensation
Supercoiling/Chromosome Packaging in Nucleiod
A nick is made in a single strand of the nucleoid domain, supercoiling relaxes and DNA stretches; this is a back and fourth process
Replicating the Chromosome
Goal is to generate 2 identical copies of genetic information; partition in chromosome so that each daughter cell receives one
Issues when replicating the chromosome
The speed of replication (doesn’t change) vs. speed of cell division (varying)
Replication fidelity: no errors (?)
Untangling chromosome to accommodate replication machinery
Replicating DNA while genes are being translated/transcribed
Semi-conservative replication
DNA pol adds new nucleotides 5’→3’
DNA pol must have a 3’-OH as a substrate (open to add phosphodiester)
Primase - (RNA primer) provides 3’-OH to begin new strand synthesis
OriC
Origin of chromosome replication
DNA A protein
Initiator protein of replication, binds to the oriC
pol III
copies chDNA bi-directionally from the oriC until the sequence/terminator of replication