PHAR 205
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 1-4 so far
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
L1 - what is epidemiology?
Study of distribution and determinants of health related states or events in specified populations. Used for the control of health problems.
L1 - What two terms can describe epidemiology?
Distribution and Frequency
L1 - What is distribution of disease with regards to epidemiology
Distribution describes: person(s), place, and time
L1 - What are the two terms that describe Frequency of disease with regards to epidemiology
Incidence (risk of disease), and Prevalence (burden of disease)
L1 - What can epidemiology do?
Describe health of a population
Explain etiology (cause) of disease
Predict occurrence of disease
Control distribution of disease
L1 - What are the two assumptions of epidemiology?
1) Diseases do not occur randomly
2) Disease has causal and preventative factors that we can identify through systematic investigation of different subgroups of individuals within a population in different places or times
L1 - What are the three types of epidemiology and their goals?
Descriptive, Analytic, and Experimental
L1 - What is the goal of descriptive epidemiology?
Examine patterns of disease, health behaviors
L1 - What is the goal of analytic epidemiology?
Evaluate relationships between risk or protective factors and disease
L1 - What is the goal of experimental epidemiology?
To evaluate a treatment to compare with other treatment
L2 - What defines Health?
The state of complete physical, mental and social well-being. Not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
L2 - What are the three aspects of the Health Triangle?
Mental, Social, Physical
L2 - Define Physical Health
The body’s ability to function:
Physical activity
nutrition
Weight management
Sleep
Alcohol/Drug use
L2 - Describe Mental Health
How we think, feel, and cope with life
Learning skills and behavior
How the body deals with stress
Mental illness
L2 - Describe Social Health
How we react with the people in our environment
Family and peer relationships
Public health
L2 - Define Public Health
“Preventing disease and promoting health through the organized efforts of society”
L2 - Give 5 examples of the top public health priorities in Canada
Obesity
Cardiovascular Disease
Diabetes
Opioid Crisis
COVID-19
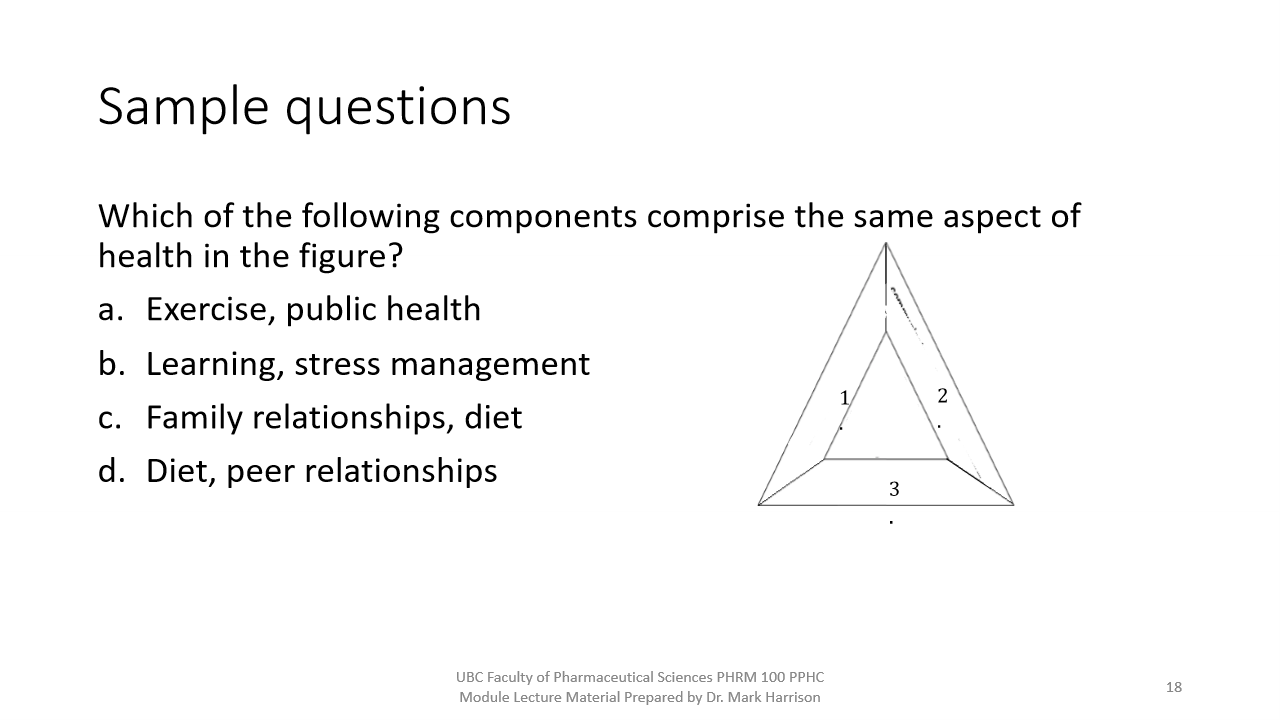
L2 -
b. Learning, stress management
L2 - Define Health Care
Refers to chemicals (e.g. drugs), devices (e.g. artificial knee) and services (e.g. physiotherapy) used by people to improve their health
L2 - What are the types of health care?
Diagnosis
Treatment
Health promotion
Disease prevention
Rehabilitation
Palliative
L2 - What is Primary Health Care?
First contact with the health care system. May involve
Diagnosis
Treatment
Health promotion
Disease prevention
Broad range of physical, mental, and social health problems
L2 - What is Secondary Health Care?
Specialist care. May involve
Diagnosis
Treatment
Must have referral from primary care provider to specialist
L2 - What is Tertiary Health Care?
Known as specialized consultative healthcare
Advanced care, involves treatment of complex illness
Involves hospital admission
Must have referral from primary or secondary health care provider
L2 - Define Health Care System
The organization of people, institutions and resources that deliver health care to meet the health needs of target populations
L2 - What is the Canada Health Act?
Legislation that defines national principles for provincial and territorial health insurance plans.
L2 - What is the Canada Health Transfer?
Federal transfer payment program to support provincial and territorial health care systems (long-term funding for health care).
L2 - What are the 5 Principles (criteria) under the Canada Health Act for full federal funding through the Canada Health Transfer?
Public administration
Comprehensiveness
Universality
Portability
Accessibility
L2 - What is Inpatient Health Care?
Regionalized inpatient health care, where a region is responsible for care of residents through facilities or hospitals.
Funded by the province within the global budget
E.g. BC has;
Northern Health
Interior Health
Fraser Health
Vancouver Island Health
Vancouver Coastal Health
L2 - What is Outpatient Health Care?
Physicians who are fee-for-service
Fee schedules negotiated and administered by the province
Funded directly by the province
L2 - Define Health Indicators
A single measure that is reported on regularly and that provides relevant and actionable information about population health characteristics or health care system performance
L2 - How are Health Indicators used?
To monitor and communicate critical information about population health
supports planning
tracks progress
builds awareness
identifies potential interventions
inform policy and policy makers