CSD 313 Exam 3
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
if you are seeing this please leave me a 5 star review it is so good for my self esteem
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
How we model the vocal tract
Can be modeled as a series of an unlimited number of tubes - “Infinite tube model”
Are the formant frequencies same for everyone
no - it is dependent on vocal tract length and resonating cavity size
Tense vowels
produced with greater muscle contraction, produced at the extremes of articulatory poster, with tongue in higher oral cavity, longer vowels
Lax vowels
shorter, less muscle contraction
Characteristics of Diphthongs
two vowels with the same syllabic nuclei, smooth glide from one vowel to the next
A consonant is inserted, ex: coordinate, cooperate (/w/)
What happens when two continuous vowels are each syllabic nucleus
Why is energy lost in the vocal tract
glottal opening, absorbent walls of pharynx and mouth, friction between air particles
Narrowband filter
provides good resolution of the harmonic (frequency) structure of the source signal
Wideband filter
provides good time resolution of the glottal pulses and formant structure (resonators) of the vocal tract
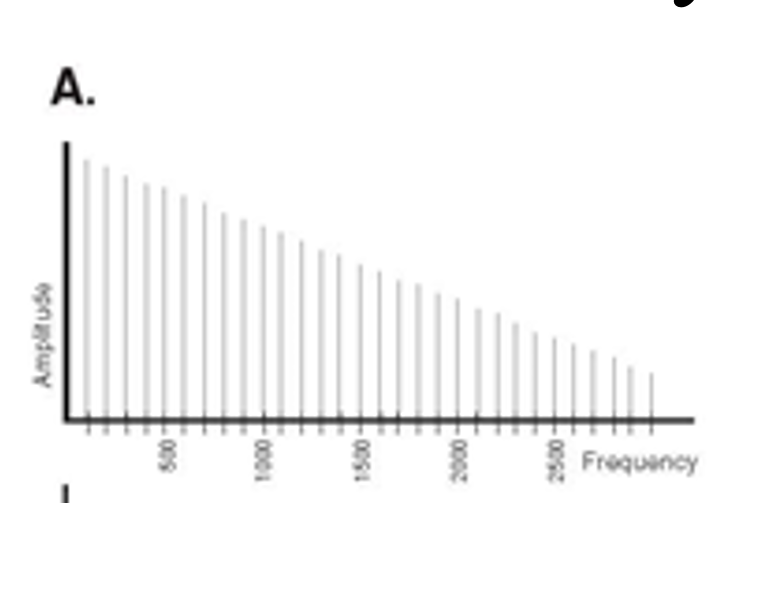
Male spectogram
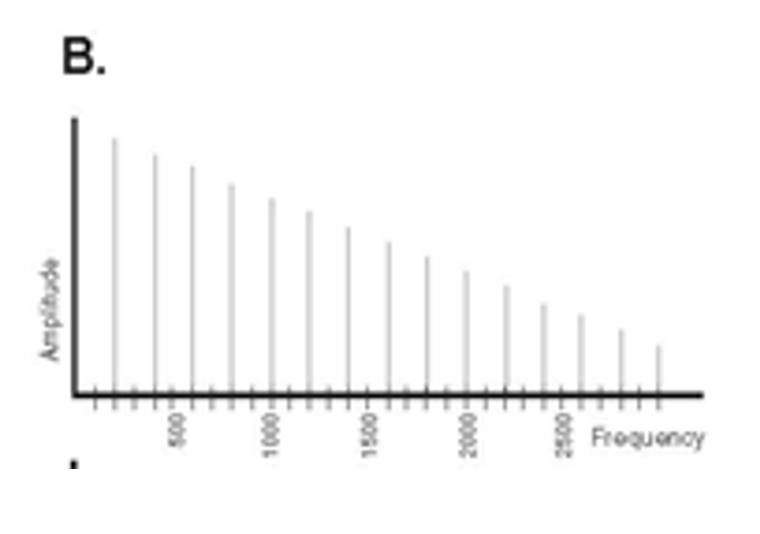
Female spectrogram
What does CPP tell us
perception of breathiness and abnormal voice qualities
High pass filter
blocks out low frequencies
Low pass filters
blocks out high frequencies
What does aperiodicity means in the CPP
Can be analyzed with aperiodic sources but CPP will be less
Conventional radiography x-ray
noninvasive, low cost, returns 2D images
Computed Axail Tomography (CAT)
3D reconstruction, similar density tissue can be distinguished, too slow for speech, higher x-ray dosage than the conventional x-ray
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
3D reconstruction, dynamic MRI enables us to record with temporal resolution, lower special resolution than CT, must remain completely still, not comfy, noisy
Ultrasound
beneficial for studying tongue movement in speech, identifying tongue contour with clarity, inability to image the tongue tip, large number of data points
Bandpass filter
Type of filter that a vocal tract behaves like
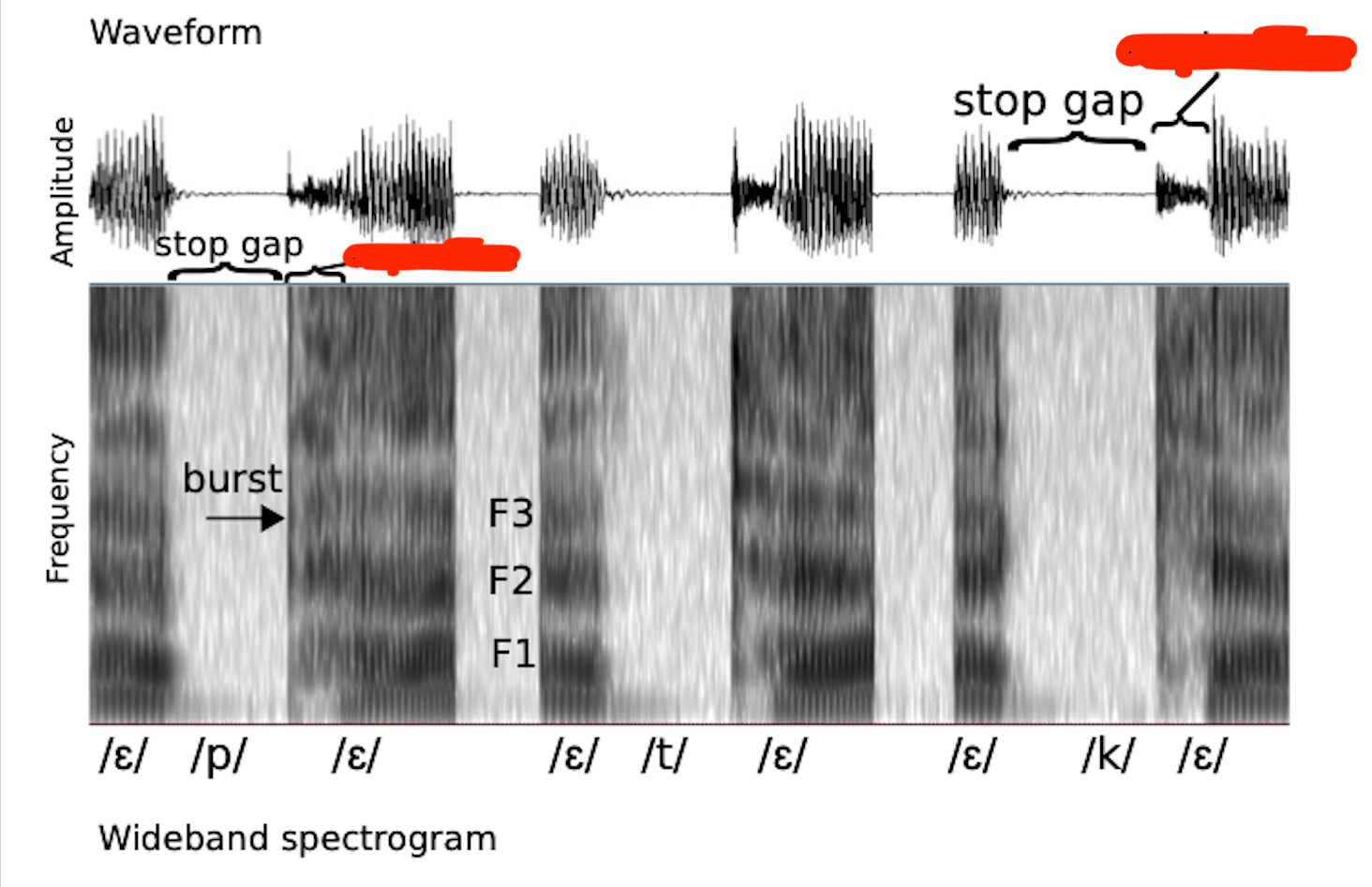
Burst
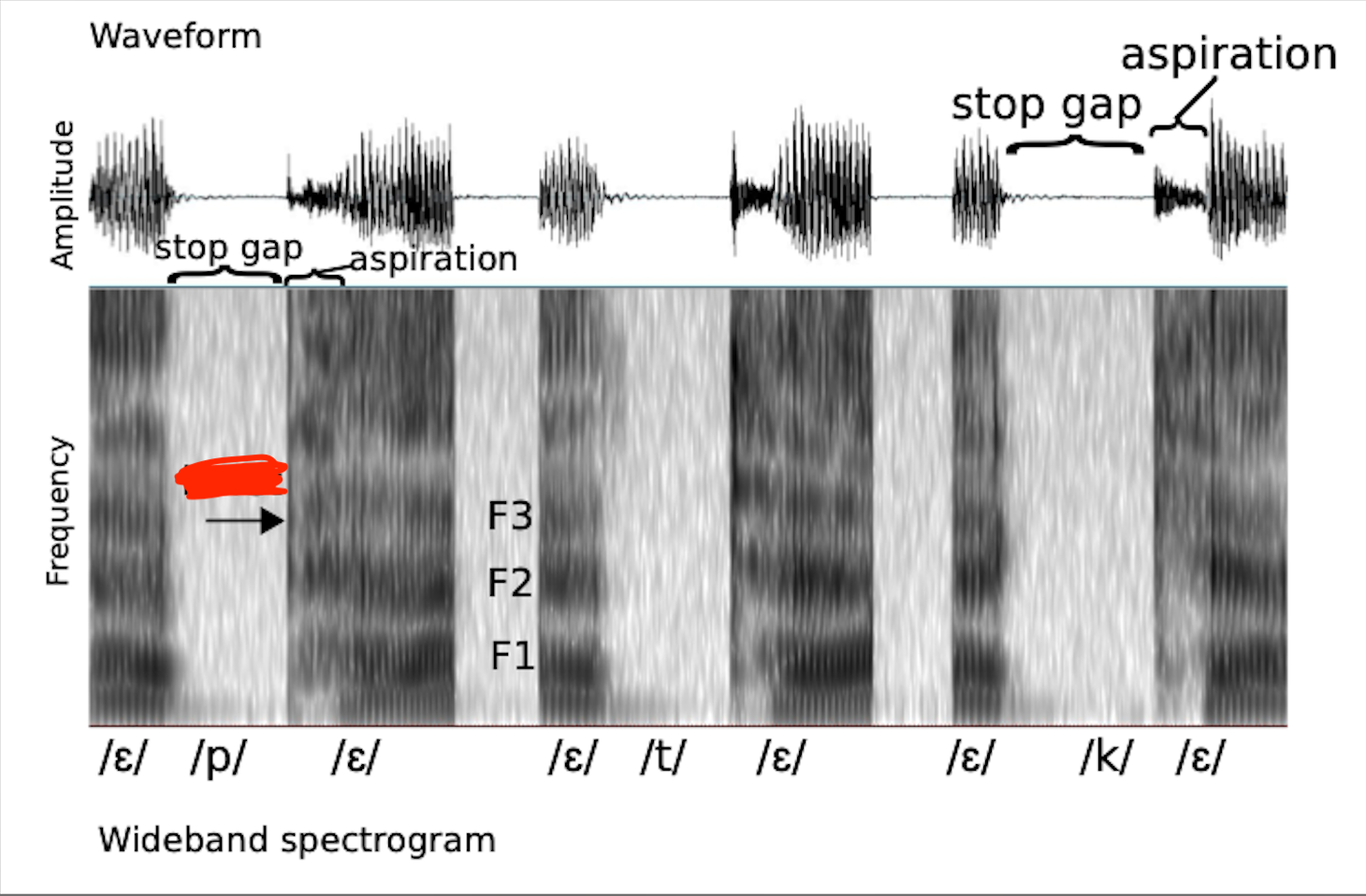
F1
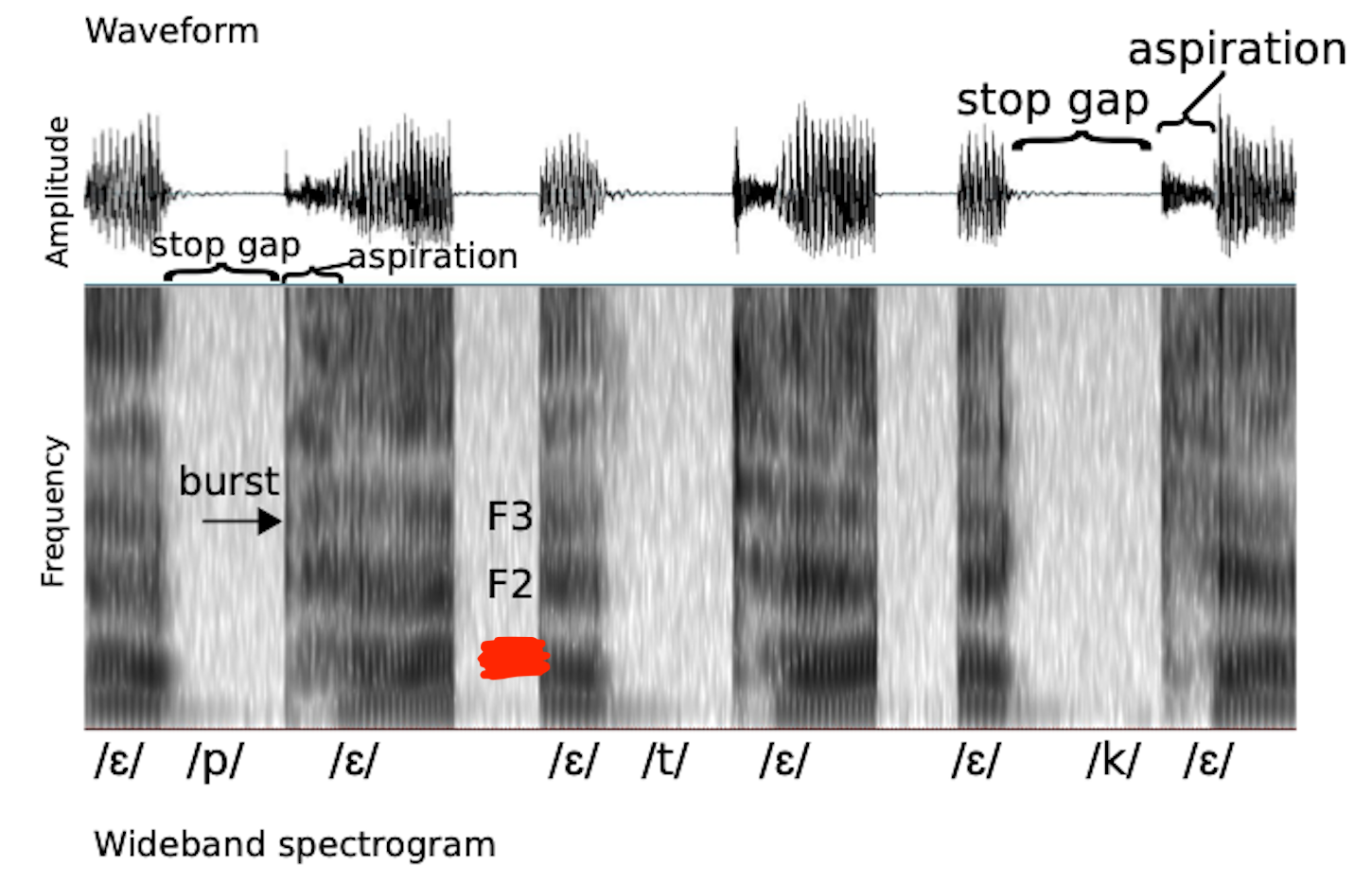
F2
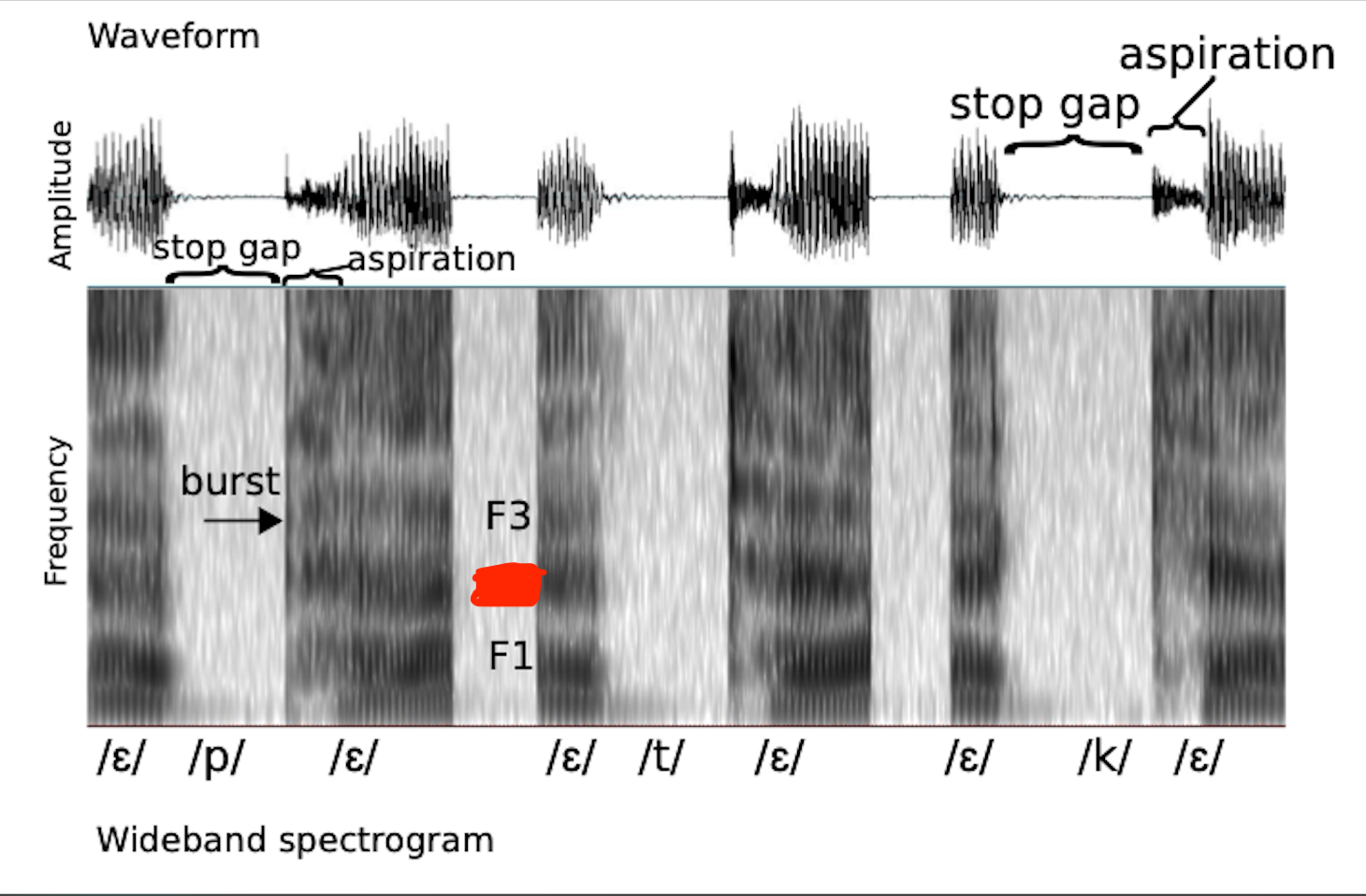
F3
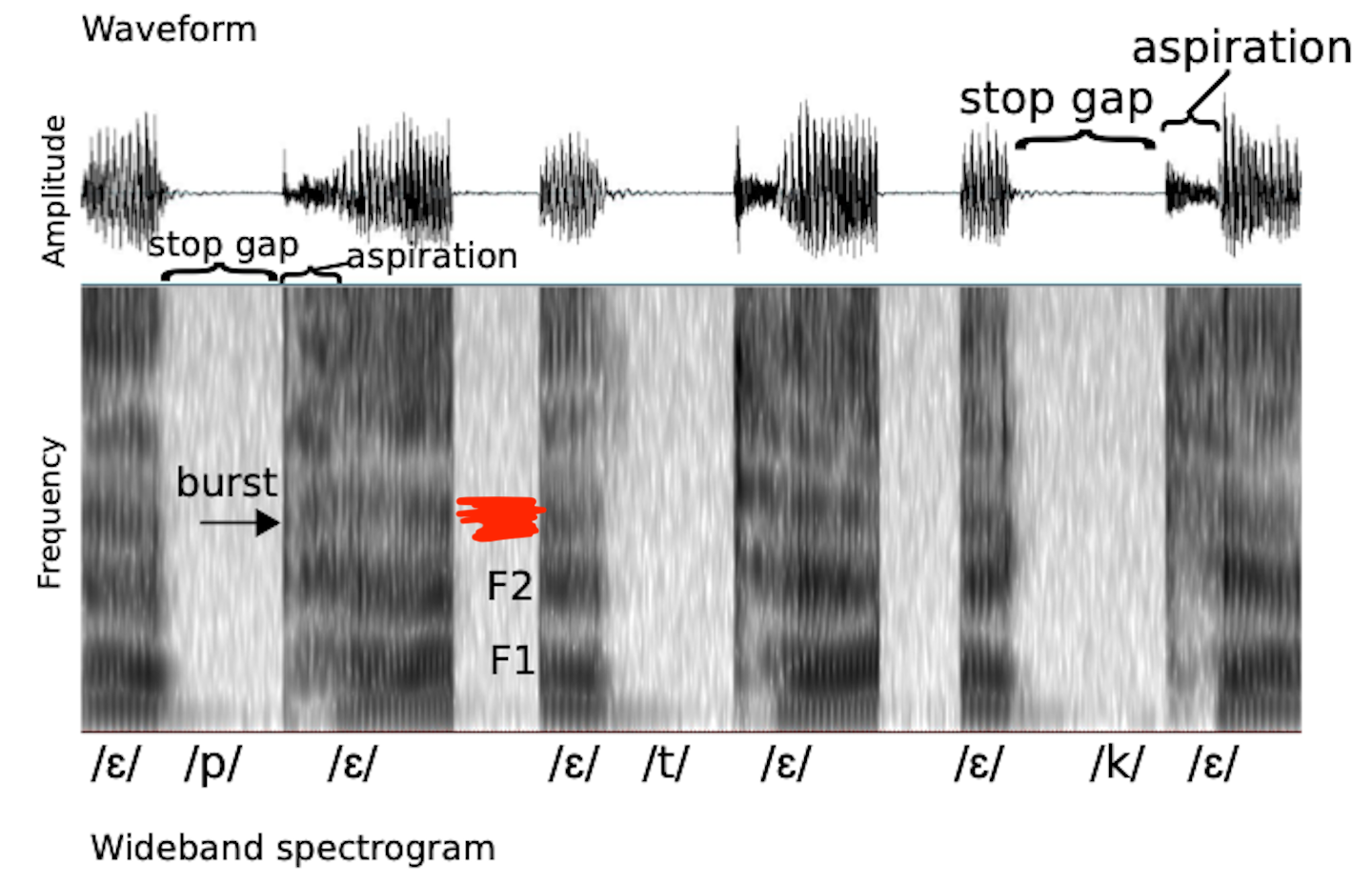
Stop gap
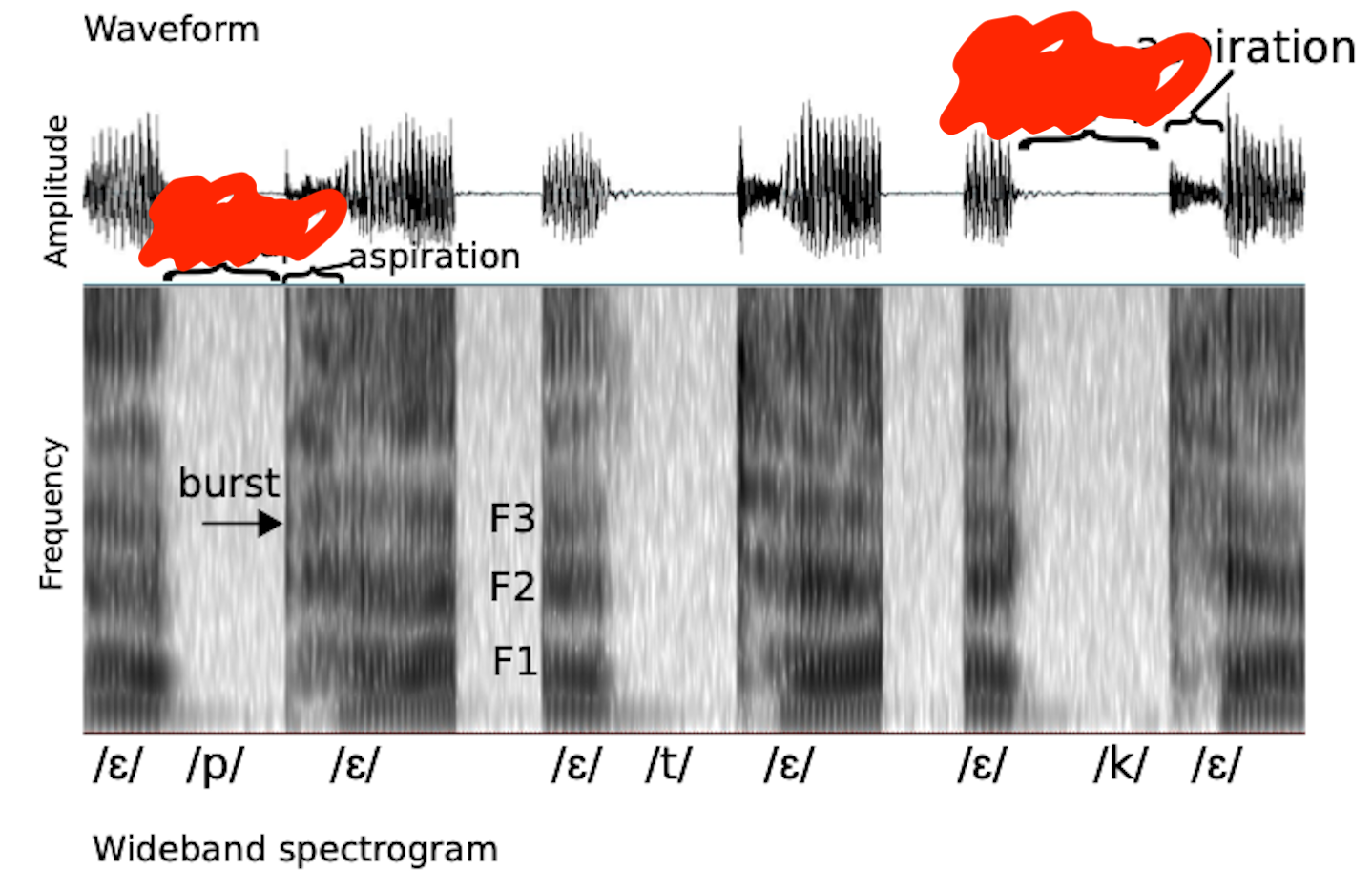
Aspiration
Properties of fricatives
narrow constriction but not complete occlusion, always sufficient to produce turbulent flow
Properties of sibilants
Greater constriction that is more posterior in oral cavity
Approximates
Glides and liquids
Glides
have a nearly periodic sound source as in vowels, acoustic evidence for place of articulation is formant transition of the neighboring vowel
When is a pseudo palate used?
an array of touch sensitive electrodes embedded in a thin acrylic palate, like a dental retainer - can give unique information about articulation
Voiceless fricatives
frication noise is the sole source
Voiced fricatives
friction noise and phonatory source
Stops formant transition
Slow formant transition in comparison to stops
Fast formant transition
Fast formant transition in comparison to diphthongs
When does the dark /l/ typically happen
after the vowel within a syllable ex: eel, pal, tall, school
Light /r/
is produced with greater tongue advancement
No
Is “road” classified as a light /r/
Low
Is consonant energy high or low
Properties of nasal production
All nasals are going to be voiced; occlude oral cavity and open velopharyngeal port
Formant structure can be syllabic like vowels, but have significant constriction
Nasal murmur = very low F1, F2 and F3 vary
What does Intra-oral Air pressure depend on
degree of constriction of the phoneme and intensity
Ways that hypernasality decreases intelligibility
Introducing antiformants and dampening acoustic energy
Introduction of noise from turbulent nasal airflow emissioins
Decreasing intra-oral air pressure, thereby, decreasing clarity of consonant production
acoustic targets, articulatory gestures, aerodynamic pressures
Targets for “output target” models
Is acoustic invariance a speech perception theory
Yes - there are invariant acoustic patterns in the speech signal corresponding to phonetic features, which remain invariant across speakers phonetic contexts and languages
True
According to motor theory, the listener accesses their own knowledge of speech production in perception
True
The connectionist model is nonlinear and contains a nonhierachical set of components
Feedforward model
signals are used to make articulatory adjustment online; would be used to initiate rapidly sequences skilled movements
Acoustic invariance theory
Acoustic landmarks are important characteristics in which of the following speech theories
Identify the spatiotemporals models
How the articulators move in space and time - refers to the path of an articulator and the timing of the sequence of positions
Criticisms of motor theory
little empirical evidence to support theory, specfic mechanisms of analysis-by-synthesis have not been clearly described, acoustic features vary greatly
Bottom up
processing works in the absence of the knowledge; receive auditory information, convert it into a neural signal, and process the phonetic feature information
Top down
processing works with knowledge a listener has about a language, context, experience; use stored information about language and the world to make sense of the speech
Characteristics of active speech perception
emphasize the cognitive control in perception; including the formation about the phonetic or linguistic interpretation of the information in the acoustic signal
Categories of speech perception
Active vs passive
Bottom up vs top down
Autonomous vs interactive
Aerodynamic targets
Limitations in acoustic feedback in a population with hearing impairment supports which of the following models of speech production?