CH4: Planning for and Recruiting Human Resources
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Explain the Why’, ‘ What’, and ‘ How’ s of Workforce planning
WHY: Carried out to meet business objectives and gain an advantage over competitors
WHAT: Compares the present state of the organization with its goals for the future
HOW: They look at operational and finance factors
Name the steps of Workforce planning
Forecasting: Labour & demand
Determining labour shortage/surplus
Goal setting and strategic planning
implementation and evaluation
What is ‘ Forcasting’ ?
Estimating tends in Labour & Supply helping to decide whether there will be a shortage or surplus of human resources for each job/skill category
Forecasting: Labour Demand
Forecasts the potential demand for a specific job category and skills areas
Uses:
Trend analysis : Using past objective statistics to build models that can predict next year’s labour needs.
Leading indicators: Objective factors within the marketing environment that could help predict level of demand
Forecasting: Labour supply
Analysis of how many people are currently in various job categories or have specific skills while examining internal and external trends.
Uses:
Transitional Matrix: a chart that tracks employee movement between job categories over time.
Goal Setting & Strategic Planning
Goals should be based on the labour supply and demand analysis and include clear targets for each job or skill area, along with a specific timeline for achieving them.
Strategies for addressing labour suplus
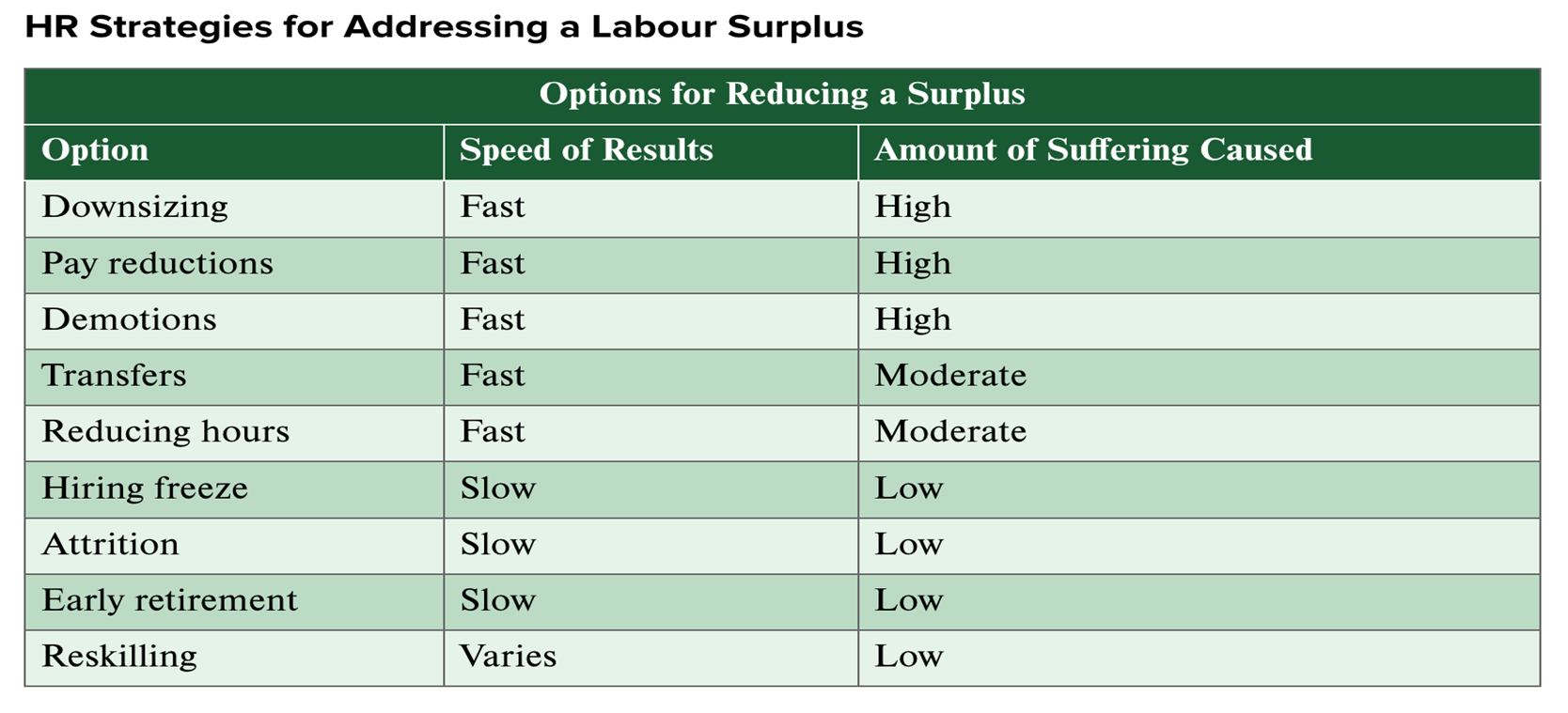
How to address Labour shortages
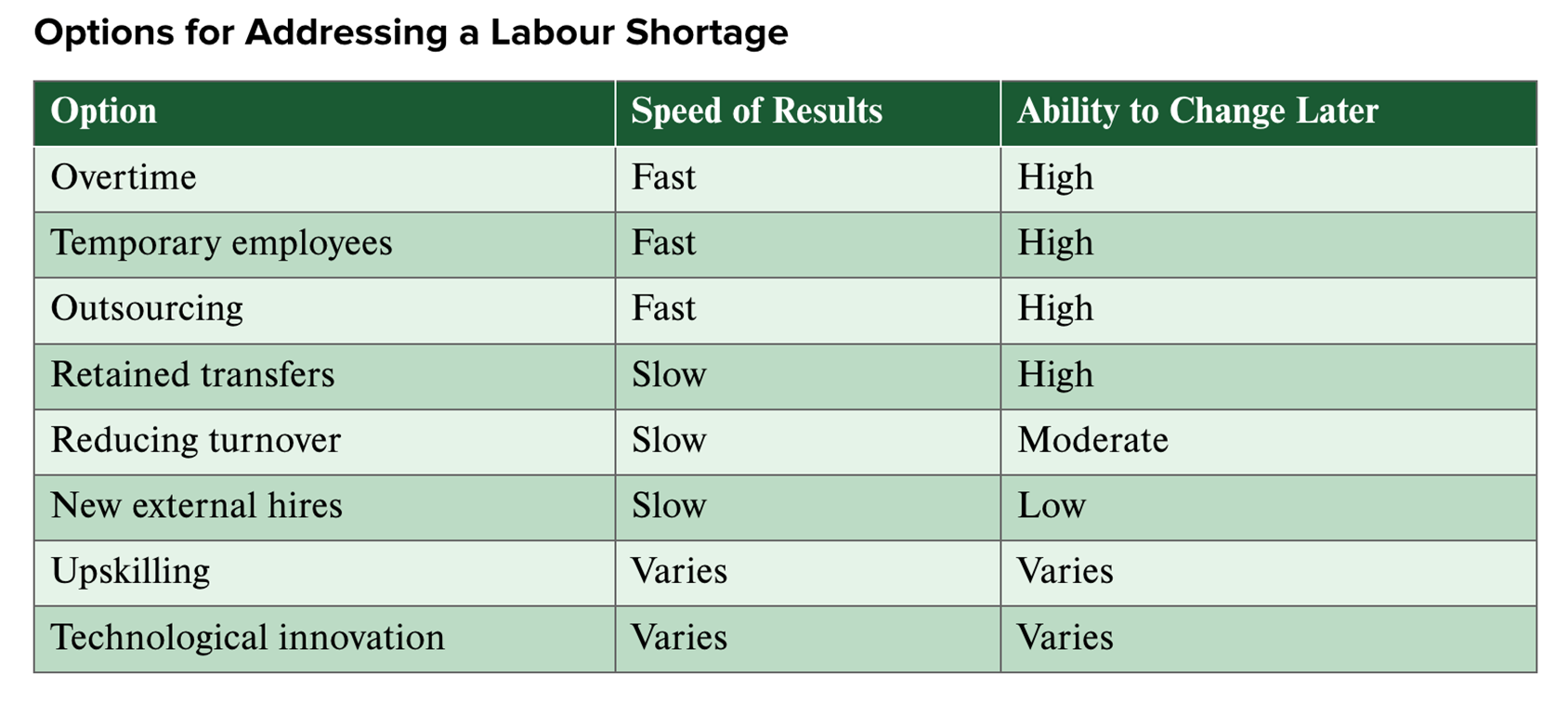
Implementing & Evaluating
Checking whether the organization has succeeded in avoiding labour shortages or surpluses
How to apply Employment equity & DEI
Reviewing workforce subgroups and using workforce utilization review comparing their representation to the labour market to identify underutilization.
Succession Planning
The process of identifying and tracking high-potential employees who will be able to fill top management positions or other key positions when they become vacant
Succession Planning: Data Analytics & AI
Organizations use multiple data sources and visualization tools to predict potential, identify development needs, and model complex future scenarios.
what is the def of Recruiting Human Resources
Any activity carried out by the organization with the primary purpose of identifying and attracting potential employees
3 aspects affect who is hired?
–Human resource policies
–Recruitment sources
–Recruiter traits and behaviours
Explain Human resource policies

Advantages to Internal and External recruitment
INTERNAL
Candidates are well-known
Cheaper and faster than external hiring
Boosts employee morale
EXTERNAL
Brings in new ideas
Attracts a more diverse workforce
External Sources of recruiting ( “Don’t Run Past Delicious Apples, Pick Some Up!”)
Direct applicants Adds
referrals Public agencies
passive candidates Staffing companies
Digital recruiting Universities & Colleges
Direct Applications
People who apply for a vacancy without prompting
Referrals
People who apply because someone in the organization prompted them
Passive Candidates
Individuals who are not actively seeking a job but are a significant source of top talent
Digital Recruiting
Involves posting opportunities at company website and/or social media platforms
Ads
Typically generate a less desirable group of applicants at greater expense
Public Agencies
Clients include both employers and job seekers
Staffing companies
Private companies provide services for a fee
Universities & Colleges
Placement services, cooperative education, internships, and job fairs
Evaluating Recruitment Sources
Monitor all recruitment sources – ensure quality.
Yield Ratio: % of applicants who move from one stage to the next.
Cost per Hire: Total cost of a recruitment source ÷ number of hires.
Recruiter Traits & Behaviours
Recruiters are HR specialists or job experts who provide realistic job previews, give timely feedback, and often recruit in teams with current employees or supervisors.