miscellaneous antibacterials - urinary agents and others (test 3)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
urinary agents
fosfomycin (oral)
nitrofurantoin (oral)
fosfomycin (oral)
inhibit peptidoglycan biosynthesis
nitrofurantoin (oral)
downregulate nucleic acids and protein synthesis
other miscellaneous
polymyxins
colistimethate (IV, IM, inhaled)
polymyxin B (IV)
mupirocin (nasal ointment)
bacitracin
polymyxin B, bacitracin, neomycin (neosporin) {topical}
polymyxins
colistimethate (IV, IM, inhaled)
polymyxin B (IV)
cell membrane disruptors
mupirocin (nasal ointment)
inhibits protein synthesis
bacitracin
polymyxin B, bacitracin, neomycin (neosporin) {topical}
cell wall synthesis inhibitor
fosfomycin tromethamine
charactistics
static or cidal?
used to treat lower _____
not indicated for _____ infections
occasionally used for _____ infections
generally taken _____
list of essential medicines — important for human medicine
is it available as a generic?
how is it made?
salt prep with ___ or known during medical use as tromethamine, is an organic compund
cidal
UTI
kidney
prostate
orally
yes
chemically
tris
fosfomycin
MOA
inhibits ______ _____, enzyme that catalyzes formation of diphosphate-N-acetylmuramic acid in peptidoglycan biosynthesis
inhibits what else?
phosphoenolpyruvate transferase
1st step in bacterial cell wall formation
fosfomycin
medical use
_____ bacteria of UTI such as multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli (1st line)
_____ bacteria like Enterococcus faecalis (alternate treatment only)
gram -
gram +
fosfomycin
name some side effects
well tolerate, low incidence of harmful side effects
D, N, headache, vaginitis
fosfomycin
DDIs?
antacids and food can decrease absorption
fosfomycin
resistance
resistance is common under therapy by _____ of enzymes that chemically modify the drug
overexpression
nitrofirantoin (macrobid)
characteristics
static or cidal?
not as effective for ____ infections
how is it taken?
list of essential medicines
cidal
kidney
orally (tabs, caps)
nitrofirantoin (macrobid)
medical use
______ bacteria of UTI such as multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli (1st line)
______ bacteria like Staphylococcus spp. (2nd or 3rd line)
used in _____ ____ ___ to other commonly used agent , such as trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and fluoroquinolones
gram -
gram +
bacterial antibiotic resistance
nitrofirantoin (macrobid)
MOA
it is a _____
bacterial flavoprotein enzyme “nitrofuran reductase” with (NAD) (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) coenzyme activity reduces what?
prodrug
nitrofurantoin to active derivatives
nitrofirantoin (macrobid)
MOA
active derivatives generate superoxide anions (O2-) that will react with what?
what is the result?
several bacterial targets ribosomal proteins, DNA, respiration, pyruvate metabolism and other macromolecules within the cell
decreases synthesis of an damages proteins, DNA, RNA, and cell wall synthesis
nitrofirantoin (macrobid)
resistance
multiple target sites or mechanism of superoxide anion make it what??
slow for bacteria to become resistant
nitrofirantoin (macrobid)
name some side effects
N, headache, flatulence (common)
GI (D, abdominal pain, C), neurologic (dizziness, drowsiness), respiratory (acute pulmonary hypersensitivity reaction, pulmonary toxicity), others (allergic and dermatologic reactions, fever, chills, discomfort)
nitrofirantoin (macrobid)
DDIs?
activity of ntirofurantoin depends on acidic pH
antacids and fluoroquinolones antagonized — can cause false urine glucose results
nitrofirantoin (macrobid)
contraindications?
must be avoided by patients with renal failure
cell membrane disruptors (polymyxins)
typical ionic detergents
forms micelles in water (hydrophobic tails cluster)
polar outside dissolves micelle in water
polymyxin B
what type of product is it?
static or cidal?
DAB ‘diaminobutyric acid‘ like protonated _____ with + charges at physiological pH
natural
cidal
lysine
polymyxin B
MOA
cationic detergent — binds to - charged _____ and disrupts what?
what is it highly selective towards?
phospholipids in gram - cell membranes; the membrane
lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on gram - outer membrane
polymyxin B
medical use
severe hospitalized/resistant ______ infections
specific pseudomonas ____ infections (topical ophthalmic ointment)
pseudomonas
eye
polymyxin B
name some side effects
neurotoxic and nephrotoxic effects
polymyxin B
explain the metabolism
not excreted by kidney
not applied in kidney infections or UTI
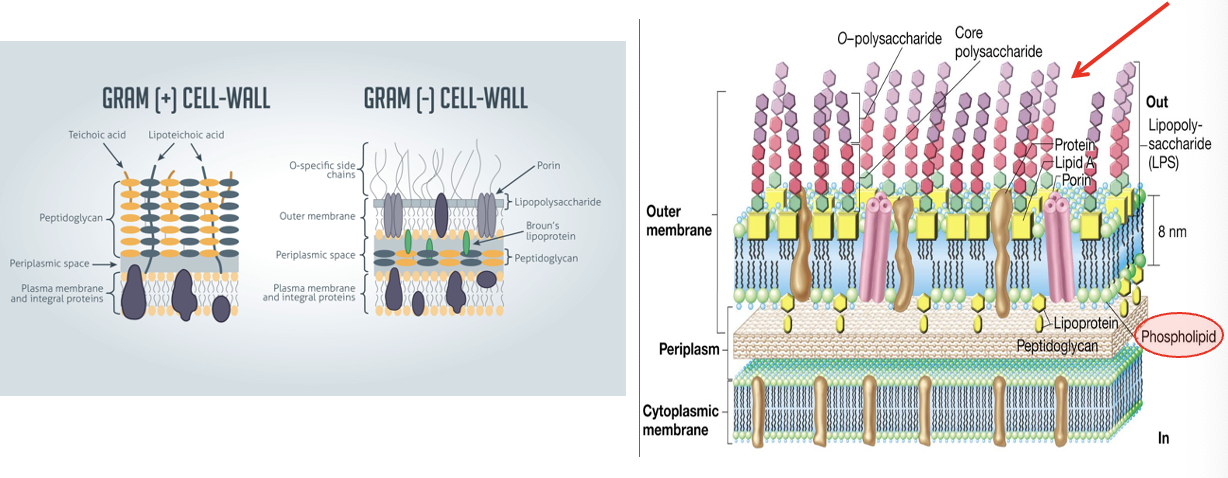
cell membrane disruptors
constitution of bacterial cell walls
role of gram - lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
polymyxin B
MOA
selectivity — binds to what?
charged s groups in gram - lipopolysaccharides (LPS) on outer membrane
colistin (polymyxin E)
static or cidal?
MOA
comprised of what?
the cationic regions interact with what?
cidal
hydrophilic and lipophilic moieties
phosphate and lipopolysaccharides in the bacterial outer membranes
colistin (polymyxin E)
medical use
multi drug resistant Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Serratia (MDR-KES)
_____/____ resistant (MDR) pseudomonas
_______ resistant pseudomonas (including UTI)
inhalation — ___ ___ (pseudomonas respiratory tract infections)
topical — pseudomonas ____ infections
penicillin/cephalosporin
g -
cystic fibrosis
ear
colistin (polymyxin E)
name some side effects
nephrotoxicity (reversible dose dependent)
neurotoxicity (dizziness, vertigo, blurred vision)
colistin (polymyxin E)
DDIs?
muscle relaxants (increase toxicity)
amikacin (aminoglycoside) increase neuromuscular blockage
bacitracin
characterics
______ antibiotic
mixture of peptides produced by Bacillus licheniformis bacteria
static or cidal?
polypeptide
both, depending on concentration
bacitracin
MOA
these peptides disrupt gram + bacteria by doing what?
interfering with cell wall and peptidoglycan synthesis
bacitracin
medical use
used to treat ____ ____ ____ surface infections
used in solutions for ______ of wounds
used IM in highly ____ ____ infections
mixed flora skin
sterilization
resistant gram +
bacitracin
MOA
inhibits cell wall synthesis by blocking ____ ____ ____ required to trafficking (answer) to cell components
this prevents ______ monomers from crossing the cytosol through he cytoplasmic membrane to form (answer) polymers and to connect the cell wall
components manufactured on cytoplasmic membrane and trasported via _____ ____ ____ to gram + cell wall
phospholipid carrier cycle
peptidoglycan
phospholipid carrier cycle

bacitracin
spectrum of activity
____ bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Staph. epidermidis,
Streptococcus pyogenes, and others Strep. pneumoniae (pneumococci),
and tetanus bacilli (Clostridium tetani)
OTC medicine can add ______ and _____
gram +
polymyxin B and neomycin
bacitracin
available in generic?
name some side effects
yes — for parenteral use can lead to high nephrotoxic effects (when used internally)
rare — hypersensitivity, allergic, or anaphylactic reactions (esp. in people allergic to neomycin)
mupirocin
characterics
chemically a ____ ____ (pseudomonic acid)
list of essential medicines
available as generic?
static or cidal?
2% ointment, cream, nasal ointment
brand name = bactroban
carboxylic acid
yes
cidal
mupirocin
name some side effects
skin cream — burning, stinging
nasal ointment — headache, rhinitis, respiratory congestion
mupirocin
MOA
containing region structurally similar to isoleucine (ILE), it inhibits protein synthesis by what?
binding selectively to the ILE tRNA ligase (responsible to incorporate ILE into proteins)
mupirocin
resistance
what does plasmid encoding ILE tRNA ligase do?
decrease activity of mupirocin
mupirocin
spectrum and medical use
_____ spectrum — name them
isolated/minor ____ infections due to Staph. / Strep. Infections (i.e. impetigo)
recurrent _____ (primarily Staph. in nasal hair follicles)
______ resistant Staph. aureus (MRSA) when present in the nose without symptoms
narrow
gram + aerobes
gram - anaerobes
skin
furnunculosis
methicillin