Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
Virus
Minuscule, acellular infectious agents with DNA or RNA.
Infectious Agents
Pathogens causing diseases in various organisms.
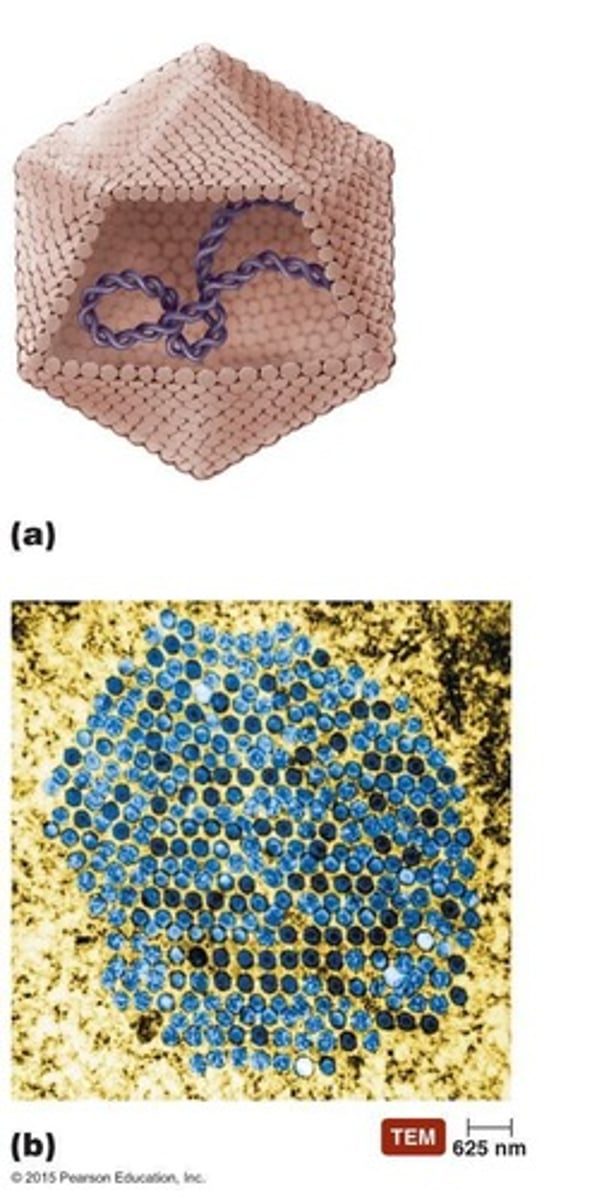
Virion
Extracellular state of a virus, includes capsid.
Capsid
Protein coat surrounding viral nucleic acid.
Nucleocapsid
Combination of nucleic acid and capsid.
Phospholipid Envelope
Outer layer providing protection and host recognition.
Intracellular State
Virus exists as nucleic acid after capsid removal.
Genetic Material
Variety in viral genomes; DNA or RNA only.
dsDNA
Double-stranded DNA, one type of viral genome.
ssDNA
Single-stranded DNA, another type of viral genome.
dsRNA
Double-stranded RNA, a viral genome type.
ssRNA
Single-stranded RNA, a type of viral genome.
Host Specificity
Viruses infect specific host cells via surface proteins.
Bacteriophage
Virus that specifically infects bacteria.
Plant Viruses
Viruses infecting food crops through cell wall abrasions.
Fungal Viruses
Understudied viruses, lack extracellular state.
Capsomere
Protein subunits composing the capsid.
Capsid Morphology
Shape and structure of viral capsids.
Viral Envelope Composition
Phospholipid bilayer and proteins from host cell.
Glycoproteins
Viral proteins aiding in host recognition.
Generalist Viruses
Infect multiple cell types across various hosts.
Viral Replication
Process of virus using host's metabolic pathways.
Extracellular State
Virus outside host; can infect new cells.
Intracellular State
Virus inside host; utilizes host machinery.
Viral Genome Size
Much smaller than cellular genomes.
Viral Infection Mechanism
Involves attachment, entry, replication, and release.
Viral Diseases
Cause significant health issues in industrialized nations.
Viral Classification
Based on genetic material and host specificity.
Glycoproteins
Proteins on virus surface aiding in attachment.
Helical capsid
Cylindrical structure enclosing viral genome.
Matrix protein
Protein layer between capsid and envelope.
Envelope
Lipid membrane surrounding some viruses.
Enveloped virus
Virus with a lipid membrane coating.
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
Body that classifies viruses based on characteristics.
Virus classification criteria
Based on nucleic acid, envelope, shape, size.
Lytic replication
Viral replication leading to host cell death.
Stages of lytic cycle
Attachment, Entry, Synthesis, Assembly, Release.
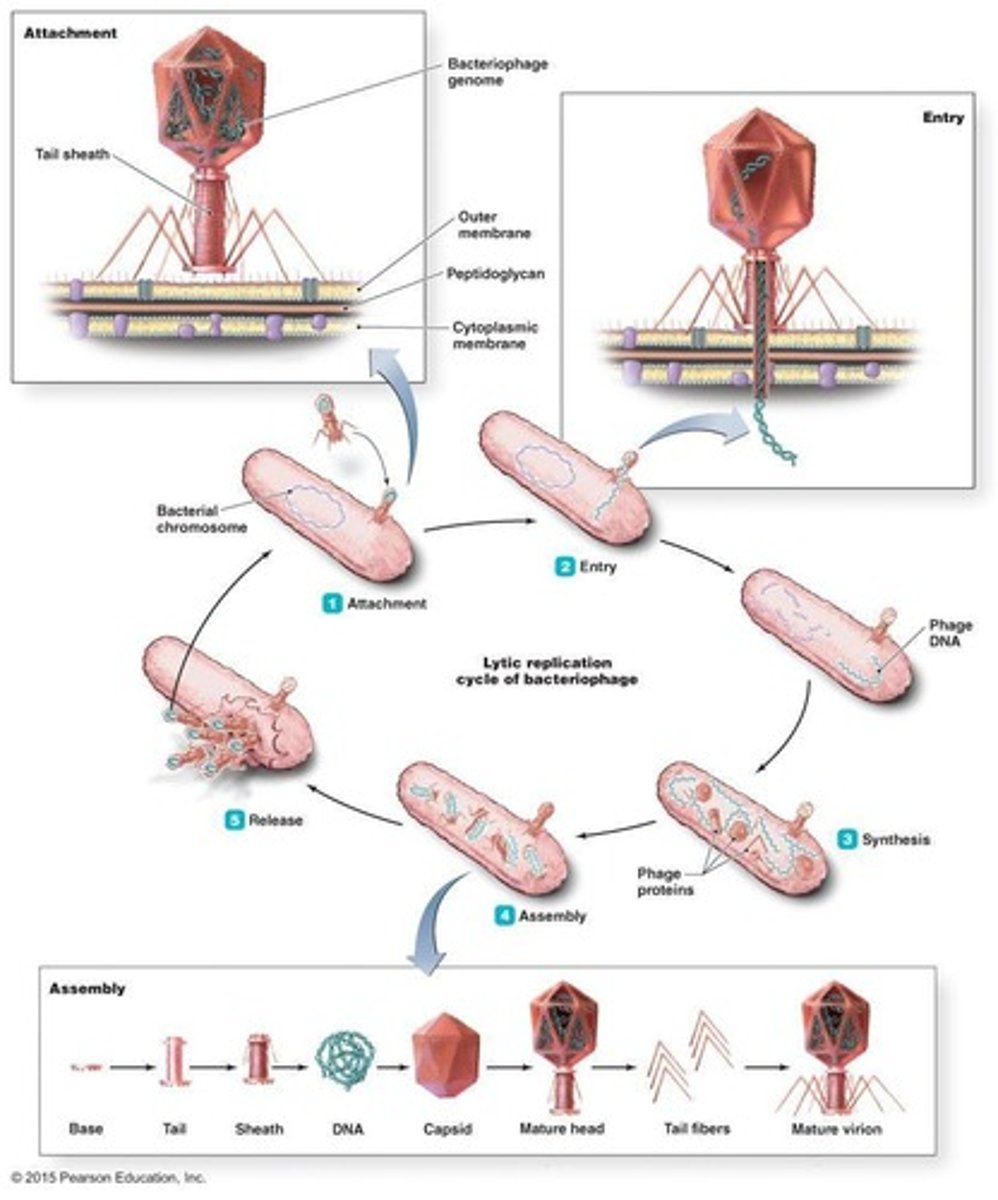
Attachment stage
Virus binds to host cell receptors.
Entry stage
Virus penetrates host cell membrane.
Synthesis stage
Host cell machinery produces viral components.
Assembly stage
New virions are formed from viral components.
Release stage
New virions exit host cell, causing lysis.
Lysogeny
Modified viral replication cycle without immediate lysis.
Temperate phages
Phages that can enter lysogenic cycle.
Prophages
Inactive phages integrated into host chromosome.
Lysogenic conversion
Phenotypic change in bacteria due to prophages.
Replication of animal viruses
Similar to bacteriophages with key differences.
Animal virus attachment
Chemical attraction between viral proteins and receptors.
Glycoprotein spikes
Molecules facilitating attachment of animal viruses.
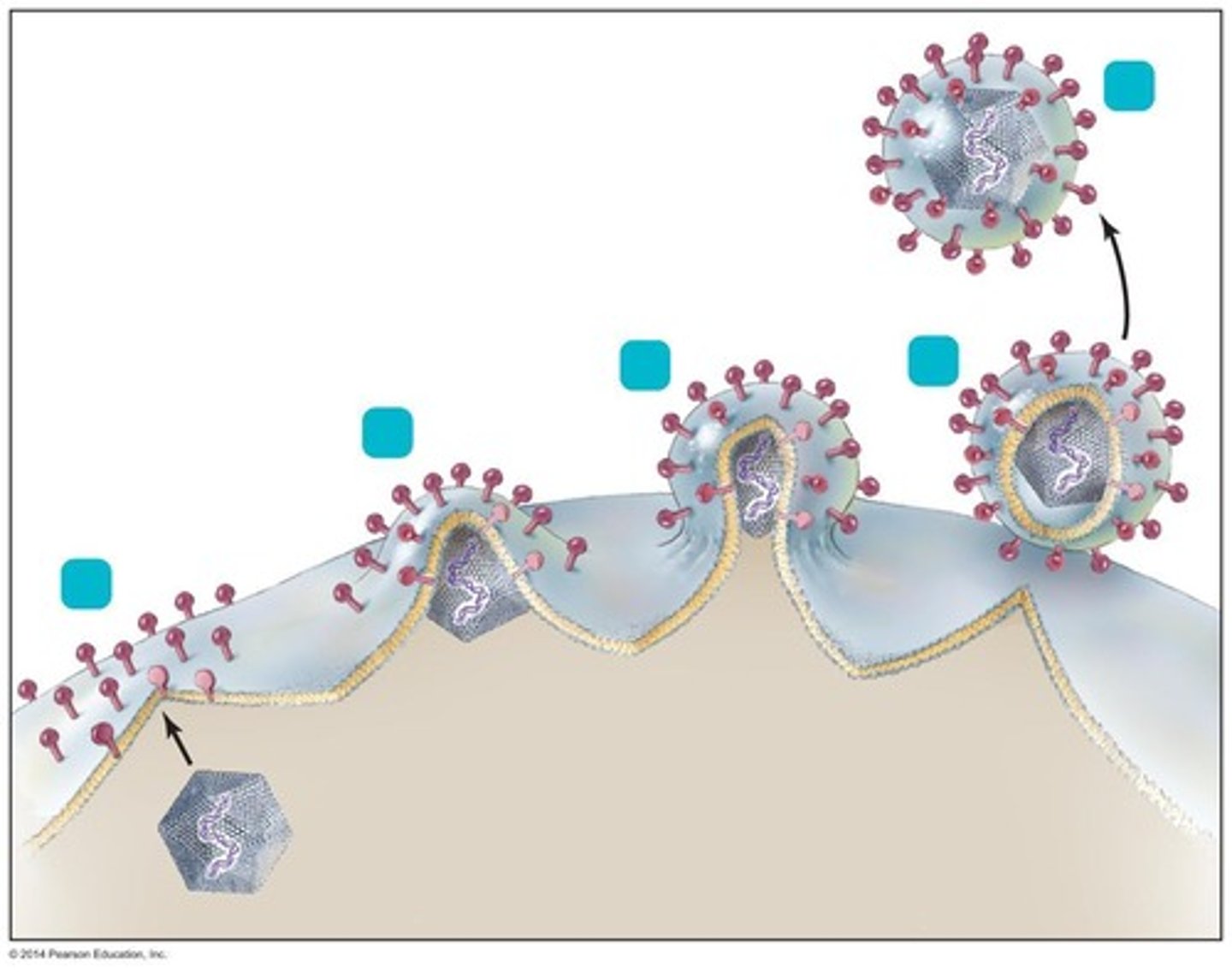
Entry mechanisms of animal viruses
Direct penetration, membrane fusion, endocytosis.
Direct penetration
Virus injects genome directly into host cell.
Membrane fusion
Virus envelope merges with host cell membrane.
Endocytosis
Host cell engulfs virus, forming a vesicle.
Uncoating
Process of removing viral capsid after entry.
Synthesis of DNA viruses
Often occurs in the nucleus of host cells.
Synthesis of RNA viruses
Typically occurs in the cytoplasm of host cells.
mRNA synthesis
Process of creating messenger RNA from DNA.
Nucleic acid replication template
Strand used to synthesize new nucleic acids.
Viral Replication
Process by which viruses reproduce within host cells.
Animal Viruses
Viruses that specifically infect animal cells.
dsDNA Viruses
Double-stranded DNA viruses replicating like cellular DNA.
Nucleus
Location where viral genome is replicated for dsDNA.
Cytoplasm
Site where viral proteins are synthesized.
Poxvirus
Exception; replicates in the cytoplasm, not nucleus.
Hepatitis B Virus
Uses RNA intermediary to replicate DNA.
ssDNA Viruses
Single-stranded DNA viruses not utilized by host cells.
Parvoviruses
Type of virus with ssDNA genomes.
Complementary DNA Strand
Formed by host enzymes to replicate ssDNA.
dsRNA Virus
Double-stranded RNA virus involved in viral replication.
Positive-sense ssRNA Virus
Acts as mRNA for protein synthesis.
Negative-sense ssRNA Virus
Requires complementary RNA for translation.
Retroviruses
Use DNA intermediary for genome production.
Viral Reverse Transcriptase
Enzyme that transcribes RNA into DNA in retroviruses.
Viral Assembly
Process where new virions are formed.
Budding
Release method for enveloped viruses from host cells.
Exocytosis
Release method for naked viruses.
Latency
Dormant state of viruses in host cells.
Latent Viruses
Viruses that remain inactive within host cells.
Proviruses
Viruses integrated into host DNA permanently.
Neoplasia
Uncontrolled cell division leading to tumor formation.
Tumor
Mass of neoplastic cells in multicellular organisms.
Benign Tumors
Non-cancerous growths that do not spread.
Malignant Tumors
Cancerous growths that invade surrounding tissues.
Metastasis
Process of tumor cells spreading to other body parts.
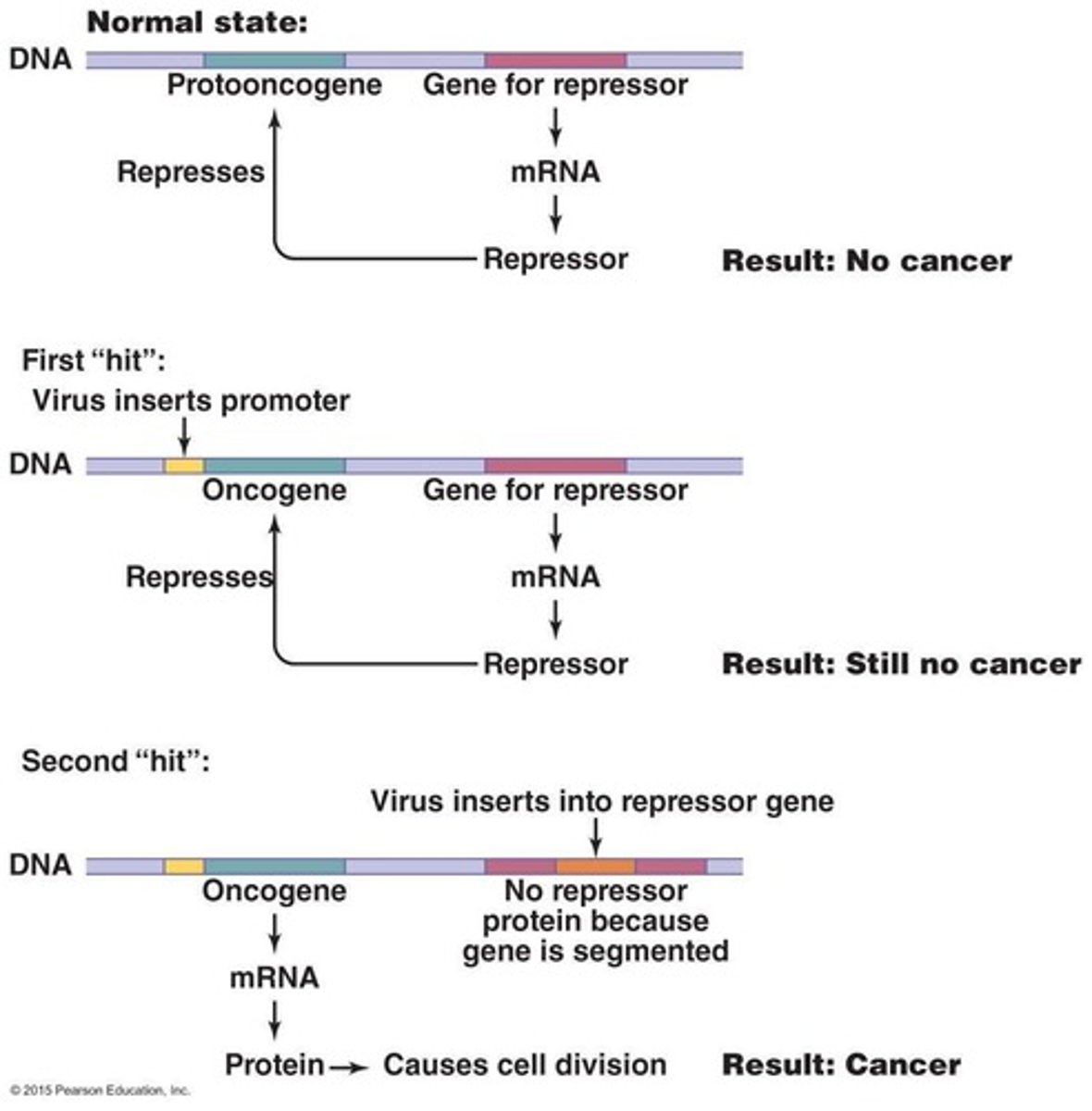
Oncogenes
Genes that promote cell division and can cause cancer.
Environmental Carcinogens
Factors like UV light and radiation that activate oncogenes.
Oncogenes
Genes that promote cancer development.
Viruses in Cancer
Viruses cause 20-25% of human cancers.
Tumor Repression
Mechanisms that prevent tumor formation.
Burkitt's Lymphoma
A type of cancer linked to Epstein-Barr virus.
Hodgkin's Disease
Cancer of the lymphatic system.
Kaposi's Sarcoma
Cancer associated with HIV infection.
Cervical Cancer
Cancer often caused by human papillomavirus (HPV).
Culturing Viruses
Viruses require host cells for growth.
Plaque Assay
Method to estimate phage numbers via plaques.
Embryonated Eggs
Used for culturing viruses; inexpensive and large.
Diploid Cell Cultures
Cell cultures with a limited lifespan.
Continuous Cell Cultures
Cell cultures that can grow indefinitely.
Viroids
Infectious RNA particles affecting plants.
Prions
Infectious proteins causing neurodegenerative diseases.