EVSC Module 9
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Novel Entity
-new substances, new forms of existing substances, and modified life forms that have the potential for unwanted geophysical and/or biological effects
-CFCS are one
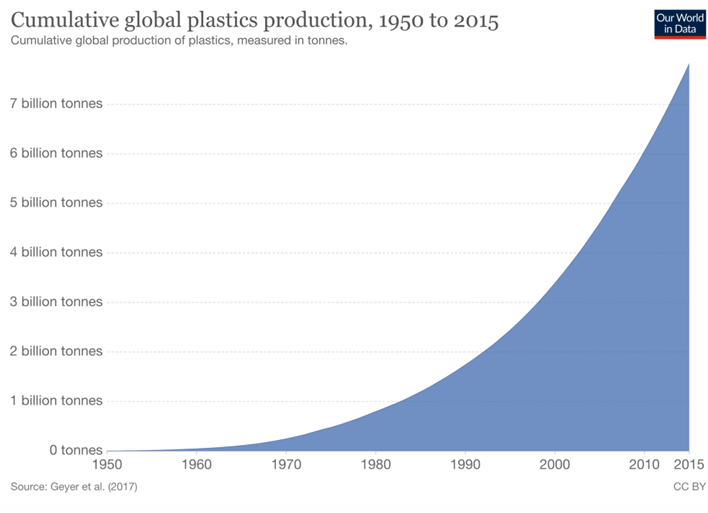
Criteria for Pollutant being designated for a planetary boundary
Must be irreversible or very difficult to reverse
The disruptive effect is only detectable when its a problem at the global scale
Pollution must disrupt the earth system processes
Chemicals Criterion 1
At least 80% of the chemicals have not been assessed for whether they are environmental threats or not.
Plastic Pollution Criterion 1
estimated 8 million metric tonnes of plastic waste enters ocean from coastal regions annually
Estimated 90% of plastics ever produced have not been recycled.
A geological marker of Anthropocene, plastics are everywhere.
Floating Islands of Plastic Criterion 1
floating plastic often gets trapped in swirling gyres, giant loops formed by ocean currents. There are five major ocean gyres, each with a “garbage patch” at its center. There plastics litter the water like confetti.
Great pacific garbage patch is the largest one
estimates suggest that 20-30% of ocean plastics come from marine sources and 70-80% from land
However, the GPGP has more than half (52%) from marine sources due to intensive fishing activity in the Pacific Ocean.
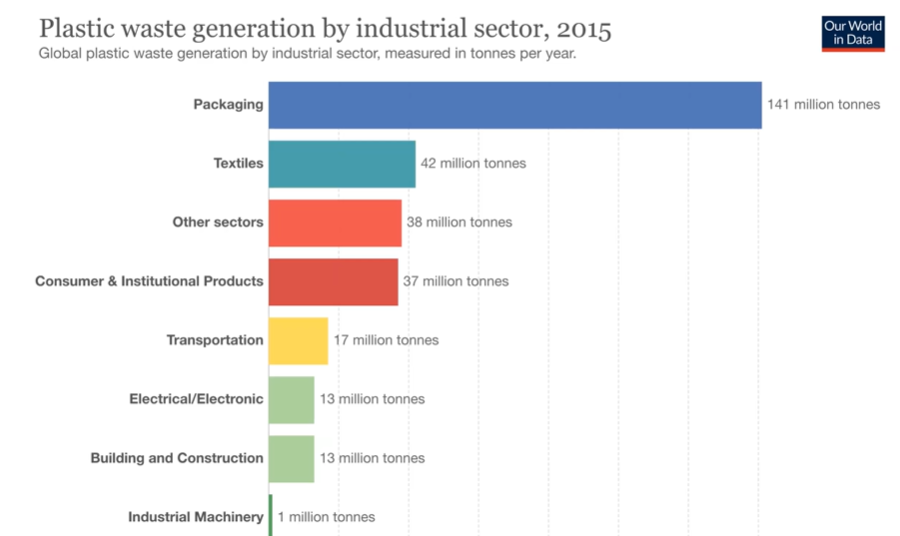
Where does all this plastic come from? Criterion 1
Largest plastic waste generation is a global issue, but this is an issue in certain countries due to inadequately managed plastic waste.
Share of global mismanaged waste are highest in Asian countries.
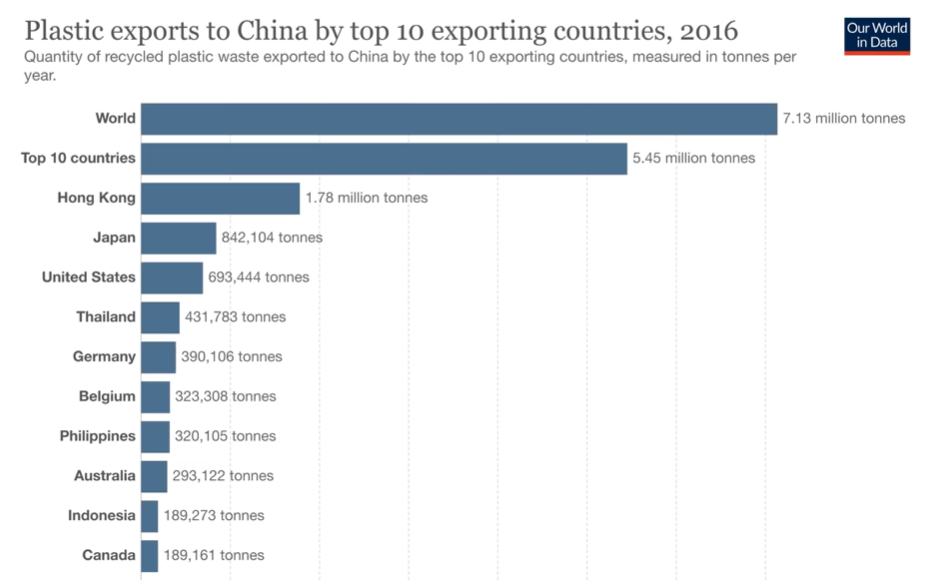
Plastic exports Criterion 1
Main reason why China is the largest share of global mis managed plastics
Disruptive effect is only detectable when it is a global scale problem Criterion 2

Pollution must disrupt Earth System Processes Criterion 3
Marine plastic pollution has direct effects on organisms, indirect effects as a vector or carrier of other pollutants, and systemic effects that cascade across ecosystems on multiple temporal and spatial scales.
The mismanagement of discarded plastic is already implicated in globally systemic alteration to food webs, habitats, and biogeochemical flows
Marine plastic pollution is linked to climate change:
– Copepods ingesting microplastics; their fecal matter doesn’t settle as quickly into marine sediments (changes ocean carbon storage)
– Sunlight accelerates disintegration of plastics, releasing methane (a powerful GHG)
– Plastics floating in Arctic waters interferes with ice formation and melt
Planetary Boundary
Release quantities of plastics into the enviornment has been crossed.
How do we approach the plastic problem? 1)
Most of our current approaches to tackling the problem of global plastic pollution focus on very small impact solutions (e.g. plastic straw bans).
These approaches, while well-intentioned, will be quickly absorbed by the growth of global plastics production.
Instead, we need to focus on high-impact, systemic solutions. Understanding the global picture of plastic pollution helps us to do this
How do we approach the plastic problem? 2) Immediate, High Impact Priorities
Development of effective waste management infrastructure in all countries
Cease plastic trade from rich to low or middle-income countries without sufficient investment in waste management infrastructure
Strict legislation and management of fishing activity and waste
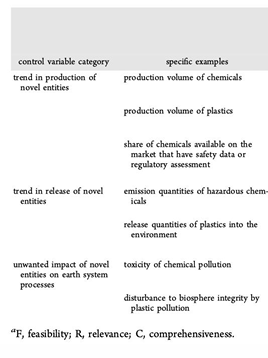
Explain at least one reason that a comprehensive set of planetary boundaries have not yet been defined for novel entities
Novel entities, by definition, are human-made and often have no natural counterpart, making it challenging to determine what constitutes a "safe" level of their presence.