Ancient and Medieval Art Exam 3
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
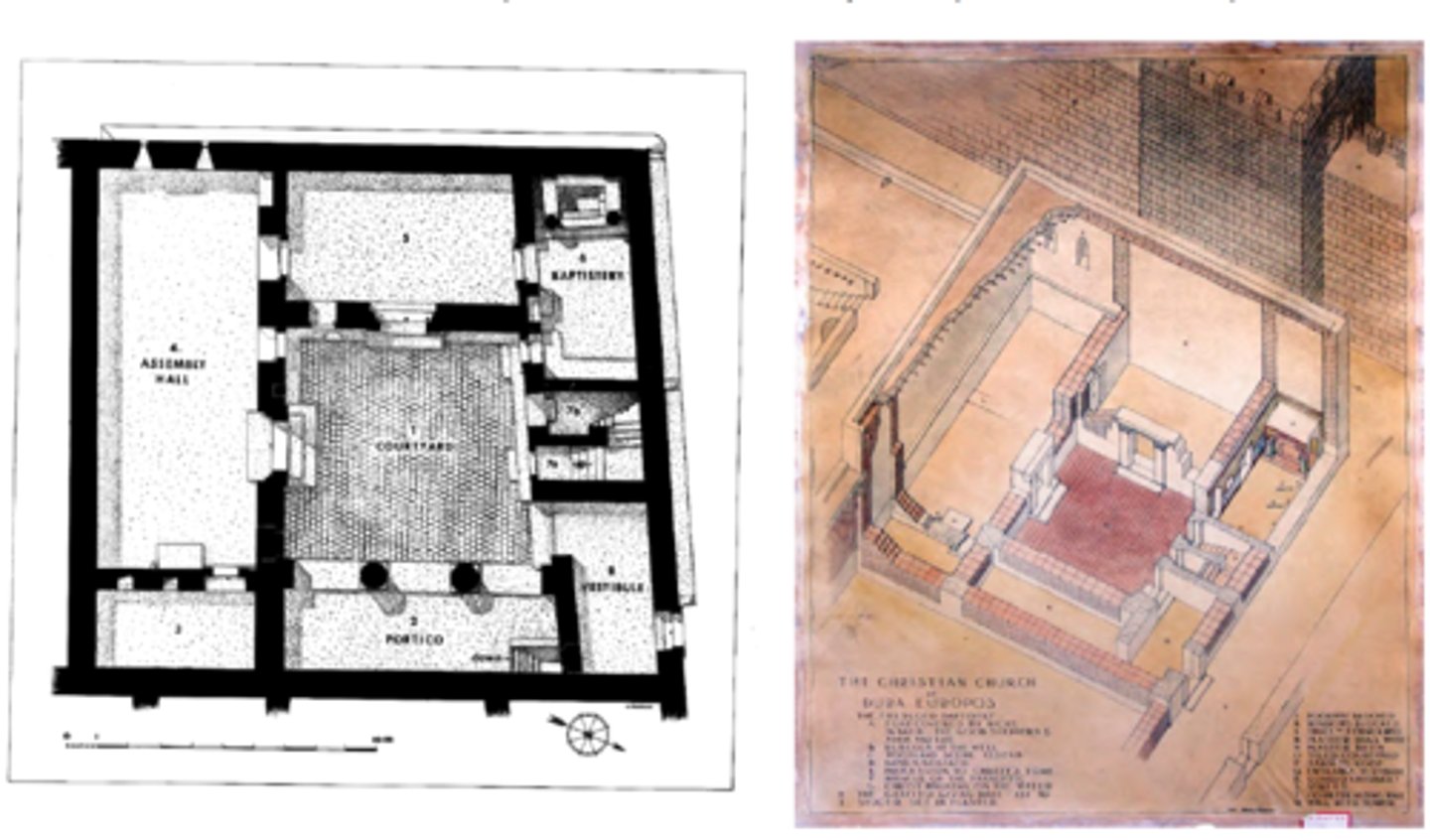
Dura Europos (Syria), The Christian community house
ca. 240-2ca56 CE
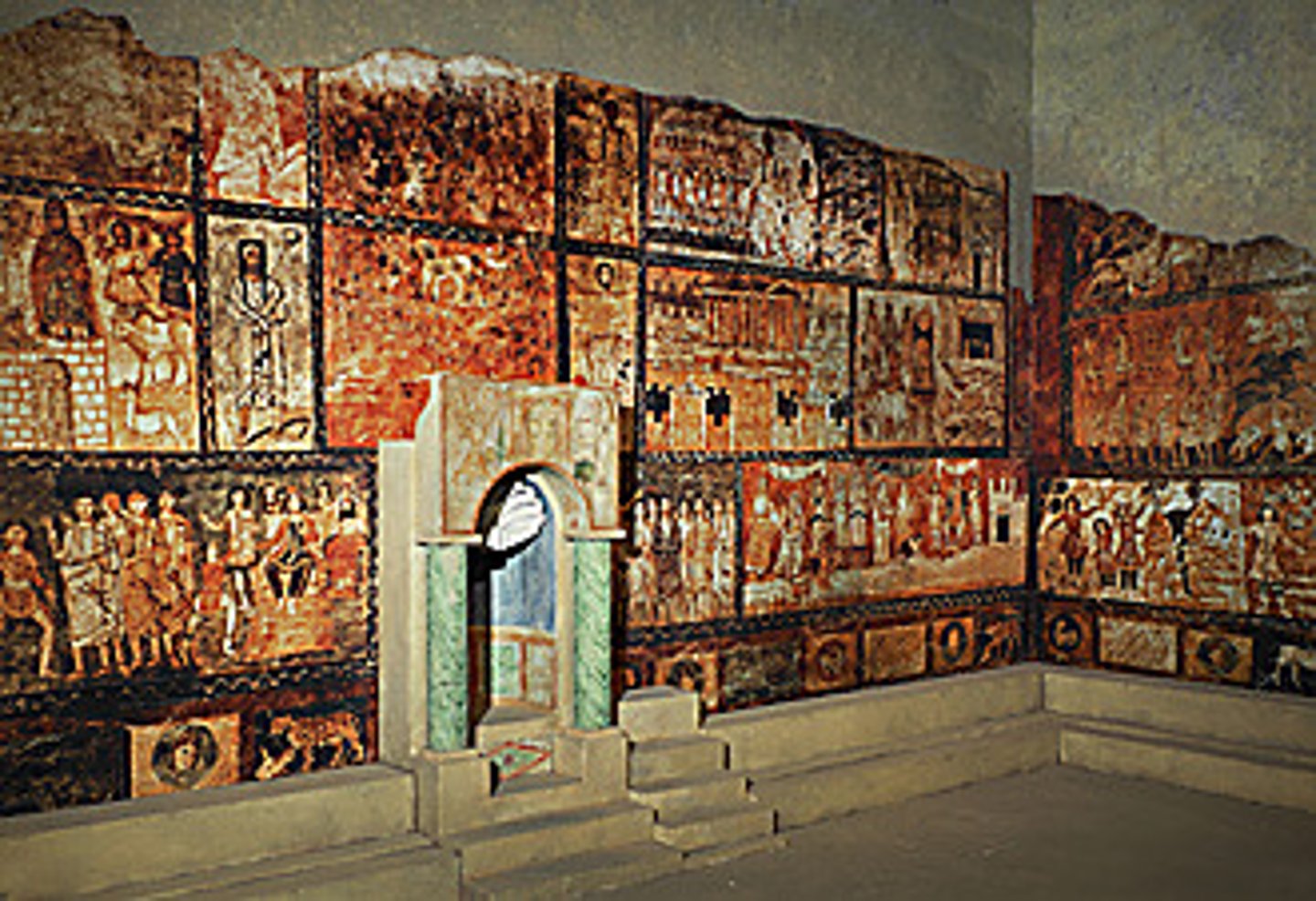
Dura Europos (Syria), Synagogue with wall paintings
from the Hebrew Bible, ca. 245-256 CE

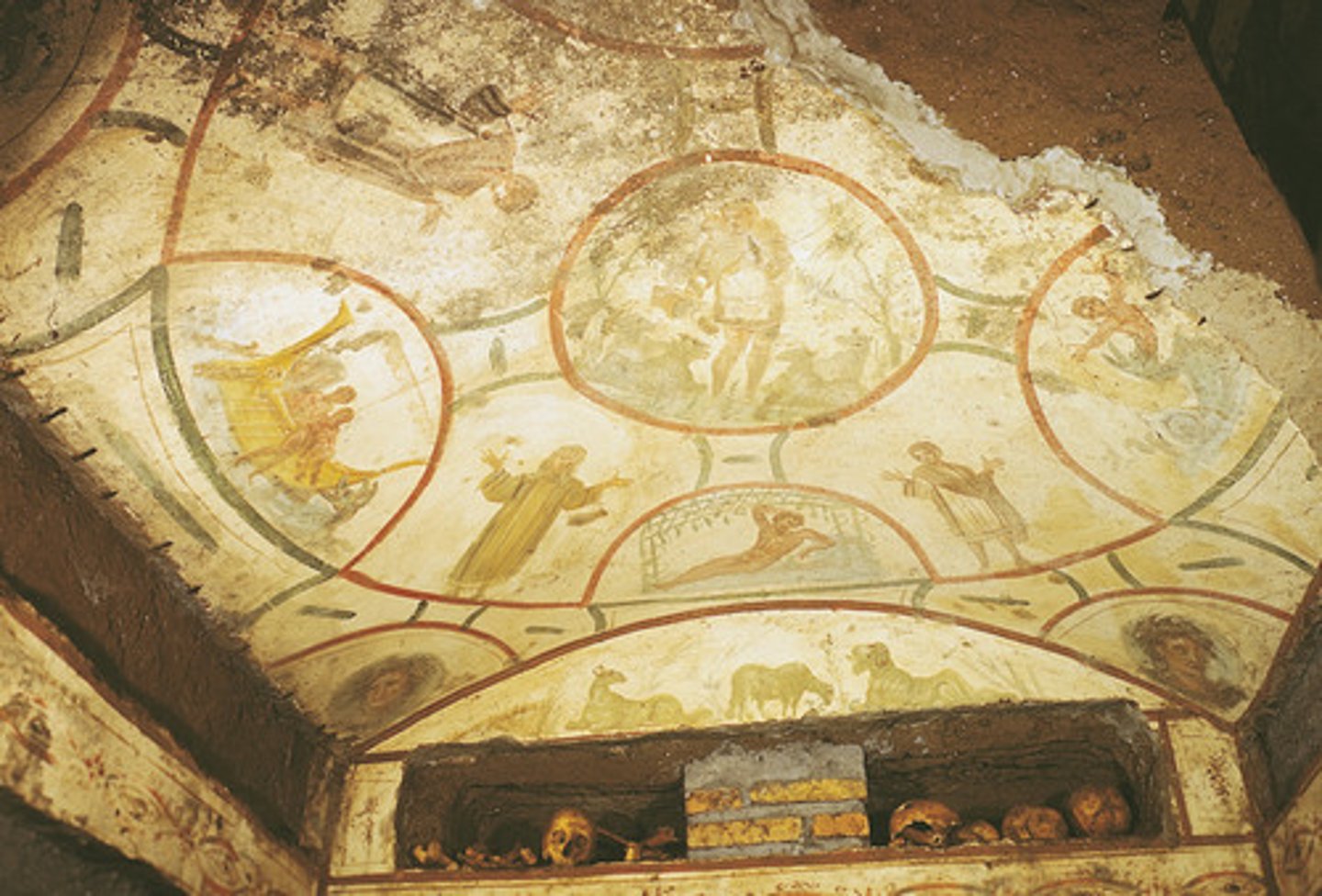
Catacomb of Peter and Marcellinus, Rome, early fourth century CE

Messianic religion
Religion centered by charismatic figure, (secret religion)
Eucharist
A Christian sacrament commemorating the Last Supper by consecrating bread and wine.
Torah niche
a recession in a wall used to house a Torah
Catacomb niche
space in the catacombs to slide a body
Menorah
(Judaism) a candelabrum with nine branches
Tufa
a porous rock similar to limestone, volcanic sedimentary soil
Orans
a gesture involving the raising of the arms in an attitude of prayer
The Church of Sant'Apollinare Nuovo, Ravenna, Italy,
dedicated 504 CE
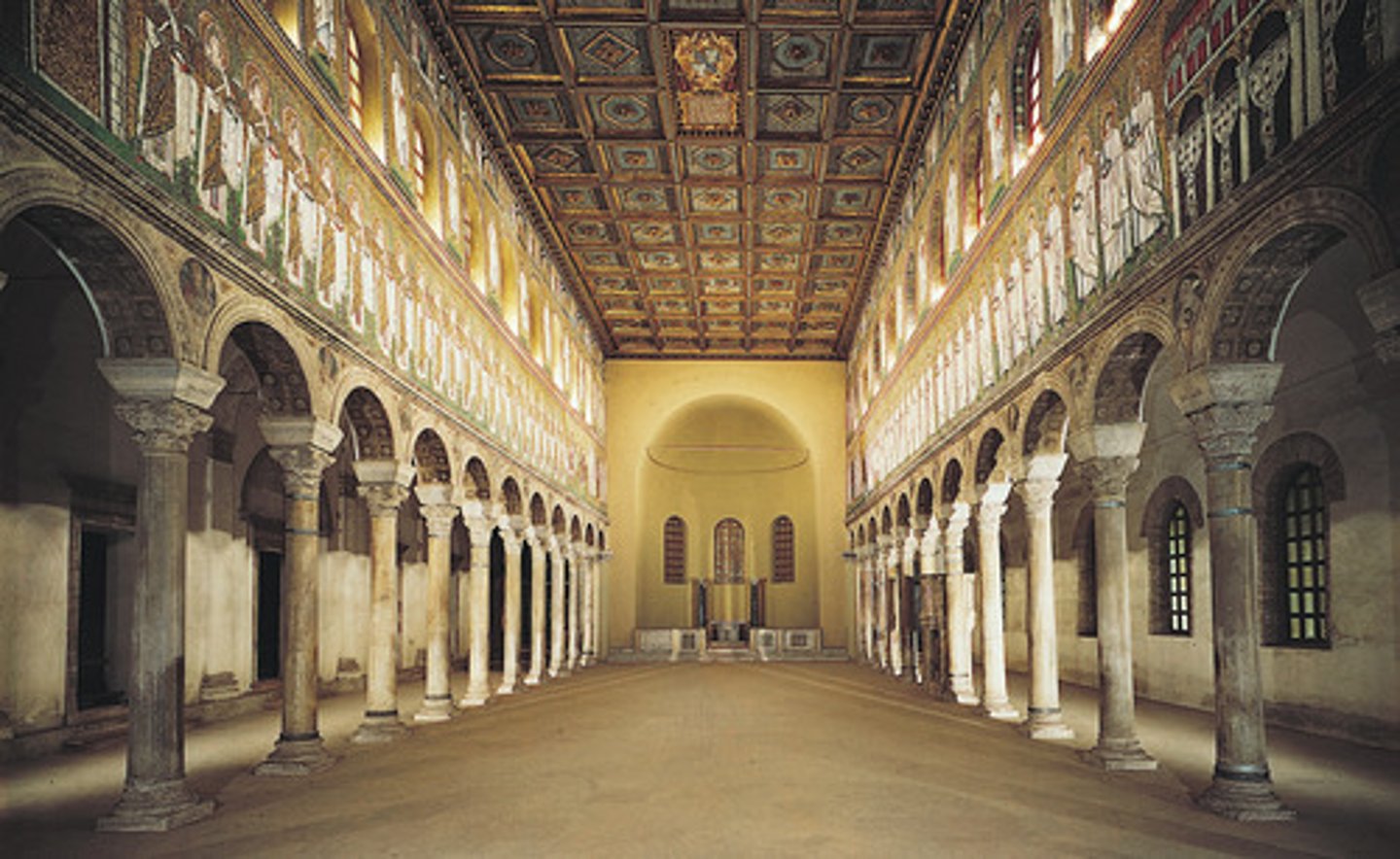

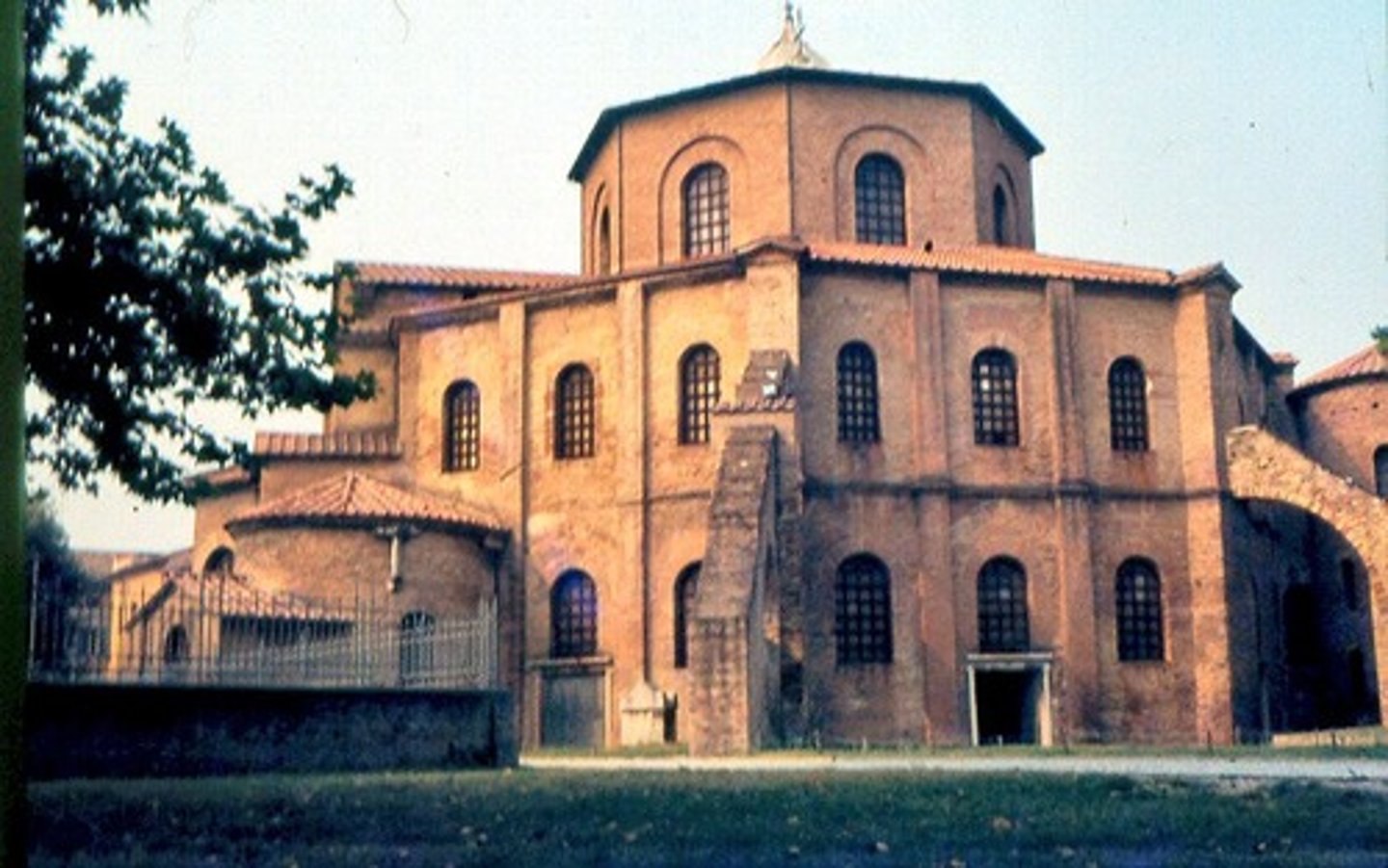
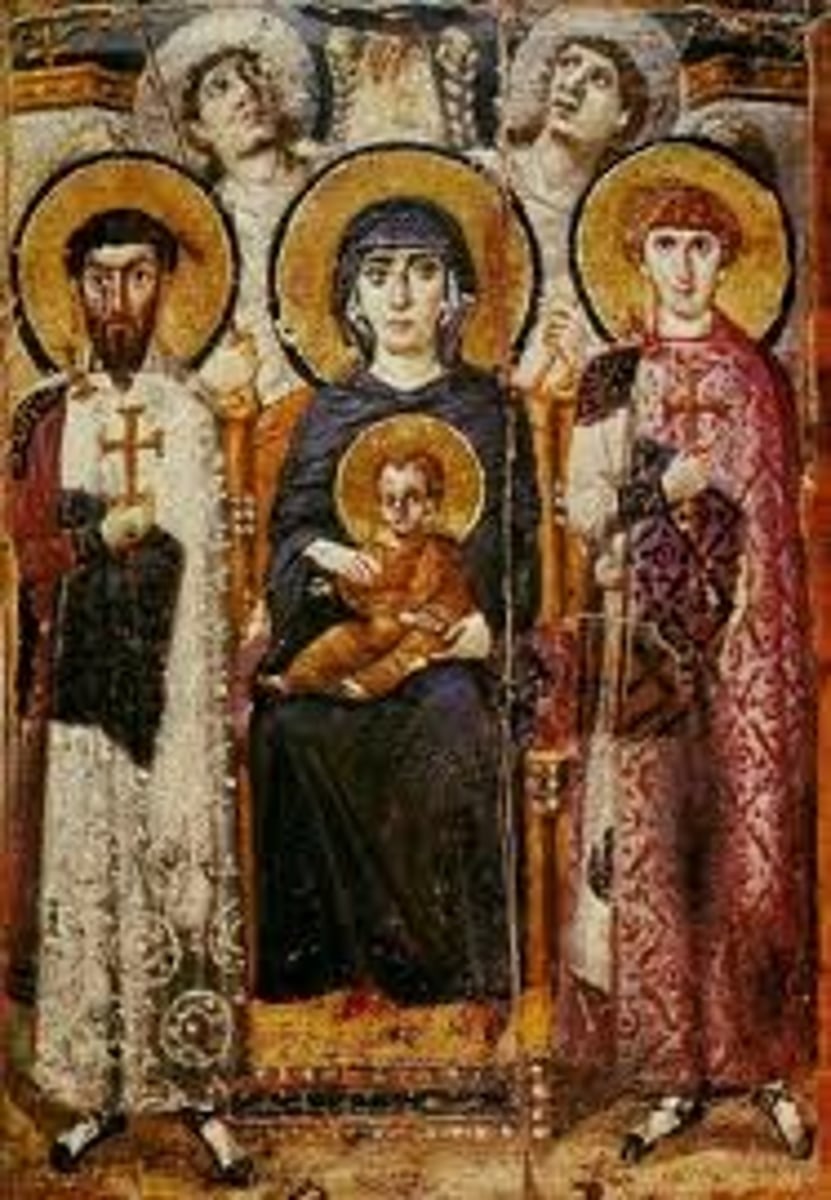
The Church of San Vitale, Ravenna, Italy, 526-547 CE

Virgin (Theotokos) and Child between Saints Theodore and George
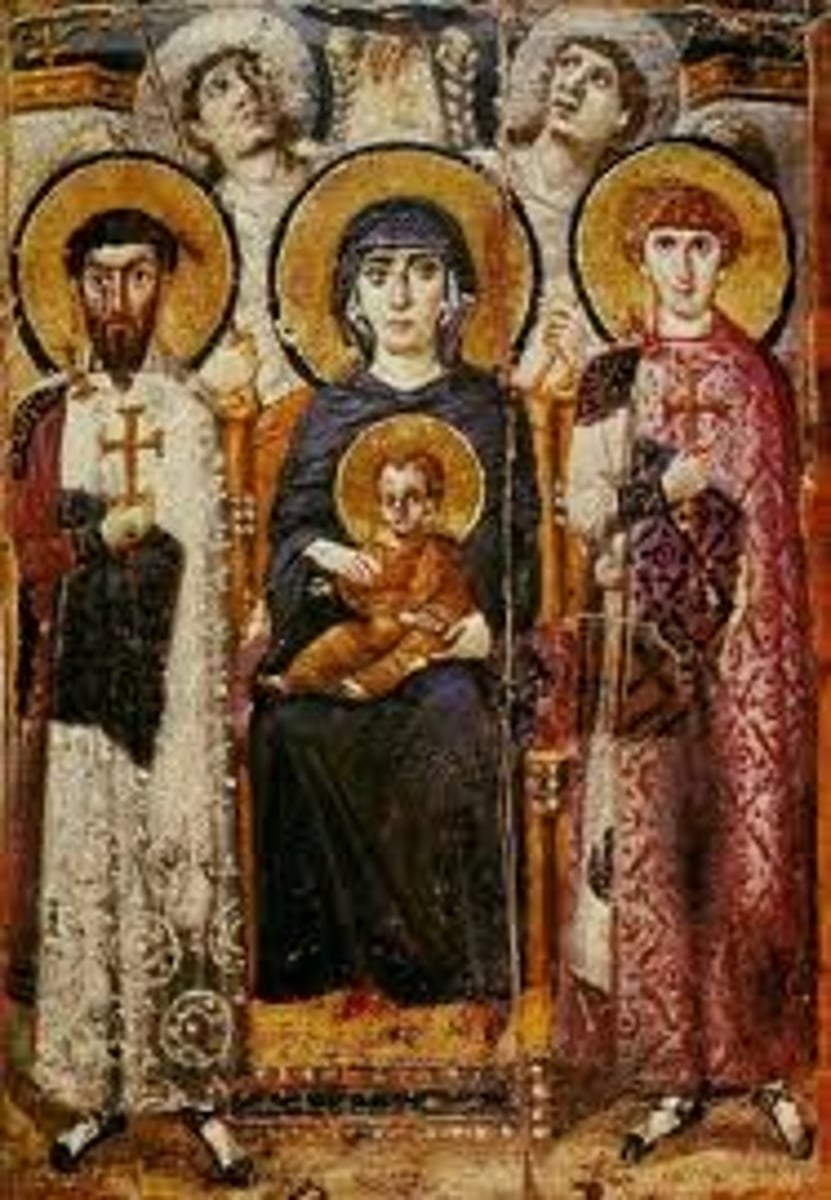

Hagia Sophia, Constantinople (Istanbul), Turkey designed by Anthemius of Tralles and Isidorus of Miletus, 532-537 (Early Byzantine)

Basilica
A huge marble government building in ancient Rome, large monumental space
Nave
the central area of a church
Clerestory
A row of windows in the upper part of a wall.
Apse
A recess, usually semicircular, at the east end of a church, which commonly housed an alter and signified the heavens
Arcade (Collonade)
A series of arches supported by piers or columns.
Virgin (Theotokos) and Child between Saints Theodore
and George, icon, sixth or early seventh century (Early Byzantine)

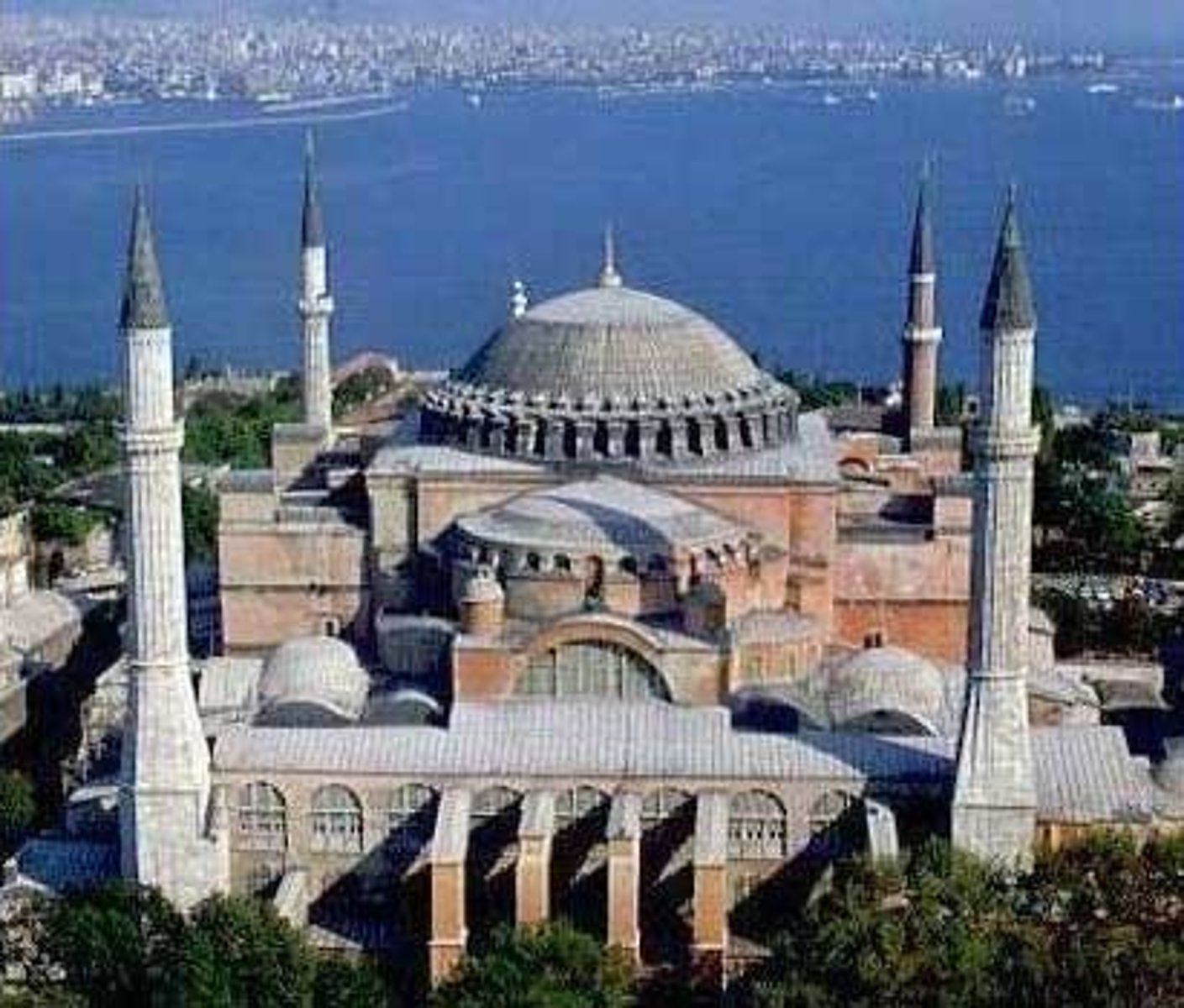
Katholikon Church, Hosios Loukas, Greece, first quarter
of the 11th century (Middle Byzantine)
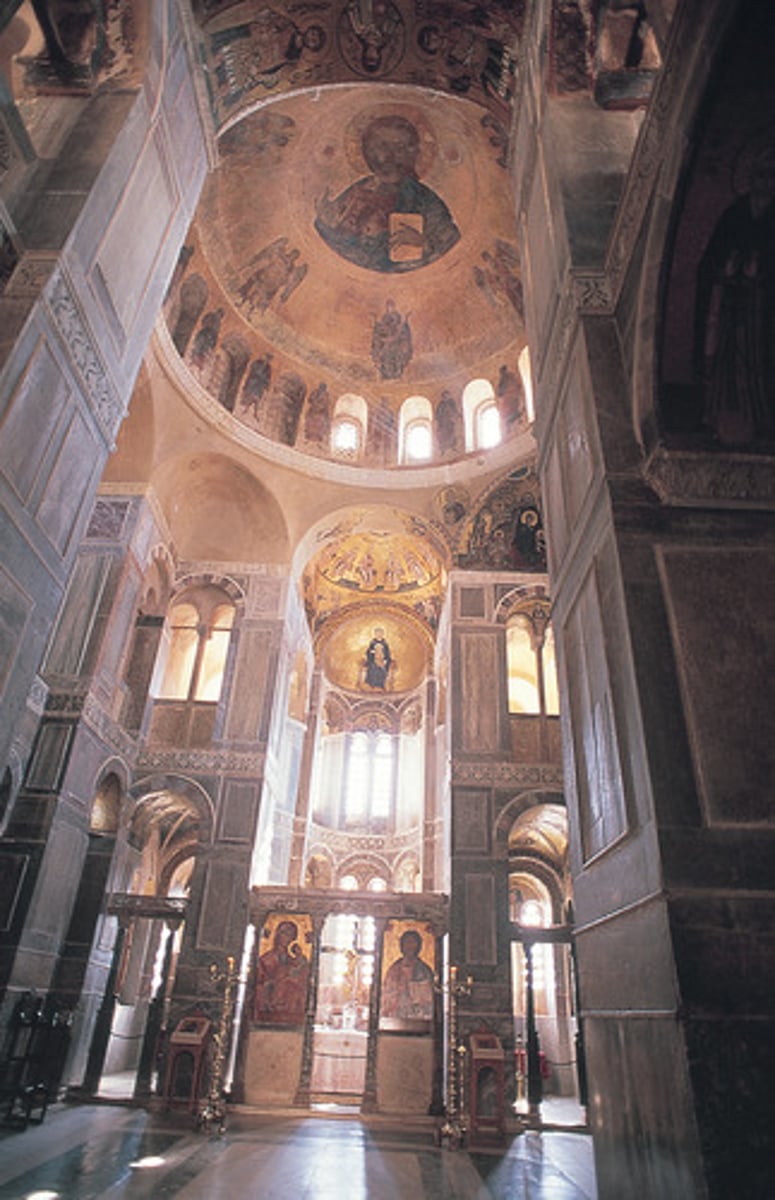

Icon
(n.) a representation or image of a sacred personage, often considered sacred itself; an image or picture; a symbol; a graphic symbol on a computer monitor display; an object of blind devotion
Iconoclasm
Opposing or even destroying images, especially those set up for religious veneration in the belief that such images represent idol worship.
Iconostasis
A screen or partition with doors and tiers of icons that separates the bema, the raised part of the church with the altar, from the nave, the main part of the church, in Eastern Churches.
Theotokos
A Greek title for Mary meaning "God bearer"
Cross-in-square plan
A Byzantine Church plan based on a square divided into 9 bays. The center bay is a large domed square, the 4 corners bays are small domed or groin vaulted squares, the remaining 4 bays are barrel-vaulted rectangles
Squinch
the polygonal base of a dome that makes a transition from the round dome to a flat wall
Pantocrator
In Christian art, the image of Christ as ruler and judge of heaven and earth.
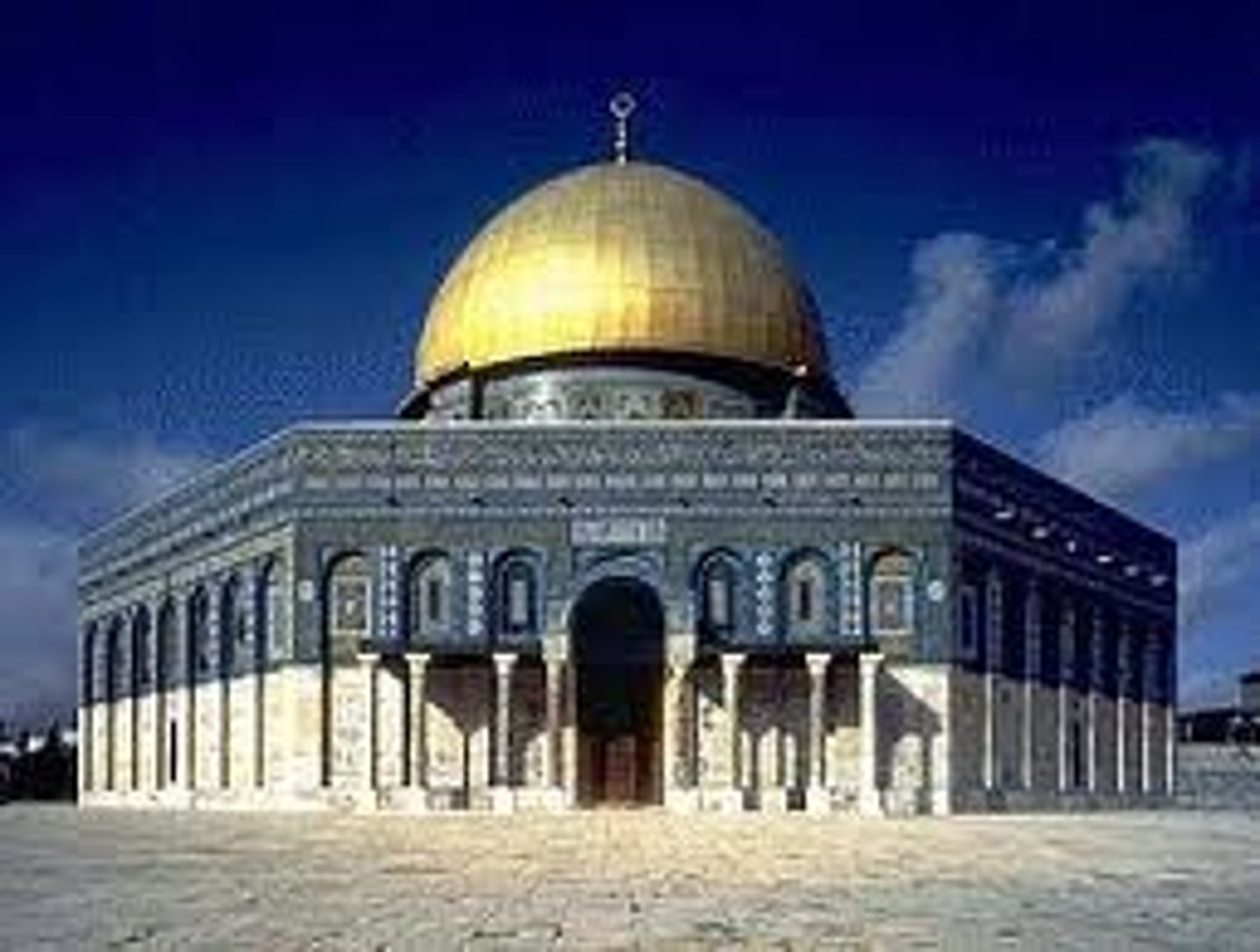
Dome of the Rock, Jerusalem, 687-692

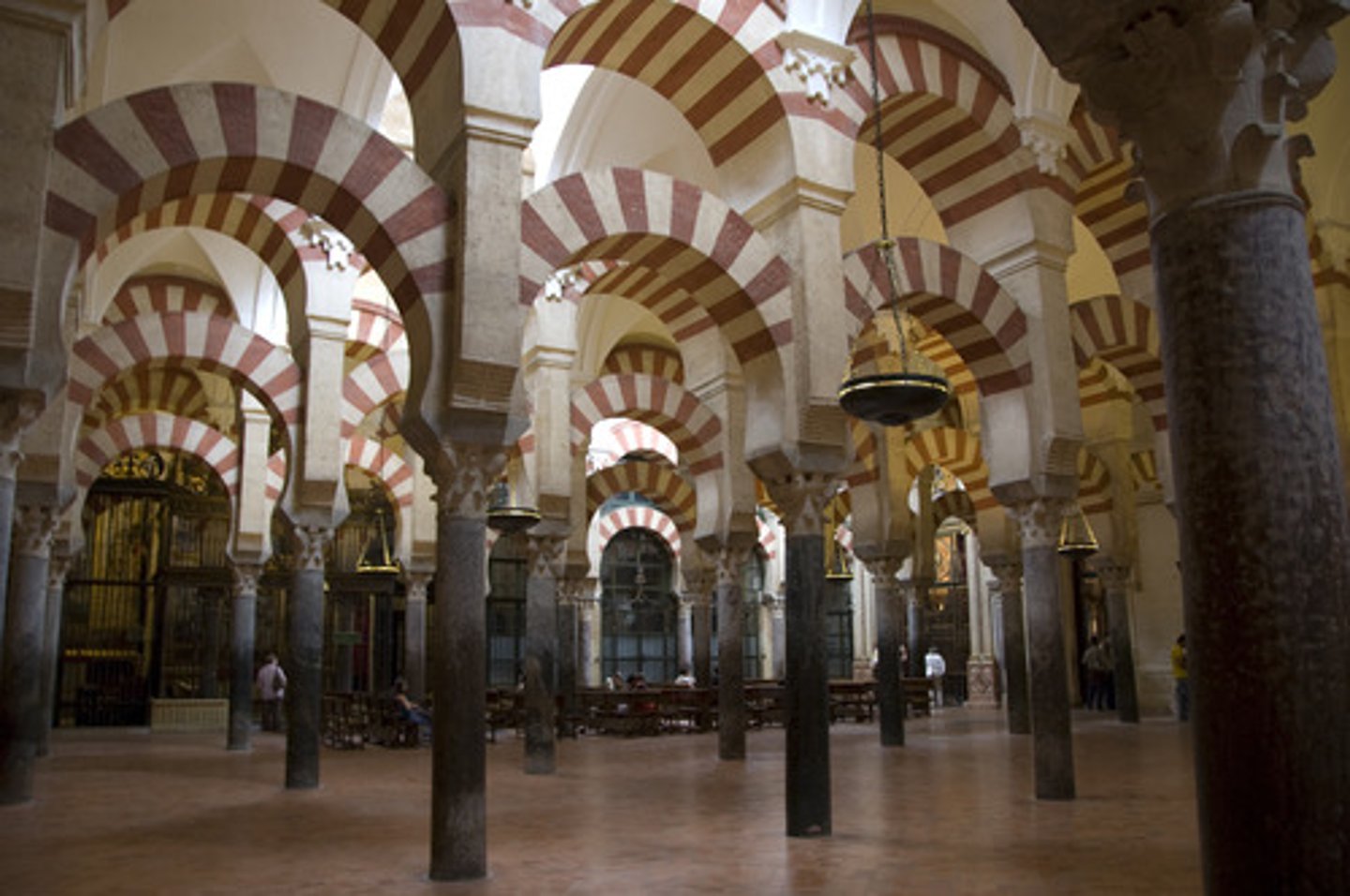
Great Mosque of Cordoba, Spain, 8th-10th centuries

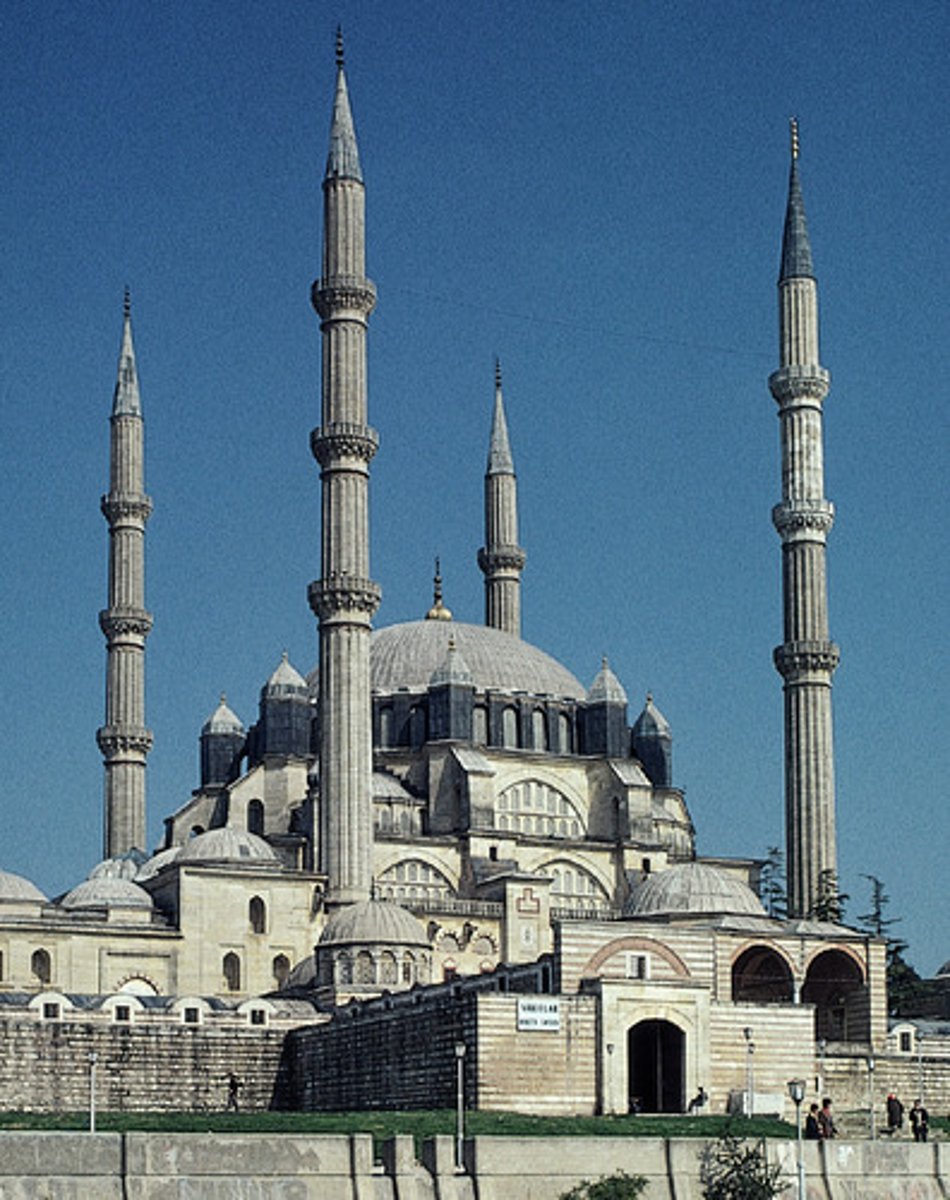
Mosque of Sultan Selim II, Edirne, Turkey, 1568-1575

ambulatory
of or for walking; capable of walking
Hypostyle mosque
A mosque whose hall is characterized by many closely spaced columns that support its roof.
Qibla wall
the wall of a mosque that faces Mecca; the wall Muslims face when praying
Mihrab
(Islam) a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the direction of Mecca
Minaret
A distinctive feature of mosque architecture, a tower from which the faithful are called to worship.
Minbar
in a mosque, the pulpit on which the imam stands
What does early Christian architecture borrow from greek and roman architecture?
1. Engaged columns (catacomb of peter and Marcellinus)
2. Artistic conventions of form and scale of important figures (Synagogue with wall paintings fro Hebrew bible)
3. Post and lintel-style architecture
How do depictions of important religious figures transform over time?
Icons of Jesus differ from the shepherd/poor man imagery in early Christian art, to a divine ruler of the heavens (older wiser) as Christianity became more mainstream and practiced by ruling families.
Differences between early Christian and Early byzantine churches
1. Byzantine churches featured more decorative aspects (windows, mosaics, separation between apse and nave)
2. Central plan churches became popular
Similarities between early Christian and byzantine architecture
1. Mosaic, decorative
2. Clerestory windows
3. Use of the apse as the altar and signal of the heavens
4. Nave
Narthex
A porch or vestibule of a church, generally colonnaded or arcaded and preceding the nave