X-Ray Final Lecture Exam
1/344
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
345 Terms
What is the dose limit of radiation for the general public?
1 mSv/year
What is the dose limit of radiation for occupationally exposed personnel?
50 mSv/year
What is the dose limit of radiation for pregnant persons?
<5 mSv/year
What does ALARA stand for?
As low as reasonably achievable
What are the three major ways to lower radiation dose?
Time, distance, and shielding
What are the main governing bodies of radiology in Canada?
Health and Welfare Canada, Ministry of Labour, and College of Veterinarians of Ontario (CVO)
What tools can be used for hands-free techniques in radiology?
Sandbags/troughs, sedation, lead gloves
What does it mean to collimate?
Limit exposure to area of interest.
True or False: dosimeters should be store in the Xray room when not being worn
False
What does attenuation mean?
The loss of sound wave energy as it travels through tissue
What does radiolucent mean?
Allows xray photons to pass through easily (not visible on xray)
What does radiopaque mean?
Does not allow xray photons to pass easily (visible on xray)
What is kilovoltage (kvp)?
The penetrating power of the xray beam
What are milliamperes (ma)?
Electrical current
What is the anode heel effect?
The intensity of radiation is greater on the cathode side of the xray tube
What does a conventional radiograph use?
Film cassettes
What does a digital radiograph use?
Digital plates
What are the two types of digital radiography?
Computed radiography (CR) and Direct digital radiography (DR)
what is the cathode?
The cathode is the negative electrode in an x-ray tube, where thermionic emission occurs to produce electrons that generate x-ray radiation.
What is the anode?
The anode is the positive electrode in an x-ray tube, where electrons collide to produce x-ray radiation.
What are some characteristics of xrays?
- Invisible
- Electrically neutral
- Can't be accelerated/made to change direction by a magnet/electrical field
- Travel at the speed of light in a vacuum
True or False: xrays are positively charged
False - they are electrically neutral and have no charge.
True or False: xrays travel in straight lines
True
1 multiple choice option
True or False: xrays cannot be optically focused
True
1 multiple choice option
What is somatic xray damage?
Affects physical structure of the body
What is genetic xray damage?
Mutation of genes
What is carcinogenic xray damage?
Formation of cancers
What is scatter radiation?
Xrays that bounced off of the target
What happens to the weak rays of an xray?
They bounce off of the target and become scatter radiation
True or False: some xrays are absorbed by the patient and do not make it to the film
True
1 multiple choice option
What determines the quality of the energy of the photons in the beam?
Kilovoltage (KVP)
What will higher kilovoltage (KVP) do to xray tissue penetration?
Increase the penetration ability of the X-rays, allowing them to pass through denser tissues more effectively.
What happens to a film when there is over penetration?
The bones in the film turn grey
What determines the quantity of photons in the beam?
Milliamperes (MA)
What two main factors do milliamperes determine?
The density of the beam and the darkness/lightness of the entire film
When more milliamperes are applied to the cathode, what happens to the rotating anode?
It rotates faster
3 multiple choice options
What is the high-voltage transformer?
Located beneath the xray table to connect to hospital power lines
What does the xray generator do?
Sends power from the high-voltage transformer through the circuit to the xray tube
What is the xray tube?
Most important part of the xray machine; produces xrays
What do grids do in an xray machine?
Absorb scatter radiation and improve contrast
What does a collimator do?
Controls the field of view
What does a cassette do and what type of radiography is it used for (film or digital)?
Film radiography - where the film sits
What does an imaging plate do and what type of radiography is it used for (film or digital)?
Digital radiography - converts the image from the plate and sends it to the computer monitor
What do intensifying screens do?
House an active layer of phosphorus which gives off light when exposed to xrays
What material is the xray cathode commonly made of?
Tungsten
What needs to happen to the cathode in order for it to produce electrons?
It needs to be heated
3 multiple choice options
Are cathodes positively or negatively charged?
Negatively charged
Are anodes positively or negatively charged?
Positively charged
How does the size of a filament affect the size of the image produced?
Larger filaments = larger images
3 multiple choice options
How are images created in film radiography?
X-rays are exposed a film which reacts to radiation. After chemical processing, areas exposed to more X-rays appear darker, forming an image
How are images created in computed radiography?
X-rays hit an imaging plate with phosphor crystals, which absorb radiation energy. The image on the plate is then converted into a digital image
How are images created in digital radiography?
X-rays directly interact with a digital detector, which immediately converts the radiation into an electronic signal, producing an image
How are images stored in film radiography?
In a dedicated storage area, images degrade over time
How are images stored in computed radiography?
In a PACS system
How are images stored in digital radiography?
In a PACS system
What is exposure latitude?
The range of exposure values (amount of X-ray radiation) that can produce an image of acceptable diagnostic quality
Which type of radiography relies on the use of chemicals?
Film radiography
Which type of radiography relies on the use of a darkroom?
Film radiography
Which type of radiography relies on the use of a phosphor crystal plate?
Computed radiography
Which type of radiography relies on the use of a PACS system for image storage?
Computed and digital radiography
Which type of radiography relies on the use of a digital detector?
Digital radiography
What are the two types of digital radiography?
Direct and indirect
What is the difference between direct and indirect digital radiography?
Indirect digital radiography has a scintillation layer and a photodetector; direct does not
What does a scintillation layer do?
Converts x-ray photons into light photons
What does a photodetector do?
Converts light photons into digital signals
What is automatic processing?
mechanized development of film radiography using an automatic processor, which controls the developer, fixer, wash, and drying steps to produce a diagnostic image quickly
How is beam direction defined?
First by where it enters the body and second by where it exits
What views make up the gold standard for thoracic and abdominal radiographs?
Right lateral, left lateral, and VD/DV
How often does PPE need to be tested?
Yearly or when damages
What does the 9 Penny test measure?
The alignment of the collimator light with the xray beam
Film fog
What type of artifact would be responsible for extra light obscuring the image?
Light leakage in darkroom, incorrect/damaged safelight
What can cause film dog?
Film fog
What artifact is seen in this xray?
Film fog
What artifact is seen in this xray?
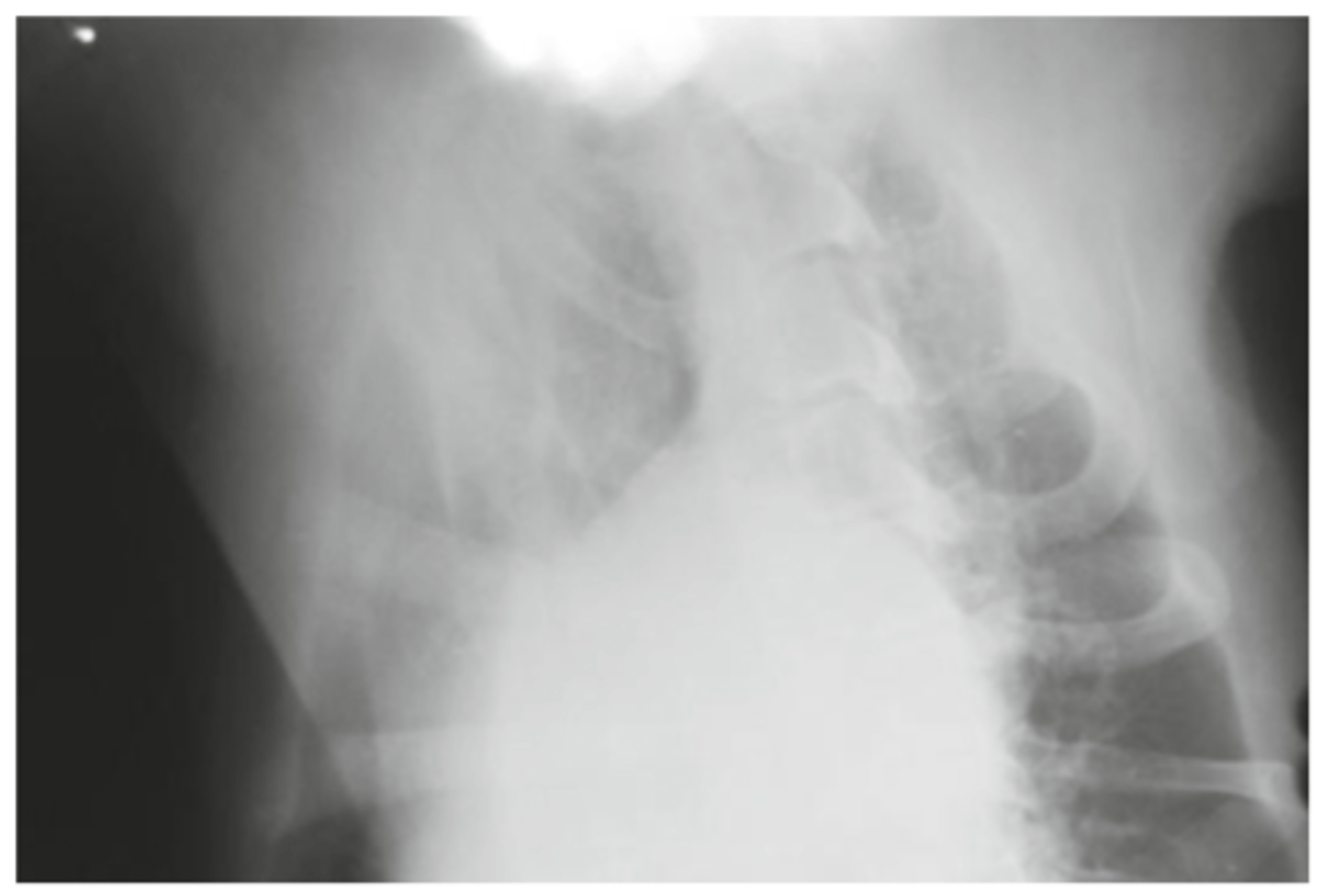
Manual and automatic processing, not digital
Which types of xrays can show film fog?
Chatter marks
What type of artifact would be responsible for evenly spaced pressure marks parallel to film travel?
Loss of contrast
What artifact is seen in this xray?
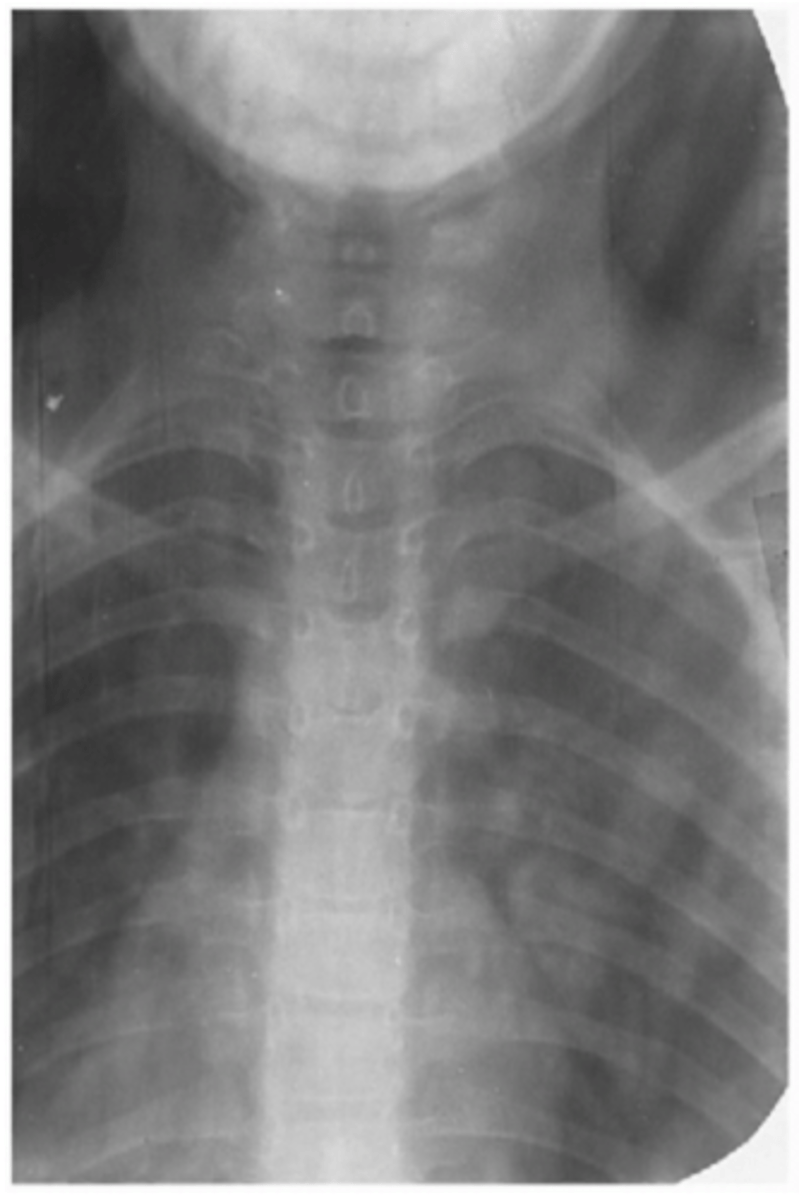
Roller marks
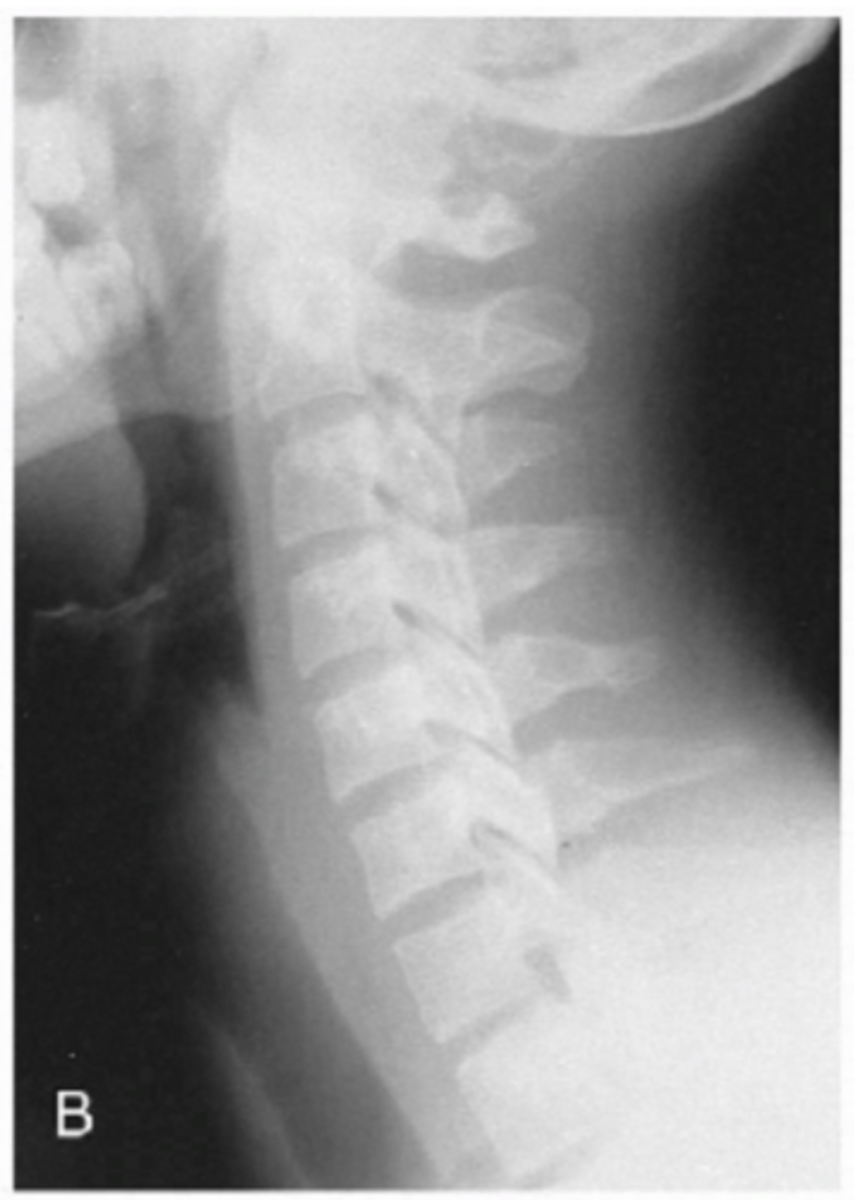
What artifact is seen in this xray?
Chatter marks
What artifact is seen in this xray?
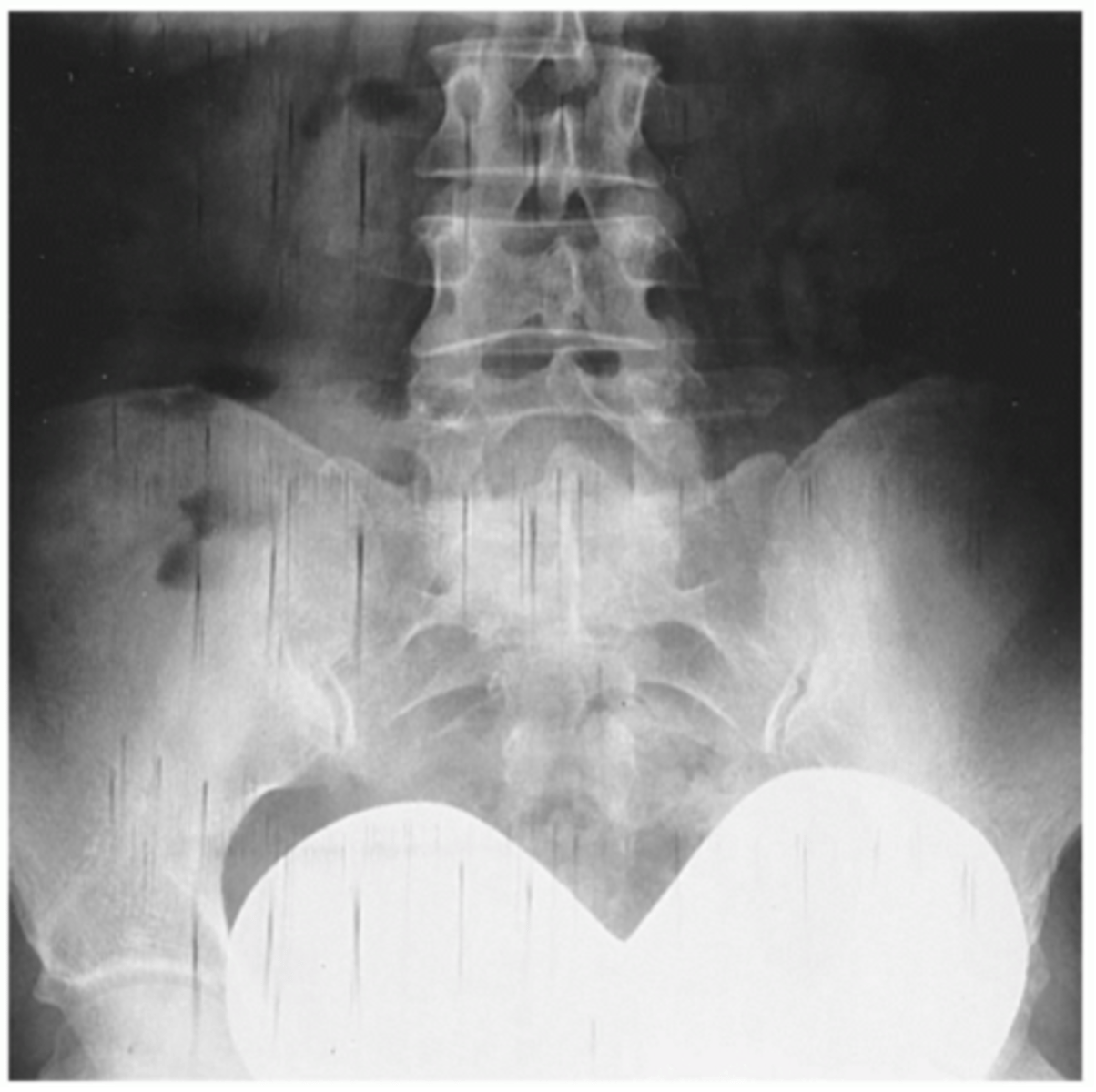
Increase mAs 30-50%
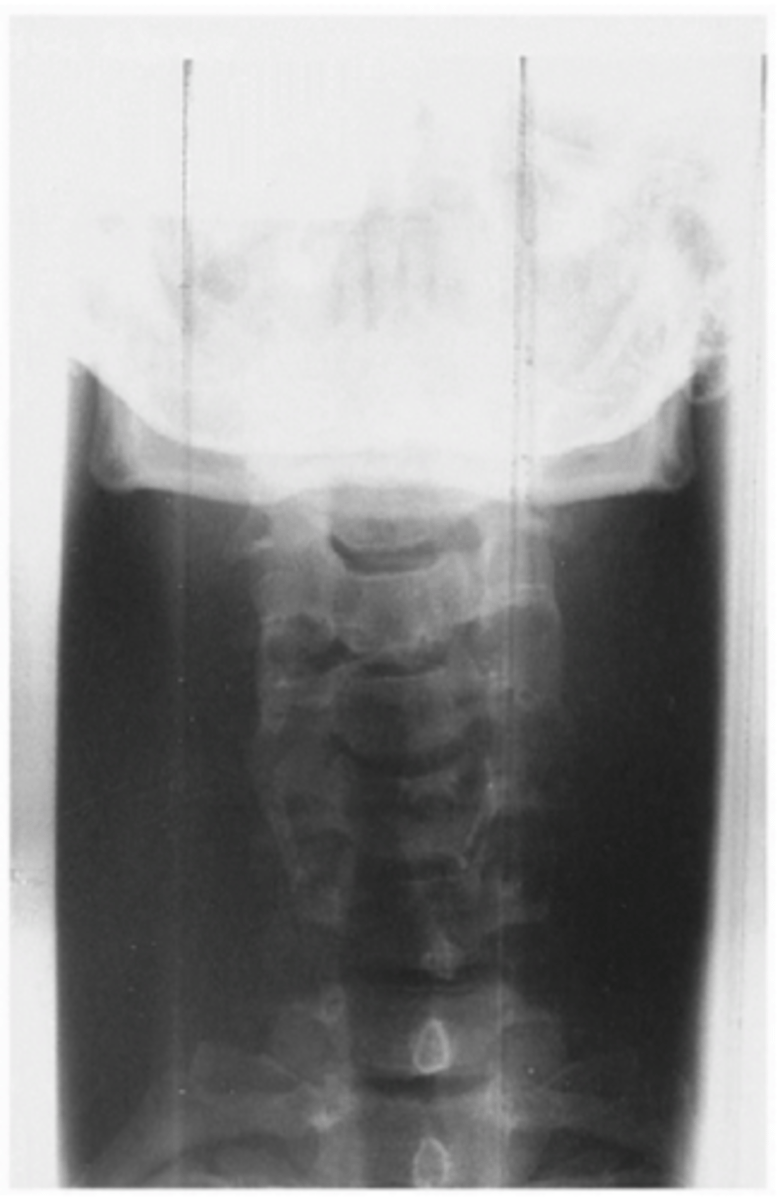
How would you adjust the xray machine to improve this image?
Increase mAs 30-50%
How would you adjust the xray machine to improve this image?
Hesitation lines
What type of artifact would be responsible for unevenly spaced pressure marks?
Automatic processing
What can cause chatter marks?
Automatic processing
What can cause hesitation lines?
Automatic processes
What can cause pressure marks?
Pressure marks
What type of artifact would be responsible for irregular density marks parallel to film travel?
Contaminated or old chemicals
What can cause a loss of contrast?
Chemical retention
What type of artifact would be responsible for a brown/yellow discolouration?
Inappropriate washing time
What can cause chemical retention?
Decrease contrast
What will an increase in kVPs do to contrast?
Increase contrast
What will a decrease in kVPs do to contrast?
Increase contrast
What will an increase in mAs do to contrast?
Decrease contrast
What will a decrease in mAs do to contrast?
Increase mAs 30-50%
How would you adjust the xray machine in response to a too light image with adequate penetration (organs/bones are easily discernible)?
Increase kVPs 10-15%
How would you adjust the xray machine in response to a too light image with inadequate penetration (organs/bones are not easily discernible)?
Decrease kVPs 10-15%
How would you adjust the xray machine in response to a too dark image with inadequate penetration (organs/bones are not easily discernible)?
Decrease mAs 30-50%
How would you adjust the xray machine in response to a too dark image with adequate penetration (organs/bones are easily discernible)?
Patient name, owner last name, date, view taken, clinic name
What information is required for an xray patient label?
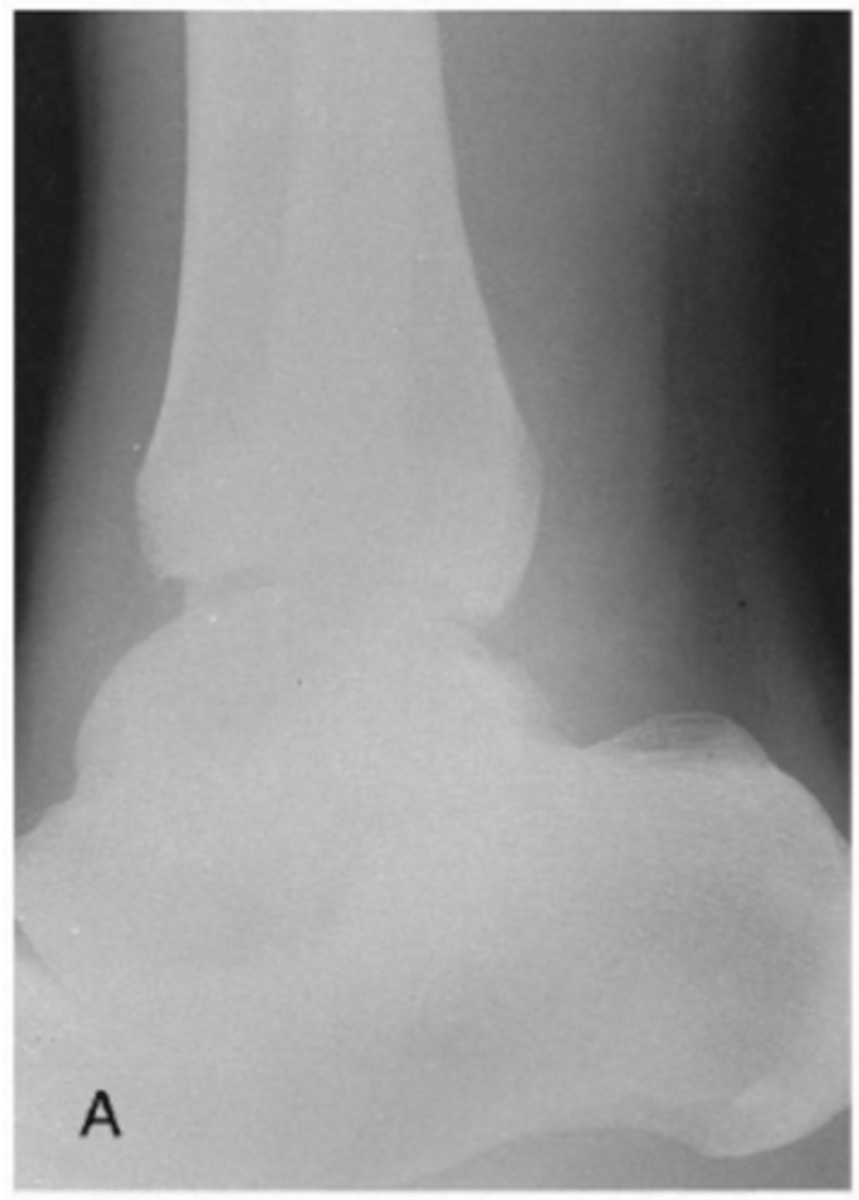
Increase mAs 30-50%
How would you adjust the xray machine to improve this image?