the control of gene expression
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Ectopic pregnancy
When an embryo starts to develop in the fallopian tube and it cannot attach to the uterus lining or the umbilical cord to access the maternal bloodstream and nutrients from the mothers
What is another name for adult cell cloning?
Somatic cell nuclear transfer
What is another name for adult body cells?
Somatic cells
Explain what somatic cell nuclear transfer is
When the nucleus from a somatic cells in implanted into an egg cell
Which is then cloned to produce stem cells which can differentiate into specialised cells
And self renew, by replacing the used up stemcells.
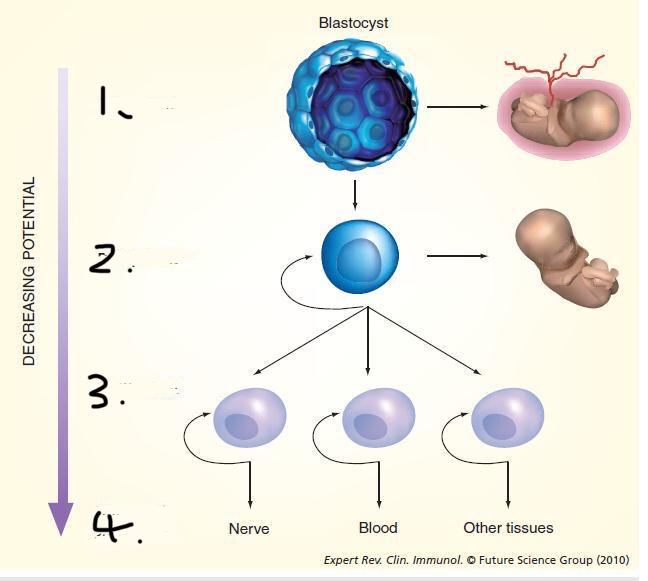
Label the types of stemcells on this hierarchy diagram

Define Totipotent cells
Cells which can mature into any body cell
Define totipotent stem cells
Cells found in the early embryo and can differentiate into any type of cell
Give an example of something made of totipotent cells
Zygotes
Define Pluripotent stem cells
Cells found in embryos and can differentiate into most cells types.
Give to examples of pluripotent stem cells
Embryonic stem cells
Fetal stem cells
Define Multipotent Stem cells
Cells found in the tissue of adults and can differentiate into limited specialised cells types
Give an example of Multipotent stem cells
Cardiomyocytes- heart muscle cells which can differentiate into heart muscle and tissue
Define Unipotent stem cells
Cells which can only differentiate inti one type of cell
What are the 2 properties of stem cells
Differentiation
Self renewal- keep producing more stem cells which replace the used ones
What does IPS stand for?
Induced Pluripotent Stemcells
How are IPS stem cells made?
When stemcells are taken from a patients uniopotenf cells to grow into specific cells by controlling their gene expression and transcription factors. Allowing them to be genetically altered to gain embryonic stem cell characteristics.
What are three advantages of using IPS
Can create new organs and tissues
No immune rejections after transplant
Better substitute to using human embryos
What are some pros and cons of using embryonic stem cells from embryos
Pros
-could help in fertility treatments
Cons
-ethical and religious issues
-can also be obtained through adult bone marrow not just embryos
Explain how Oestrogen hormone bind t receptors to create transcriptional factors and how they function in the transcription of DNA
Oestrogen diffuses across the cell membrane
Oestrogen binds to the receptor, forming a transcriptional factor
causing a conformational change in the shape of the DNA binding site
The transcriptional factor moves through the nuclear pores and binds to the DNA promoter region
To drive the transcription of the DNA
Define Chromatin
DNA associated with histones, and is covered in chemicals called tags which form a second layer called an epigenome
Define Epigenetic mechanisms
Environmental factors which can causes heritable changes in gene expression function without changing the base sequence of a DNA-links to Lemarkcism
What Does metastatic mean in metastatic cancer?
Malignant cancer
Explain how cancer is caused (3 marks)
Cancer is caused by damage to the genes that regulate mitosis and the cell cycle.
Leading to uncontrollable cell division
Creating Tumours (groups of abnormal cells)
Either malignant or benign tumours
Explain how the methylation of tumour supressing genes can lead to cancer
Methylation prevents the transcription of gene. Protein is not produced
Therefore no control over cell cycle and mitosis causing cell death/apoptosis
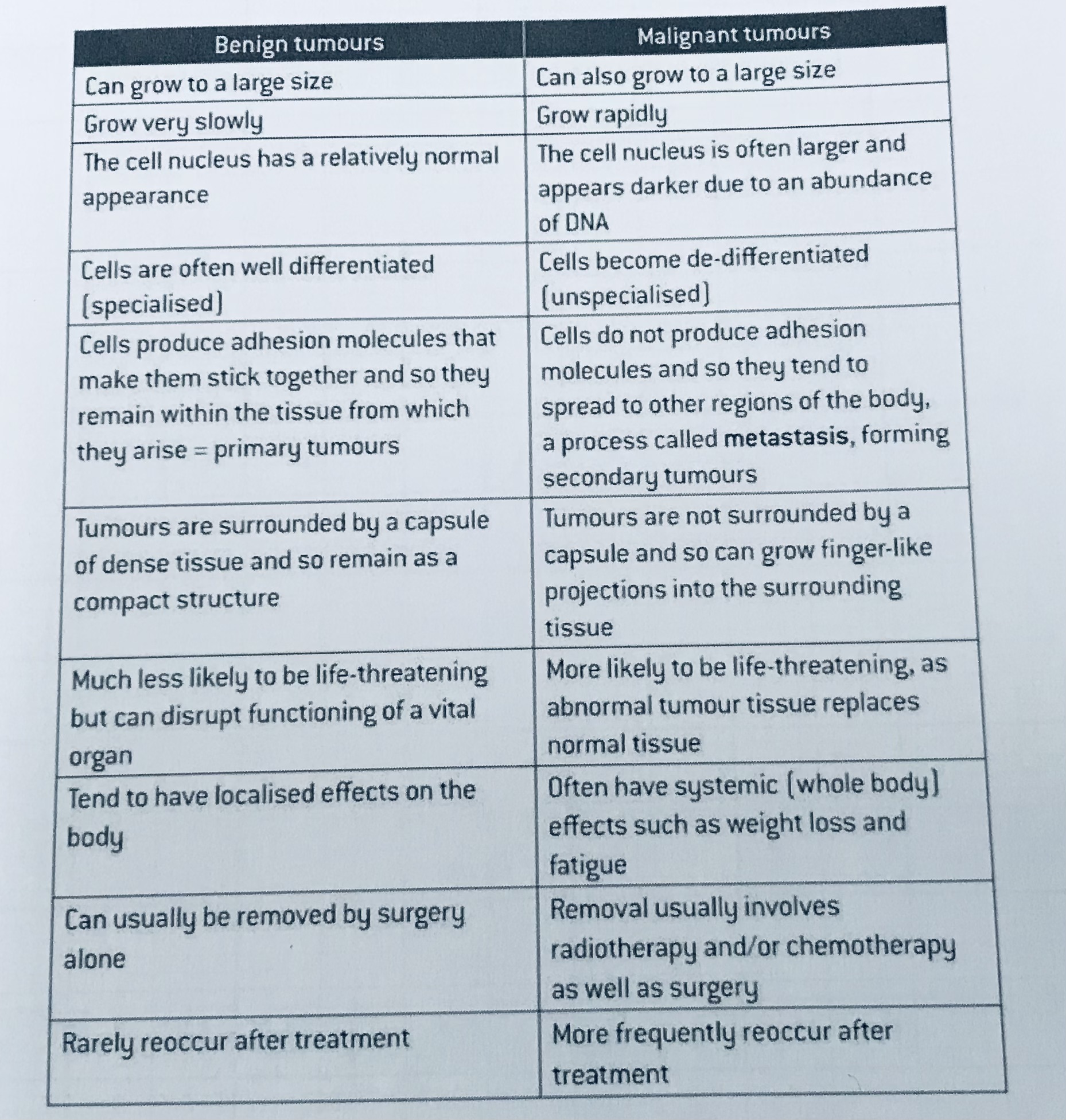
Complete the column for malignant tumours

Complete the column for when the DNA bases are accessible
