Things to Note - Topic 17B Carboxyl, Ester & Acyl Chloride
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
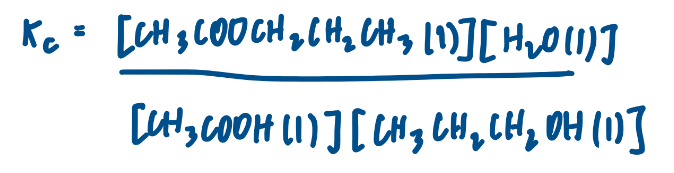
Explain why it is possible, in this case, to calculate Kc using equilibrium amounts in moles, rather than in equilibrium concentrations.
Same number of moles on both sides of the equation
So volume cancels in Kc expression
The pink colour of the phenolphthalein fades after the end-point of the titration has been reached. Give a possible explanation for this observation.
the equilibrium shifts to the left / the mixture absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
So the mixture is becoming more acidic / the acid reforms
Explain what you could do to confirm that one week is sufficient time for the mixture to reach equilibrium.
carry out / repeat experiment and leave for longer than a week
The titre value / Kc value will remain unchanged (if equilibrium has been established)
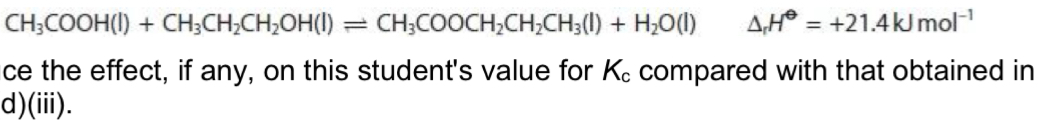
A student repeated the experiment, but left the mixture in a water bath at 40 degrees Celsius until equilibrium was reached. Deduce the effect, if any, on this student’s value for Kc compared with that obtained at room temperature.
Kc value will be greater than that calculated when experiment was carried out at room temperature
Because the forward reaction is endothermic
Ethyl ethanoate can also be formed by reacting ethanol with ethanoyl chloride, CH3COCl. Identify three differences in the esterification reaction when ethanoyl chloride is used instead of ethanoic acid.
the reaction is irreversible compared to reversible
Hydrogen chloride is the by-product rather than water
The reaction is very fast / occurs at room temperature so an acid catalyst is not needed
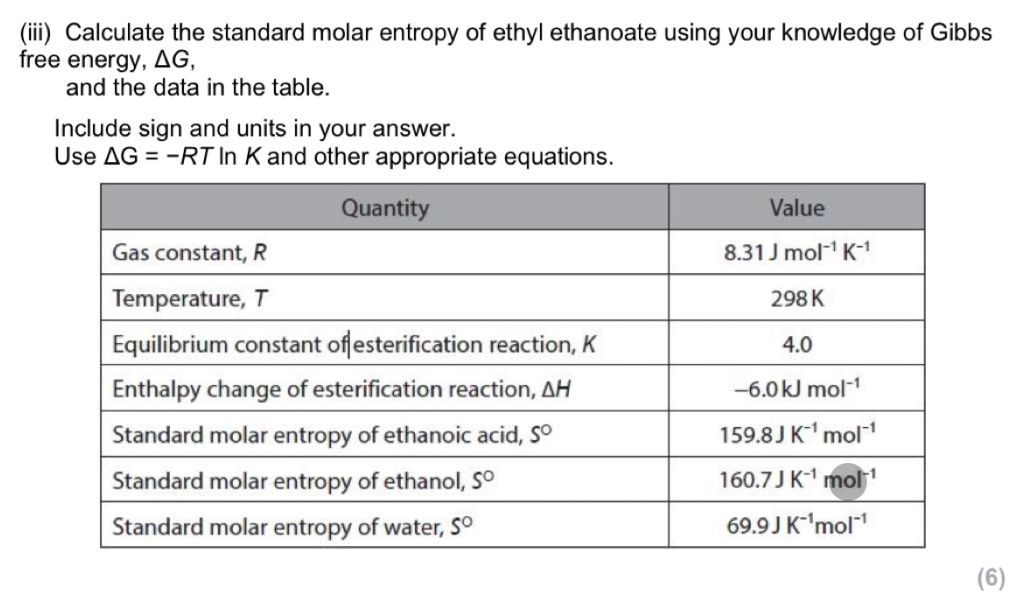
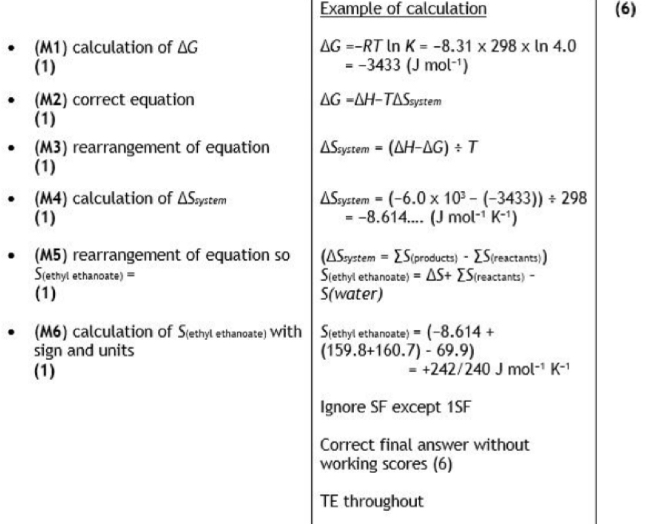
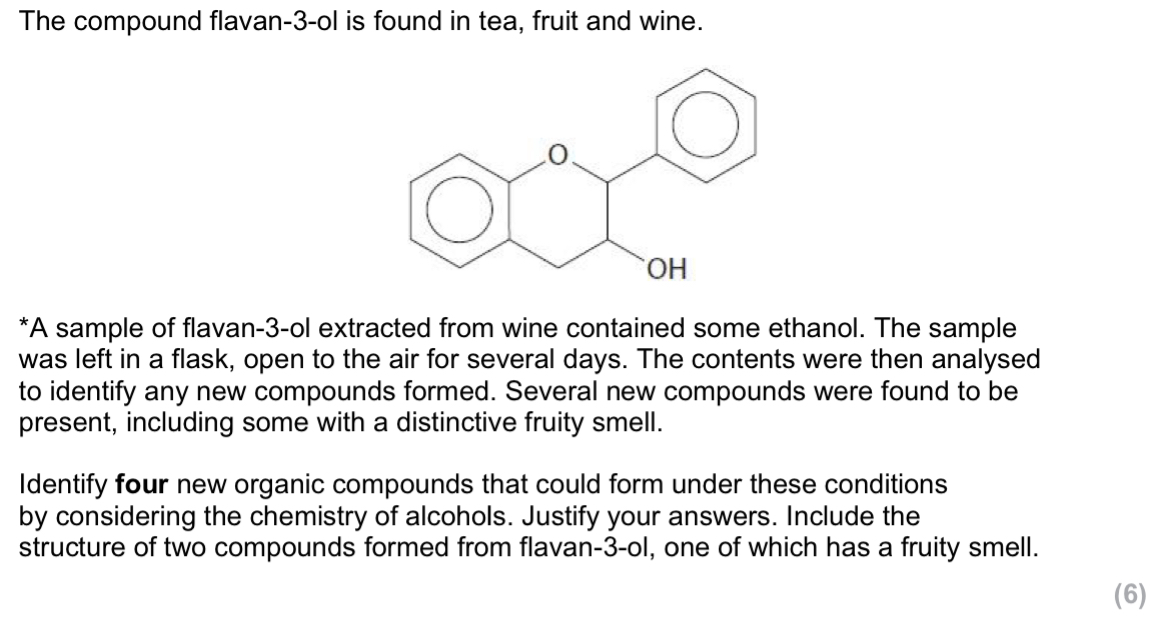
oxidation of ethanol or oxidation of flavan-3-ol (by oxygen in the air)
Formation of either ethanoic acid or ethanal (from ethanol)
Flavan-3-one
OH group on flavan-3-ol forms an ester with ethanoic acid
(Structure of ester formed between flavan-3-ol and ethanoic acid


Esters have many uses due to their characteristic aromas and often have common names. For example, isomyl acetate is referred to as banana oil and amyl acetate has a scent similar to apples. Esters can be hydrolysed by heating under reflux with aqueous acid or alkali. Compare and contrast these two methods of hydrolysis for amyl acetate.
(Similarity)
both make (the same) alcohol / pentan-1-ol
(Differences)
acid hydrolysis is reversible, alkaline hydrolysis is irreversible
Acid hydrolysis produces the carboxylic acid / ethanoic acid and alkaline hydrolysis produces the carboxylate / ethanoate (ion)
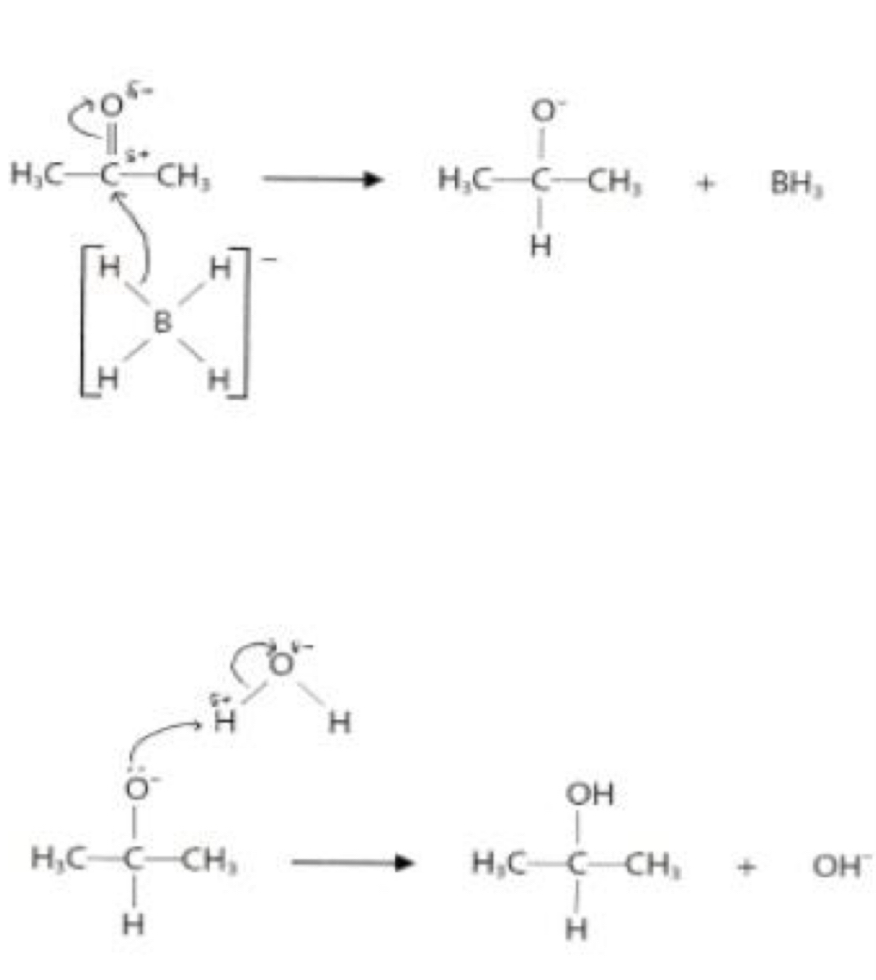
The product of this reaction (nucleophilic addition of CN to pentan-2-one), 2-hydroxy-2-methylpentanenitrile, has a chiral centre. Explain why a racemic mixture of 2-hydroxy-2-methylpentanenitrile is formed in this reaction.
Pentan-2-one is planar about the carbonyl carbon
The CN- nucleophile attacks equally from above and below / either side of the plane