histo 3: pls be file heavy pls Maria I am begging you to not let me down girlypop
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
what causes a gastric ulcer?
Mucosa (?) <-- according to files
This is partly true, a break in the mucosal lining can lead to a gastric ulcer. I guess you should know that gastric ulcers are associated with H. Pylori and can be caused by H. Pylori, NSAIDs, stress, smoking, alcohol, and genetics
you have a patient with high levels of gastrin. Autoantibodies are acting on?
a. Acting on enterocytes (G-cells, specifically) <--
b. But the autoantibodies would be associated with Paneth cells since those are immunologically related
^^^ this is the answer provided by files, but from what I was researching, I think the answer may be parietal cells that they would be acting on? Someone smarter than me can send me a correction because idk crap man lol
What does the pars infundibulum secrete?
ACTH and MSH (had both answers on our exam, so I dunno which one she'll ask of your class)
What is the periodontal ligament derived from?
a. Dental follicle
b. Enamel organ
c. Root sheath
d. Weil
a. Dental follicle
What develops first, ameloblasts or odontoblasts?
Ameloblasts, but odontoblasts differentiate (start producing dentin) before ameloblasts start producing enamel
T/F: Ameloblasts and the enamel organ start degenerating at the time of tooth eruption.
TRUE
Which cells secrete PTH?
Chief cells
--> She had two arrows pointing to oxyphil cells, so it couldn't be either of those answers, and then she had one pointing to fat, which also doesn't make sense. So by process of elimination, it was the darker, smaller chief
cell. Just in case you can't remember what it looks like.
Which cell type has a receptor for calcitonin to stop resorption?
Calcitonin
--> Just FYI, osteoblasts have PTH receptors
The secretory ends of ameloblasts form what?
Tomes processes (not fibers! Fibers come from odontoblasts)
If you have damage to the myenteric (Auerbach) plexus, what would you see clinically?
Decreased motility only
(- can someone verify that you don't inhibit gastric secretions? ) --> according to extremely brief research, no you don't inhibit gastric secretions but you may want to do your own research
If you have a patient who has low B12, what cell might not be functioning correctly?
parietal cell
Which cell of the DCT works with acid-base balance and secretes bicarbonate?
Intercalated cell
Which ducts are lined with cuboidal epithelium and secrete bicarbonate?
intercalated duct
Which pancreatic secretion doesn't secrete in its active form?
trypsin
What hormone stimulates and releases bile from the gallbladder?
CCK
What cell of the islet of Langerhans secretes glucagon?
Alpha cells
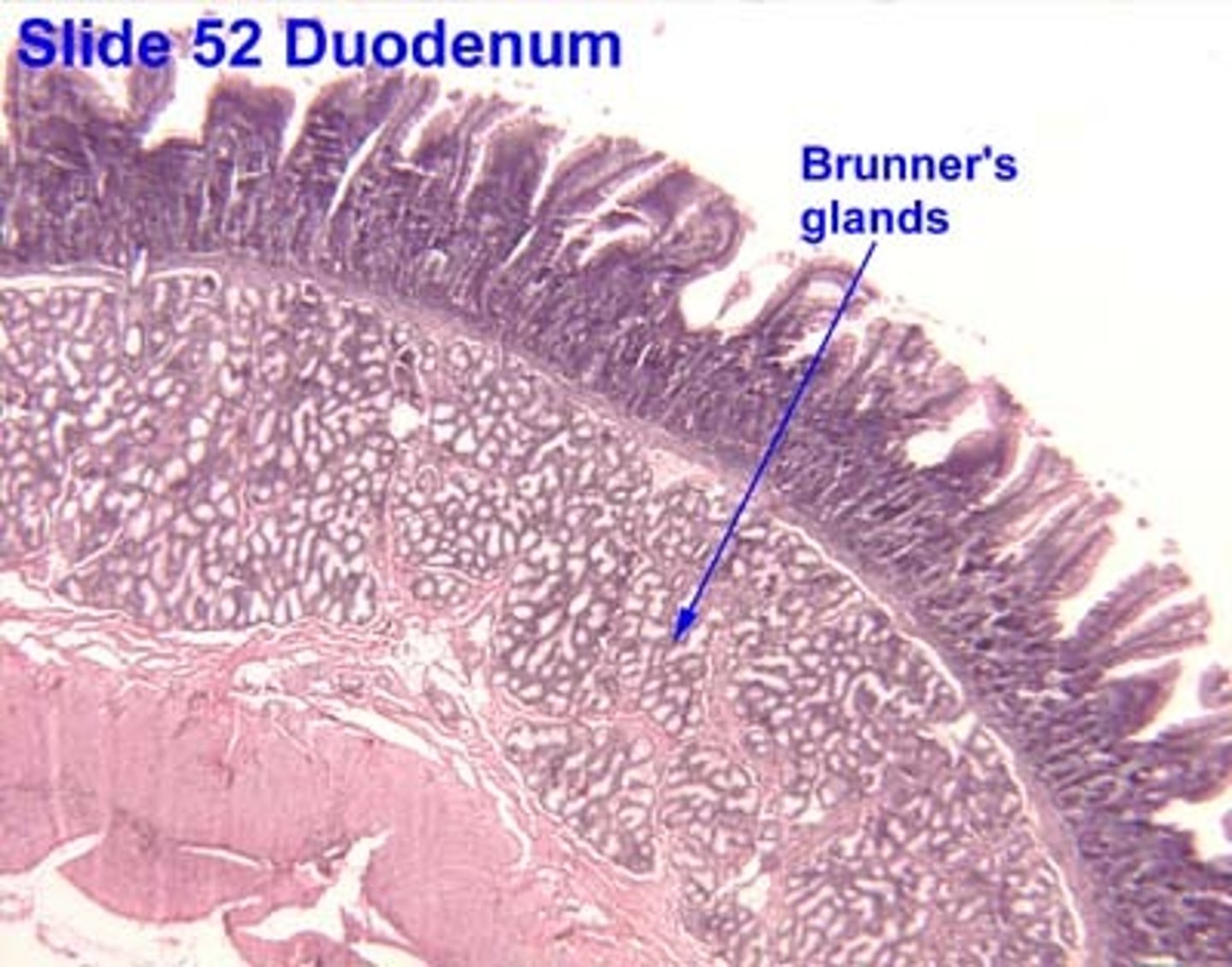
What does Brunner's glands secrete?
alkaline mucus
Patient has Barrett's esophagus and has metaplasia from what kind of normal epithelium found in the esophagus?
Stratified squamous epithelium, non-keratinized
which cell secretes pepsinogen?
Chief cell
which cell secretes antibacterial substances
paneth cells
Patient has adenocarcinoma and is diagnosed with Cushing's Disease. What hormone do they have in excess?
ACTH
Celiac disease affects the folds in the small intestine and leads to the blunting of the structures. What are these called/what makes these?
plicae circulares
hormone that increases hunger and may stimulate GH
Ghrelin
What part of the GI tract is important for digesting fiber and balancing fluids?
Large intestine/colon
What is not a function of gastric mucosa?
a. Absorption
b. Secretion
c. Protection
d. Peristalsis
d. Peristalsis
Where are oxytocin and ADH secreted from?
Supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei
What are Ito / stellate cells used for?
Vitamin d and a storage
What cells are phagocytic in the liver?
Kupffer
What is the order that a substance passes through to get into the PCT from the glomerulus?
glomerulus?
a. Fenestrated capillary → basal lamina → negatively charged podocytes of visceral layer of bowman's capsule
--- If you don't remember which order it is, she has another answer that has it backward (so from PCT into glomerulus). Just pick the opposite one of that. Make sure it's also negatively charged, not positive
What structure creates osmotic pressure?
Loop of Henle
What part of the nephron is responsible for most water and ion reabsorption?
PCT
Which salivary gland opens up opposite the upper second molar?
Parotid
Which cells in the macula densa have baroreceptors to sense blood pressure changes?
Juxtaglomerular cells (JG cells)
Which zone of the adrenal gland secretes aldosterone?
Zona glomerulosa
You take a biopsy of the esophagus. How do you differentiate which section you're in?
Look at the muscularis externa
Which part of the nephron forms peritubular capillary network and drains the glomerulus?
Efferent arterioles
What is the function of the pineal gland?
Relate light and something to endocrine functions.
--> Just pick the answer that says something about light or the circadian rhythm or hormones
Which papillae lack taste buds?
Filiform
What is the visceral layer of the glomerulus or Bowman's capsule?
Podocytes
What glands are associated with circulate and foliate papillae and suspend taste molecules?
Von Ebner's glands
What enzyme in the oral cavity aids in breaking down carbs?
Amylase
What is not a part of the enamel organ?
a. Stellate reticulum
b. Odontoblast
c. Ameloblasts
d. Root sheath
b. Odontoblast
Throughout the entire GI, the submucosa is associated with?
PS ganglia and meissner's plexus
You see a brunner's gland. Where are you?
Duodenum
What hormone stops gastric secretion and increases smooth muscle contractions of the stomach?
Secretin
Which of these raises blood pressure by acting on the kidneys?
Aldosterone
--> She lists all the other hormones in the RAAS system, but it's aldosterone that actually raises BP
What is the primary functional role of the portal lobule
to drain bile toward the bile duct in the portal triad
(idk there is some question that shows a SEM of a portal lobule so know what that looks like and what a portal lobule does I guess)
When is calcitonin released?
when blood plasma is high
what makes LSH and FH
Gonadotrophs
What does Von Ebner's gland secrete?
Ligual lipase