1.09 Optic nerve head
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What are ganglion cells
A type of neurone/nerve cell and their axons gather at the optic disc where they become myelinated aand form the optic nerve
What do ganglion cells do
Connect our eyes to the brain
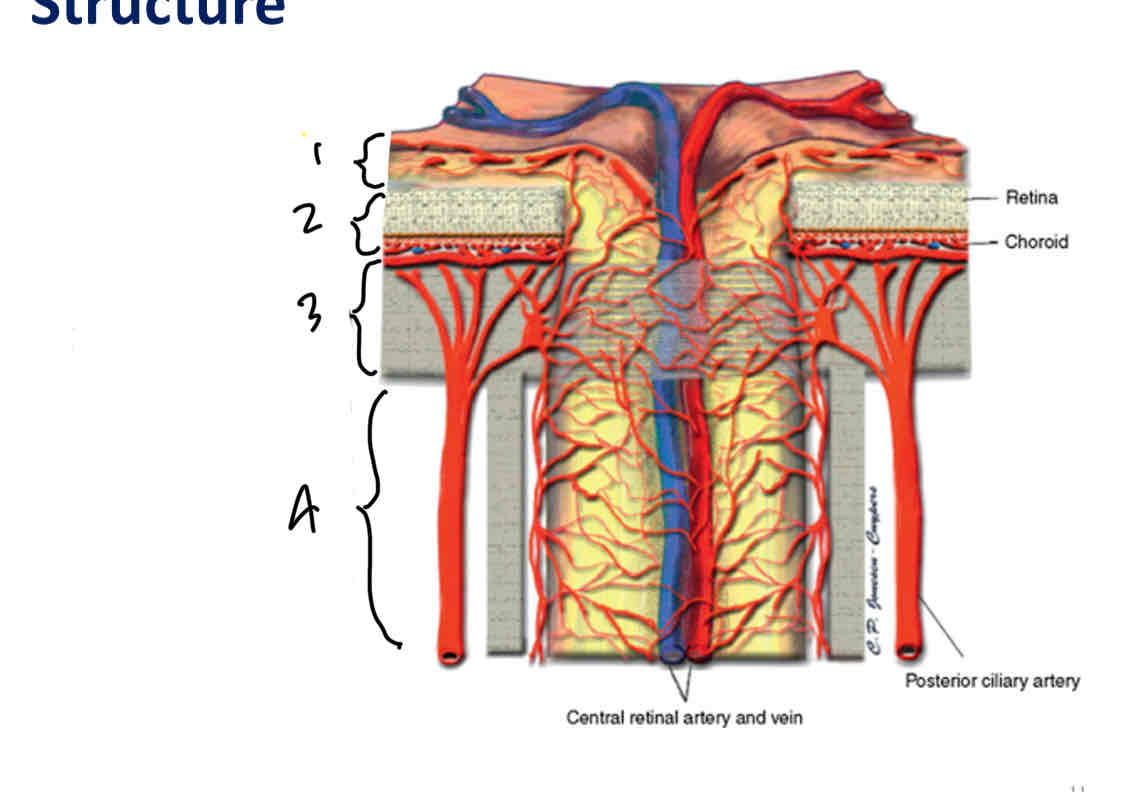
Label ONH
Superficial nerve fiber layer region
Prelaminar region
Lamina cribrosa region
Post/retrolaminar region
What is the lamina cribrosa and its structure
Part of the sclera situated at the site of attachment of the optic nerce.
Its a seive like membrane through which the fibres of the optic nerve pass
Weaker than the rest of the sclera as it has many holes which vary in size and lots of open space (less collagen)
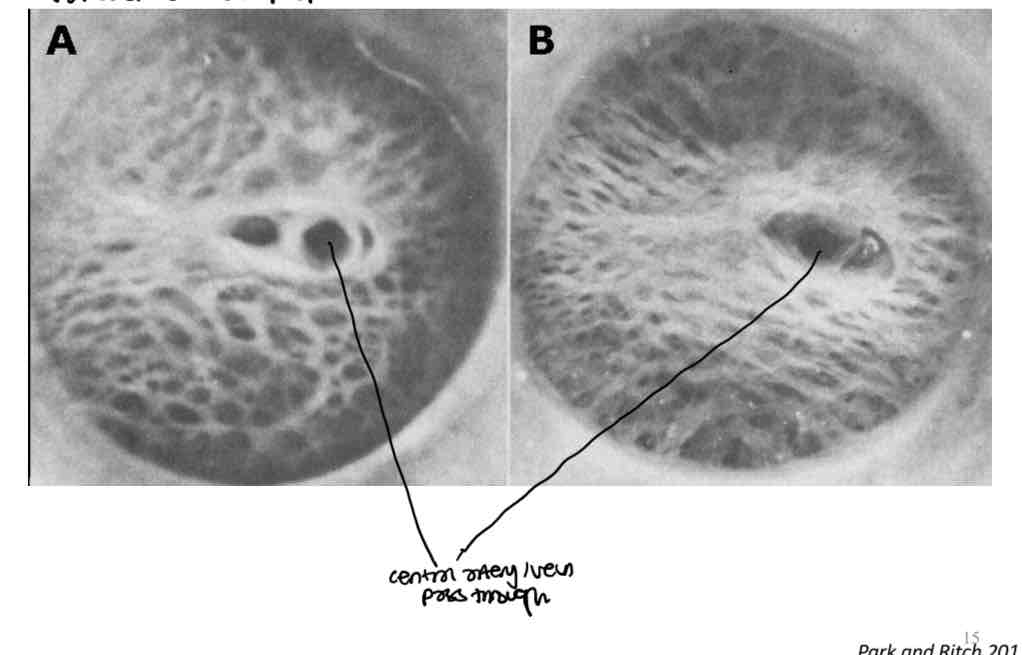
Difference in number of holes at the anterior and postierior face of the lamina cribrosa
Posterior - more holes - 500
Anterior - less holes - 300
A bundle of nerve fibres pasasing through the LC pass through one large hole at the anterior surface and then separate to pass through 2 smaller holes at the posterior surface
What is the lamina cribrosa region defined by
The sclerla fibres that intersect the axon as they exit the eye
Where is the optic nerve head in the superficial nerve fiber layer/prelaminar region
Nerve head lies between the lamina cribrosa and vitreous
What is the retrolaminar region
1st mm of optic nerve behind the eye
Optic nerve head formation
Formed by ganglion cell axons which converge onto the ONH in bundles. Axons in each bundle come from an entire strip of retina over which that bundle has passed
Each bundle is surrounded by other tissue
What does the prelaminar region contain
Most of the tissue around the axon bundle consists of glial cells - specifically astrocytes
What does the post laminar region contain
Contains more connective tissue
Fewer astrocytes
More oligodendrocytes
What do oligodendrocytes do
Produce myelin around axons
What are glial cells
Non neuronal cells in the nervous systen that dont produce electical impulses
What is myelin and its purpose
An insulating layer (sheath) that forms around nerves allowing electrical impulses to transmit quickly and efffeciently
Where are axons myelinated
Myelination is usually only found outside the eye in the post laminar region
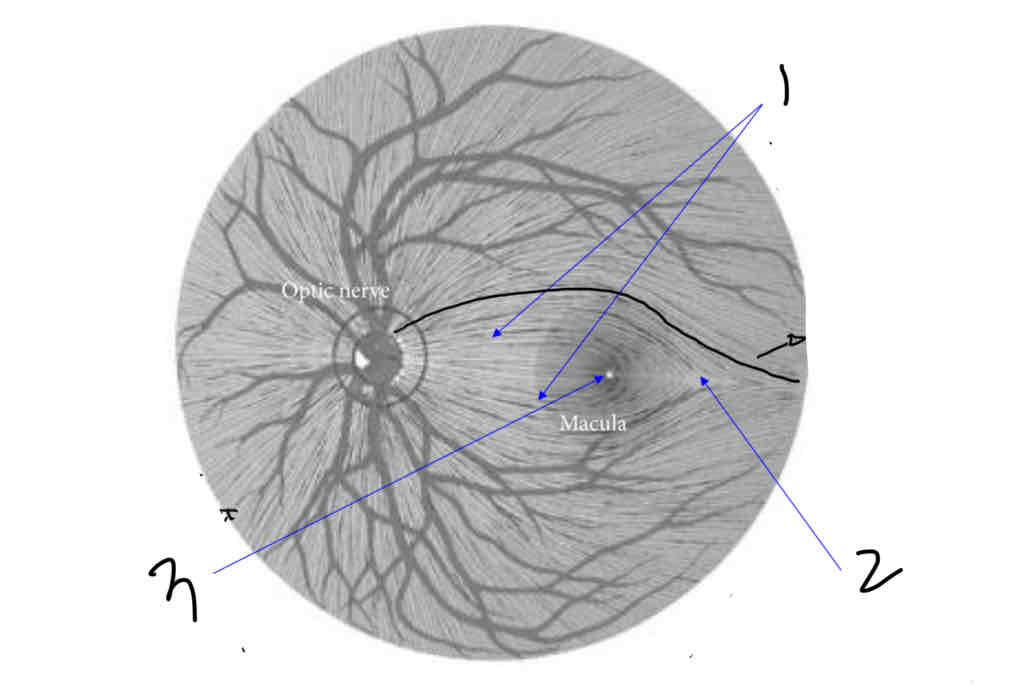
Label
Papillomacular bundle
Raphe
Fovea
What is the papillomacular bundle
Bundle of nerve fibres coming from the macula directly
What is the raphe
Point where nerve fibres almost meet
They dont pass from superior to inferior
What is the fovea
The dip at the retina becuase the retinal layers are pushed to the side so light has direct access to photoreceptors
Fovea is avascular, no capillaries, no ganglion cell axons
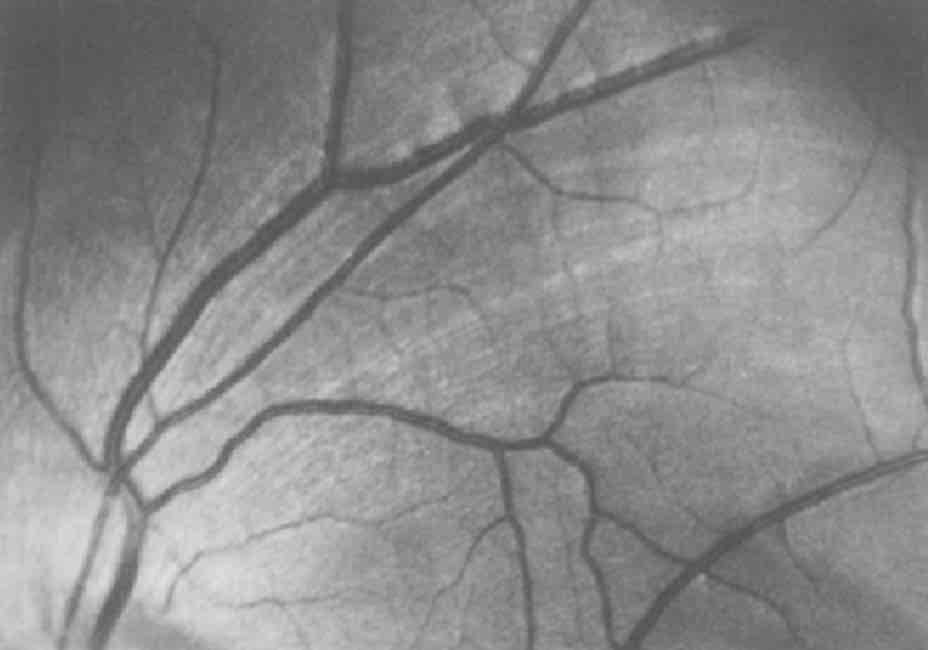
What are the pale striations in this image
Axon bundles
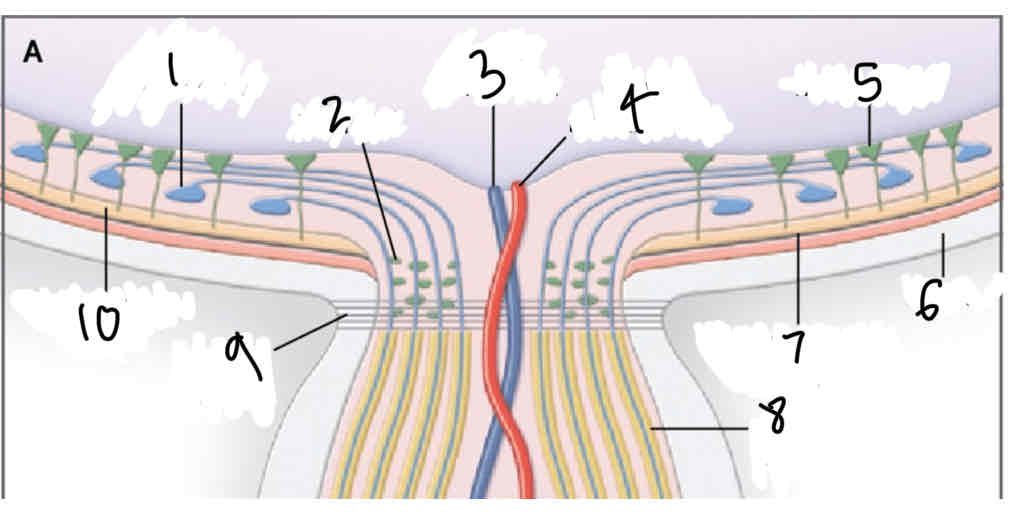
Label
Retinal ganglion cell
Glial cell
Central retinal vein
Central retinal artery
Mullers cell
Sclera
Retinal pigment epithelium
Myelinated retinal ganglion cell axon
Lamino cribrosa
Photoreceptor layer
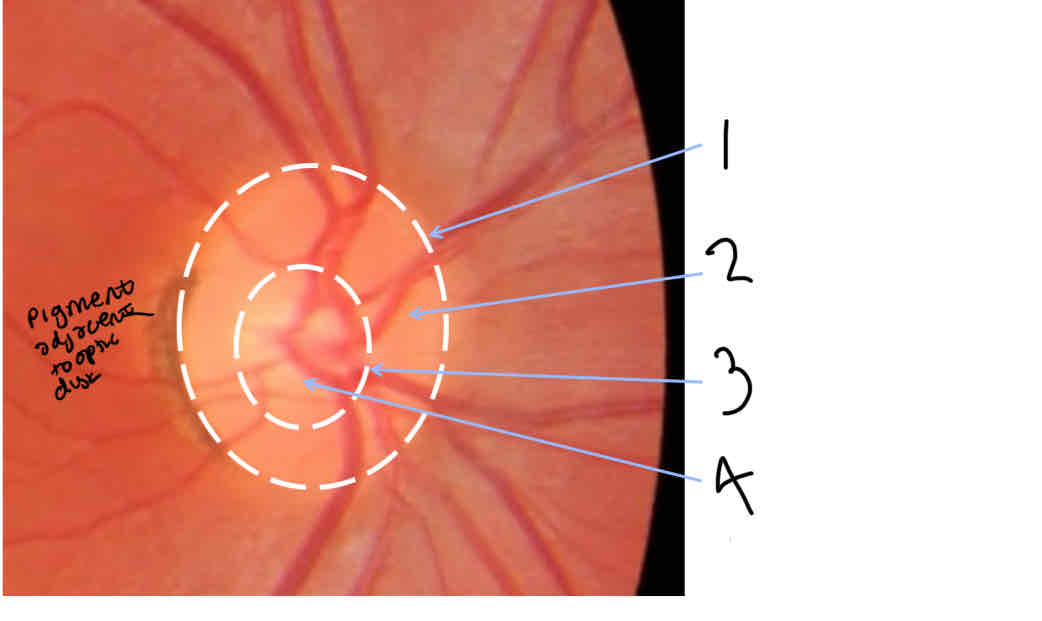
Label ONH
Optic disc edge
Neuroretinal rim
Optic cup edge
Optic cup
What is the neuroretinal rim
Area between edge of cup and disc
Made up of axons of retinal ganglion cells
What is the optic cup
Space with the absence of nerve fibres
What is glaucoma
Loss/damage to retinal ganglion cells which causes the cup to get larger
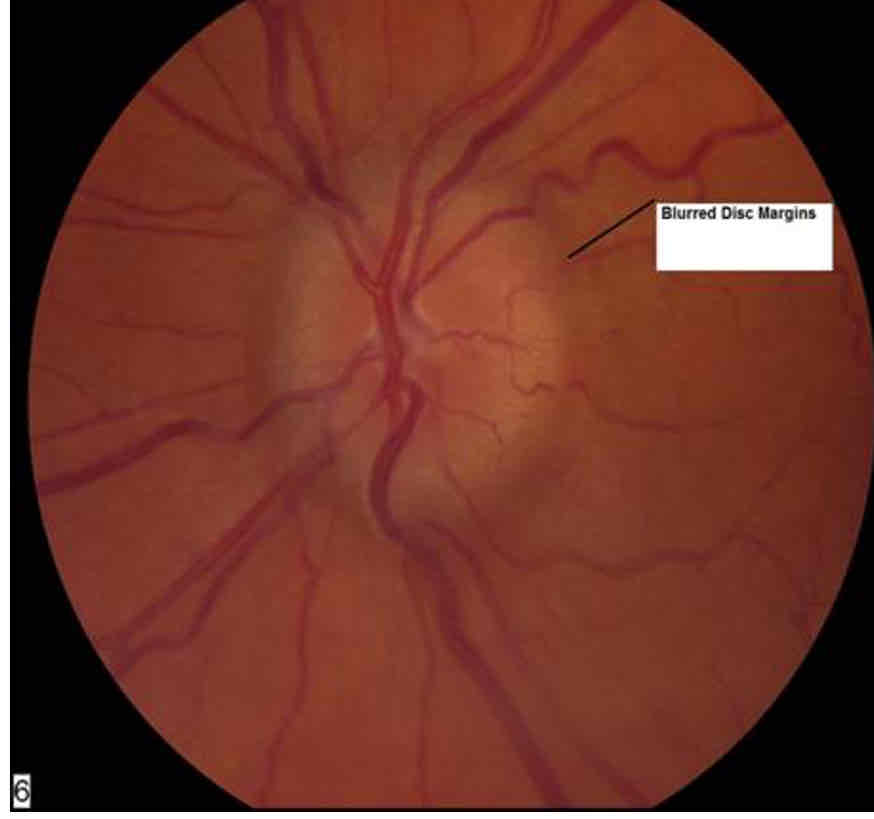
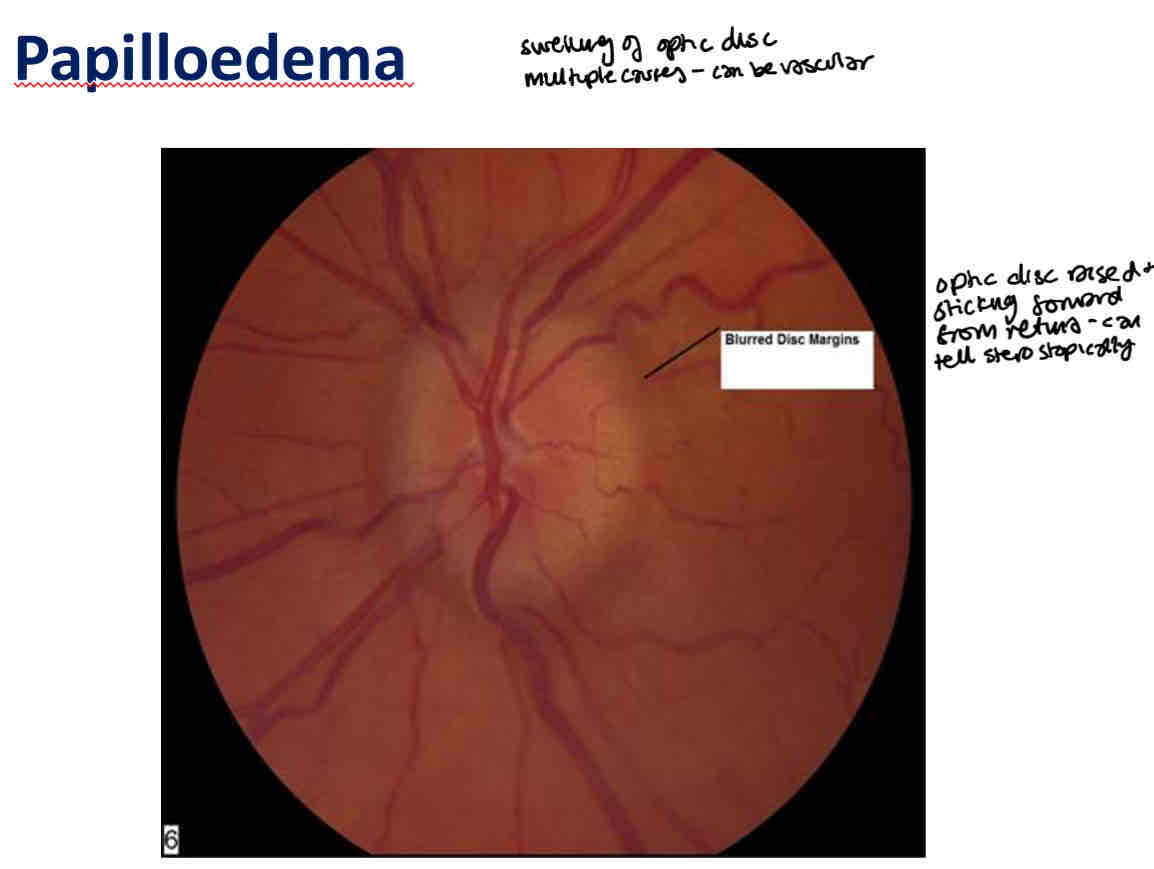
What is papilloedema
Optic disc swelling
What is considered a small or large optic disc
Small = less than 1.5mm
Large = more than 2mm
What is the outer border of the optic disc made of and how
Collagen
Arises from sclera to join bruchs membrane
What is elschnigs rich
Another word for optic disc border
Volk bio lens correction factors - 90D
x1.32
Volk bio lens correction factors - 78D
x1.08
Volk bio lens correction factors - Super 66
x1.0
Volk bio lens correction factors - 60D
0.87
Volk bio lens correction factors - DIgital wide field
1.39
Volk bio lens correction factors - Superfield
1.30
How to calculate disc size using slit lamp and volk lens
Make slit height the same as the disc height (vertically)
Look at slit height on slit lamp
Slit height x volk lens correction factor (eg 90D = 1.32)
How many nerve fibre axons do we have per eye
Around 1 million
Difference in where axons are packed in small and large discs
In small discs, axons are packed in more tightly as theres a smaller cup and thicker neuroretinal rim
In large discs, axons are around the edge (^opposite reason)
What is the neuroretinal rim
Where the nerves actually are
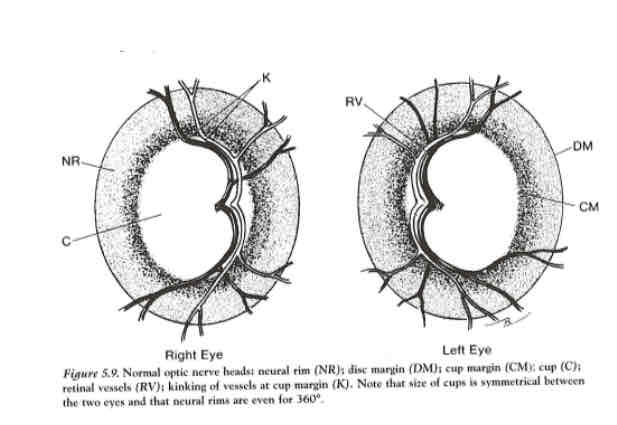
What forms the neuroretinal rim
The retinal nerve fibre layer
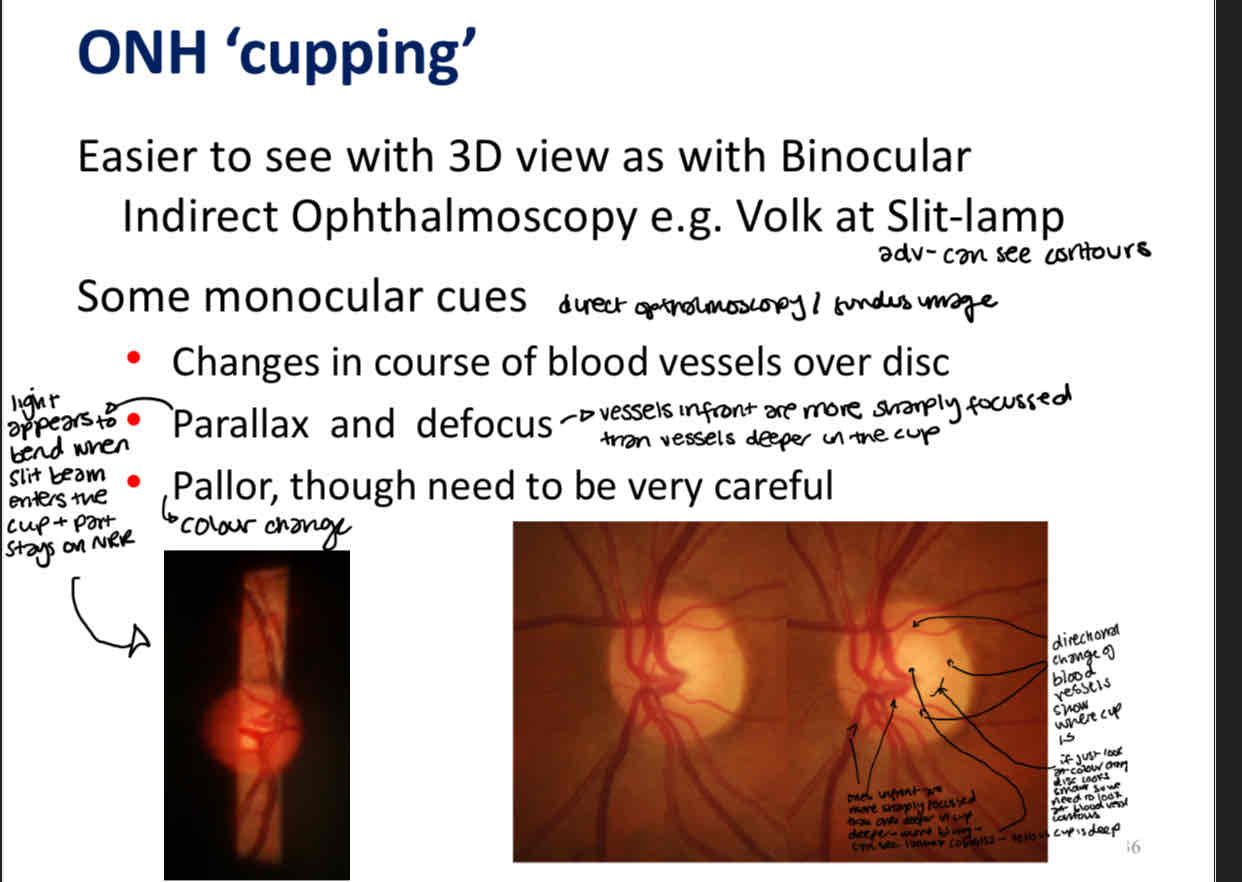
Monocular cues to find the ONH cup
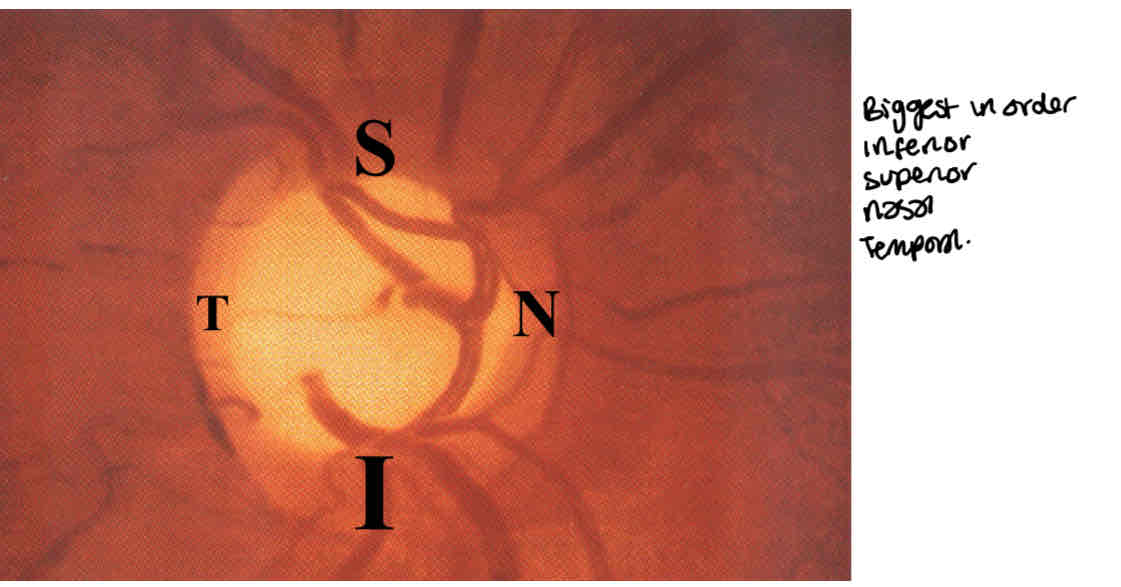
What is the ISNT rule
Tells you in order the thickness of the neuroretinal rim (however some normal eyes may not follow this rule)
Recording CD ratio
Record it horizontally and vertically
CD ratio in relation to glaucoma
Glaucoma is damage to ganglion cell axons so you get more space in the optic disc so CD ratio increases
You get a larger cup (cup is the absence of axons)
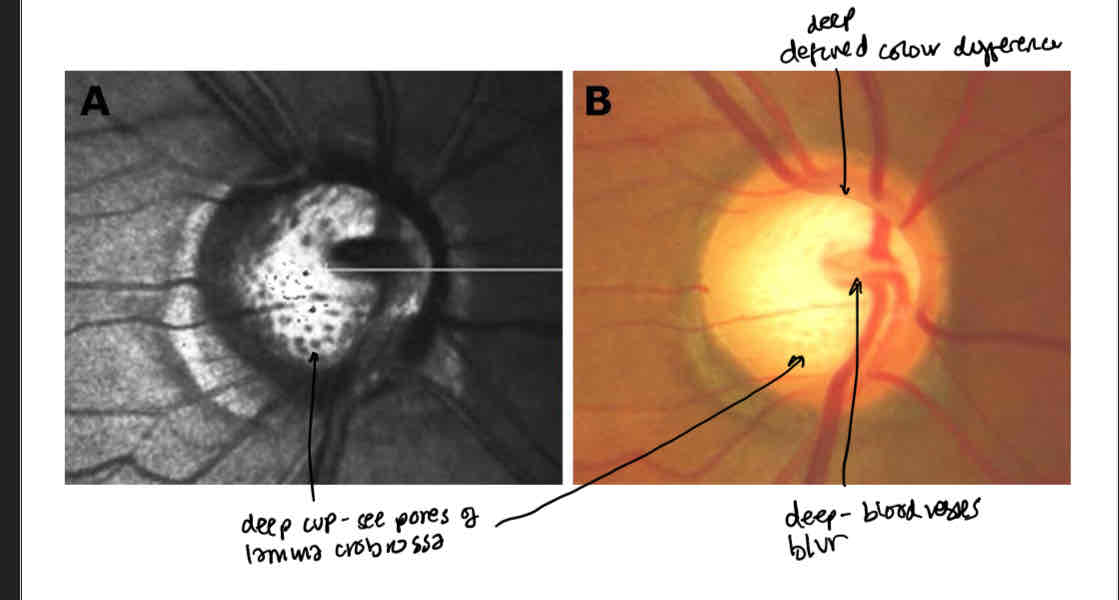
How do you know if the cup is deep
Defined colour difference
Can see the pores of the lamina cribrossa
Blood vessels are more blurred deeper in the cup
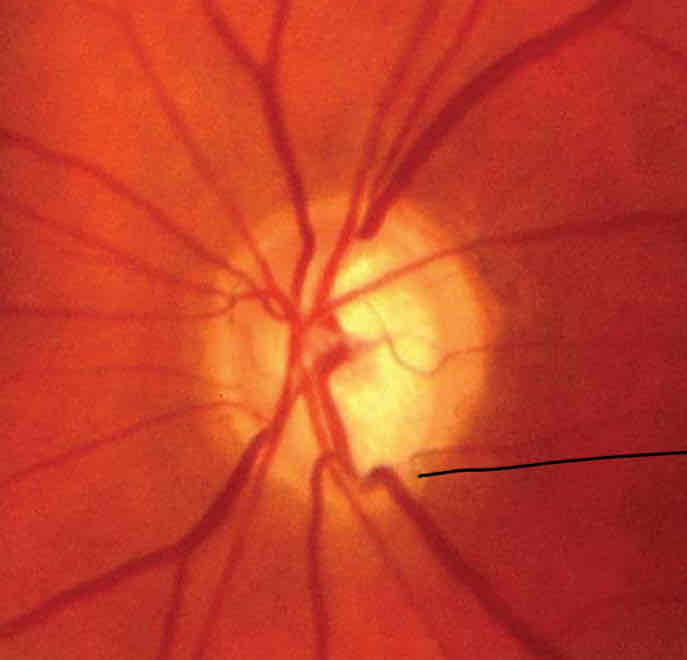
What is neovascularisation and what is this a sign of
Abnormal growth of new blood vessels
Could be a sign of serious systematic vascular problems or as a result of ocular vascular ‘accidents’
Vascular changes associated with glaucoma
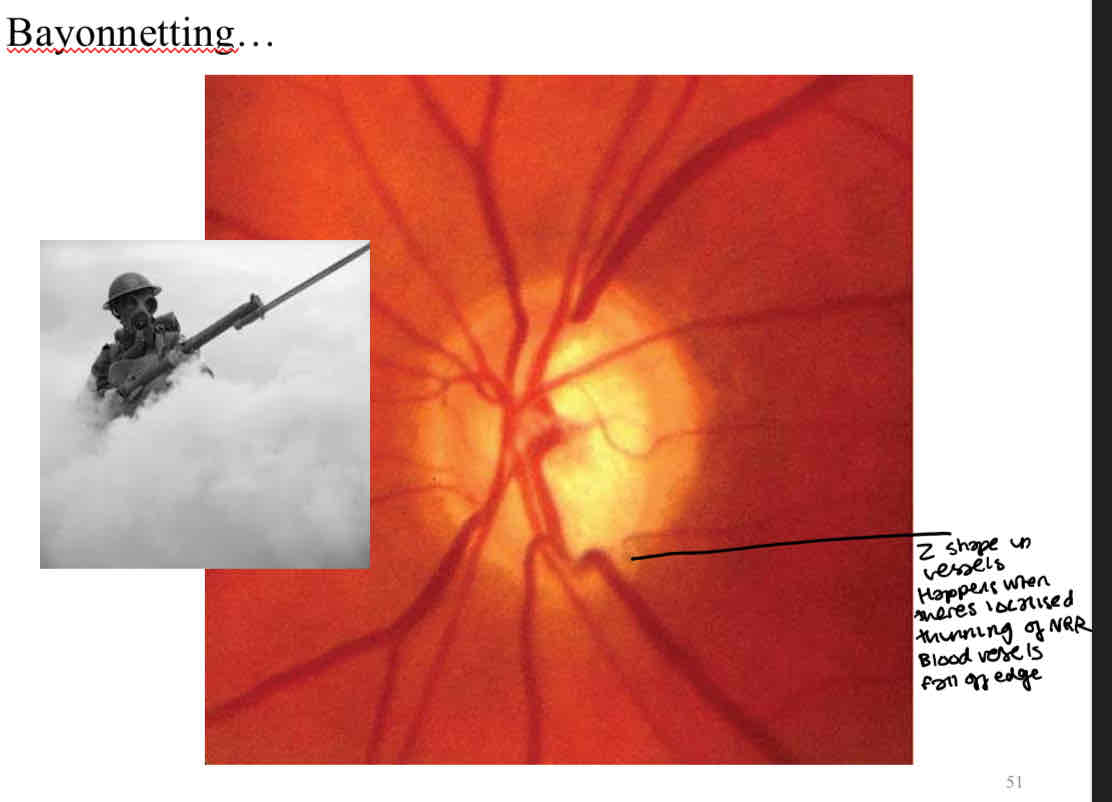
Bayonetting
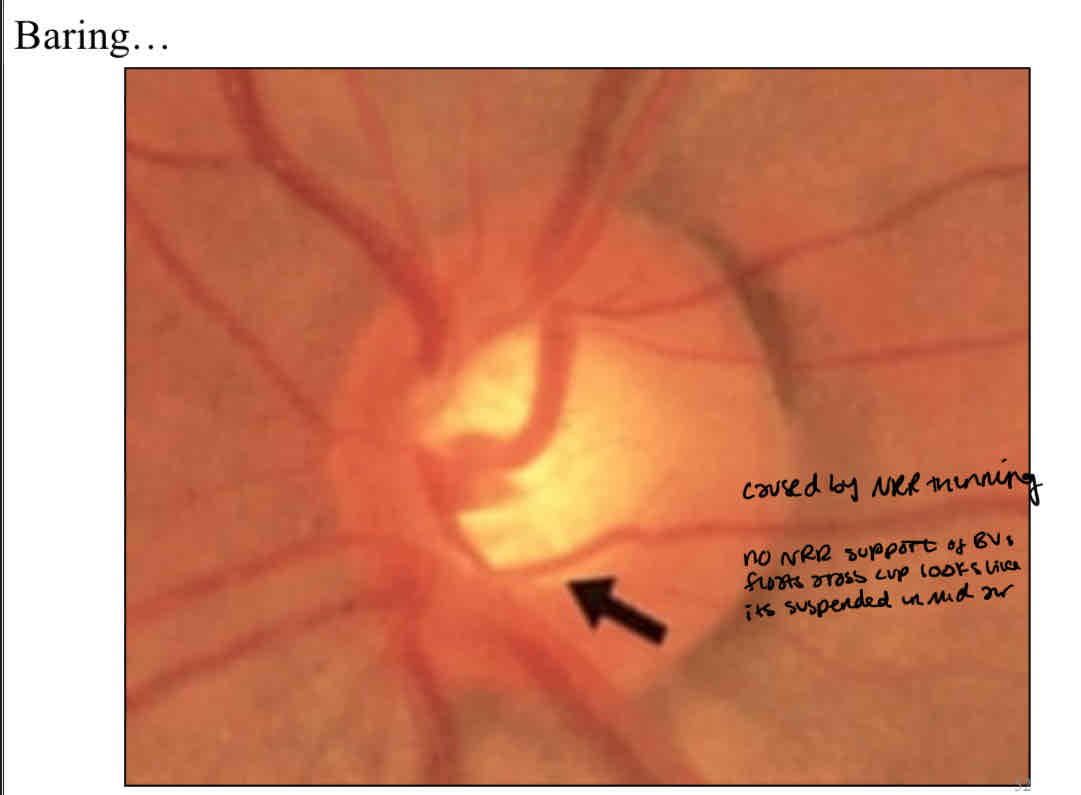
Baring
Flame haemorrhage
Non vascular changes associated with glaucoma
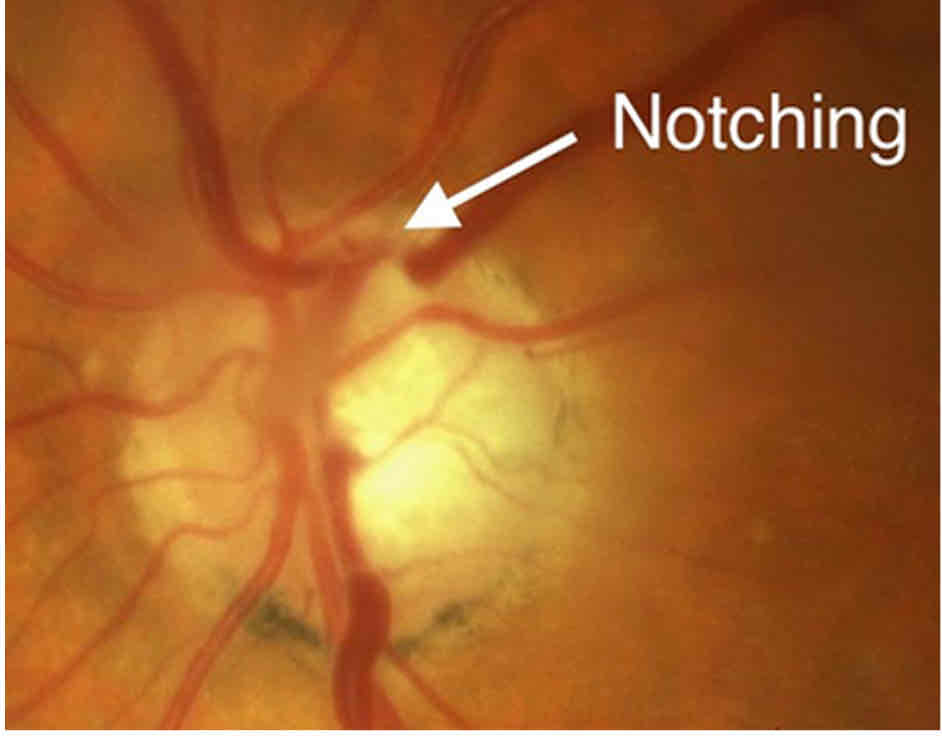
Notching of the disc
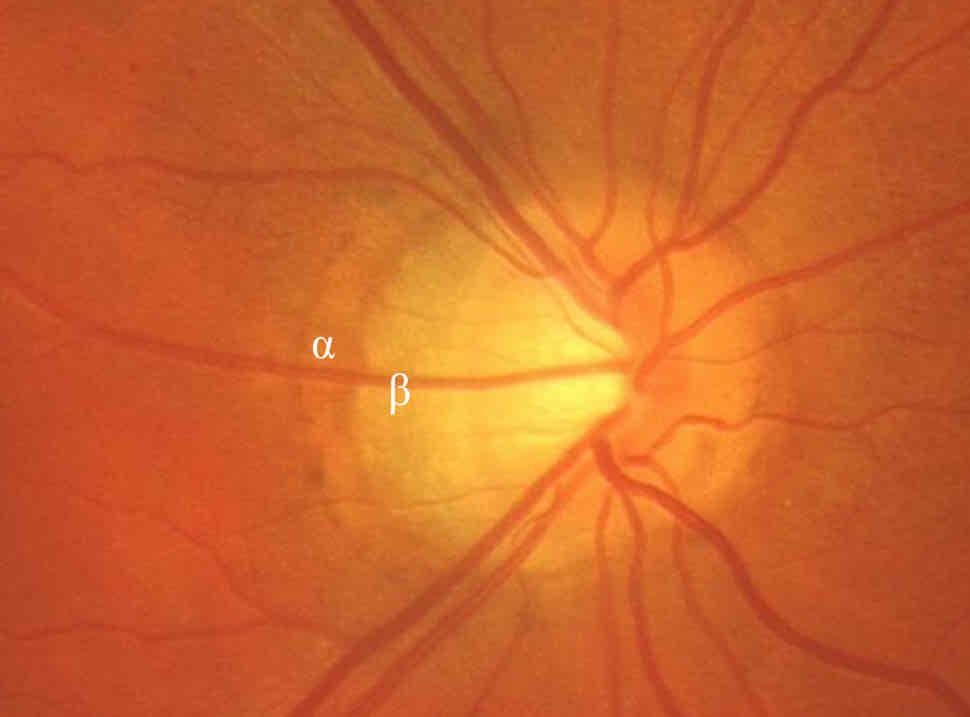
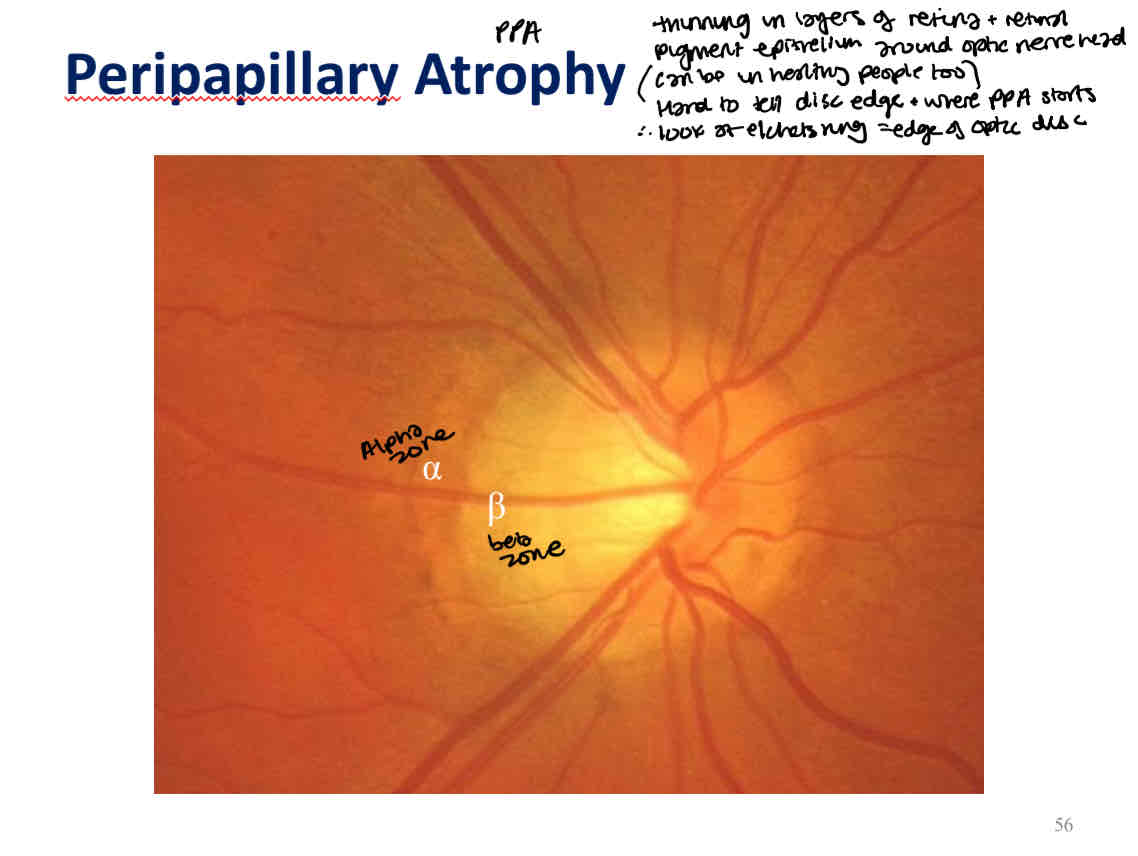
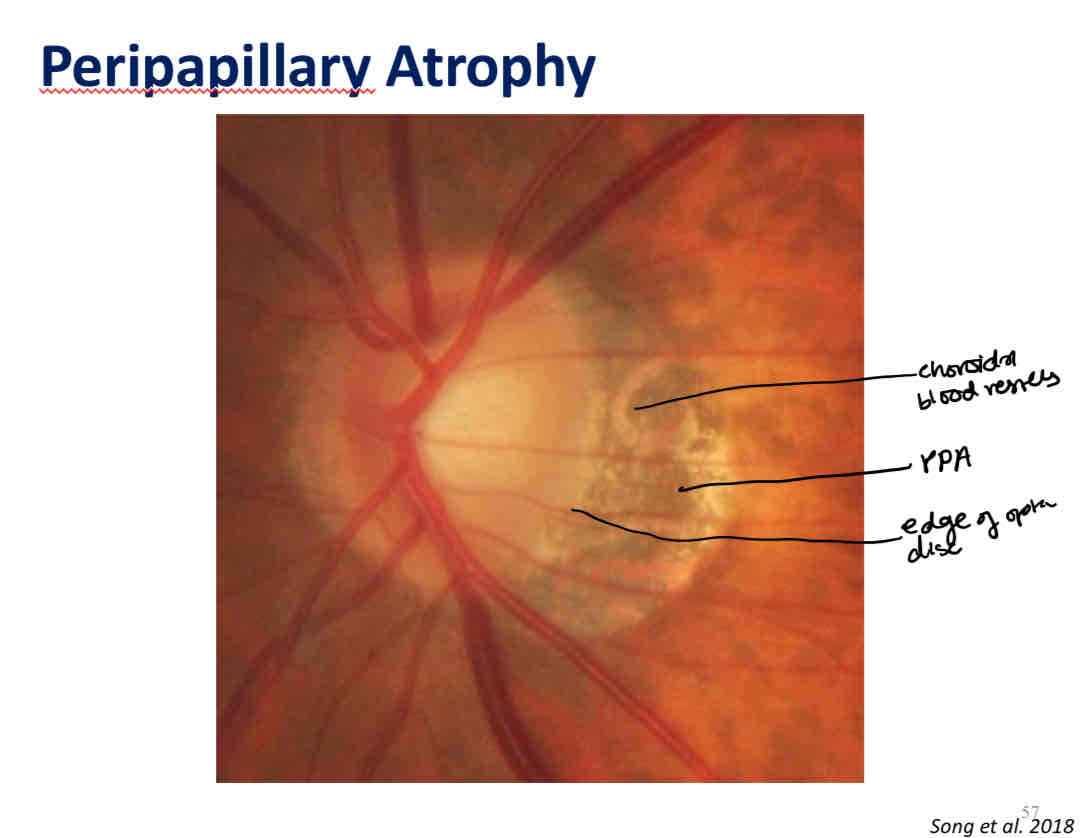
Peripapillary changes
Peripapillary atrophy
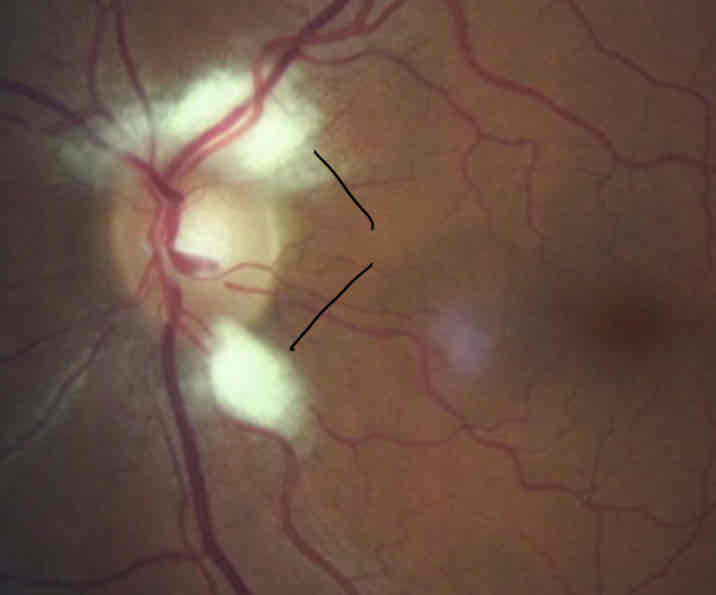
What is this
Bayonetting
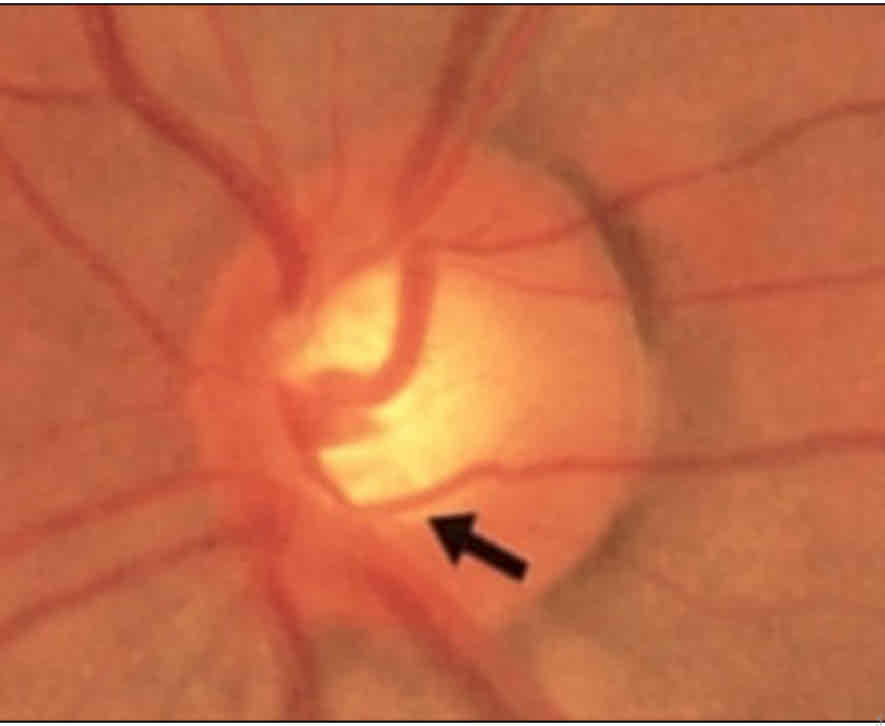
What is this
Baring
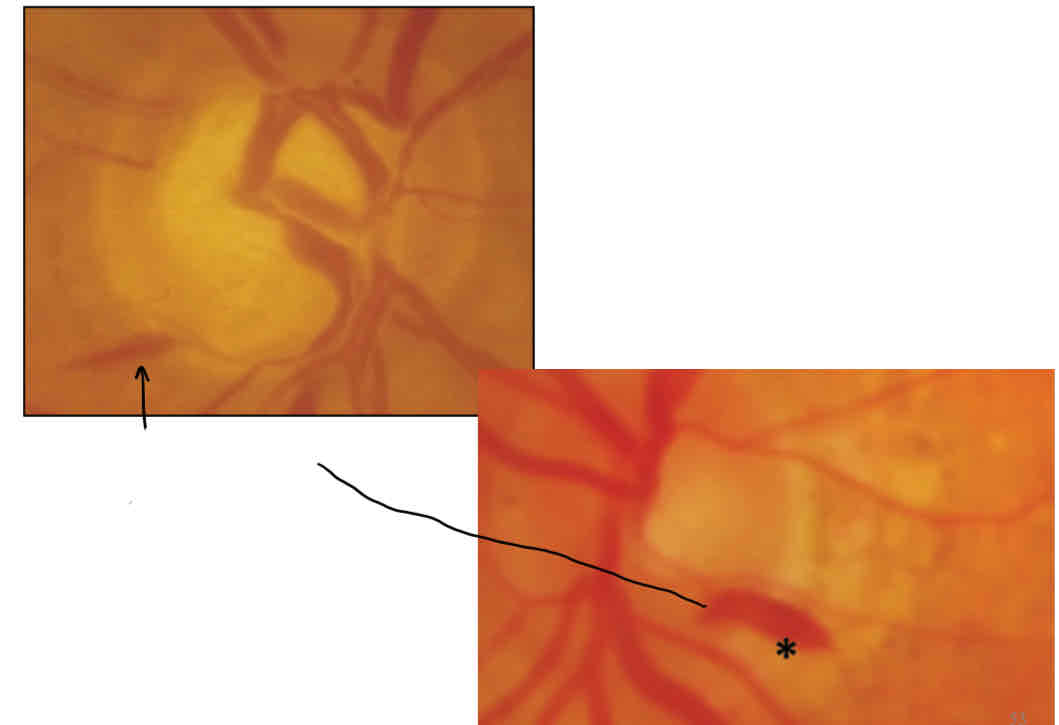
What is this
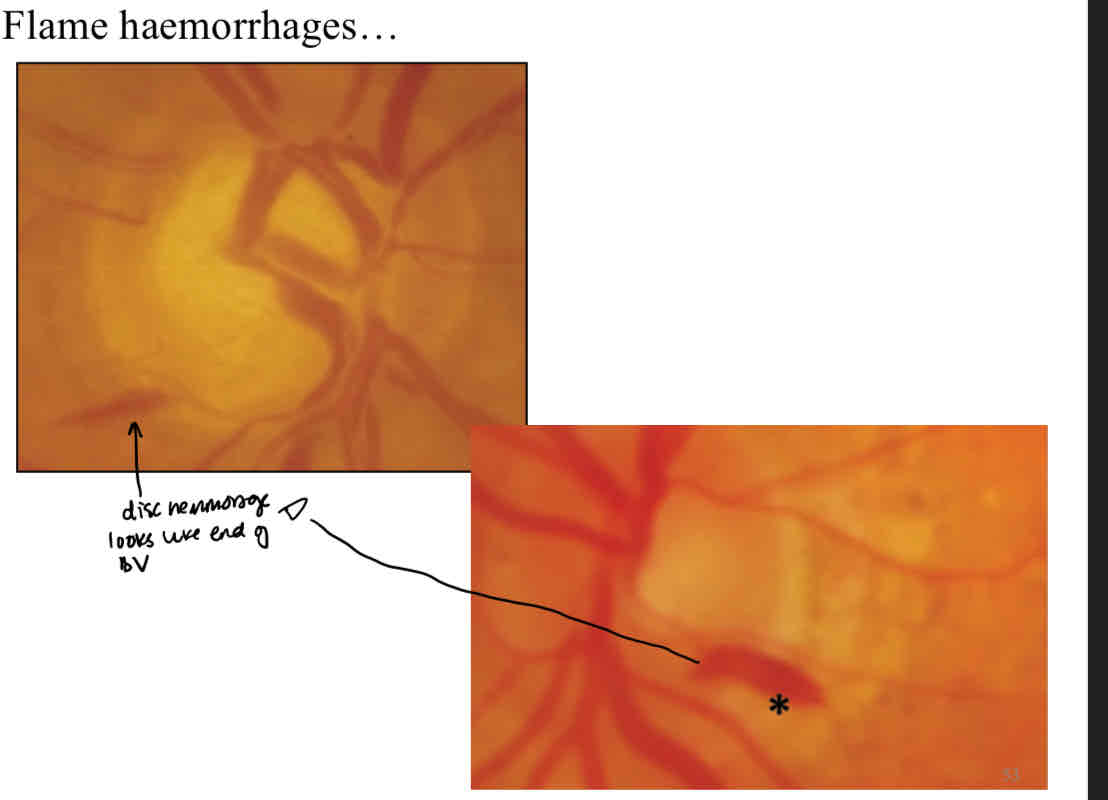
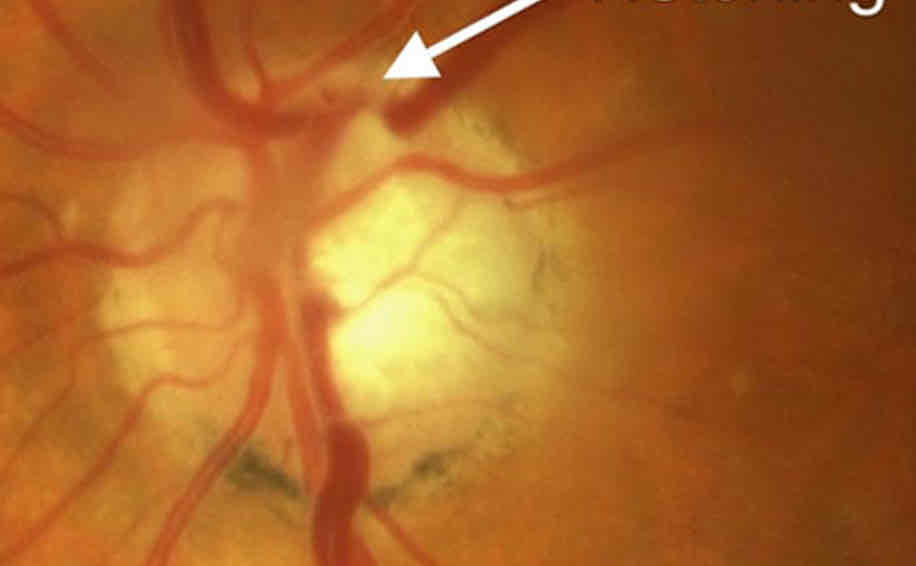
What is this
Notching
What is this
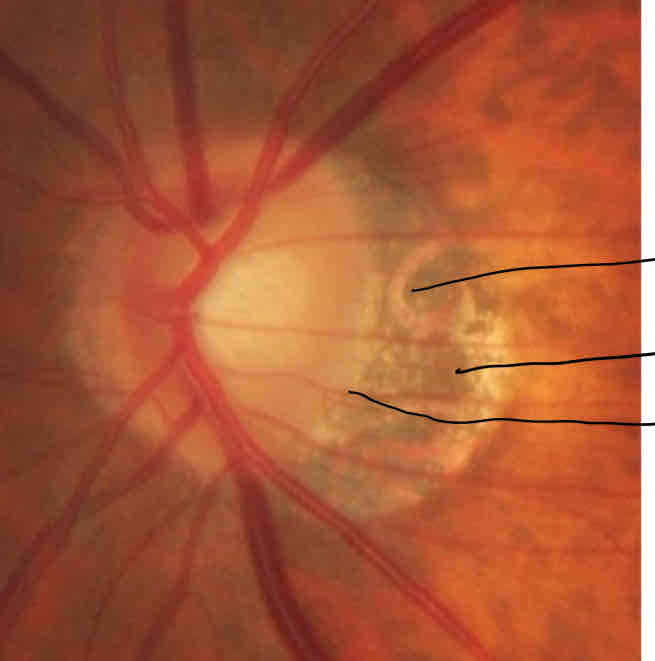
What is this
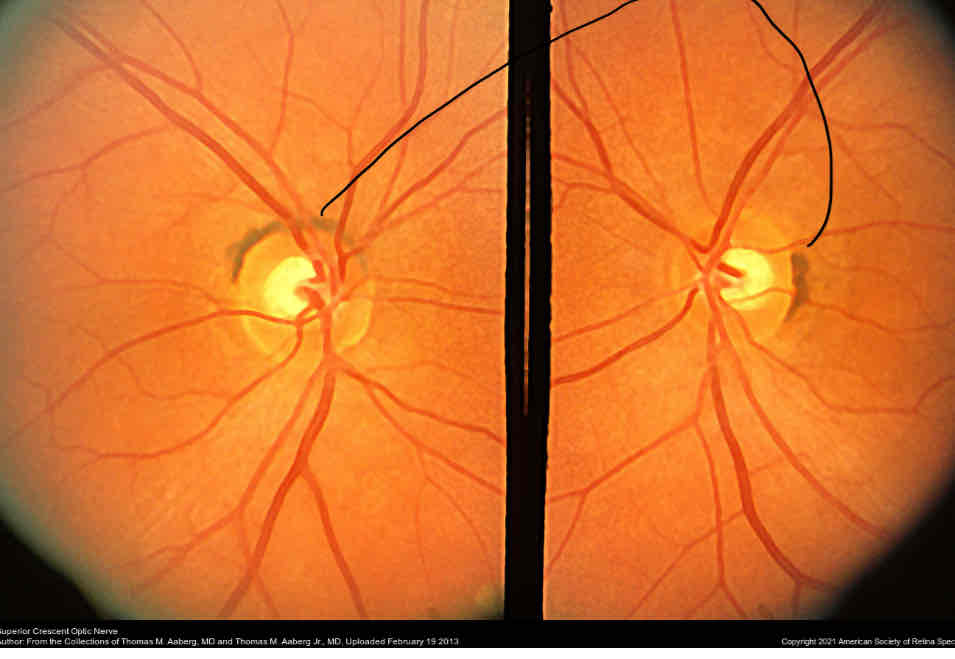
What is this
Melanin/pigment
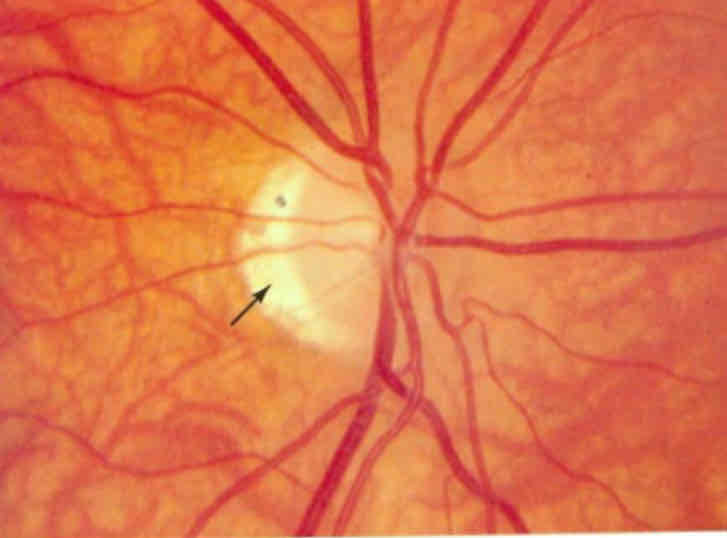
What is this
Thinning of the retina in myopia
Can see the sclera
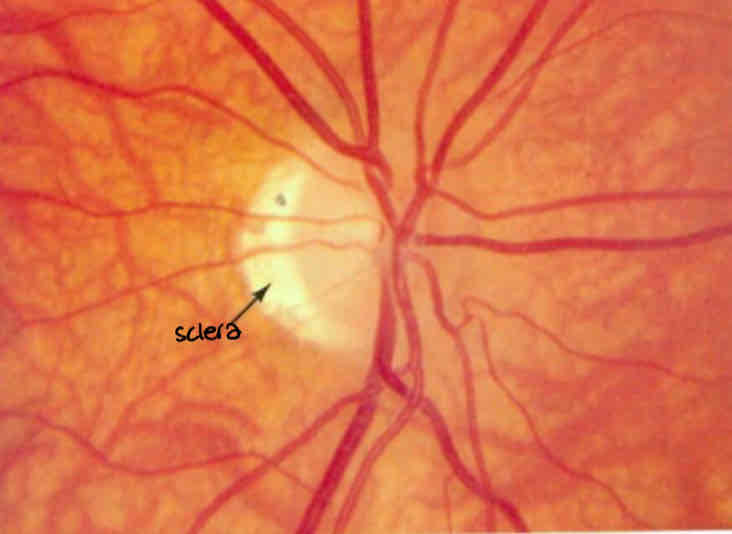
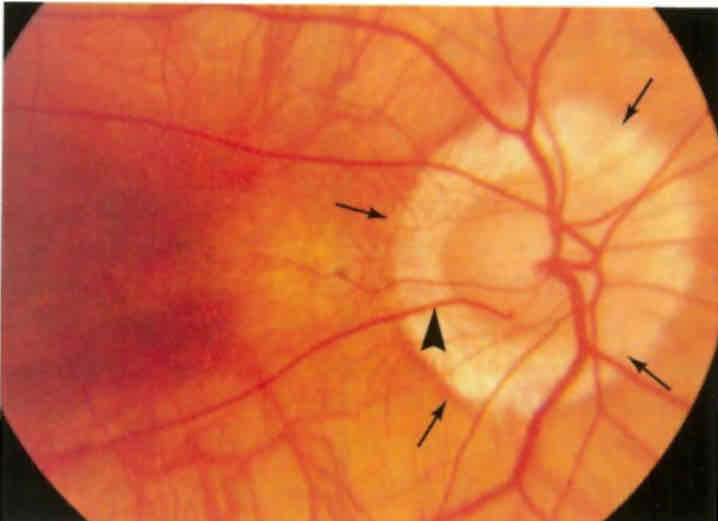
What is this
Thinning of the retina due in myopia
Can see the sclera
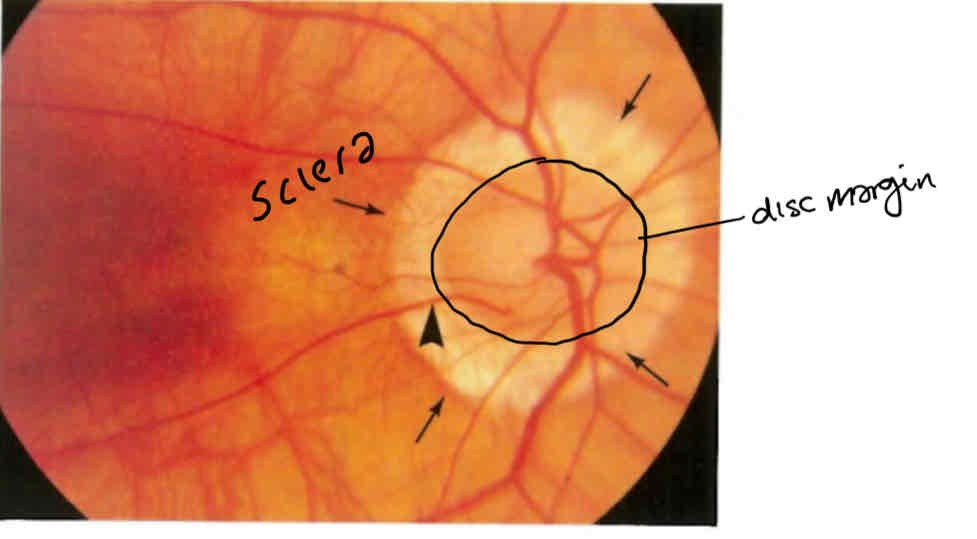
What is this
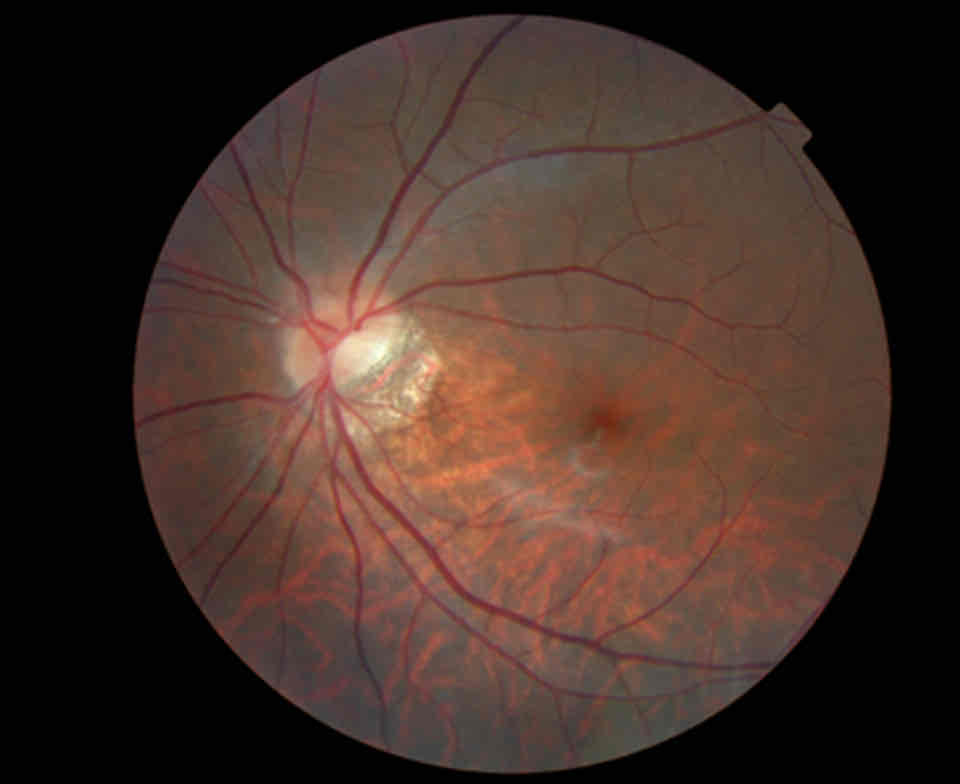
What is this
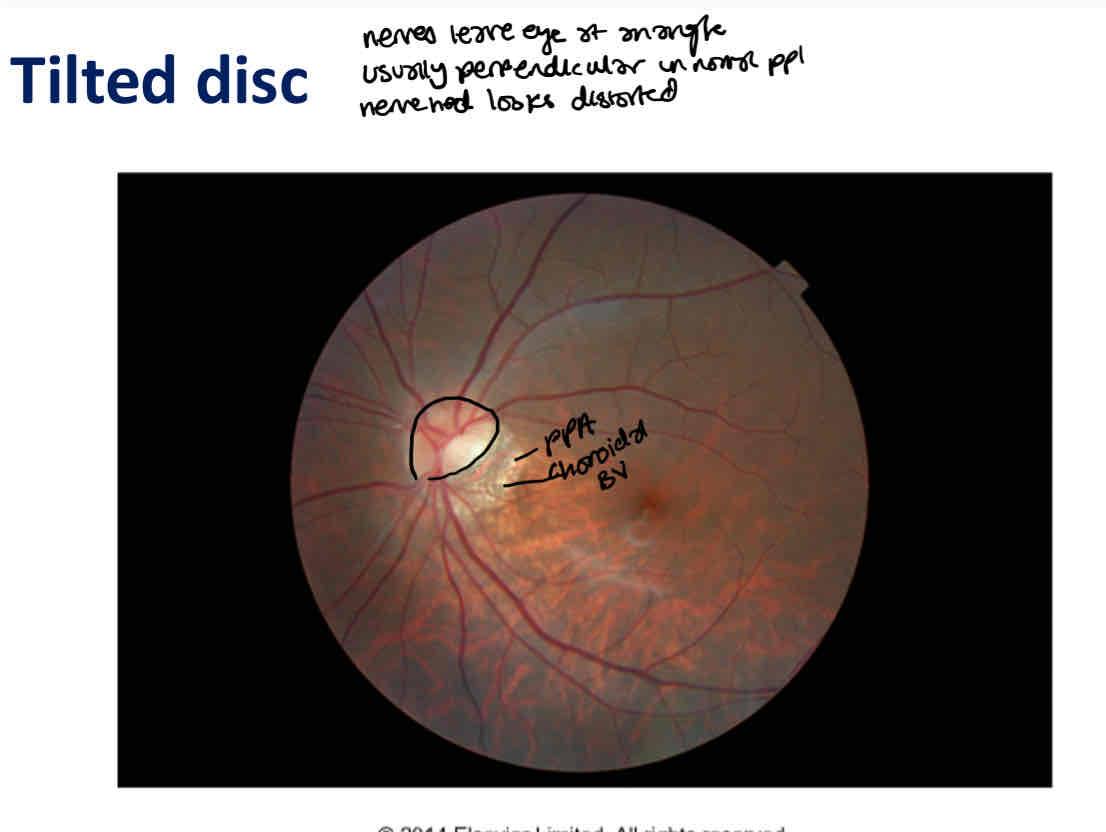
What is this
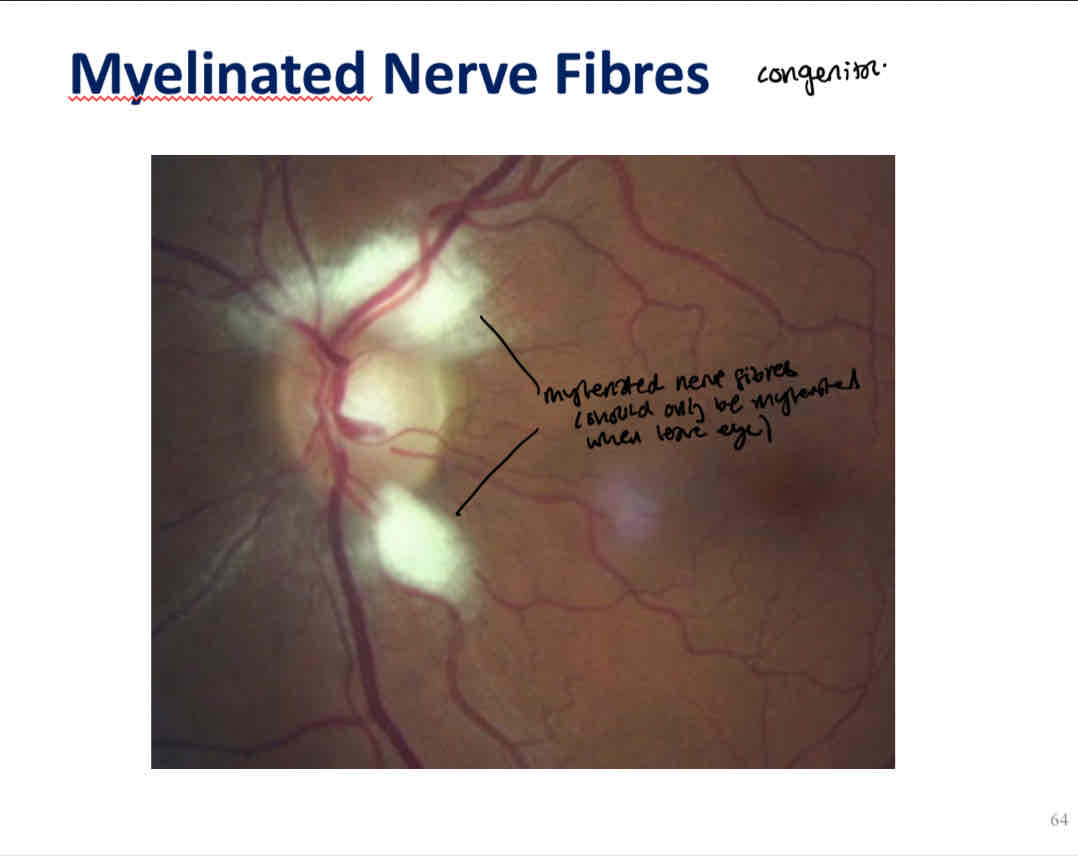
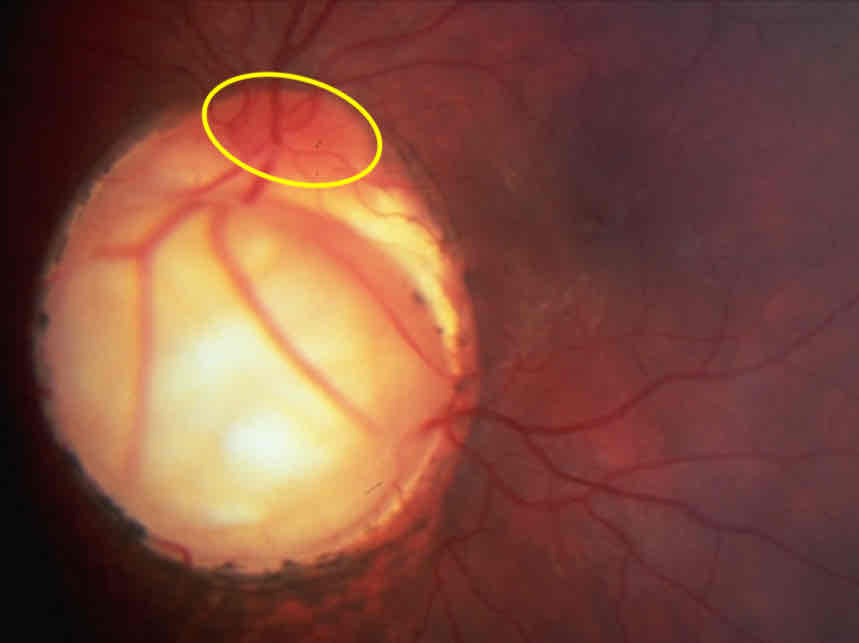
What is this
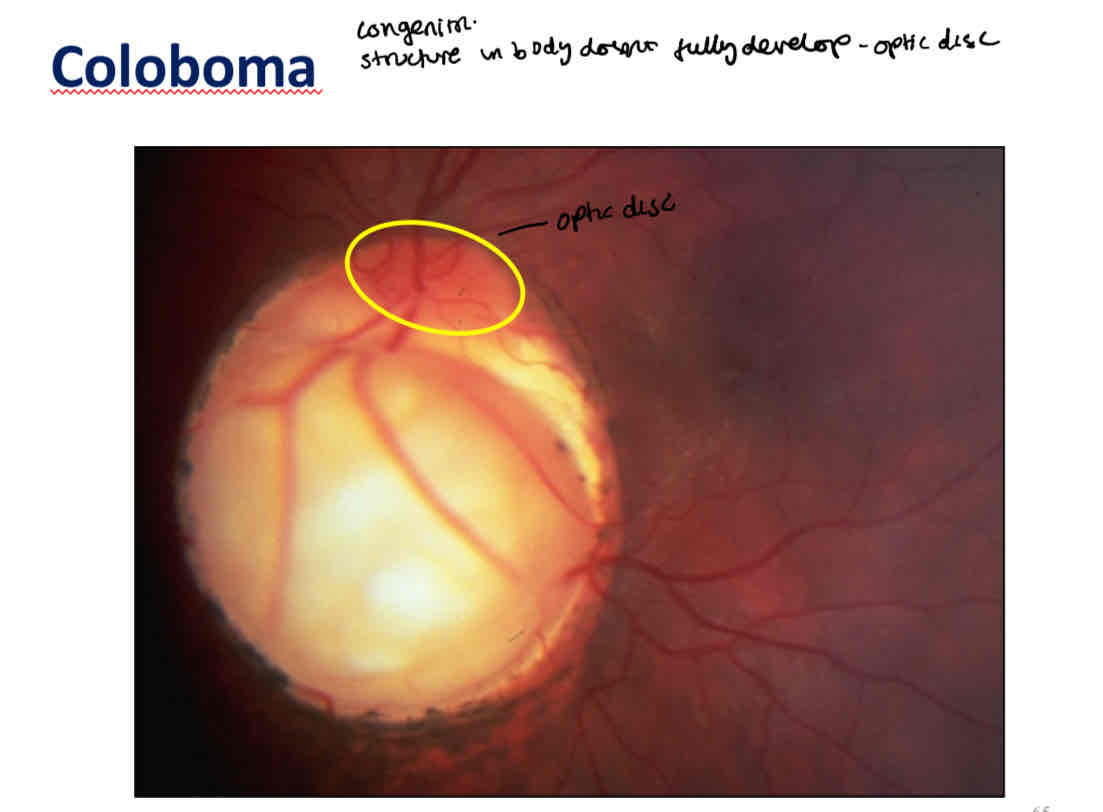
What can you use as a reference to see if the ONH is normal
Use the other eye as reference
If theyre symmetrical- more likely to be normal
Cup to disc ratio difference of _ is suspicious
More than 0.2
70% of people with glaucoma have unequal CDRs
What to include in ONH recording/assessment
Draw the disc and inner margin of NRR
Vertical length of disc and if its small/medium/large
Horizontal and vertical CDRs
NRR - ISNT
Depth of cup
Add anything abnormal eg pigment, PPA