Introduction to Radiation Therapy Clinical Applications, Pelvic Anatomy and Lymphatic System Overview
1/226
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
227 Terms
Radiobiology
The science that evaluates the effects of radiation in living organisms.
The largest lymphatic duct in the body
The thoracic duct
Fractionation (4 R's)
Radiation therapy treatments given in daily fractions (segments) over an extended period of time.
Repopulation
Normal tissue regeneration that occurs during fractionated radiation therapy.
Redistribution
The process of cells moving through different phases of the cell cycle in response to radiation.
Repair
The ability of normal tissue to recover from radiation damage, most important in terms of why we fractionate.
Reoxygenation
The process that applies to tumors only, where oxygen levels increase in tumor cells after radiation treatment.
dmax for cobalt
.5cm
Dmax for 4mev
1 cm
Dmax for orthovoltage and superficial
0 cm(kvp energy)
Dmax for 6mv
1.5cm
Dmax for 10 Mv
2.5
Dmax for 15 Mv
3 cm
Dmax 20 Mv
3.5cm
Dmax for 25mv
5 cm
P53 gene works in what part of the cell cycle
G1
Y do we fractionate the rad treatment
So the healthy cells can repair
What is the most radio resistant part of the cell cycle
S phase because cells r replicating
What part of cell cycle most radiosensitizer
G2 and M
Tumor has how many group layers of cells
4 layers
Top layer of tumor is oxygenated or not
It’s oxygenated (oxic)
Group 2 cells
Mix of hypoxic and oxic cells
Group 3 tumor cells
Hypoxic cells
Group4 tumor cells r
Anoxic or Necrotic or dead
Thoracic duct drains itself into the circulatory system at
The left subclavian vein
What level is the cisterna chyli
L2
Common iliac nodes directly drain
Bladder
Prostate
Cevix
Vagina
Paraaortic provides drainage from
Cisterna chyli
Paraaortic drains directly from
Uterus
Ovaries
Kidney
Testicles
External iliac nodes drain
Urinary bladder
Prostate
Cervix
Testes
Vagina
Ovaries
Internal iliac nodes or hypogastric nodes drain
Vagina
Cervix
Prostate
Bladder
Obturator nodes drain
Prostate cervix
First side of prostate spread comes from what lymph node
Obturator foramen
Inguinal nodes drain
Vulva
Uterus
Ovaries
Vagina
Anus
wHat lymph node is common treated with electrons because it’s very superficial
Inguinal nodes
What is myelitis
Inflammation of spinal cord
Do sacro as spread thru lymph
No only blood
Grading is what
Cell differentiation
If they take two biopsy of the prostate in one quadrant one is g 2 and the others is a score of 8 and another Quadrant comes out with a 2 and a3 what score is it
Gleason score of 10 the highest score is the score
Staging is made by
American cancer society
Lung cancer ad breast cancer is by worse if it's bigger or smaller tumors
Bigger
Gi cancer is based on what layer it's in
So mucosa is a stage 1 and serosa is stage 4
What labs r done when someone cancer could metatstize to the liver
AST and lst liver functions taken thru blood
What is the tumor marker for prostate
psa
Positive pregnancy test for men indicate what cancer
Testicular
Most common pop portals
Ap/pa
Right and left lateral
Pop portal r for treatment or imaging
Treatment
Orthogonal r for treatment or images
Images
Common orthogonal ports
Ap/ and a lateral
pa/ and a lateral
What does temodar do
Radiosensitizer brain breaks blood brain barrier
Cisplatin
Combo drug of a few chemo therapies
When r perm tattoo place during no shift
During simulation
When r perm tats placed during shift method
During first day of treatment
ITV
Involunatary motion
What makes up the itv
Gtv and ctv
Portal image is
Image of the treatment areas CANT portal image vmat or imrt because collimators r closed for those treatments
Where does the most accurate separations come from
Ct images
If u can’t use ct for separations what can u use
Calibers
What is the equivalent square equation
Eq= 4(A/P)
Intrafraction
What’s going on while treating
Respiration
Heart beat
Interfraction
Between fraction to fraction
Ex weight lost
Inter field distance
Patient Separations
What is the average energy of cobalt
1.25 MeV
2 photons of 1.33 and 1.17
Which two dmax r the most similar
Cobalt and 4mev
odi
Optical distance indicator
Ruler for ssd reading
Parallel opposed contradincatd
When patient sep to thin or too small
Graticule
Radioopaque markers on xray helps u make shifts
Parelleopposed make what shape
Hourglass
What is involved in daily qa
Dosimetery
Photon and electron output constancy (3% error range acceptable)
Mechanical
Laser localization
Odi
Colimator size indicator (2 mm error)
safety
Door interlock cuts off beam when door opens
Audio visual monitors do they work
Rad monitor area (prime alert) lights that flash when beam is on
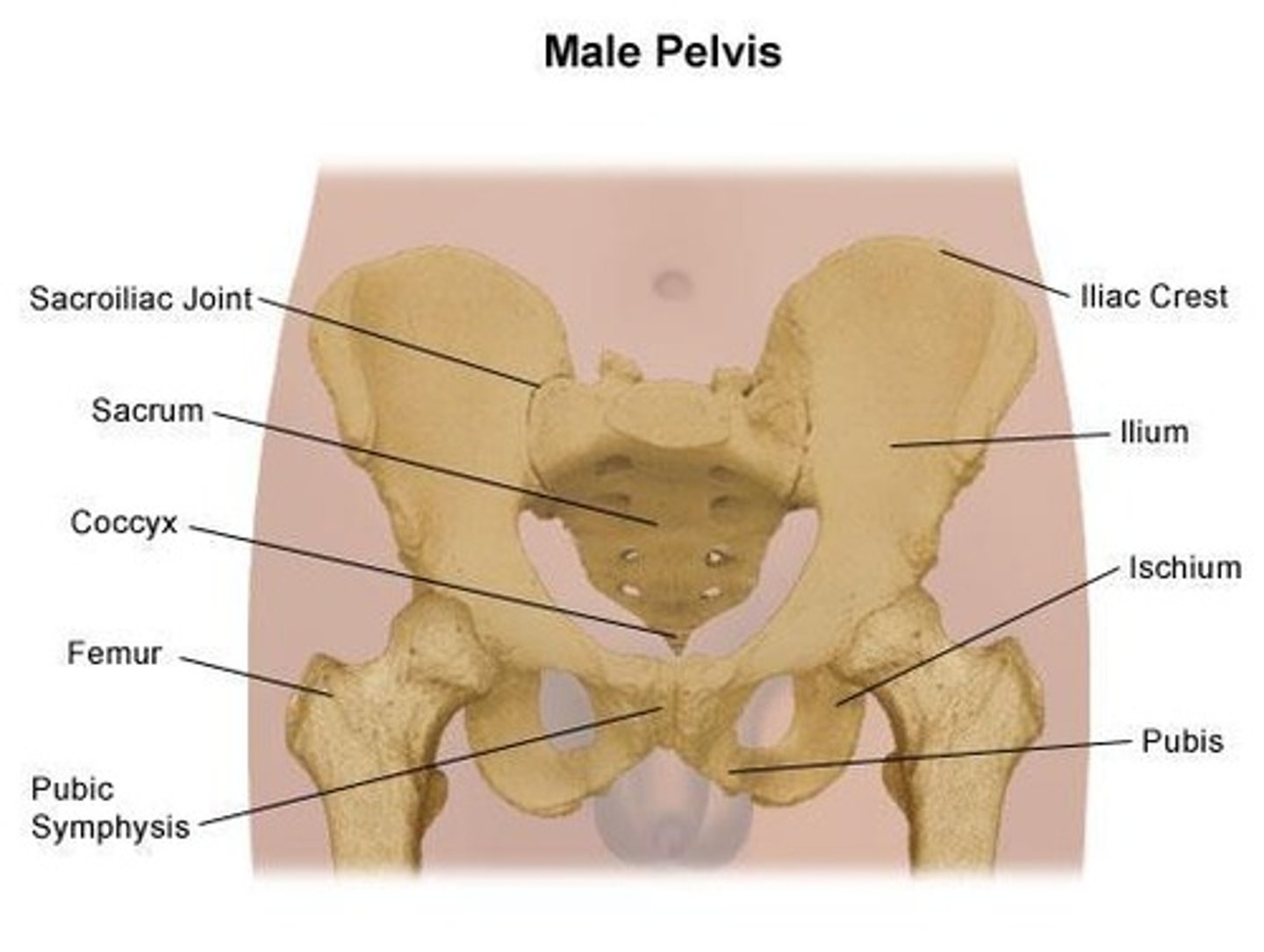
Where do u extend the treatment portal edges when treating lymph nodes of pelvis
Upper border at midsacral level
Lower border is inferior part of prostate
Lateral border 2cm outside Pelvic brim
Anterior is 1cm anterior to pubic symphysis
Posterior border is the partial lateral rectal wall
Function of lymph
Drain interstitial fluid
Absorb fat and transport to blood stream
Major role in the body immunity
What is the main lymph duct
Thoracic duct
What is the only lymph node that dont have afferent function
Spleen
Largest lymph node in body
Spleen
Efferent
Exits lymph nodes
Afferent
Enters lymph nodes
Where’s does lymph dump into circulatory system
Subclavian veins
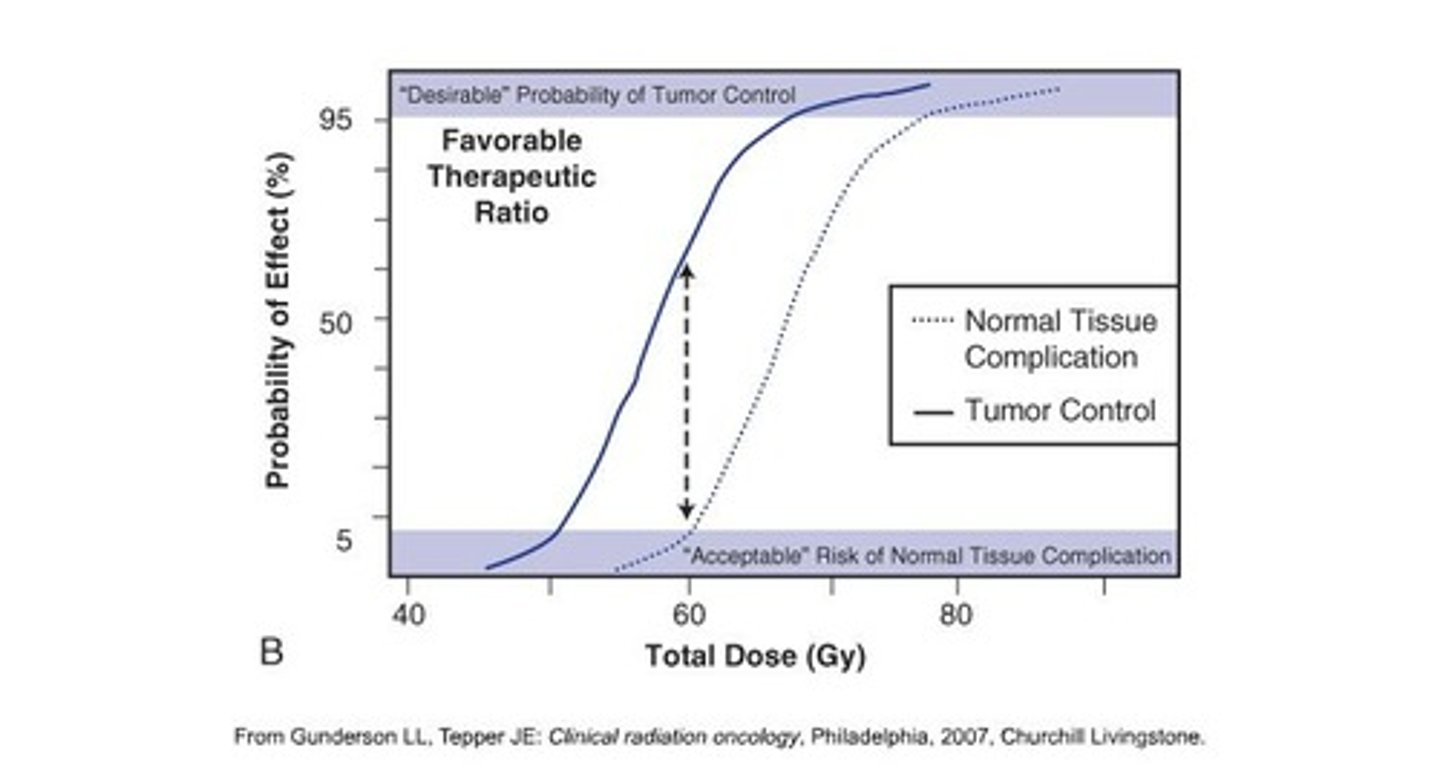
TD 5/5
Doses of radiation expected to produce a 5% complication rate within 5 years.
Critical Structures
Also referred to as organs at risk (OAR), these are normal tissues whose radiation tolerance limits the deliverable dose.
Therapeutic Ratio
Denotes the relationship between the probability for tumor cure and the likelihood for normal tissue damage.
Simulation
The process of creating a treatment plan for radiation therapy.
Immobilization Devices
Tools used to keep patients in a fixed position during radiation treatment.
Radiopaque Marker
A marker that is visible on imaging studies, used to indicate specific locations on the body.
Field Size
The dimensions of the area being treated with radiation.
ICRU 50 Tumor Volumes
Guidelines for defining tumor volumes in radiation therapy.
ODI - Optical Distance Indicator
A device used to measure the distance from the radiation source to the patient.
AP/PA
Anteroposterior (CAX directed from anterior to posterior) and Posterioranterior (CAX directed from posterior to anterior) positioning terminology.
Parallel opposed (POP)
Treatment given 180 degrees apart, commonly using AP/PA or right lateral/left lateral portals.
Orthogonal Images
Port images taken 90 degrees apart.
Source to Skin Distance (SSD)
The distance from the radiation source to the patient's skin surface.
Source to Axis Distance (SAD)
The distance from the radiation source to the central axis of the treatment beam.
Separations
Measurement used for treatment planning, determining the thickness of the body part from entrance to exit point of the treatment beam.
Calipers
A tool used to measure separations in treatment planning.
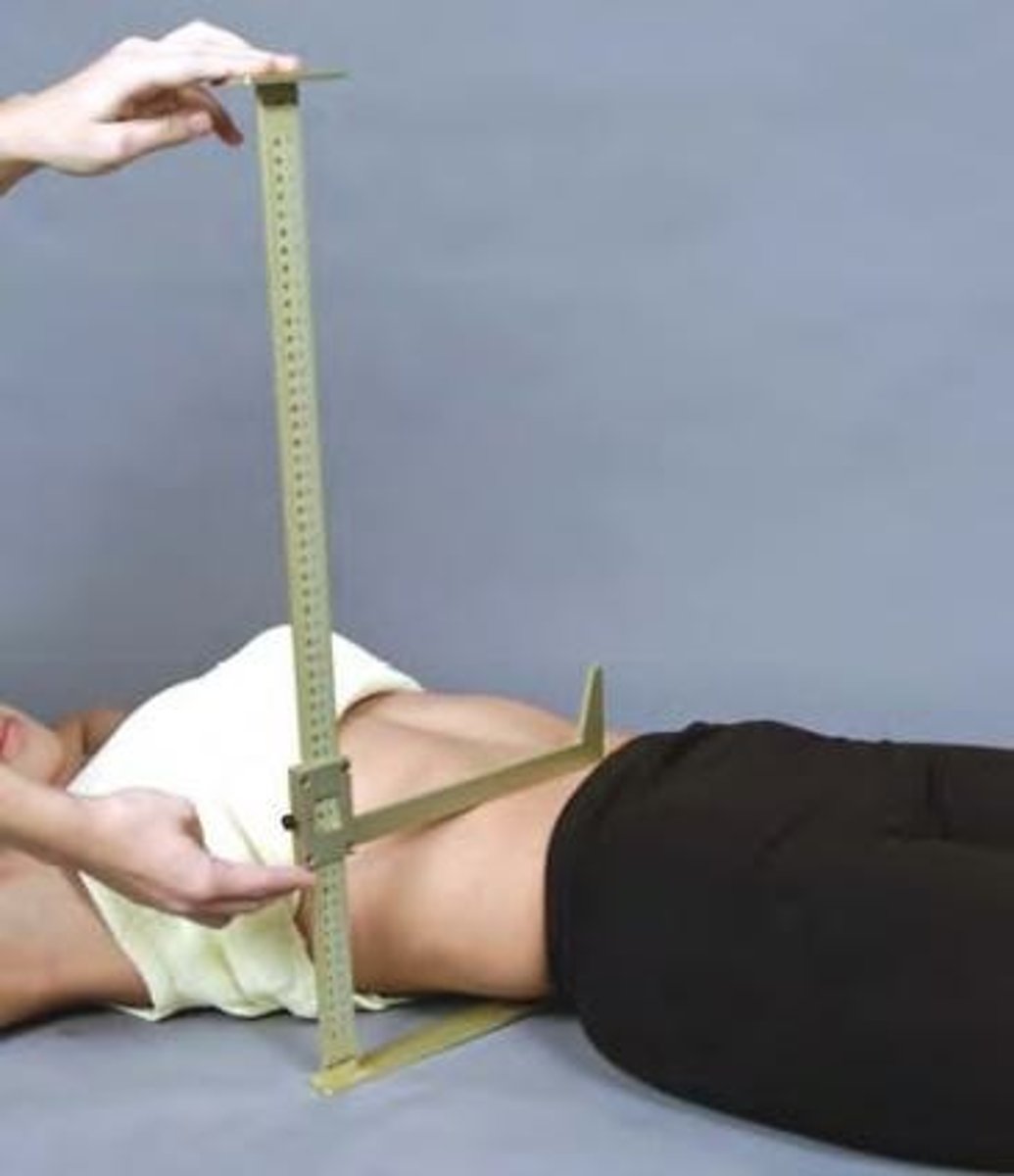
Leveling
The process of ensuring that the patient is set up correctly for every treatment.
Patient Marking System
A system used to mark the patient's position for consistent treatment delivery.
What is the anatomical position of the subject?
The subject stands upright, with feet flat together, toes pointed forward, arms straight down by the sides with palms facing forward, fingers extended, and thumbs pointing away from the body.
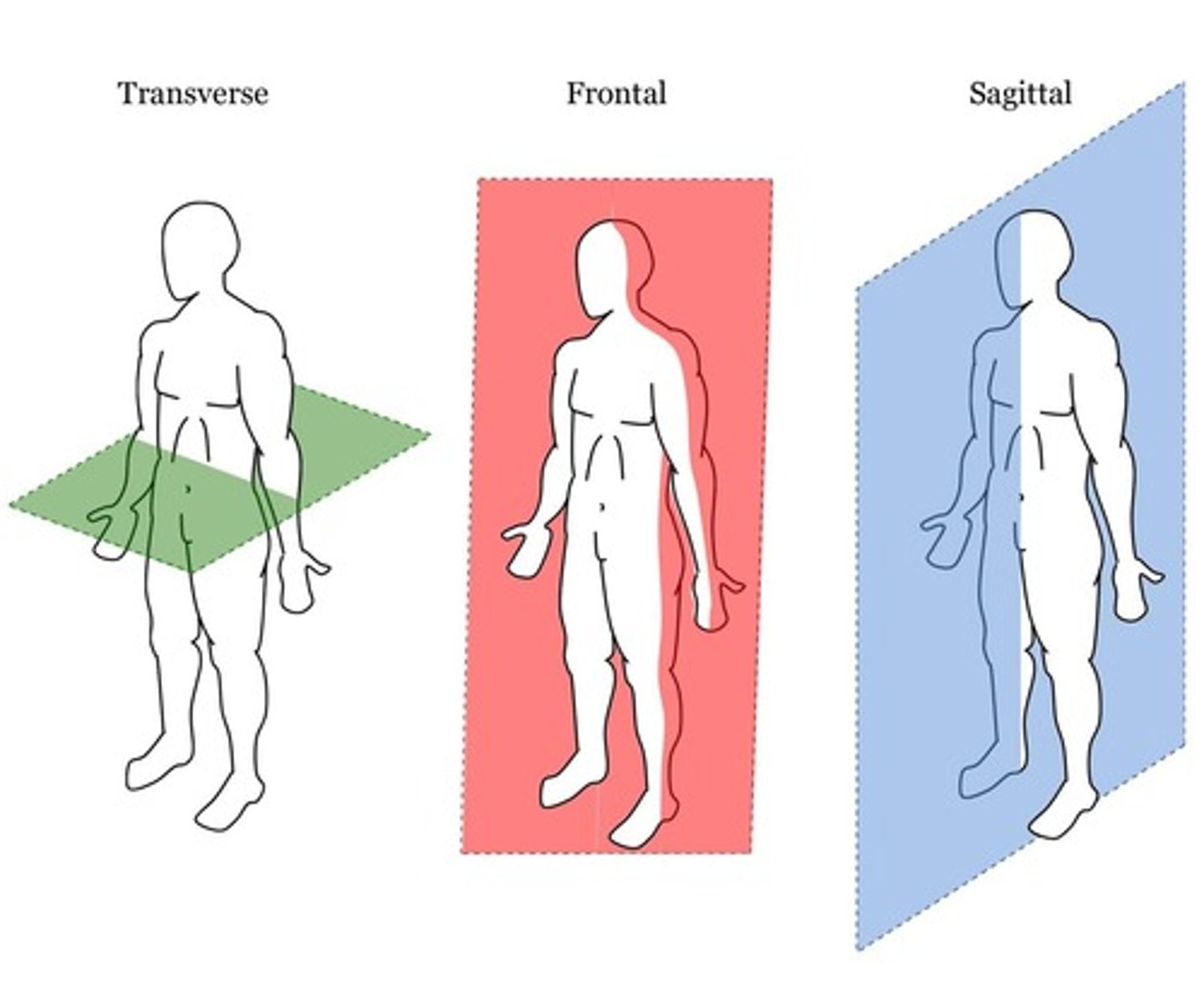
What are the three planes of the body?
1. Sagittal: Divides the body into right and left sides.
2. Coronal (Frontal): Divides the body into anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) parts.
3. Axial (Transverse): Divides the body into upper (superior) and lower (inferior) portions.
What are the two main body cavities?
1. Dorsal Cavity: Located posteriorly, includes cranial and spinal cavities
2. Ventral Cavity: The largest body cavity, subdivided into thoracic cavity and abdomino-pelvic cavity.
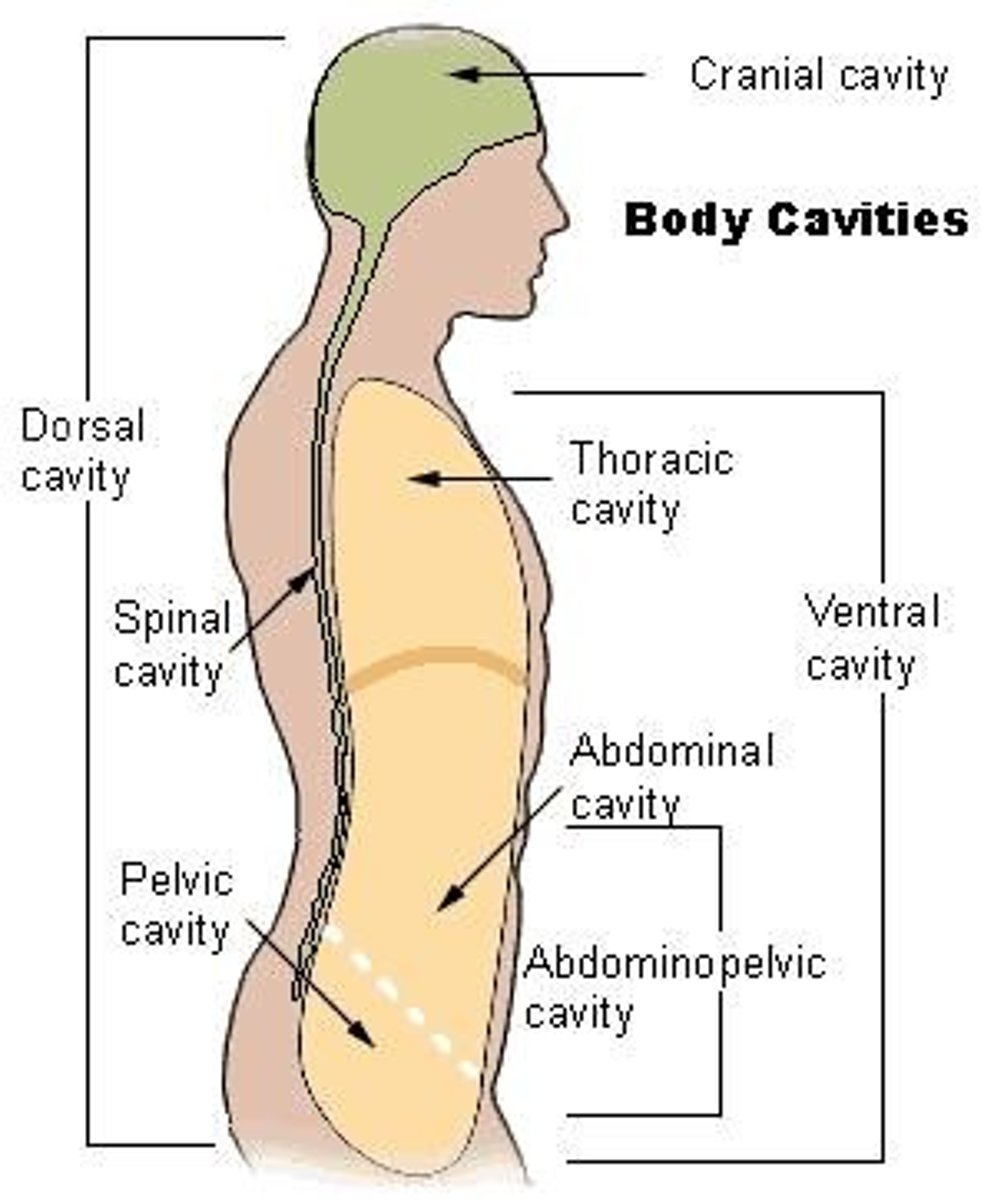
What subdivisions are found within the thoracic cavity?
The thoracic cavity is subdivided into two lateral pleural cavities and the mediastinum.
What is the difference between the male and female pelvis?
The female pelvis is wider because the wings of the ilia are more open.