Maternal Nursing Exam 2 (labor, pain, FHR)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
factors affecting labor
passengers, presentation, passageway, powers, position, psychological factors
passengers
fetus & placenta
-head size
—anterior fontanel = diamond, 3×2 cm
—posterior fontanel = triangle, 1×2 cm
—head must mold to fit through, goes back to normal w/in 3 days
-placenta previa = in front of head
presentation
which part of the fetus enters first
-cephalic = occipit (“vertex”)
-breech = sacrum (butt/feet)
-shoulder = scapula
factors determining fetal presentation
-lie = spine of fetus r/t mom’s spine: may be longitudinal, transverse (need C-section), or oblique
-attitude = relation of body parts (general flexion is normal)
-position = portion that overlies pelvis inlet
-station = relationship of presenting part to line between ischial spines (narrowest part of pelvis)
—measured in cm, (-) means above, (+) means below (+4 or +5 means birth is coming)
-engagement = largest diameter has passed the pelvic inlet (station = 0)
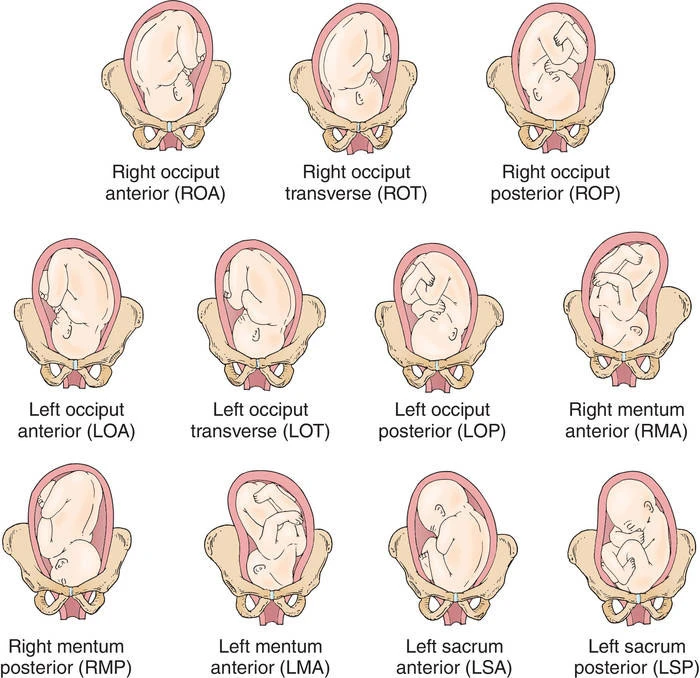
fetal position
where is the presenting part (what part of pelvis)
-R or L (determine by feeling fontanel)
-Occipit, Sacrum, Mentum/chin, or SCapula
-Anterior, Posterior, or Transverse
e.g. “RST” (baby’s sacrum is on mom’s right side & baby is facing the [left] side)
-OA is best (baby is facing the back)
fetal positions image
passageway
bony pelvis
-depends on subpubic angle, diameters, etc
-4 possible shapes/types of pelvis
soft tissues
-in labor, uterus becomes thick at top and thin at bottom, physiologic retraction ring separates
-cervix effaces (thins) and internal os dilates
—effacement at 100% feels paper-thin
—dilation goes 2-10 cm (10 = cannot feel cervis around baby’s head) *6-7 cm is more measuring what’s left around baby’s head
cervical exam
report dilation (in cm), effacement (%), station (-5 to +5)
powers
-primary = involuntary contractions (cause effacement, dilation, & descent)
—frequency = time from start of one to start of next
—duration = length
—intensity = peak strength
-secondary = bearing down (discourage Valsalva b/c holding breath is bad)
—involuntary urge to push, then voluntary pushing: to cause descent
process of labor
-true labor = contractions AND cervical change
-stages
1) onset to full dilation
2) dilation to birth
3) birth to placenta (3-4 contractions)
4) placenta to stability (1-2 hours)
7 cardinal movements of labor
*ready to deliver = head stays in place during contractions
-engagement = head in pelvic inlet
—asynclitism (head deflected) vs synclitism (parallel to AP plane of pelvis)
-descent (head moves through pelvis)
-flexion (of head)
-internal rotation (occipit rotates anterior)
-extension
-restitution and external rotation (after head is out)
-expulsion (after shoulders are out)
signs before labor*
-1st time: uterus moves down 2 weeks before term (lightening)
—multipara: after contractions
—less pressure on lungs, more on bladder (urinary frequency)
-low backache
-Braxton Hicks
-vaginal mucus increases (brownish red = bloody show)
-cervix softens/ripens
-1-3.5 lb weight loss
-energy burst
-membrane rupture
fetal adaptations to labor
-FHR normally 110-160, drops closer to term, then changes during labor
-fetal circulation compensates for stress of contractions
-fetal respirations:
—lung fluid clears
—decreased O2 concentration, CO2 increased
-blood pH lowers
-bicarb lowers
-respiratory movements decrease
maternal adaptations to labor
-CVS
—CO increases 12-31% d/t higher SV
—BP increases
—WBC increases
-maternal respirations: hyperventilation
-proteinuria 1+
-maternal integument stretches, maybe tears
-euphoria→seriousness→amnesia→elation or fatigue
-decreased pain threshold, sedation
pain
threshold = same for everyone
tolerance = what pt is willing to endure
pain in labor
visceral
-organ pain
-stages 1, 3, 4
-ischemia d/t low blood flow to uterus during contractions
-cervical stretching
-pressure on organs and nerves
-radiating pain
somatic
-skin/muscle
-stages 2, 4
-sharp/burning/localized
-d/t distention, pressure on bladder & rectum, stretching, lacerations
pain management
-do not assess w/ 0-10 scale; ask pt what she felt
-gate control theory: only a limited number of sensations can be felt at a time (i.e. distraction can block pain)
non-pharm pain control
-focal point
-breathing (slow at first, then lighter/faster)
—3:1 or 4:1 in-out/blow at 8 cm (use paper bag)
-wait to push till 8 cm
-effleurage = light stroking of abdomen
-counterpressure = circular movement/pressure on sacrum w/ fist
-TENS (on back, 1 min at a time)
water therapy
-contra: FHR monitor on, fever, infection, bleeding, preterm
-never leave pt alone
-temp 96.8-99.5
ID water block: sterile H2O injection
-0.05-0.1 mL into 4 points on lower back
meds for pain
-implement early: first stage (late narcotics affect baby)
-sedatives: avoid (barbiturates, phenothiazines, benzos)
analgesics
-IM or IV
-opioids are limited
-risk of aspiration or low FHR/RR
-avoid meperidine/Demerol
-usually Nubain, Stadol, hydromorphone, morphine, maybe fentanyl or remifentanil
nerve block
-local perineal infiltration anesthesia
—for episiotomy or sutures
—lidocaine or chloroprocaine, plus EPI
-pudendal
—give late in stage 2 for episiotomy or operative vaginal birth, or stage 3 for stitches
-spinal anesthesia
—inj into subarachnoid space at L3-L5
—C-section: T6 down, vag: T10 down
—numbs to nipple line, works by gravity
—moves up for 5-20 mins, lasts 3 hr
reminders for spinal anesthesia
-AEs: hTN, low perfusion, ineffective breathing, HA (need blood patch)
-elevate head/shoulders/one hip
-assess VS, EFM, F&E q5min
-give bolus of LR or NS (500-1000 mL over 30 min) 15 min before to prevent hTN
-hTN
—decrease by 20%, SBP <100, FHR decrease
—turn laterally, increase IV rate, give O2 via nonrebreather mask at 10-12 L
-elevate legs, give vasopressor like ephedrine
epidural*
-catheter inserted (usually after)
-anesthetic or opioid
-L4-L5 (numb to belly line)
-least CNS depression
-C section: T8-S1, vag: T10-S5
-position pt lateral, rotate q1hr
-continuous or PCA
-pulse ox ON!
-contra: hemorrhage, coagulopathy, infection, IICP, heart conditions
-will feel pressure
-might be able to move after
other nerve blocks
-combined spinal-epidural: does not immobilize
-epidural & intrathecal
—no VS change
—can still push
—also used post-op
-contra: hemorrhage, hTN, bleeding disorder, blood thinners, infection, IICP, heart conditions
nitrous oxide
-AEs: N/V, dizzy
-rapid onset, no accumulation, self-admin
-pt is the only one allowed to hold mask
general anesthesia
-for regional contraindication or rapid birth
-risks: intubation difficulty, gastric content aspiration
-elevate one hip
-preoxygenate
-anesthetic given, then muscle relaxer, then ETT, then NO & O2, maybe amnesic
-may cause neonatal narcosis or hemorrhage
nursing management before epidural**
-signed consent
-bathroom
-IV fluid bolus
-sit on side of bed
-pulse ox on
after:
-stay at bedside for 20 mins
-watch for HR drop in mom and baby
methods of birth
-Lamaze: enjoy process, rely on support person
-Bradley: all decisions made before, partner is final decision-maker in the moment
-hypno-birthing: self-hypnotize, pt will not remember anything after
fetus during labor*
low O2
-low blood supply d/t mom’s BP change or low BV
-mom’s hemorrhage or anemia
-cord compression
-low blood flow to fetus from placenta
FHR changes d/t hypoxemia
FHR monitoring: intermittent auscultation
intermittent auscultation
-need special stethoscope or fetoscope or Doppler ultrasound
-palpate fetal position first
-compare to mom’s radial pulse
-count for 30-60 sec after contraction
-for low risk, no Pitocin
-contractions: intensity, duration, frequency, resting tone (soft or hard)
FHR monitoring: EFM
-to assess O2
-external (transducers on abdomen)
—no pressure measurement
—weak signal d/t obesity, anterior placenta, fetal movement
—elastic belt holds in place
—not always good for preterm
—mom cannot get up
-internal (electrode on fetus)
—requirements: ROM, cervix 2-3 cm, can access presenting part
—catheter (IUPC) inserted into fluid pocket to measure pressure
normal uterine activity during labor
-contraction frequency: 2-5 per 10 min
-contraction duration: 45-80 sec
-contraction strength: 40-80 mmHg
-resting tone: 10 mmHg
-relaxation time: >45-60 sec
FHR baseline*
average during 10 minute segment (rounded to closest 5 bpm)
—normal = 110-160
-accelerations normal, decelerations are not
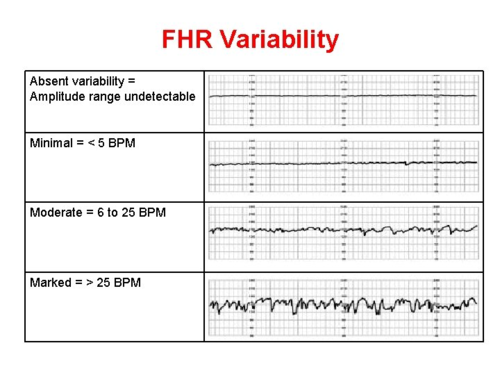
-variability = irregular fluctuations in baseline of 2+ cycles per min
—absent = amplitude range not detectable, 0-2 bpm (not good)
—minimal = 3-5 bpm (monitor)
—moderate = 6-25 bpm (normal)
—marked = 26+ (monitor, usually during pushing)
—*number one indicator of fetal well-being
baseline tachycardia & bradycardia
-tachy = >160 for 10+ min
—early sign of low O2
—also d/t mom: fever/infection, anemia, meds, drugs, hyperthyroidism; fetus: movement, stress
—Rx: reposition, check temp, give antipyretics/antibiotics
-brady = <110 for 10+ min
—d/t head coming out, HF, virus, maternal hypoglycemia or hypothermia
periodic & episodic FHR changes*
periodic = w/ UCs, episodic = not
increase by 15+ bpm for 15+ sec
accelerations or decelerations
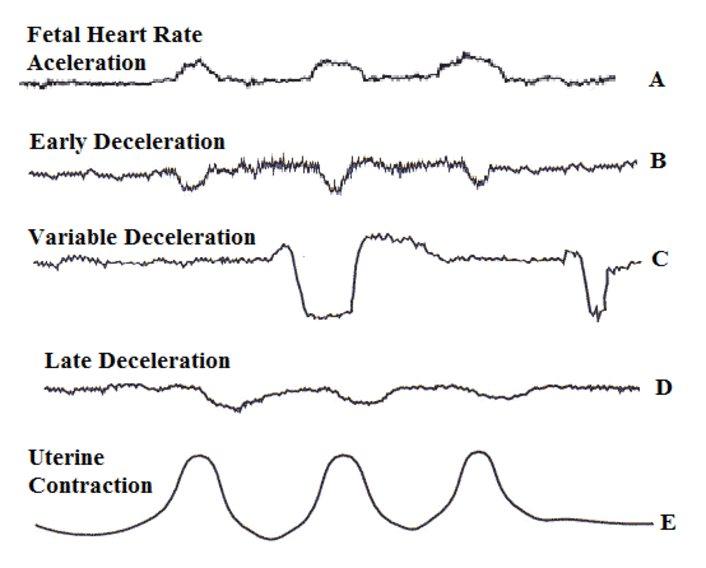
accelerations
—abrupt = <30 sec
—return w/in 2 min
—d/t compressed vein, movement, stimulation, breech, OP position, UCs
—normal, indicate good O2/neuro status
decelerations*
(>30 sec)
—early = beginning of UC (nadir aligns w/ UC peak)
—r/t UCs, CPD (benign)
-late = end of UC (nadir is after UC peak)
—d/t low O2 (less benign)
—give IVF/O2, reposition
-variable
—sudden, shaped like a V/U/W on monitor
—d/t cord compression
—reposition, give amnioinfusion
-prolonged = 2+ min
variability image
periodic/episodic changes image*
non reassuring FHR patterns*
-baseline bradycardia or tachycardia
-absent or minimal variability
—d/t sleeping, sedation, or lack of O2
—prevent from getting worse
-variable or late decelerations
-prolonged decelerations
*may indicate hypoxemia or acidemia
EFM methods
-US transducer on upper abdomen, goes over baby’s back at heart level, measures FHR
-tocotransducer over uterus on hardest part of fundus, measures UCs
-evaluate baseline rate, baseline variability, accelerations, decelerations, changes, trends (indicate fetal O2)
assessment of fetus
-fetal scalp stimulation (tickle baby’s head) & vibroacoustic stimulation
—FHR should increase (indicates no acidemia)
—contra: decelerations or bradycardia
-cord acid-base testing
—test pH of placental artery & vein
—test PCO2 & PO2
-scalp blood sampling
interventions for fetus*
-amnioinfusion
—NS or LR bolus into uterus
—for deep or frequent variables, low amniotic fluid volume, or meconium-stained fluid
—relieves cord compression
-tocolytic therapy
—meds to inhibit UCs
—e.g. terbutaline
—used if position change, IVF, or stopping Pitocin fails
nursing care for abnormal FHR*
*standing orders (but call HCP after)
-intrauterine resuscitation
—reposition to side
—short-term O2 via nonrebreather mask at 10-15 L
-bolus of 500-1000 mL LR or NS
-turn off Pitocin or remove cervadil
-tocolytic meds
categorizing FHR
-category I (green): normal
—no acidemia, no risk
—no Rx needed
-category II (blue): indeterminate
—no central acidemia, no risk, low risk of progression to acidemia
—conservative management
-category II (yellow)
—intermittent hypoxia, no risk, moderate risk of progression
—conservative management w/ surveillance
-category III (orange)
—potential decompensation, no risk, high progression risk
—conservative management w/ prep for delivery
-category IV (red): abnormal
—possible asphyxia, high risk, present risk of progression
—baby needs delivered immediately
mnemonic for FHR*
V.E.A.L. C.H.O.P.
-Variable deceleration = Cord compression
-Early deceleration = Head pressure
-Acceleration = Okay
-Late deceleration = Placental insufficiency
fetal compensation*
HR drops to compensate for low BP or BV (opposite of adult)