Experimental designs
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What is Thalidomide and its effects
originally prescribes as a extremely safe drug for sleeplessness, that was then discovered could be prescribed off-label for morning sickness. Was later found to cause phocomelia
What year was thalidomide created? Where
1953 by Grunenthal Group in Germany
When was thalidomide first licensed in the UK
1958
When was thalidomide ADRs discovered? By whom?
1961 - Dr. William McBride
When completing a clinical trial, what type of participants are involved in phase 1
“20-100 healthy volunteers or people with the disease/condition”
very homogenous group
When completing a clinical trial, what type of participants are involved in phase 2
“up to several hundred people with the disease”
start to see some deviation from “healthy”
When completing a clinical trial, what type of participants are involved in phase 3
“300 to 3,000 volunteers who have the disease or condition”
When completing a clinical trial, what type of participants are involved in phase 4
“several thousand volunteers who have the disease/condition”
this is who is representative of the population
When completing a clinical trial, what is the typical length of study for phase 1
several months
When completing a clinical trial, what is the typical length of study for phase 2
several months to 2 years
When completing a clinical trial, what is the typical length of study for phase 3
1-4 years
When completing a clinical trial, what is the typical length of study for phase 4
> 4 years
When completing a clinical trial, what is the purpose of the study for phase 1
safety and dosage
When completing a clinical trial, what is the purpose of the study for phase 2
efficacy and side effects
When completing a clinical trial, what is the purpose of the study for phase 3
efficacy and monitoring for ADRs
When completing a clinical trial, what is the purpose of the study for phase 4
safety and efficacy
Approximately what percentage of drugs move on to phase 2
70%
Approximately what percentage of drugs move on to phase 3
33%
Approximately what percentage of drugs move on to phase 4
25-30%
Define Effficacy
benefit of an intervention as compared to a control/standard program
does it work?
define effectiveness
benefit of an intervention in the “real world”
how well does it work?
What are 2 things we will need to be able to identify in a study
randomization schemes and number of independent variables
What are 2 types of randomization schemes
completely randomized/between subjects
repeated measured/within subjects
What are 2 types on are named after the number of IVs
single factor/one-way design
multifactor design
What type of data do we analyze with unpaired t-tests
2 groups, interval/ratio data
What type of data do we analyze with analysis of variance
3+ groups, interval/ratio data
What type of data do we analyze with Mann-Whitney U-test
2 groups, ordinal data
What type of data do we analyze with Kruskal-Wallis analysis of varance
3+ groups, ordinal data
Define treatment arms
independent groups of subjects
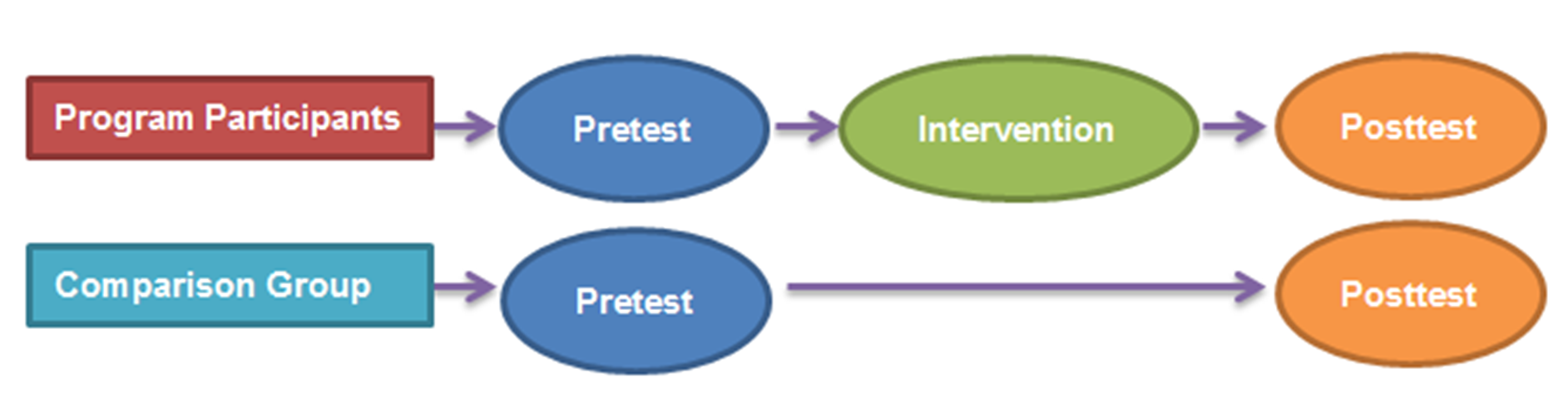
What is the scientific standard for determining cause and effect
pretest and posttest control group design
What does a pretest and posttest control group design flow chart look like
What is the IV?
RCT to study the effects of exercise program for improving venous hemodynamics in patients with chronic venous insufficiency
31 subjects randomly assigned to 2 groups
•Experimental group received physical therapy with specific exercises for calf strengthening and joint mobility
•Control group=Nothing
•BOTH groups received compression stockings
Dynamic strength, calf pump function and quality of life were assessed at baseline and after 6 months
exercise
How many levels to the IV?
RCT to study the effects of exercise program for improving venous hemodynamics in patients with chronic venous insufficiency
31 subjects randomly assigned to 2 groups
•Experimental group received physical therapy with specific exercises for calf strengthening and joint mobility
•Control group=Nothing
•BOTH groups received compression stockings
Dynamic strength, calf pump function and quality of life were assessed at baseline and after 6 months
2 (exercise and no exercise)
How many DVs?
RCT to study the effects of exercise program for improving venous hemodynamics in patients with chronic venous insufficiency
31 subjects randomly assigned to 2 groups
•Experimental group received physical therapy with specific exercises for calf strengthening and joint mobility
•Control group=Nothing
•BOTH groups received compression stockings
Dynamic strength, calf pump function and quality of life were assessed at baseline and after 6 months
3 (strength, pump function, QoL)
What does a multigroup pretest and posttest design flow chart look like
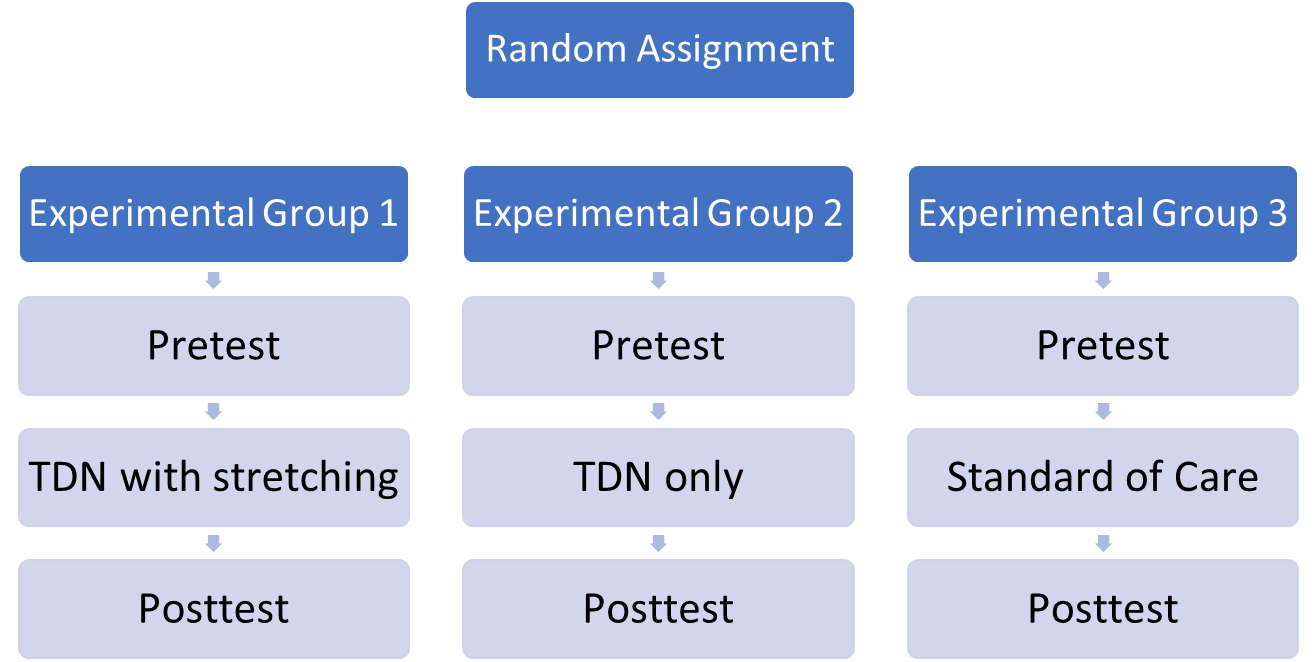
Is it possible to just compare the posttest
Yes, typically used for practical purposes (FIM scores/ length of stay), or when the pretest can bias the posttest (attitude/behaviors)
What is a factorial design for independent groups
incorporated 2 or more IV, with independent groups of subjects randomly assigned to various combinations of levels of the 2 variables
How are factorial designs usually diagrammed
matrix notation
What are the IVs?
Location | Exercise Intensity | ||
Moderate | Vigorous | ||
Home | Home-Mod | Home-Vig | |
Community Center | CC-Mod | CC-Vig | |
Exercise and location (each have 2 levels)
What is the main effect?
Location | Exercise Intensity | ||
Moderate | Vigorous | ||
Home | Home-Mod | Home-Vig | |
Community Center | CC-Mod | CC-Vig | |
is there a difference between exercising at home or CC?
is there a difference in mod vs vig exercise?
What is the interaction effect?
Location | Exercise Intensity | ||
Moderate | Vigorous | ||
Home | Home-Mod | Home-Vig | |
Community Center | CC-Mod | CC-Vig | |
Is there a relationship between exercise intensity and location
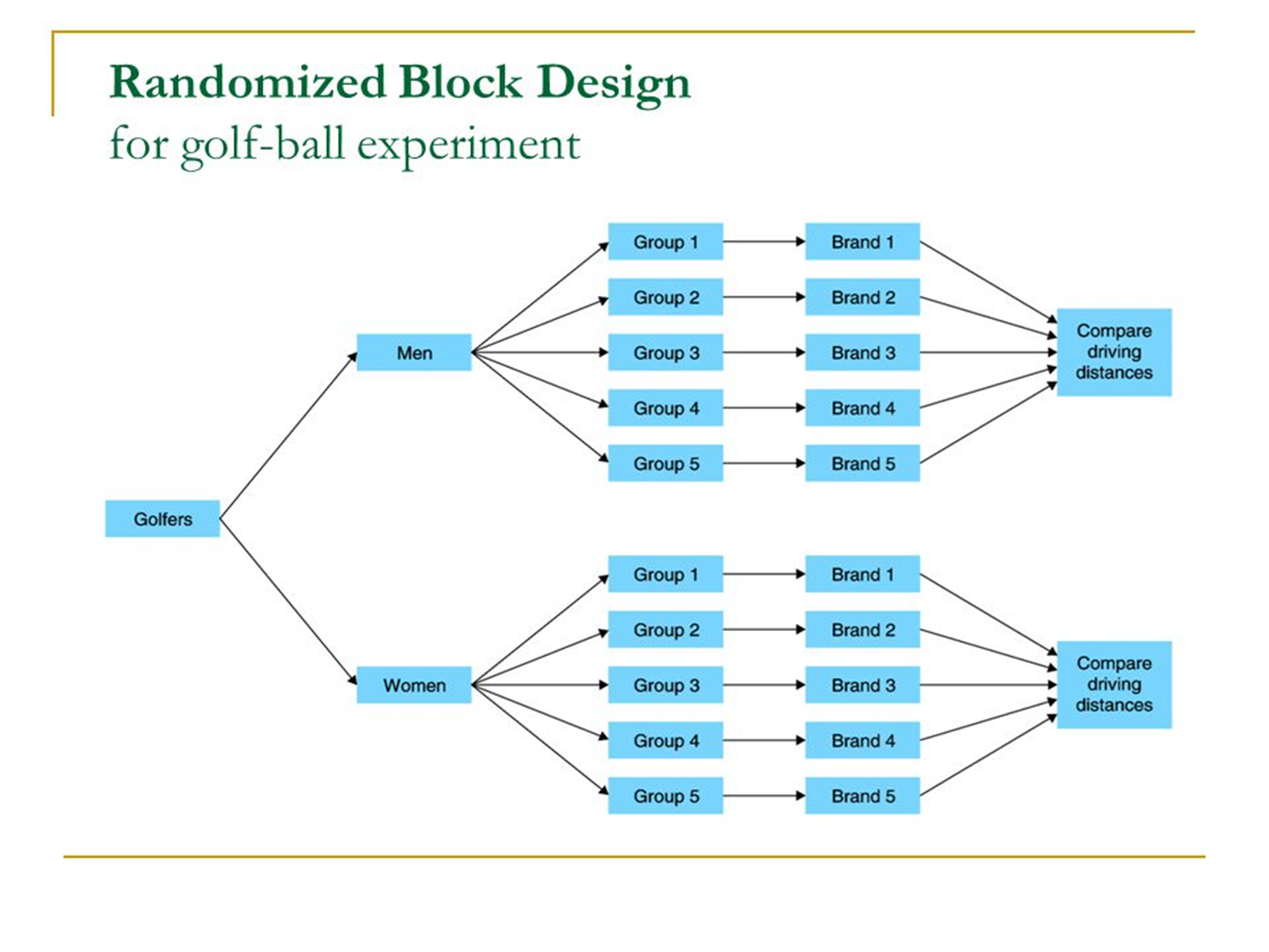
When is a randomized block design used
when an attribute variable (blocking variable) is crossed with an active independent variable
What is the most commonly used blocking variable
gender
What is the key when using blocking variables
the blocks should have some impact on your outcome/DV
What does a randomized block design flow chart look like
What is a repeated measured/within subject design
each subjects acts as his/her own control
What is the advantage of repeated measured/within subject design
controls for individual differences
Disadvantages of repeated measured/within subject design
practice/learning effect/ carry over effect
What is a learning effect
When a subject is exposed to a test over and over again, they will learn how to take the test better
What is a carry over effect
When a subject is exposed to multiple treatments, one treatment effect carries over up to the next
Is a repeated measured/within subject design truly an experiment
not exactly, but if multiple treatments are randomized, then yes
How can we combat learning and carry over effect in a repeated measured/within subject design
providing sufficient time for recovery
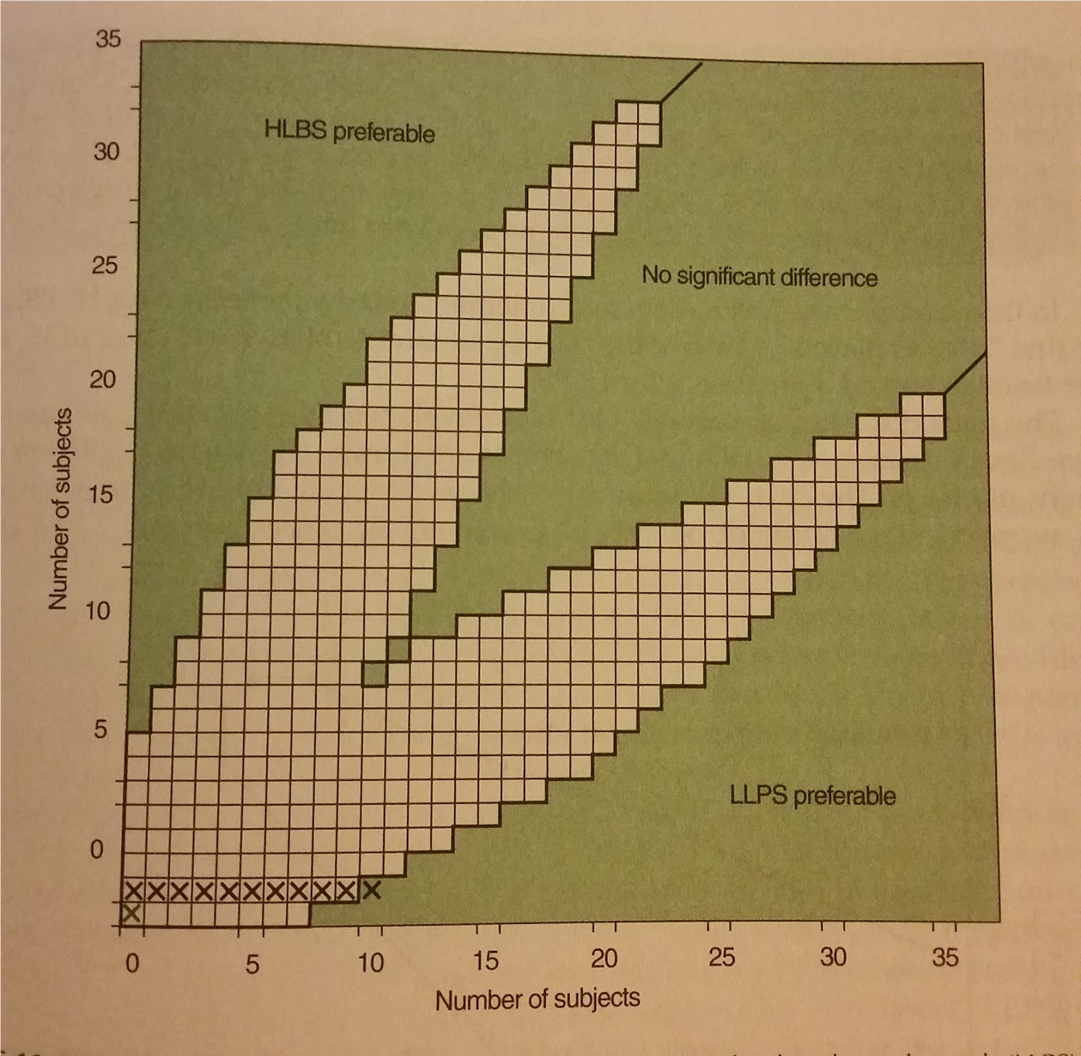
What is a sequential trials design
a version of RCT that allows for data to be collected and analyzed in “real-time”
basically a large experiment consisting of many “little experiments”
When does a terminal decision occur with a sequential trials design
when one boundary is crossed
What is the problem with sequential trials design
ties get thrown out, and there tends to be a lot of them. This causes you to essentially get nowhere
How are sequential trials design kept track of