Unit 4 Quizzes
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
The group of diverse diapsids, present in the early Mesozoic before the dinosaurs are collectively known as:
a) thecodonts
b) mammal-like reptiles (theropods)
c) reptiles like lizards and snakes
d) gorns
a
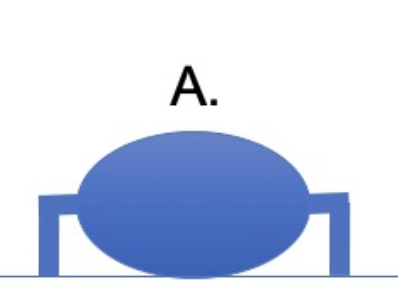
which group of animals does this leg position represent?
amphibians
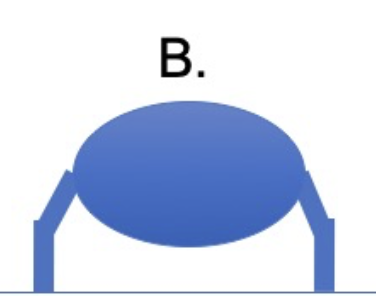
which group of animals does this leg position represent?
reptiles
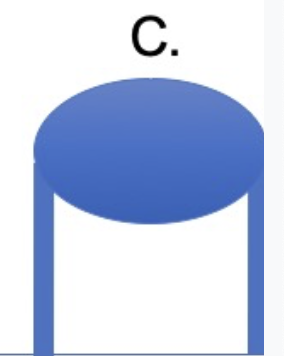
which group of animals does this leg position represent?
humans and dinosaurs
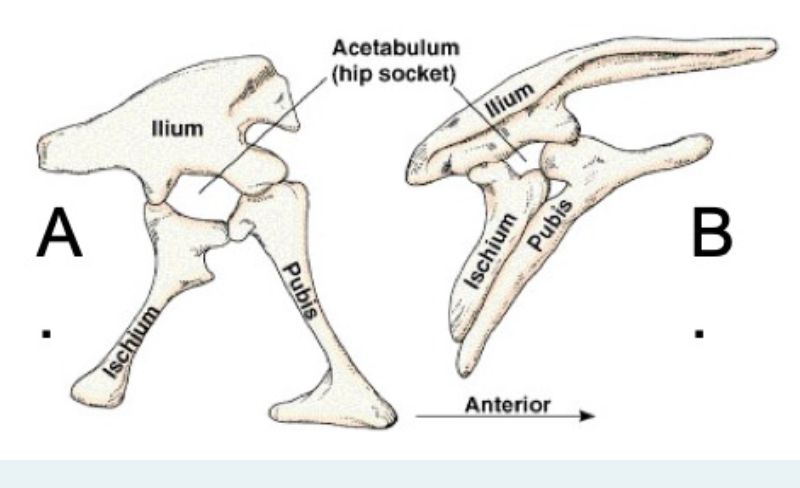
what does hip structure “a” represent?
sauritia
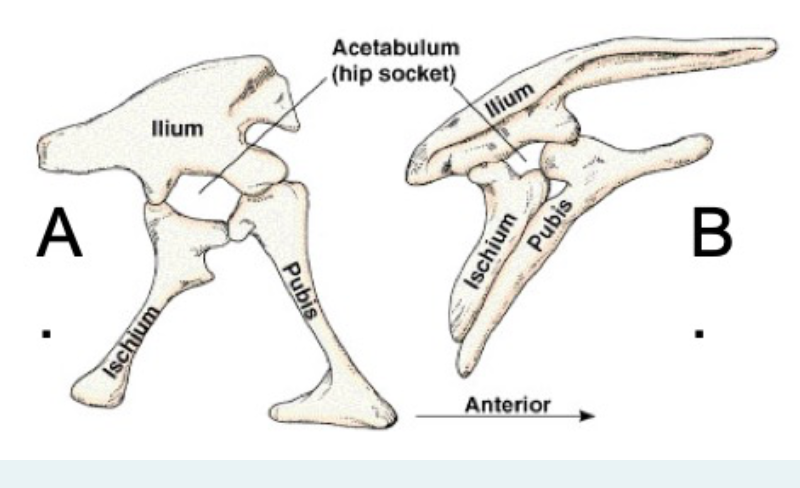
what does hip structure “b” represent?
ornithischia
when do dinosaurs first appear?
a) toward the end of the Paleozoic
b) at the beginning of the Mesozoic
c) early Mesozoic but not right at the start
d) beginning of the Jurassic period
c
Which of these organisms is defined by being diapsid?
a) dinosaurs
b) Tiktaalik and Ichtheostega
c) mammal-like reptiles (therapsids)
d) non-archosaur reptiles like lizards and turtles
a
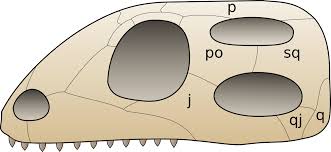
Which vertebrate skull structure is represented in this figure?
a) diapsid
b) synapsid
c) canapsid
d) euryapsid
a
True or False? Whales and their relatives like dolphins evolved from land dwelling mammals.
true
Grass and grasslands first appeared when?
a) Middle Paleozoic (400 my)
b) Middle Mesozoic (150 my)
c) Early Cenozoic (40 my)
d) at the end of the last ice age (10,000 yrs ago)
c
True or False. Many, if not most, mammal lineages have at one time evolved exceptionally large representatives.
true
What was the Great North America - South America Exchange?
a) the event when modern humans (originally from Asia) migrated from North America to occupy South America
b) when rivers stopped flowing south to north and began flowing the other direction
c) when mammals, isolated for 10s of millions of years crossed a new land bridge at Panama
d) when mountain uplift stopped in North America and began in South America
c
In response to grass having silica crystals in its body, how did horses evolve?
a) longer teeth
b) stronger hooves
c) larger saliva glands
d) shorter noses
a
True or False. Whales and their close relatives evolved independently from all other mammals and have their origin in the Mesozoic.
false
Opossums are North America's only marsupial. Why is this?
a) opossums have been migrating north from South America for many generations
b) opossums were brought over from Australia as pets in the 1800s
c) opossums are native to North America and their meager lineages goes back to the Mesozoic.
d) opossums are an evolutionary missing link
a
Which one of these is not a living mammal group?
a) placentals
b) marsupials
c) monotremes
d) multiturburculates
d
At the end of the Mesozoic mammals were small, generalists that looked like a shrew. After the end Mesozoic mass extinction mammals had rapidly evolved into most known major groups within 15 million years.
This is an excellent example of:
a) an adaptive radiation
b) a key innovation
c) the red queen hypothesis
d) iterative evolution
a
Much of the fossil mammal record is based on their teeth. Why?
a) teeth are more abundant that other parts of the body
b) paleontologists prefer teeth because they are easier to collect
c) teeth are harder than other parts of the skeleton
d) it was a 19thCen practice, now everyone collects and studies their hip bones exclusively
c
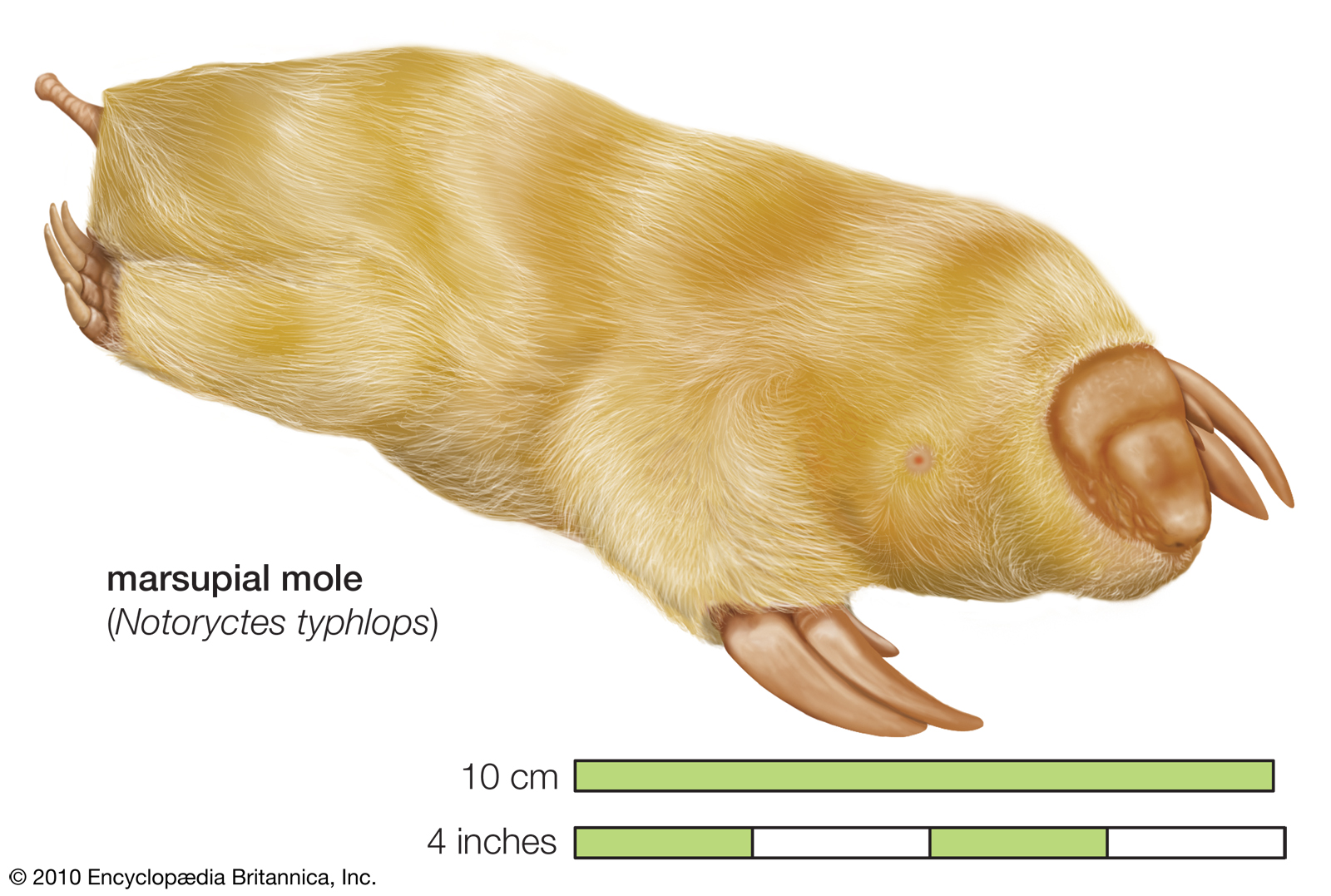
This is a marsupial (has a pouch). Why does it have the form of a proper mole, even though it last shared a common ancestor with moles 70+ million years ago.
a) divergent evolution
b) convergent evolution
c) adaptability
d) gene flow
b
The dominant mammal group today is the placentals. What is a placenta?
a) the more efficient lining of the lungs in some mammal groups
b) the organ the surrounds and protects the brains of some mammals
c) an organ in the uterus of some pregnant mammals, that nourishes the fetus.
d) tissue of the nervous system with a more rapid neuron firing
c
True or False? There is a group of mammals in Australia that lay eggs.
true
True or False? Mammals were able to dominate and over take dinosaurs by out competing them.
false
What are two features that are unique to mammals?
a) warm bloodedness and live birth
b) synapsid skull structure and warm bloodedness
c) Hair/fur and lactation/milk
d) hip structure and stance
c
When did the transition from primitive reptiles to true mammals take place?
a) in the Middle Paleozoic (Devonian) about 400 million years ago
b) from the Late Paleozoic (Permian) to the Early Mesozoic (Triassic) about 250 million years ago
c) in the Early Cenozoic, after the dinosaurs went extinct about 60 million years ago
b
Which of these was not a trend in early mammal evolution?
a) reduction in the number of ribs in the ribcage
b) differentiation of the types of teeth in the jaw
c) the splaying (spreading) of the legs away from the body
d) reduction in the number of bone elements in the jaw
c
What is a synapsid skull structure, with an example?
a) no holes in the skull, like turtles and snakes
b) single hole in the skull, mammals and their ancestors
c) one, two or three holes in the back of the skull, birds and their ancestors
d) two holes in the skull, dinosaurs and their ancestors
b
What is a therapsid?
a) evolutionary intermediates between reptiles and mammals
b) the bone structure of mammal's inner ear
c) the form that results from convergent evolution
d) all of the material in the dust resulting from an asteroid collision with the Earth
a
True or False? The mammal clade and dinosaur clade originated at about the same time and have coexisted through to today.
true
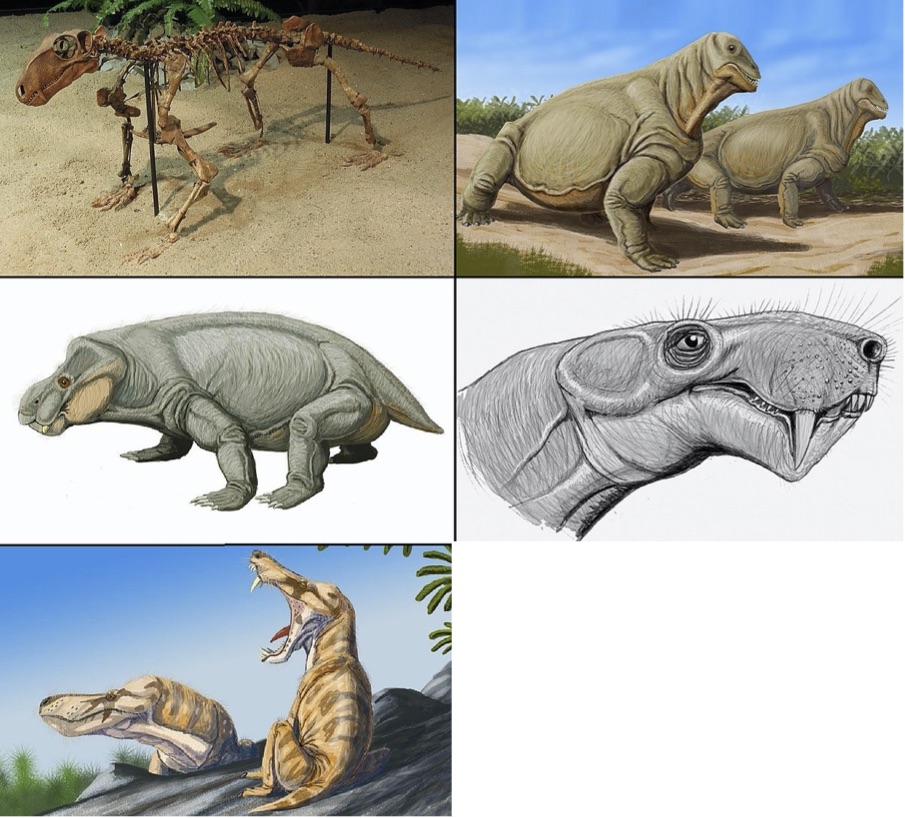

What are these early Mesozoic animals?
a) therapsids - mammal ancestors
b) thecodonts - dinosaur ancestors
c) monotremes - an extinct clade with no descendants
d) kommodians - ancestor to all dinosaurs and mammals
a

dinosaur?
no
is a komodo dragon a dinosaur?
no
is a brontosaurus a dinosaur?
yes
is a pterodactyl a dinosaur?
no
is a plesiosaur a dinosaur?
no
In addition to a common ancestor, what must be in a group for it to be considered a clade?
a) its complete ongoing family lineage (tree)
b) all of its lineal designates
c) all of its ancestors
d) those that evolved during a adaptive radiation
a
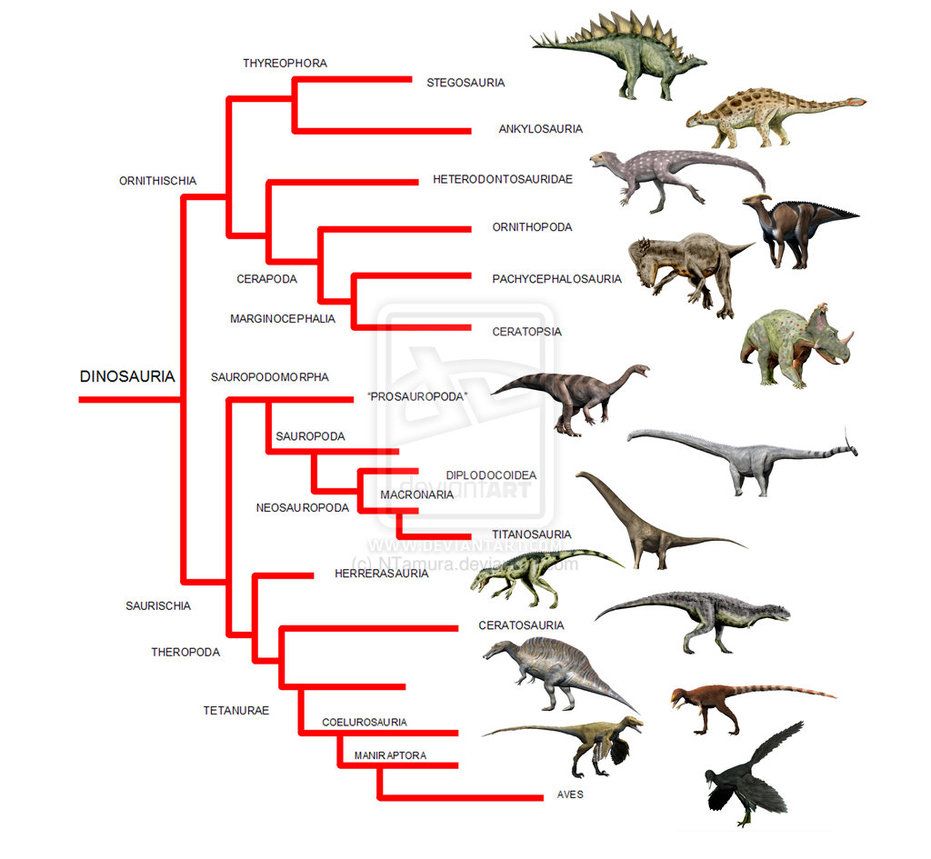
What does this image portray?
a) dinosaur phylogeny
b) dinosaur ecology
c) convergent evolution
d) key innovation
a
What kind of information is not used to create a family tree?
a) comparison of the evolutionary relationships of anatomy
b) stratigraphic position of fossils
c) DNA relationships of modern forms
d) the lifestyle and overall body form
d
The dinosaur clade is defined as:
a) The common ancestor of a house sparrow & a triceratops and all of its descendants.
b) T-rex to Triceratops, down to the base of the Triassic
c) Ancestor of crocodiles and all of f its descendants up to the mass extinction
d) Most large reptiles that lived during the Mesozoic (excluding large lizards)
a
True or False? Birds belong to the dinosaur clade.
true
Which of these is not an Era of the Phanerozoic?
a) Paleozoic
b) Mesozoic
c) Cenozoic
d) Proterozoic
d
Select all of the challenges that both plants and animal had to overcome to live on land. SELECT MULTIPLE ANSWERS as appropriate.
a) keep their bodies from drying out
b) avoid sunlight in the ultra violet spectrum
c) have structures to support the body out of water
d) have structures for attachment or locomotion
a, b, c, d
What was the key innovation that allow for animals to first occupy and then dominate land?
a) lungs to process oxygen
b) appendages (legs) so they could get around
c) resistance to rain water
d) ability to see in color
a
cenozoic paleozoic boundary
there is no such boundary
mesozoic cenozoic boundary
66 mya
paleozoic mesozoic boundary
252 mya
precambrian paleozoic boundary
541 mya
True or False? Prior to the Paleozoic, the land surface of the Earth looked surprising like it does today.
false
The Mesozoic is which unit of geologic time?
a) Eon
b) Era
c) Period
d) Age
b
About when did animals and plants first start to live on land?
a) Middle Paleozoic (Silurian-Devonian)
b) Proterozoic (Ediacaran)
c) Mesozoic (Jurassic)
d) Late Paleozoic (Pennsylvanian-Permian)
a
What was the key innovation that allowed for plants to first diversify and dominate the land?
a) vascular tissue
b) seeds
c) photosynthesis
d) collagen
a
The Triassic period at the beginning of the Mesozoic is an odd time in geologic history because:
a) it is bounded by major mass extinctions at its beginning and end.
b) it is the longest duration of any of the periods, more than 200 million years
c) most of the continents were submerged and there was basically one large sea
d) it experienced six major asteroid strikes all in about a three million year interval
a
The largest mass extinction in the history of the Earth occurred at the end of the:
a) End Paleozoic (Permian)
b) Early Mesozoic (Triassic)
c) End Mesozoic (Cretaceous)
d) The Cambrian
e) The Archean
a
True or False? Mass extinctions shows us that evolution must work at two levels, background natural selection (fitness and specialization) and random events millions of years apart that favor generalist lifestyles.
true
Which major groups of organisms went extinct at the End Paleozoic (Permian) Mass Extinction?
a) trilobites, major groups of corals, brachiopods, crinoids and bryozoans
b) dinosaurs and ammonites
c) almost all plants
d) stromatolites, sponges and non-boney fish
a
The End Paleozoic (Permian) mass extinction was a perfect storm of multiple extinction events. Which one of these do we not have evidence for as contributing to this even?
a) asteroid impact
b) extraordinarily large basalt flow (traps)
c) formation of a supercontinent (low sea level & poor circulation)
d) stagnation of oceans (anoxic)
a
True or False? The idea that an asteroid impact at the end of the Mesozoic (Cretaceous) contributed to a mass extinction is an interesting hypothesis, but there is little empirical evidence for such an event.
false
Which item is not evidence a large asteroid impact if found in a world-wide clay layer:
a) shocked quartz
b) metal fragments (nickel & iron)
c) droplets of glass (tektites)
d) the element Iridium
b
Iridium is a chemical element that is rare on Earth but common in asteroids and meteors. How does Iridium support the impact hypothesis for the end Cretaceous mass extinction?
a) it does not support the impact hypothesis
b) it is found in high concentrations in the boundary clay (with fall out debris)
c) it allows for precise dating of the boundary clay at end Cretaceous
d) Iridium is evidence of an extremely low sea level condition at the end of the Cretaceous.
b
Presence of shocked quartz with lamellae in a sediment layer is indicates:
a) the timing of origin of the Earth
b) regional metamorphism
c) presence of a subduction zone
d) the impact of a large asteroid
d
Where did the astroid impact the Earth at the end of the Mesozoic (Cretaceous), causing a mass extinction?
a) on the Yucatan Peninsula of adjacent to the Gulf of Mexico (only visible to geophysical detectors in the subsurface)
b) out in the open ocean somewhere (crater has been lost to subduction)
c) if an asteroid did hit the Earth then, the resulting crater would not have been large enough to be preserved
d) Hudson Bay in Canada (crater rim is still visible)
a
Which one of these best describes the kinds of organisms most likely to survive a mass extinction?
a) organisms that do not have specialized life modes (generalists).
b) the organisms that were most fit to their environment prior to the event.
c) the largest and strongest of each group
d) the smallest and fastest of each group
e) it is random
a
In this example not all of the species within the three classes of organism represented go extinct. Could the red bar still be considered a “mass extinction?” (Yes = True; No = False)
true
Which of these is not a main causes of mass extinctions?
a) rapid climate change
b) stagnation ocean currents
c) extraterrestrial object impacts
d) disease
d
True or False? The properties of ocean currents do not affect the climate on land.
false
Which of the following are potential causes of mass extinctions:
a) global climate change or meteor impact
b) global sea level change or increased volcanic activity
c) change in the worlds ocean circulation and chemistry
d) all of these events are possible causes
e) none of these events is a possible cause
d
A significant cause of global warming through release of CO2 is from “basalt traps”. What are these?
a) large, subcontinental scale flows of basalt unlike any scale we see today
b) places where basaltic magma was stuck in the subsurface and only the gases could escape
c) volcanos like Hawaii that are isolated in the middle of a tectonic plate
d) like the New Jersey Palisades
a
Greenhouse gasses can warm the planet for a long time. Which of these is not a source of greenhouse gasses.
a) volcanos
b) frozen gas hydrates
c) changing the Carbon cycle (humans causing release of CO2 & Methane)
d) overuse of aerosol spray products
d
What happens when an ocean goes stagnant from lack of mixing by currents?
a) bottom waters become anoxic, and the layer with no oxygen can expand
b) all of the nutrients (food) get concentrated in the upper layers
c) the whole ocean gets very, very cold
d) most of the ocean life moves off of the continental shelf and down into the ocean depths
a
five biggest mass extinctions (end of)
Ordovician, Permian (Paleozoic), Triassic, Cretaceous (Mesozoic), Devonian
True or False? An extinction is defined as the event at which the last individuals of a genetic lineage die out.
true
In practice we use the terms FAD (first appearance datum) and LAD (last occurrence datum) rather than "origin" and "extinction" because:
a) the actual origin/extinction events are not expected to be preserved in the fossil record
b) the FADs and LADs serve to normalize the curve statistically
c) FADs and LADs are a more accurate representation of the timing of the biological events
d) actually, they can be used interchangeably because they are synonyms (same meaning)
a
A mass extinction is defined as “a short time interval with a marked increase in the number of extinctions relative to expected background extinction rates”.
How are these values quantified?
a) extinction rate must be increased by 200% beyond back ground levels
b) the "short time interval" must be less than 5 million years
c) both A & B are required
d) there are no set values, it is open for interpretation
d
Which one of these is not a requirement for an event to be considered a mass extinction.
a) all members of major groups must be removed
b) be a global event
c) affect organisms on both land and sea
d) must have extinction rate significantly higher than background rates.
a
On average about how long do species last between their origin and extinction (marine invertebrates)?
a) three to thirty thousand years
b) one to five million years
c) one-hundred to five-hundred million years
d) one to five billion years
b
Natural process that can remove green house gas and cool the Earth include increased rates of: (select two)
a) plant productivity
b) formation of limestone by shells of marine organisms
c) volcanic activity
d) sea floor spreading
e) extinction
a, b
The Permian Siberian Traps and Cretaceous Deccan Traps were:
a. asteroid impact sites that may have caused mass extinctions
b. massive basalt flows that released large amounts of greenhouse gas
c. mass extinction events caused by widespread sinkholes
d. times/places of continental ice sheets (ice ages)
e. none of these answers are correct
b
Which of these processes can Milankovitch cycles (parameters) affect/influence:
a) glaciation and world-wide sea level
b) mountain building
c) seafloor spreading rates
d) mass extinctions
e) all of these are correct answers.
a
Which of these is NOT a parameter/feature in Milankovitch cycles?
a) degree of tilt of the Earth on its axis
b) change in direction that the Earth's axis points (wobble)
c) the shape of the Earth's orbit around the sun
d) None: all of these are Milankovitch parameters
d
True or False. We can recognize times of ancient ice ages based on evidence that is left in the sedimentary rock record.
true
During the Phanerozoic (Paleo+Meso+Ceno), the trend in the global temperature based on the amount of CO2 greenhouse gas in the atmosphere has:
a) remained about constant, very little variation, since the beginning of the Phanerozoic
b) slowly and steadily increased over the past 550 million years, since the beginning of the Phanerozoic
c) randomly and significantly changed unpredictably at scale of millions years since beginning of the Phanerozoic
d) followed a broad cycle of increasing and decreasing at scale of 100s million years since beginning of the Phanerozoic
d
How many Ice House events have resulted in a prolonged Ice Age (glaciers on continents) during the Phanerozoic?
a) One (late Cenozoic, our present one)
b) Two (both in the Paleozoic)
c) Three (early Paleozoic, late Paleozoic and late Cenozoic)
d) None (we have no evidence of ancient ice ages)
c
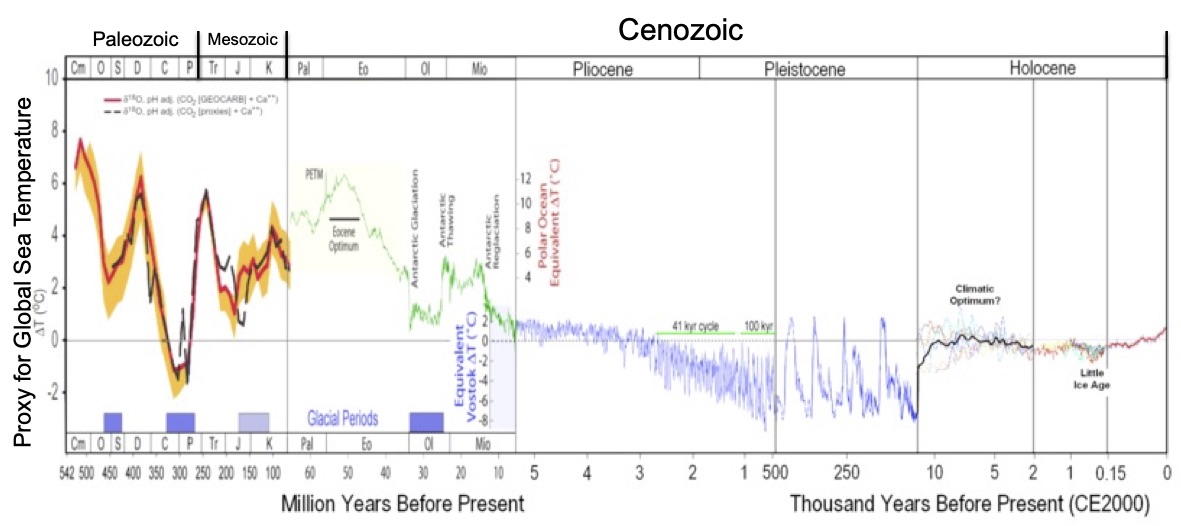
True or False. During the early Cenozoic, the Earth experienced a change from a Green House, with some of the warmest temperatures ever to an Ice House with a period of glaciations?
true
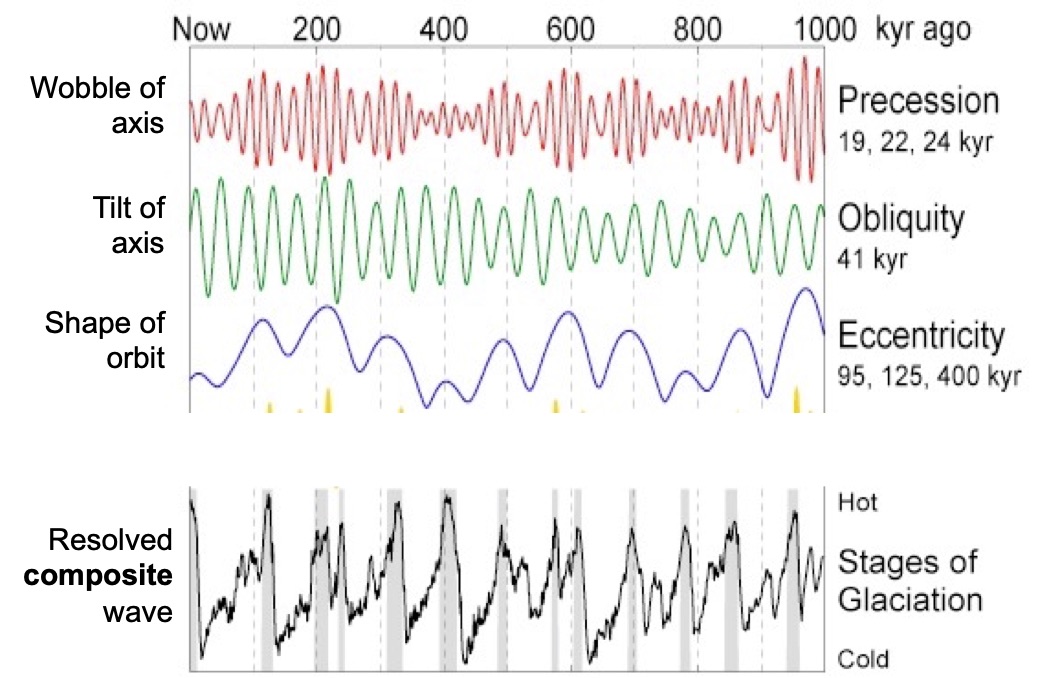
Which one of these curves associated with Milankovitch parameters will have the greatest influence on climate (as preserved in the geologic record)?
a) Wobble - precession
b) Tilt - obliquity
c) Shape of orbit - eccentricity
d) Resolved composite wave (harmonics)
d
During the most recent ICE House glaciation, continental ice sheets (glaciers) formed and advanced and then decline and retreated several times. What controlled/caused this 40-150 thousand year cycle?
a) Milankovitch orbital parameters
b) Wilson cycle
c) Sea floor spreading
d) Sun spots
a
Overall, the current global climate of today is:
a) warmer than the average temperature for the Phanerozoic
b) cooler than the average temperature for the Phanerozoic
c) about the same as the average temperature for the Phanerozoic
b
Why is/(isn’t) the current rise in global temperature due to anthropogenic increase in atmospheric CO2 alarming to many scientists? select all appropriate anwers
a) there is great concern because the rate at which CO2/temperature has changed in decades is unprecedented at geologic scales
b) there is great concern because we do not understand the consequences of passing tipping points with related systems with have positive feedbacks
c) there is little concern because the Earth was much warmer in the past and we will just return to normal
d) there is little concern because plants and animals are always evolving to live in changing climates
e) there is little concern because new technology will solve the problem
f) there is little concern because there is little evidence (data) to support climate science in general
a, b