Fichas de aprendizaje Motivation, Emotion, stress and health | Quizlet
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Motivation
a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior
instinct
a behavior that an organism inherits

drive-reduction theory
approach to motivation that assumes behavior arises from physiological needs that cause internal drives to push the organism to satisfy the need and reduce tension and arousal

need
Basic requirement for survival

drive
generalized state of readiness precipitating or motivating an activity or course of action. Drive is hypothetical in nature, usually created by deprivation of a needed substance
primary drives
innate drives, such as hunger, thirst, and sexual desire, that arise from basic biological needs

secondary drives
drives that are learned or acquired through experience, such as the drive to achieve monetary wealth

Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state
Glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low, we feel hunger.

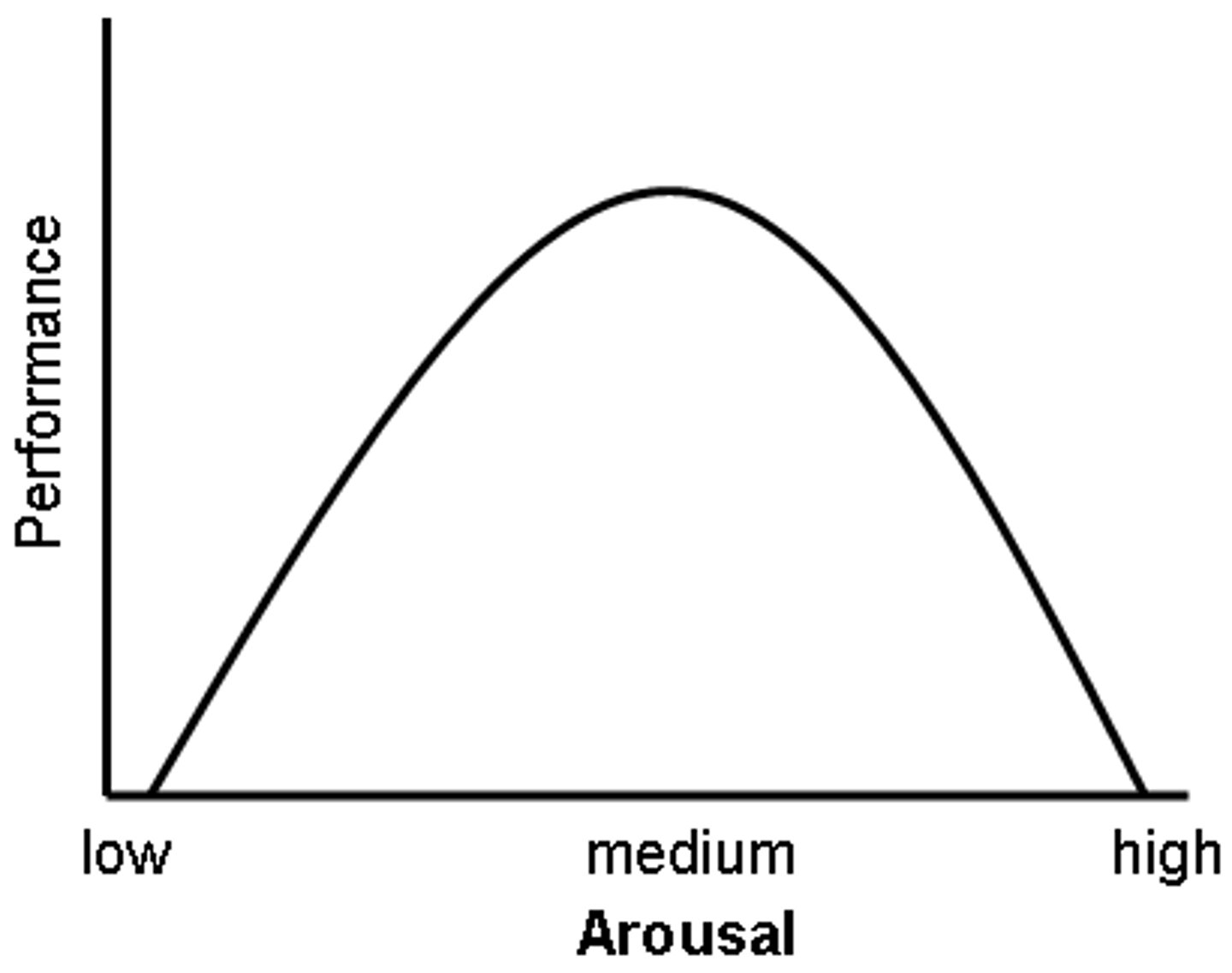
Yerkes-Dodson Law
the psychological principle stating that performance is best under conditions of moderate arousal rather than either low or high arousal
opponent-process theory of emotion
Theory that when a strong emotional response to a particular stimulus disrupts emotional balance, an opposite emotional response is eventually activated to restore emotional equilibrium. That when one emotion is experienced the opposite is repressed. Ex:fear and relief

incentive theory
A theory of motivation stating that behavior is directed toward attaining desirable stimuli and avoiding unwanted stimuli.
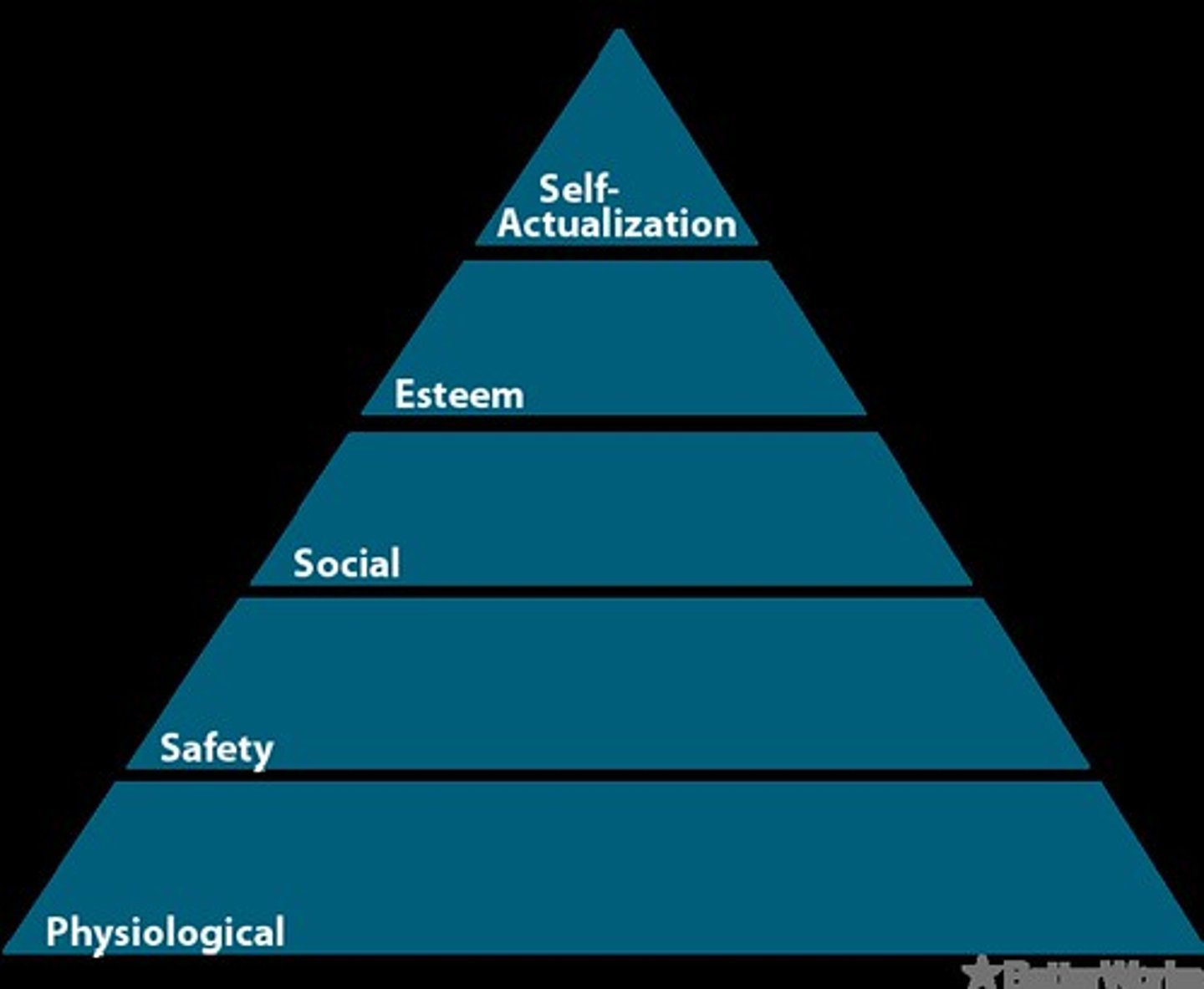
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
(level 1) Physiological Needs, (level 2) Safety and Security, (level 3) Relationships, Love and Affection, (level 4) Self Esteem, (level 5) Self Actualization
lateral hypothalamus
The part of the hypothalamus that produces hunger signals, when stimulated brings hunger, when destroyed stops eating
ventromedial hypothalamus
The part of the hypothalamus that produces feelings of fullness as opposed to hunger, and causes one to stop eating. when stimulated stop eating, when destroyed over eat.
set point theory
belief that hypothalamus plays a role to regulate body weight around a genetically predetermined '____' This ____ is determined by genetics, gender, exercise, metabolism and more.
basal metabolic rate
the body's resting rate of energy expenditure
Bulimia
an eating disorder characterized by episodes of overeating, usually of high-calorie foods, followed by vomiting, laxative use, fasting, or excessive exercise

anorexia nervosa
An eating disorder characterized by an obstinate and willful refusal to eat, a distorted body image, and an intense fear of being fat
obesity
having an excess amount of body fat

achievement motivation
a desire for significant accomplishment: for mastery of things, people, or ideas. Top 10 american core value (specifically individualistically)

extrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishment

intrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior effectively for its own sake
sexual motivation
the natural impulse to gratify sexual needs

James-Lange Theory/Two-Factor arousal theory
the theory that emotion results from physiological states triggered by stimuli in the environment
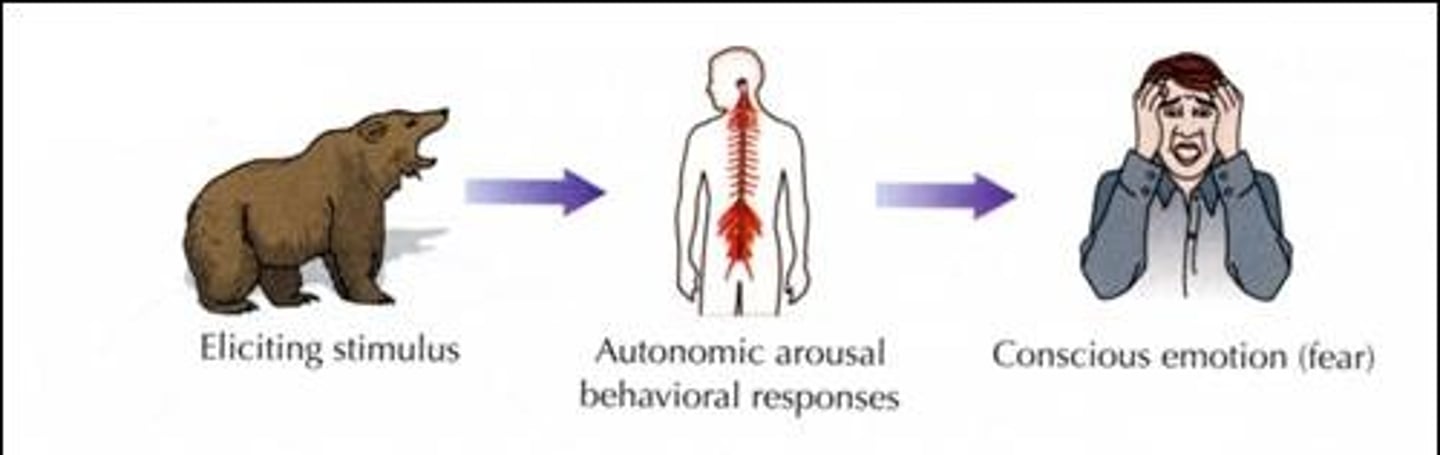
Cannon-Bard Theory
the theory that an emotion-arousing stimulus simultaneously triggers (1) physiological responses and (2) the subjective experience of emotion
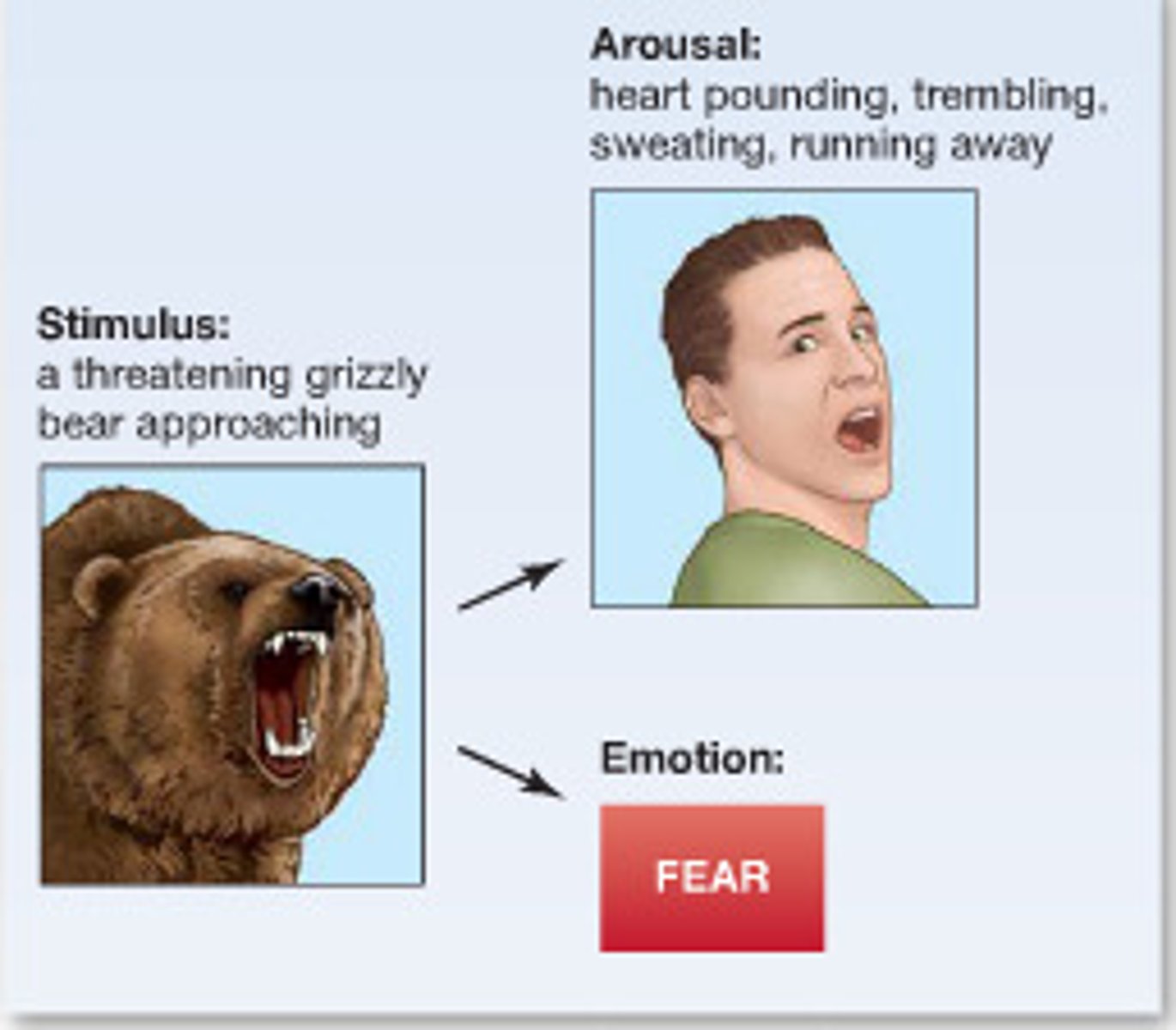
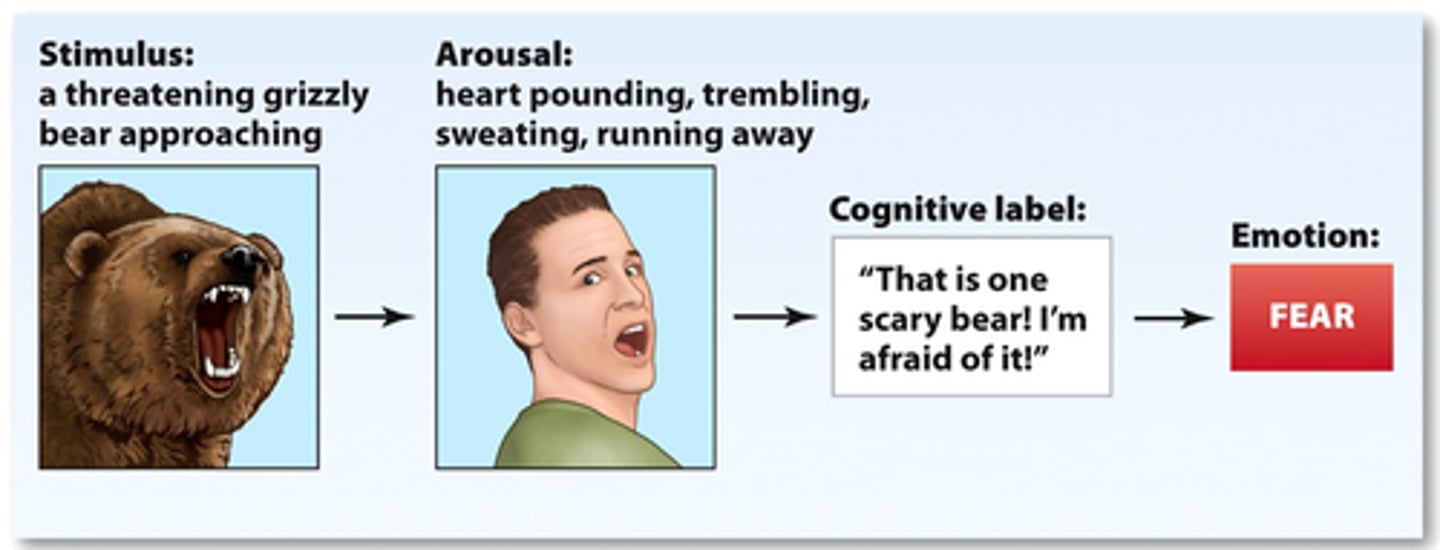
Schachter-Singer Theory
A theory of emotion that states that both physiological arousal and cognitive appraisal must occur before an emotion is consciously experienced.
Testosterone
the most important of the male sex hormones. Both males and females have it, but the additional testosterone in males stimulates the growth of the male sex organs in the fetus and the development of the male sex characteristics during puberty

Estrogen
A sex hormone, secreted in greater amounts by females than by males. In nonhuman female mammals, estrogen levels peak during ovulation, promoting sexual receptivity.
grit
passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals
Stress
the process by which we perceive and respond to certain events, called stressors, that we appraise as threatening or challenging
Increase Appetite hormones
ghrelin and orexin

Ghrelin
secreted by empty stomach; sends "I'm hungry" signals to the brain (small stomach=less secretion)

Orexin
hunger-triggering hormone secreted by hypothalamus

Decrease appetite
insulin, leptin, PYY
Insulin
Hormone produced by the pancreas that helps to decrease blood sugar.
Leptin
A hormone produced by adipose (fat) cells that acts as a satiety factor in regulating appetite.

PYY
digestive tract hormone; sends "I'm not hungry" signals to the brain
Taste Prefrences
sweet vs salty is genetic. Hot climates prefer spice food. All that is biological, but psychologically friends, serving size, and nutrition affect
4 basic psychological motivations
affiliation, achievement, intrinsic/extrinsic, psychology at work
Affiliation Theory
We are motivated by a need to belong

Motivation by Psychology at Work
In career there is room for advancement, a calling brings highest fulfillment, flow (when one is engaged in an activity that fully engages our skills), an organizational Industrial is a person will try to motivate employees to be more productive
Emotion
mix of physiological arousal, expressive behavior, and consciously expressing thoughts and feelings.
Biological influences on emotion
-physiological arousal
-evolutionary adaptiveness
-response pathways in the brain
-spillover effect
social culture influences on emotion
expressiveness
presence of others
cultural expectations
Psychological Influences on emotion
.cognitive labeling
.gender differences - women better at reading & displaying
emotions except for ANGER
10 basic emotions
joy, excitement, surprise, sadness, anger, disgust, contempt, fear, shame, guilt

Fear
-both experiences and genes shape this
-activates amygdala (if amygdala is destroyed you are __full or __less)
-bypasses cortex area (like a reflex)
-Sympathetic nervous system will release norepinephrine, and epinephrine (adrenaline)

Phobias
most are learned except for those that result in biological preparedness
biological preparedness
a propensity for learning particular kinds of associations over others. For instance a fear of snakes and spiders will lead to better survival
Aggression
any physical or verbal behavior intended to hurt or destroy. Can be heritable, and forgiveness stops this emotion. Frustration leads to more of this emotion
Freud instinct theory
Hydraulic model - aggression instincts build with time
- Catharsis - acting on aggressive energy to rid yourself of it
- Sublimation - Taking aggressive energy and channeling it into socially acceptable outlets
Thanatos (Freudian concept):
an instinctual drive toward death, leading to aggressive action. Freud stated, "It is at work in every living being and is striving to bring it to ruin..."
Bandura Social Learning
- Learning through observation & imitation
- we observe people b/c we admire or respect them
- we can learn "vicariously" through other people
Ex. Baby imitating mother's clapping, Teenager dressing the same way as kids at school

happiness
the state of being happy
adaptive-level phenomenon
our tendency to form judgements relative to a neutral level defined by our prior experience. Especially prevelant in happy experiences (eh not as cool as the past)
relative deprivation
the perception that one is worse off relative to those with whom one compares oneself
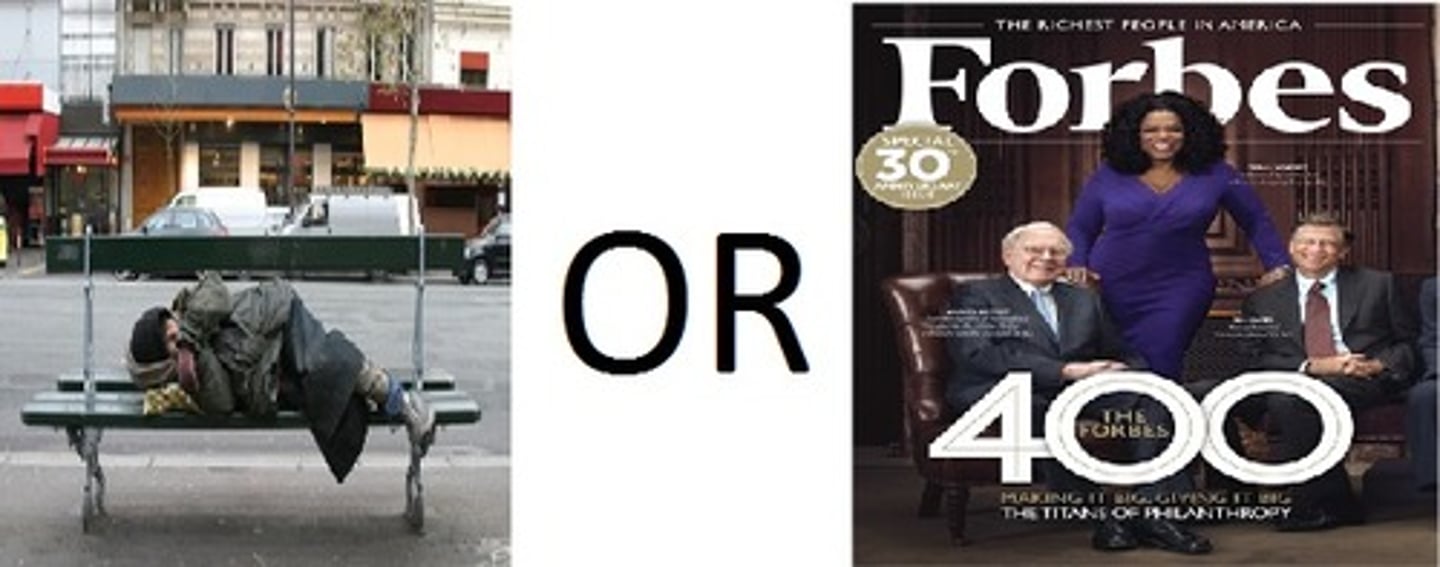
Factors related to happiness
High self-esteem, being optimistic, outgoing, and agreeable, having close friendships or a successful marriage, having work and leisure that engages ones skills, having a meaningful religious faith, and sleeping well and exercising.

factors not related to happiness
age, gender, physical attractiveness, parenthood, education

nonverbal communication
communication using body movements, gestures, and facial expressions rather than speech

Proximity in Nonverbal Communication
-6ft is aquaintance distance
-0 to 3 ft is close relationship
-conveys different messages (can be cultural)
Kinesthetics in nonverbal communication
Big O mouth shape for shock
Body language shows a lot
ParaLanguage in nonverbal communication
tone of voice, texts don't have tone so harder to communicate

6 major stressors
Acute stressors, chronic stressors, frustration, conflict, change, and pressure
acute stressors
threatening events that have a relatively short duration and a clear endpoint. Not as detrimental to body
chronic stressors
threatening events that have a relatively long duration and no readily apparent time limit. More likely to worsen health. Leads to excessive inflamation which leads to depressive symptoms and cardiac disease.
frustration
A negative emotional state that occurs when one is prevented from reaching a goal.

Conflict
a perceived incompatibility of actions, goals, or ideas

approach-approach conflict
Conflict that results from having to choose between two attractive alternatives

avoidance-approach conflict
Conflict arising when the same choice has desirable and undesirable features
avoidance-avoidance conflict
Conflict that results from having to choose between two distasteful alternatives

change
significant alterations in one's living circumstances that require adjustment. SRRS (social readjustment and rating scale) made by Holmes and Rahe

Social Readjustment Rating Scale (SRRS)
assessment that measures the amount of stress in a person's life over a one-year period resulting from major life events
pressure
Expectations or demands that one behave in a certain way.

emotional responses to stress
annoyance, anger, rage
apprehension, anxiety, fear
dejection, sadness, grief

fight or flight response
an emotional and physiological reaction to an emergency that increases readiness for action

General Adaptation Syndrome
Selye's concept of the body's adaptive response to stress in three phases—alarm (recognize threat, fight or flight, start rushing), resistance (fight or flight stabilizes and coping mechanisms begin) , exhaustion (physiological changes impact organs, and resources begin depleting).
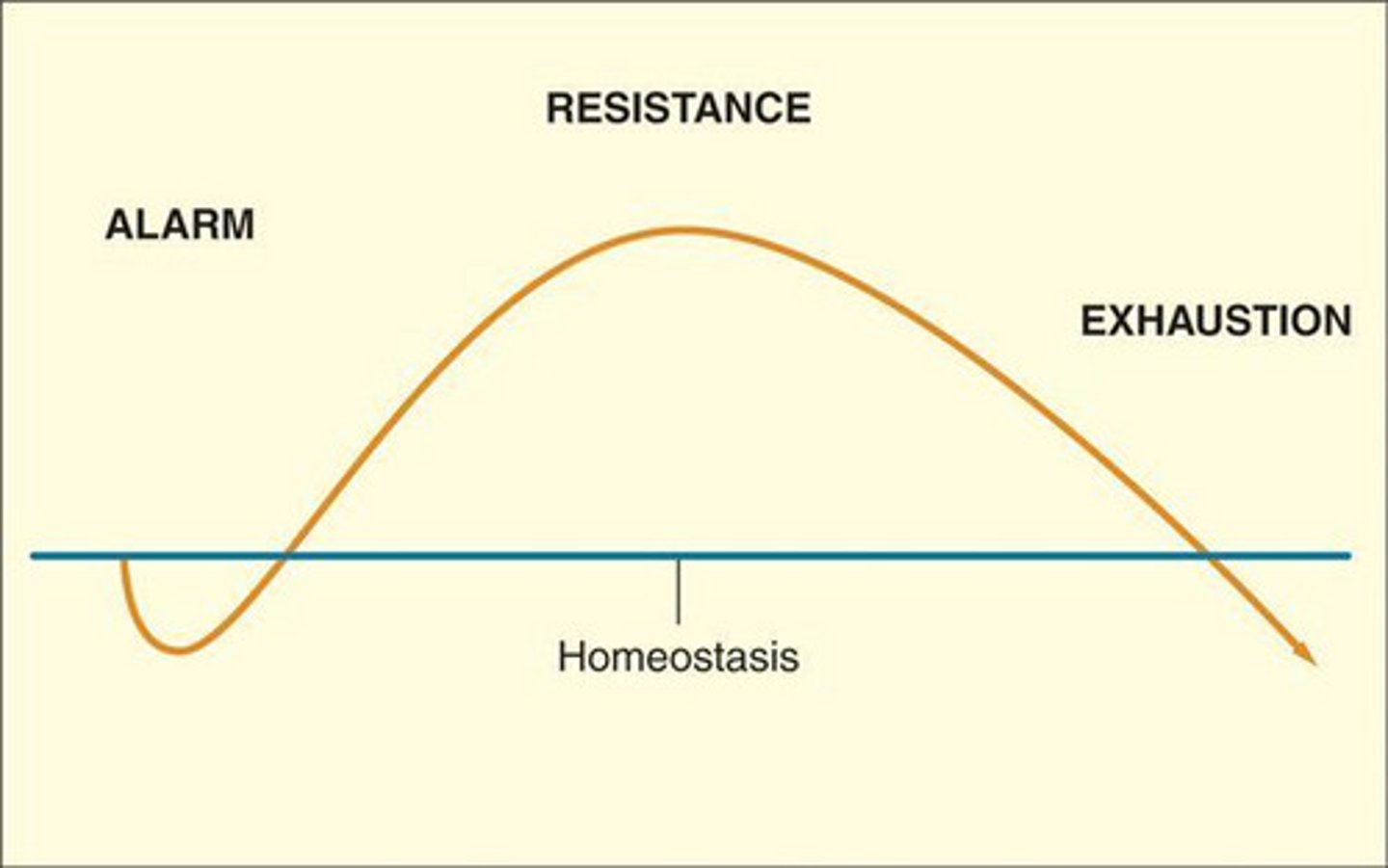
Pathways Hypothalamus can activate in response to stress
endocrine and nervous
hypothalamus nervous system stress
ANS(sypathetic system) --> adrenal medulla--> secretion of catecholomines
hypothalamus endocrine system stress
pituitary gland --> ACTH (adrenocoritropic)--> adrenal cortex
--> secretion of corticosteroids
Cortisol
stress hormone released by the adrenal cortex
Alfred Kinsey: sexual motivation
-attempted to assess sexual practices thru surveys and confidential interviews
-Kinsey Scale: 0-6 = heterosexual to homosexual; X = no interest in sex
-women = more varied/experimental than men
-variations in "normal" sex globally
-premarital sex, masturbation
-Kinsey Institute for Sex Orientation and Reproduction Research
sexual response cycle
the four stages of sexual responding described by Masters and Johnson - excitement, plateau, orgasm, and resolution
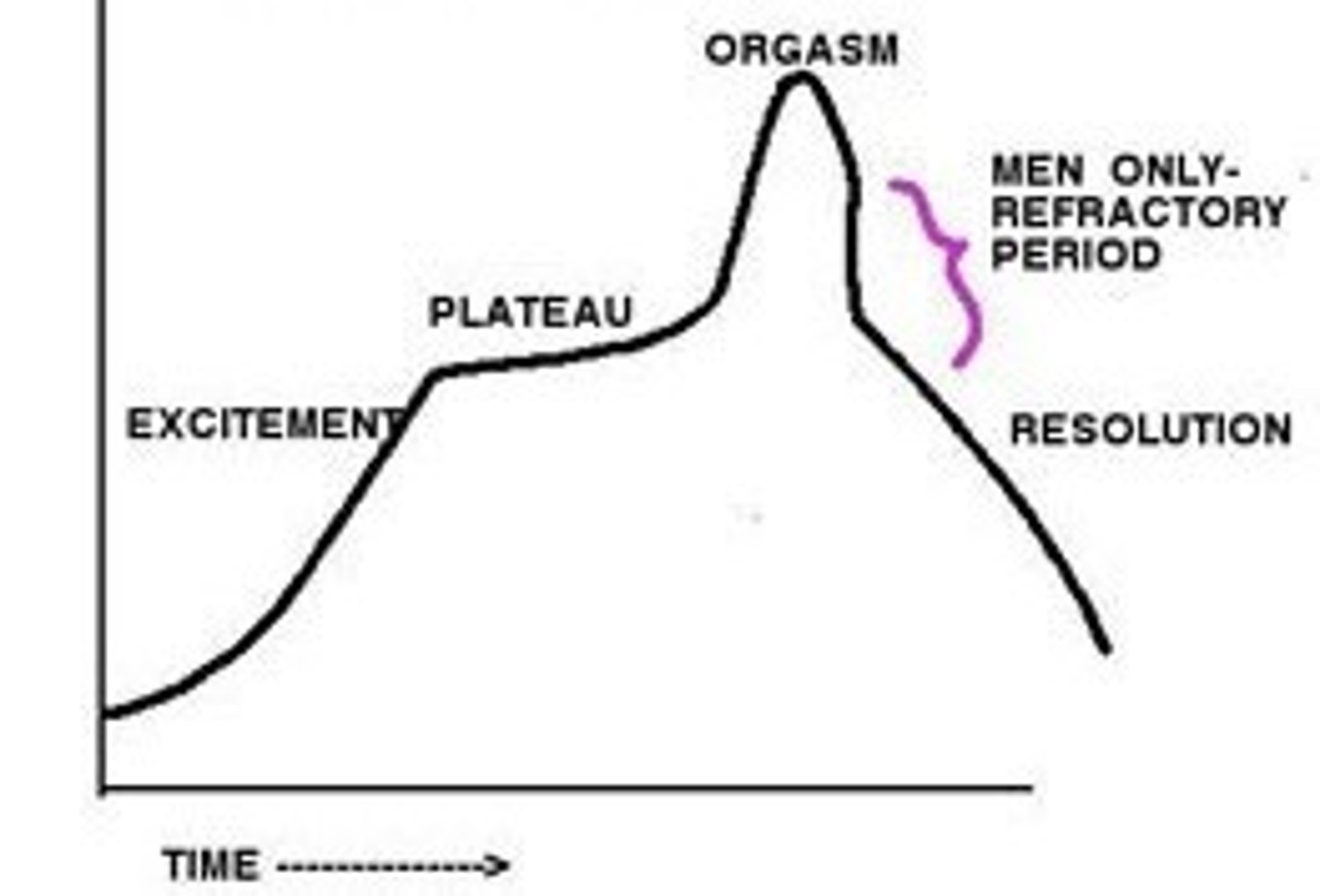
excitement (sexual response cycle)
Results in genital areas becoming engorged w/ blood, vagina expands/secretes lubricant, breasts/nipples enlarge
plateau (sexual response cycle)
excitement peaks such as breathing, pulse, and blood pressure
orgasm (Sexual Response Cycle)
rhythmic genital contractions that may help conception, respiration and heart rate increase further, males ejaculate, often accompanied by a pleasurable euphoria
resolution (Sexual Response Cycle)
respiration and heart rate return to normal resting states,
refractory period (sexual response cycle)
in human sexuality, a resting period that occurs after orgasm, during which a person cannot achieve another orgasm
Paul Ekman
emotion; found that facial expressions are universal

learned helplessness (behavioral response to stress)
the hopelessness and passive resignation an animal or human learns when unable to avoid repeated aversive events. Blaming of oneself.
indulging oneself (behavioral response to stress)
When super stressed we have reduced impulse control
Defensive coping (behavioral response to stress)
Sigma Freud. Ego struggles with stress so we unconsciously turn to ____. EX:Yelling at wife after hard day at work.

Constructive Coping (behavioral response to stress)
relatively healthful efforts that people make to deal with stressful events.

Task Performance (psychological response to stress)
too much stress hinders memory. Yerkes dodson law

Burnout (psychological response to stress)
physically and emotionally exhausted from doing a task

Psychological Disorders (psychological response to stress)
Too much stress can lead to anxiety, PTSD, depression, etc
positive effects of stress
stress promotes resilience,and pushes you
Type A(personality)
competitive, impatient, time emergency, quicker to anger. More prone to having health and cardiovascular issues

Type B (personality)
nonchalant,amicable, agreeable, and patient

extreme emotional responses
may lead to cardiovascular issues.