Software Development
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
What does UX Design stand for?
User Experience Design
UX Design (definition)
Focuses on the feel of the user's interaction with a system. Aims to make the product easy and enjoyable to use
Goals of a UX Designer
Think about the entire journey of a user when interacting with a product/system
What does UI Design stand for?
User Interface Design
UI Design (definition)
The elements of the product e.g. colours, fonts. How things look and how the user interacts with them.
Goals of a UI designer
Ensure the product/system is aesthetically pleasing and easily u
Examples of UI Design
Instagram: size of the upload icon, layout of profile page and feed
Usability (definition)
How easy and efficient it is for a user to achieve their goals using a system. Focuses on how functional and user-friendly the design is
What makes a product have good usability?
Ensures users can complete tasks with minimal frustration
Example of usability
Task: upload photo. Easy to understand buttons, process of adding a caption is quick and clear.
Comparison of UX, UI and usability
UX is how satisfying the journey of using the system is to the user. UI is the look of the system. Usability is the efficiency and easiness of a system
Wireframing (definition)
A visual representation of the structure and functionality of a single web page or a mobile app screen when it is in the design stage.
What is the purpose of wireframing?
Allows stakeholders to “understand” and visualise what is being created by the team. Demonstrates the interface elements that will appear on the page
Draw the graph for degree of change vs time
…
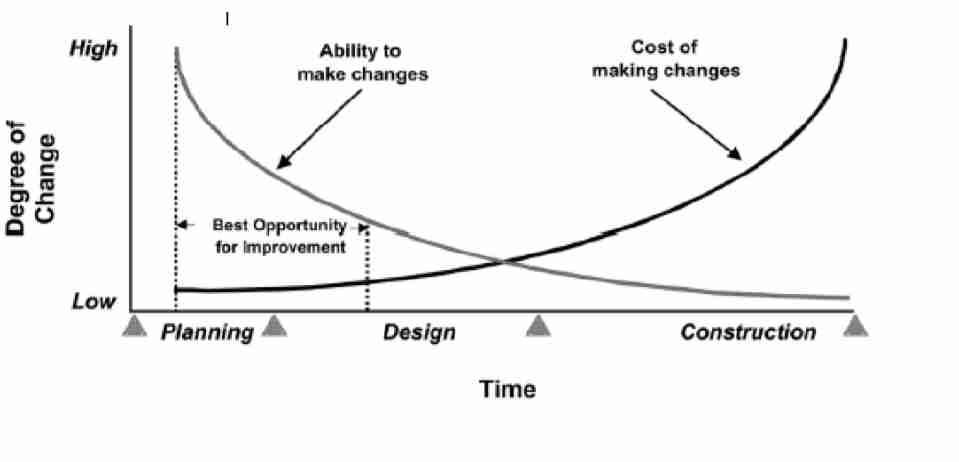
How can wireframes be made?
On paper, HTML, software
Website optimisation (definition)
Ensuring a website works across all platforms e.g. smartphone screen, tablet screen, desktop screen
What are annotations?
Notes on the wireframe. Communicates intent of the wireframw
Draw a simplified wireframe
…
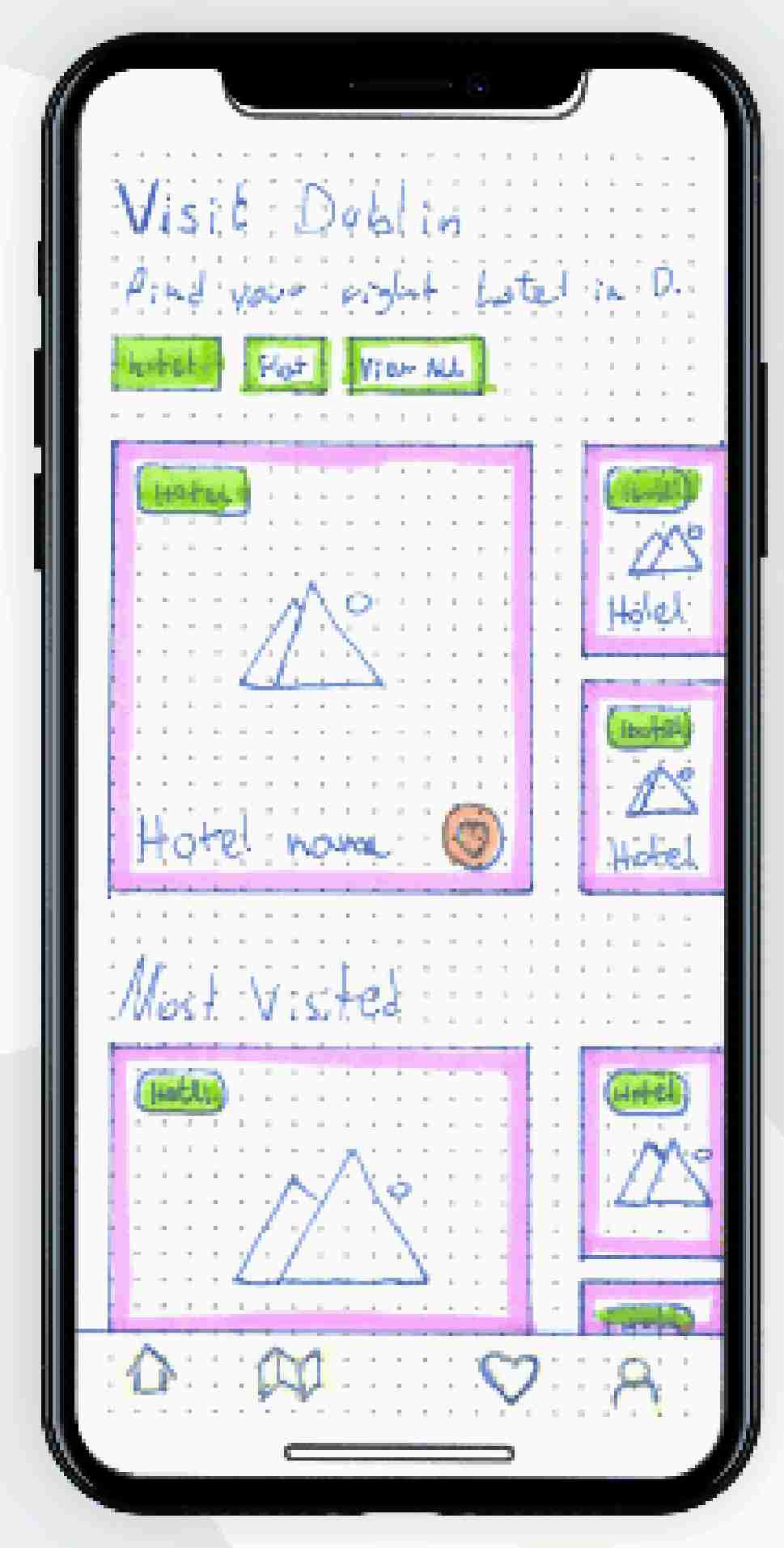
Name the stages in the process of software development
Investigate. Plan. Design. Create. Evaluate. Report
Questions that need to be answered during the investigate stage (4)
Who’re the users? What do certain groups of need? Expectations of users? Contraints?
Examples of contraints
Time, money
What things need to be investigated?
The users, hardware, what coding language
Examples of criteria for hardware that need to be investigated/considered
Cost. Storage capacity. Warranties? Support current and future software?
Who is the client?
The person commissioning the project
Who is the user?
The person using the software
Ways to gather information during investigation (3)
Interviews. Questionnaires. Recording observations while work-shadowing a user
What is a feasibility study?
A document produced at the end of the feasibility stage. Report giving client an opinion as to if a practical and possible solution to the problem exist.
What does the feasibility study include? (4)
Options for the solutions (pros & cons). Timescale for completion. A recommendation as to whether the project is feasible. Specification of requirements
Examples of specification of requirements
User requirements. Client requirements. Hardware and software needs
Examples of client requirements
Increased sales. Greater customer retention. Better products/services
Factors for selecting the programming language (2)
If the system matches a particular language well. If mobile apps are needed or a website.
Why is a software development plan necessary?
Ensures everyone understands the what, when, and whom of the new system. Helps ensure project manager will stay on track
Is a timescale included in the plan for each task?
Yes
What is dependency?
When one task cannot start until another has been completed e.g. can’t test code before the stage of making it is completed
Examples of non-staff resources identified in the plan
Software and hardware
Factors of staffing considered in the plan (4)
How many needed for the project? Skills needed by staff? Who’ll manage the project? How often will progress be reviewed?
Explain top-down design
Starts with the main system at the top and is broken down into simpler units in a hierarchy. Each unit is broken down until it’s manageable
Draw a top down design diagram (sterling to euro conversion
…
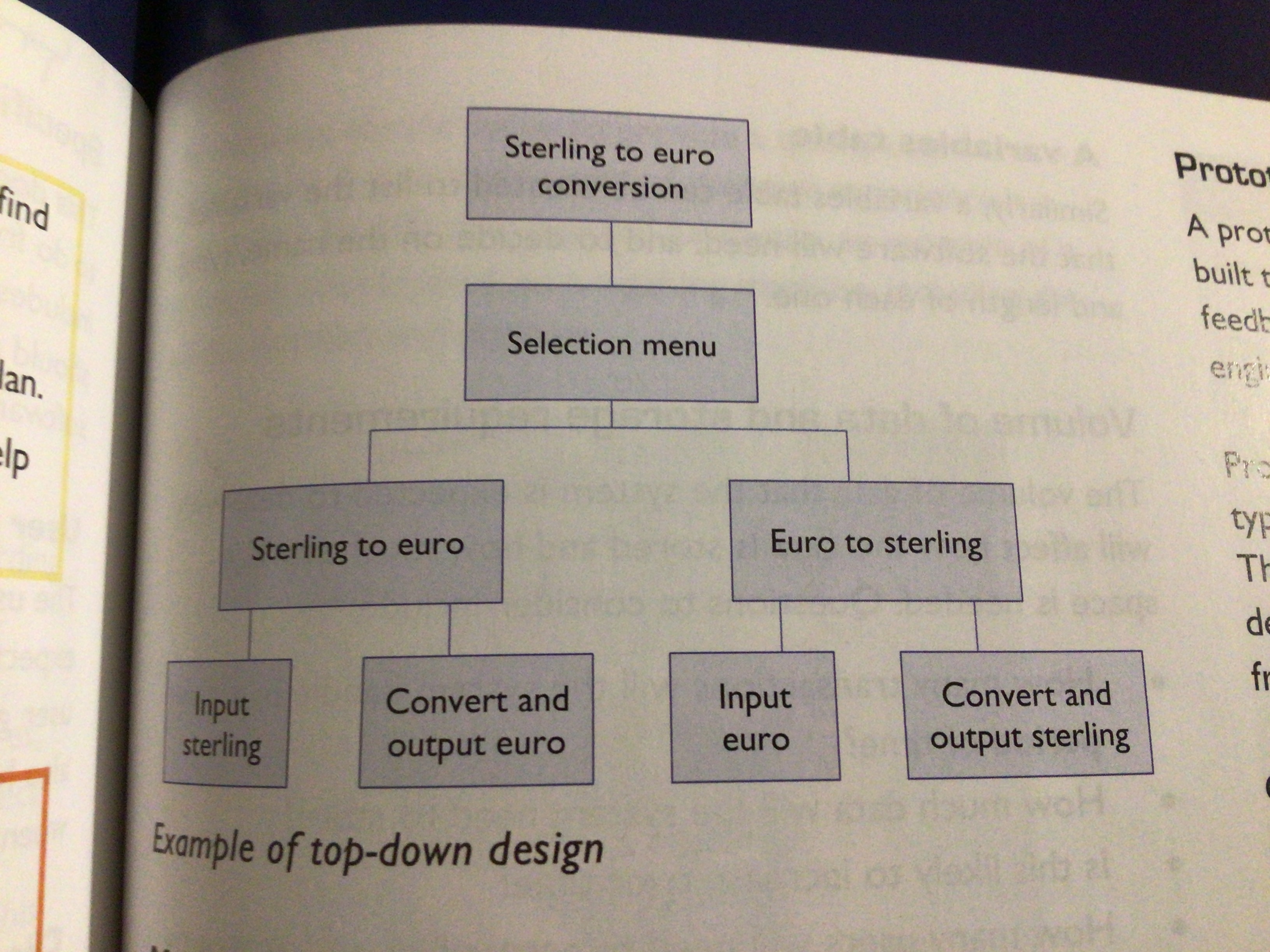
What is modular design?
Broken down into modules. Each module is an independent task that is used by many parts of a system e.g. function
Benefits of modular design (4)
Modules can be reused for other projects. They’re small making bugs easier to deal with. Design of the system is simplified, easier to understand. Process of complex system is easier to manage.
Draw a diagram of modular design
…
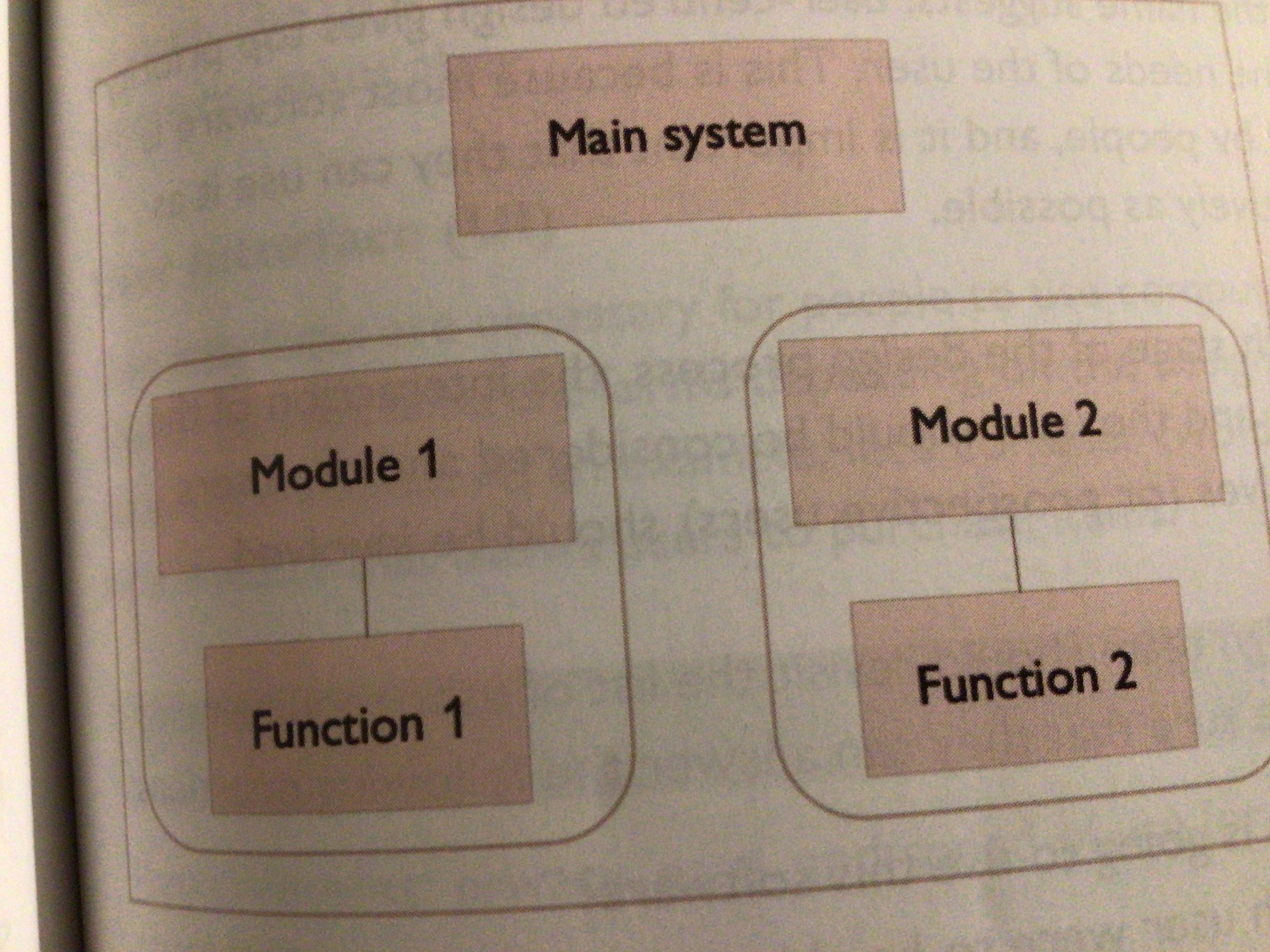
What are prototypes?
An early version or model of a product. Used to test a concept or process to get feedback.
What is the benefit of prototyping?
Main benefit is allowing developers to get feedback from users
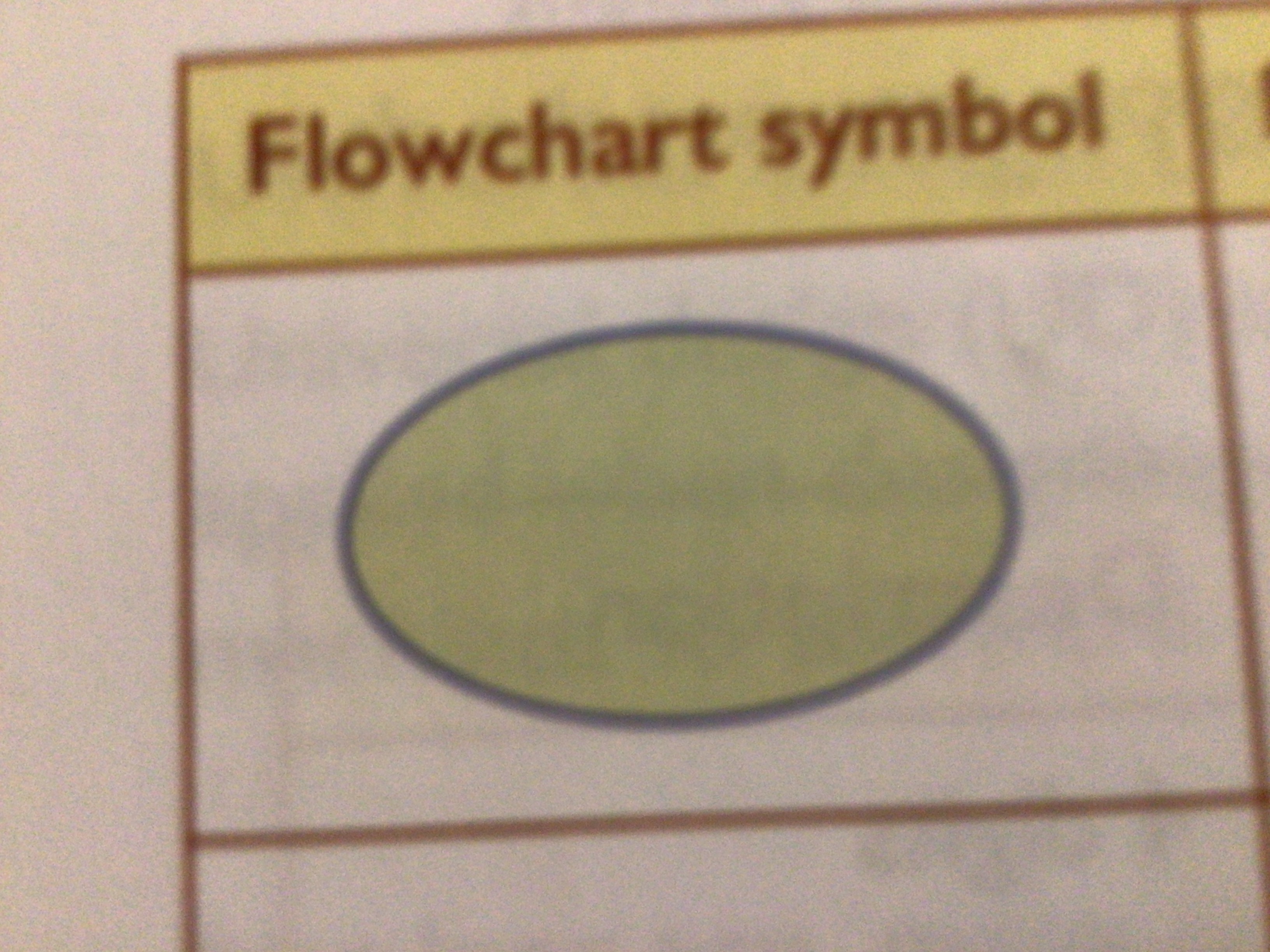
What does this symbol mean?
Start or end
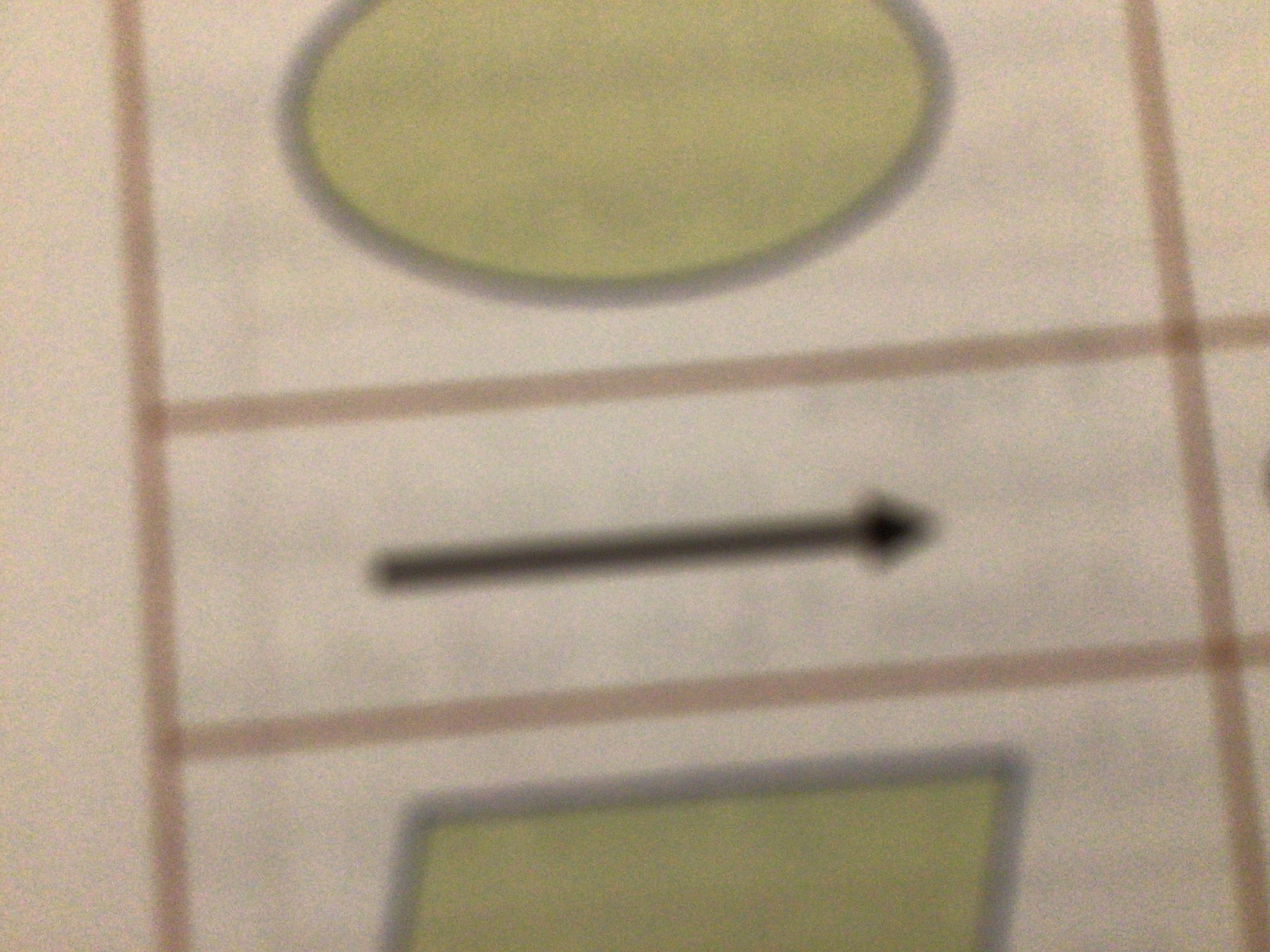
What does this symbol mean?
Connector
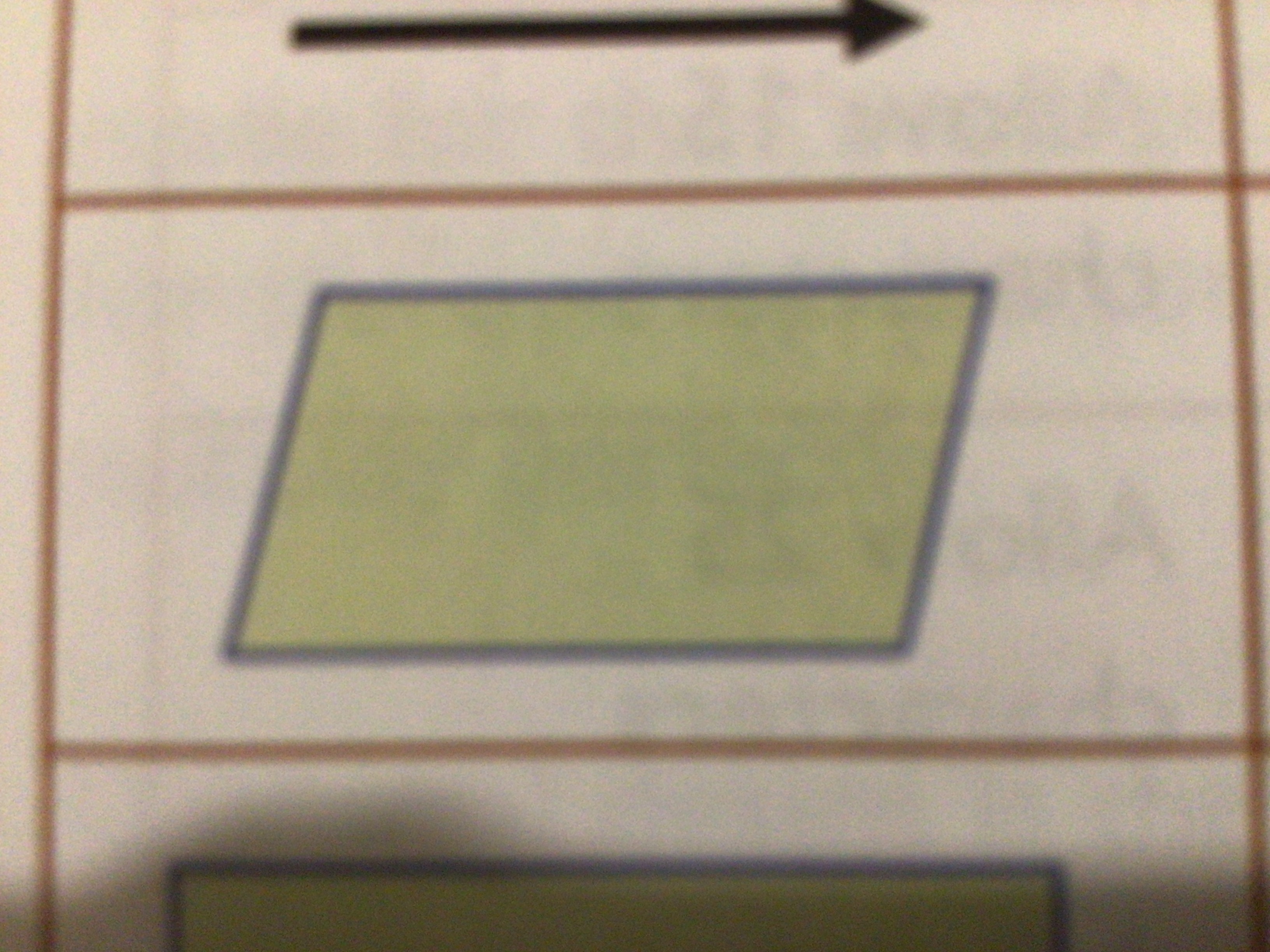
What does this symbol mean?
Input/output
What does this symbol mean?
Process
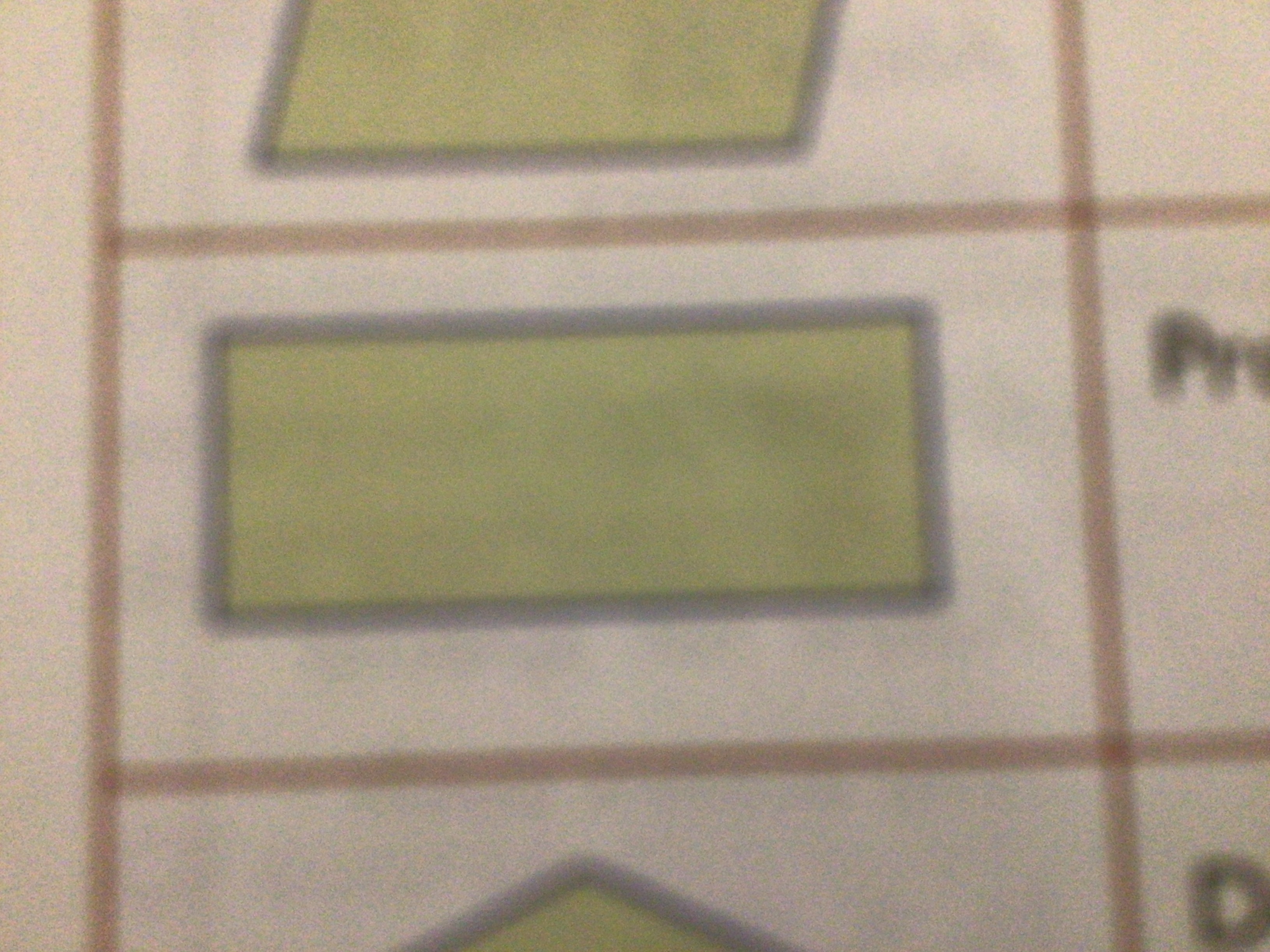

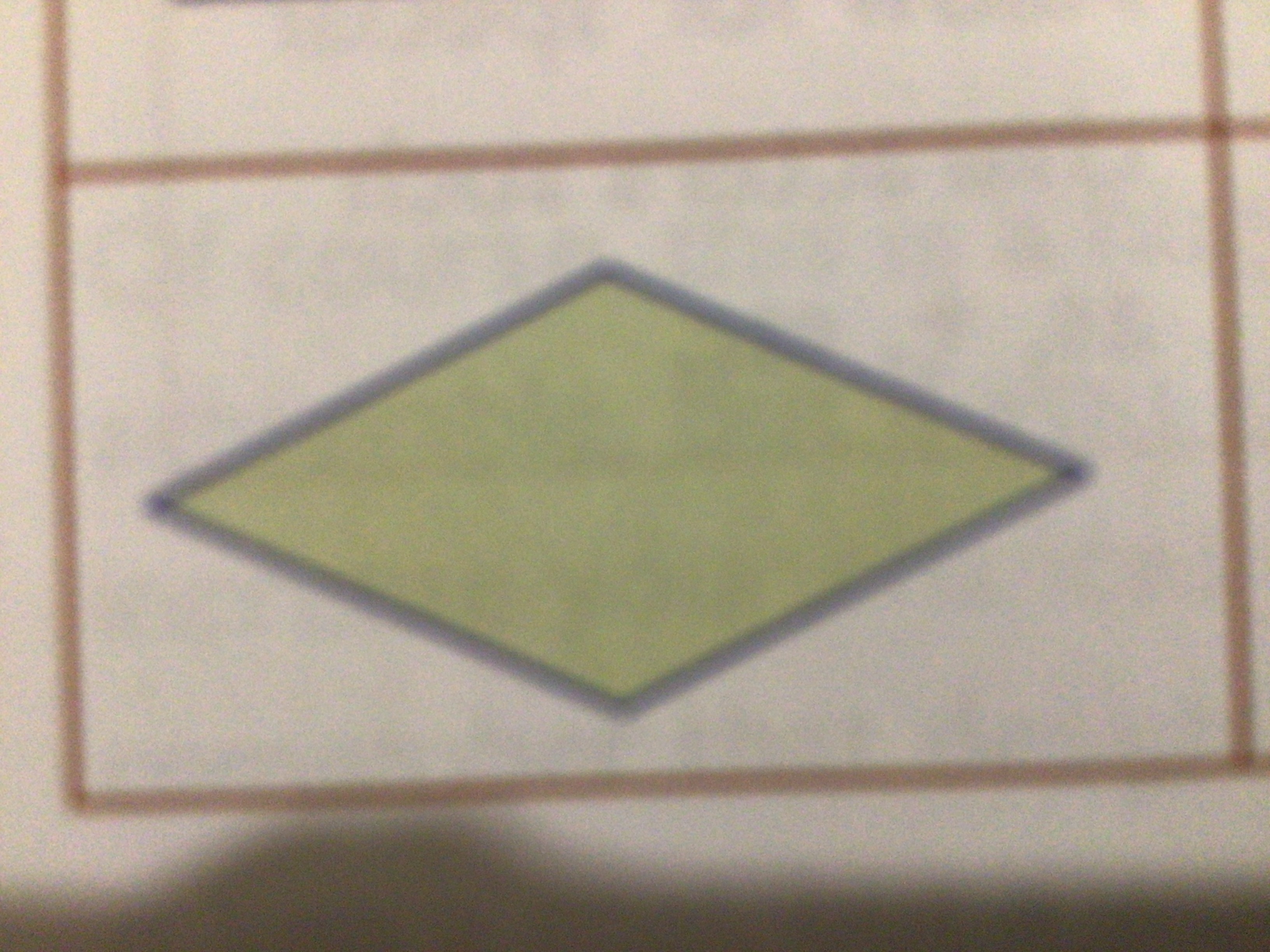
What does this symbol mean?
Decision
What is a data table?
Lists all the data to be used, how to store it, and its type
What is a variables table?
List of variables needed by software
What are the seven principles of universal design?
Equitable use. Flexibility in use. Simple and intuitive use. Perceptible information. Tolerance for error. Low physical effort. Size and space for approach and use
Explain equitable use
The design is useful for everyone regardless of abilities e.g. automatic doors
Explain flexibility in use
Design can adapt to work with a wide range of preferences and abilities e.g. scissors that work for both right handed and left handed people
Explain Simple and intuitive use
Design is easy to understand regardless of a user’s knowledge/experience e.g. one button emergency phone
Explain perceptible information
Allows for the clear communication of information through multiple sentences e.g. traffic lights with colours and sounds
Explain low physical effort
Design can be used comfortably and efficiently with minimum fatigue
Explain Size and space for approach and use
Appropriate size and space is provided for use and manipulation regardless of user’s body size, posture, or mobility
Explain tolerance for error
Allows for mistakes to be undone easily and minimises the risks of mistakes
Example of accessible software
Quorum, a programming language which is used by the visually impaired
What is adaptive and assistive technology
Provides features to existing technologies to help people with disabilities.
Can assistive technology be used by the non-disabled?
Yes
What is localisation
Localisation allows software to meet linguistic and cultural requirements e.g. changing currencies
Example of internationalisation providing localisation
Unicode
What is the create stage?
The software is written.
What kind of testing occurs in the create stage?
Unit testing
What happens in the evaluation stage?
Compares finished project with the requirements. System might’ve met user requirements but not every detail due to constraints. It’s reliability, performance, efficiency will be evaluated
What happens in the reporting stage?
Stakeholders reported to at intervals outlined in the plan. Cost and success of the project should be reported on.
Explain the role of business analyst (5)
Involved in investigation. Identifies users. Establishes business and user requirements. Works with project manager on feasibility study. Works with system analyst to make the specification requirements
Explain the project manager (5)
Produces feasibility study and specification of requirements. Forms project team. Supervises project team. Reports to clients. Handles delegation and requests for change
Explain system analyst (4)
Establishes the hardware and software requirements. Helps business analyst to produce specification of requirements. Documents/investigates technical aspects of problem. May provide input on feasibility study
Explain designer (2)
Designed software to meet specification. Provides design documentation and changes it
Explain developer (4)
Writes programs. Keeps backup copies of programs. Does unit testing. Makes software documentation
Explain tester (3)
Produces test plans and data. Carries out tests. Documents results of tests are reported and documented.
Explain user liaison and training (3)
Ensures communication between users and project team. Ensures user support is in place when system is introduced. Organises training
Explain administrative support (2)
Organise meetings. Organises documentation.
Factors that influence teamwork (3)
Quality of communication. Quality of the working environment. Understanding of the role of the team and individuals in it.
Benefits of team working (3)
Learning new skills from other members. Gaining experience of conflict resolution. Access to support and guidance from team members
Why is testing important? (2)
Eliminates issues before they arise. Spots issues early before there is too much code to sift through.
Name the different types of testing
Unit testing. Black box testing. White box testing. Integration testing. Smoke testing. Regression testing. Non-functional testing
Unit testing (definition)
Testing individual components or functions of a program in isolation
Unit testing (examples)
Testing the add function in calculator to ensure it returns the correct sum
Black box testing (definition)
Testing the software without knowledge of the internal workings. Focuses on inputs and outputs
Black box testing (example)
Testing a login feature by entering valid and invalid usernames to see if the expected outputs are returned
White box testing (definition)
Testing the internal structures or workings of an application. Requires knowledge of the code.
White box testing (example)
Checking all possible paths in a loop to check the outputs
Integration testing (definition)
Testing combined parts of an application to ensure they function together correctly
Integration testing (example)
Testing if a shopping cart works with a payment processing module
Smoke testing (definition)
Basic tests to check if the main functions of a software application work after a new build
Smoke testing (example)
Verifying that an app launches and its features are usable after an update
Regression testing (definition)
Re-running previously completed tests to ensure that existing functionalities work after changes
Regression testing (example)
After adding a new feature to an app, testing existing features to ensure they still work
Non-functional testing (definition)
Testing aspects that are not related to specific functions like performance and usability. It’s how well the requirements are met.
Non-functional testing (example)
Testing how well a website performs under a high load.
Considerations when designing a test plan
Identify resources for testing. Test cases that align with the software’s functionality. Receive feedback from client
What does TDD stand for?
Test Driven Development
What is Test Driven Development?
Involves writing automated test cases before writing actual code. Run repeatedly to ensure new code doesn’t produce bugs. All code tested before implemented in main program
Agile approach (definition)
An iterative and incremental approach to software development. Emphasises collaboration, customer satisfaction, and flexibility by adapting to changing requirements.
Example of agile approach to software development
App developed with limited features → feedback → more features → feedback e.g. Spotify
Waterfall approach (definition)
Linear approach to software development. Sequential flow of steps where each pjase must be completed before the next phase can begin. Includes requirements maintenance, design, testing e.g. Microsoft OS
Examples of Stakeholders (3)
Business making project, owner, end user/customer