Enzyme Function and Carbohydrate Chemistry
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Enzyme
Biological catalyst increasing reaction rates without change.
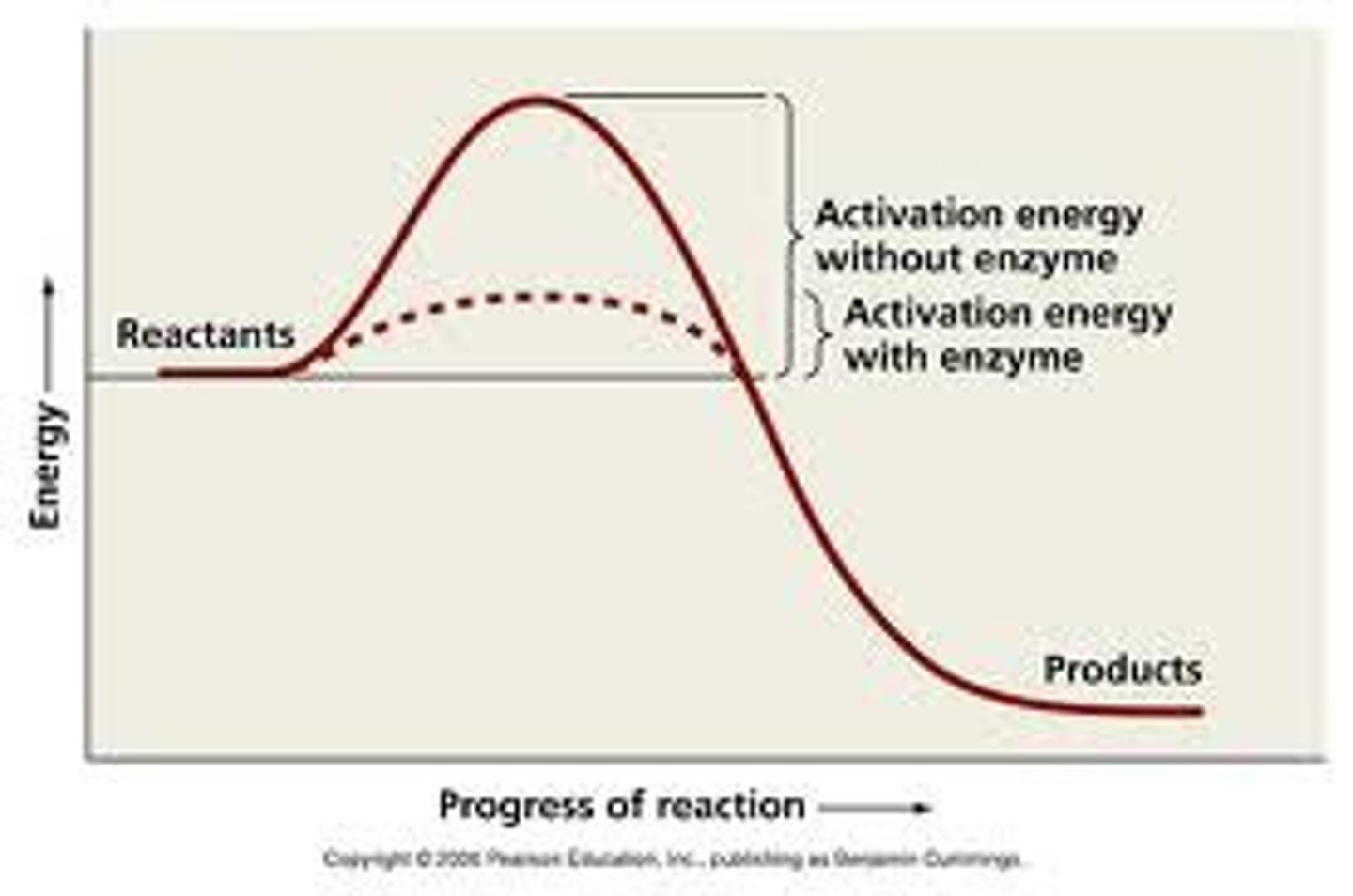
Activation Energy
Energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
Carbonic Anhydrase
an enzyme that converts CO2 and H2O into carbonic acid and then turns into bicarbonate +hydrogen ions
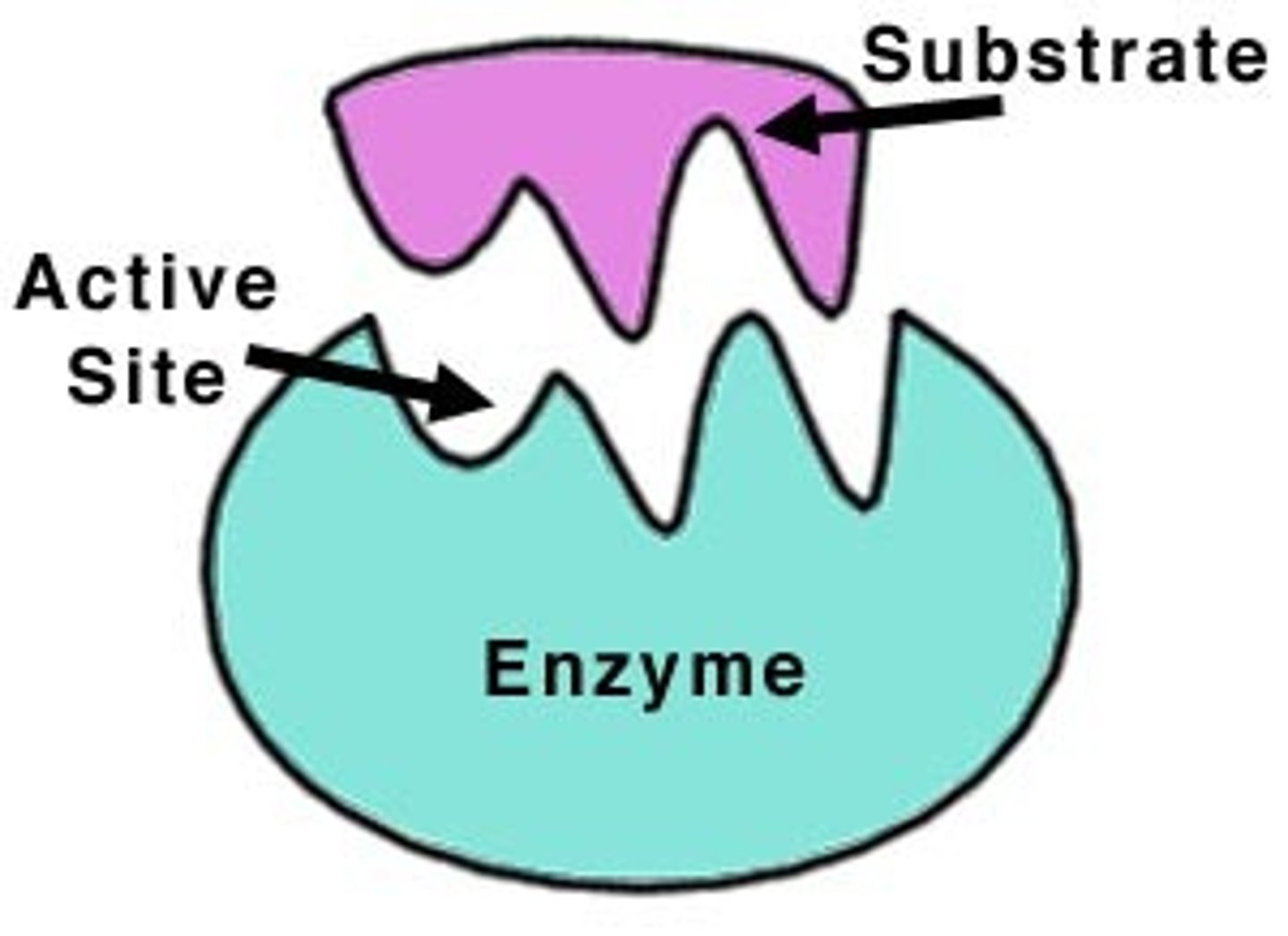
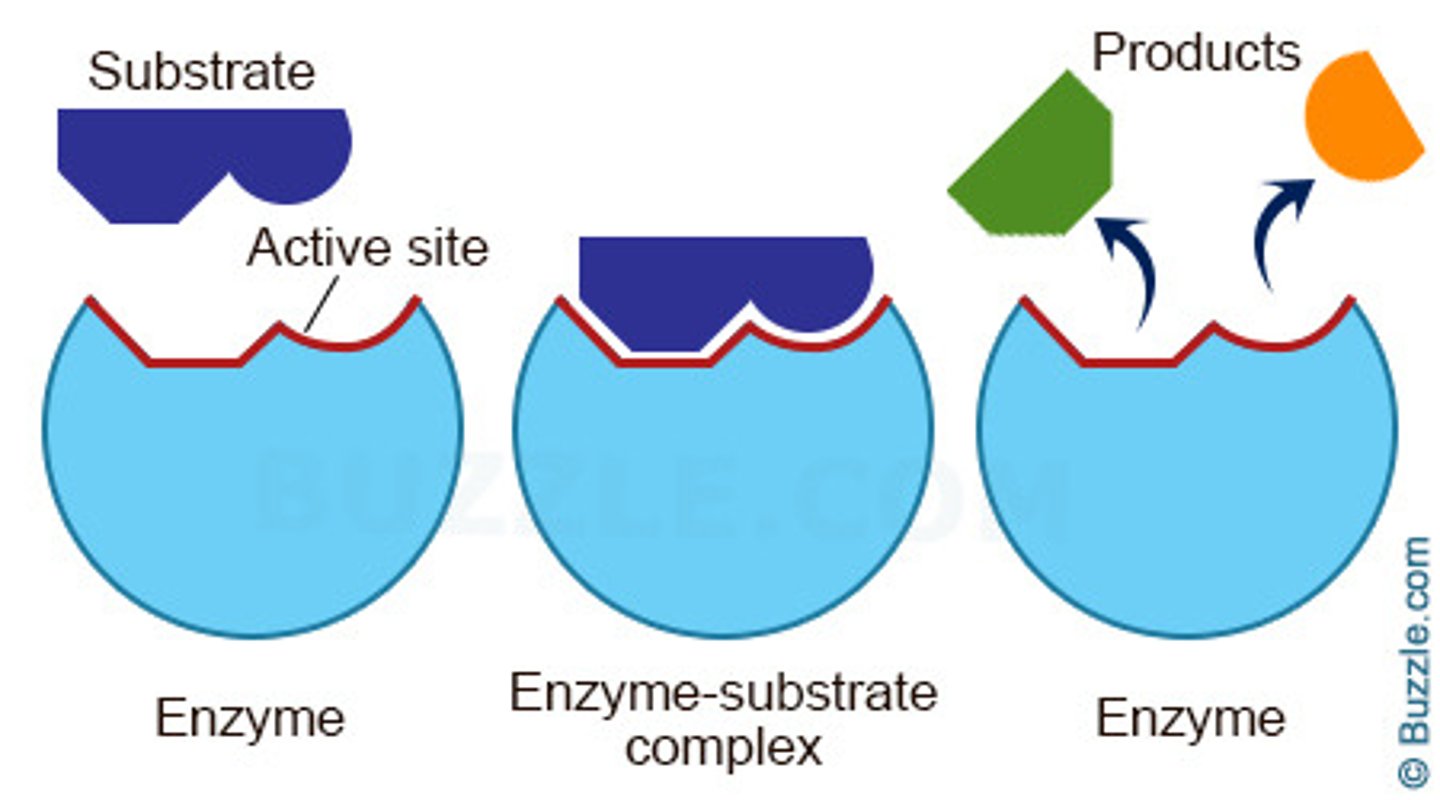
Substrate
Molecule that binds to an enzyme's active site.
Active Site
Region on enzyme where substrates bind for reaction.
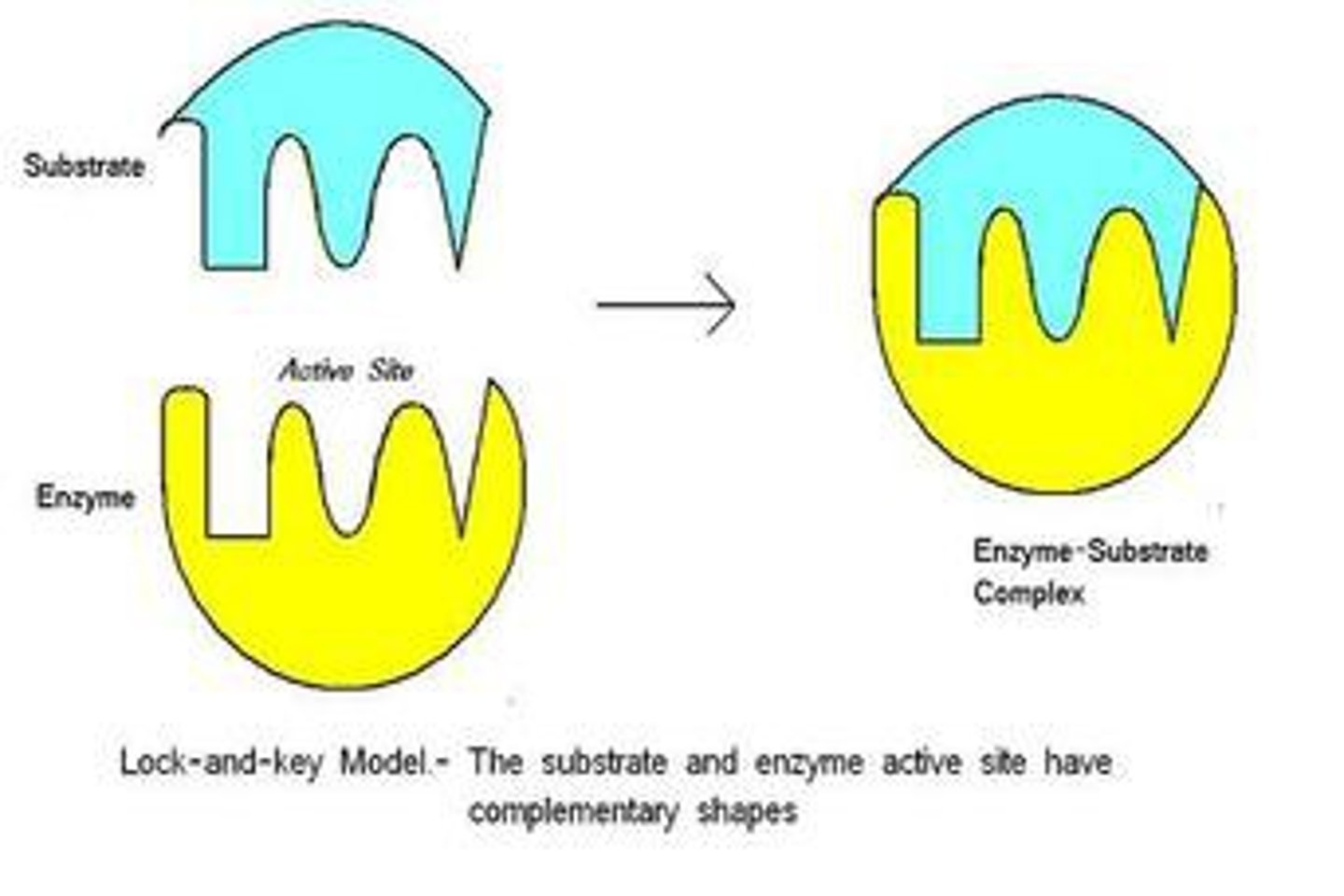
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
Combination of enzyme and substrate during catalysis.
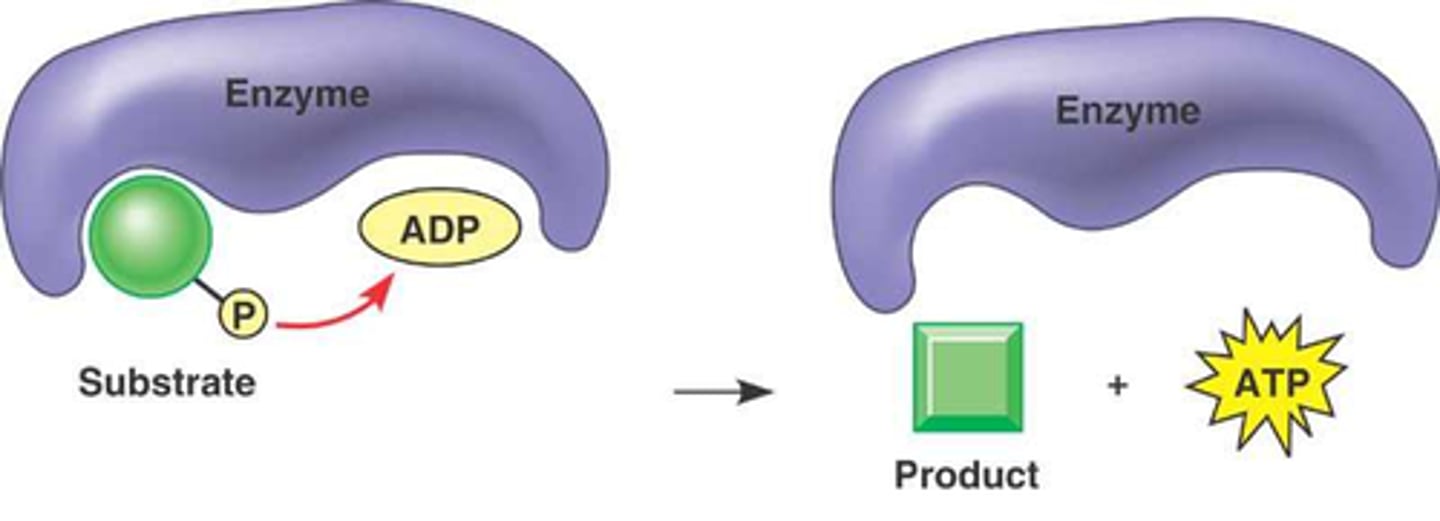
Enzyme-Product Complex
Intermediate formed after substrate conversion in enzyme.
Lactase
Enzyme that catalyzes lactose hydrolysis into monosaccharides.
Quaternary Structure
Protein structure with multiple subunits, like lactase.
Absolute Specificity
Enzymes catalyzing only one specific substrate reaction.
Lock-and-Key Model
Rigid substrate fits rigid enzyme like a key.
Induced-Fit Model
Flexible enzyme adapts to substrate shape for catalysis.
Phosphorylation
Covalent modification activating or deactivating an enzyme.
Kinase
Enzyme that activates others by adding phosphate groups.
Phosphatase
Enzyme that removes phosphate groups to activate enzymes.
Allosteric Enzymes
Enzymes regulated by binding at sites other than active site.
Positive Regulator
Molecule enhancing substrate binding to the active site.
Negative Regulator
Molecule preventing substrate binding, decreasing reaction rate.
Feedback Control
Regulatory mechanism using end product to control enzyme activity.
Regulatory Enzymes
Enzymes controlling reaction rates based on substrate levels.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak interactions stabilizing enzyme-substrate complexes.
Salt Bridges
Ionic interactions contributing to enzyme structure stability.
Hydrophobic Interactions
Nonpolar interactions aiding enzyme-substrate binding.
Feedback control
End product binds to allosteric enzyme, regulating synthesis.
Allosteric enzyme
First enzyme in a reaction sequence, regulated by end product.
Noncompetitive inhibitor
Does not resemble substrate; binds elsewhere on enzyme.
Inhibitors
Molecules causing loss of catalytic activity in enzymes.
Reversible inhibition
Loss of enzyme activity that can be restored.
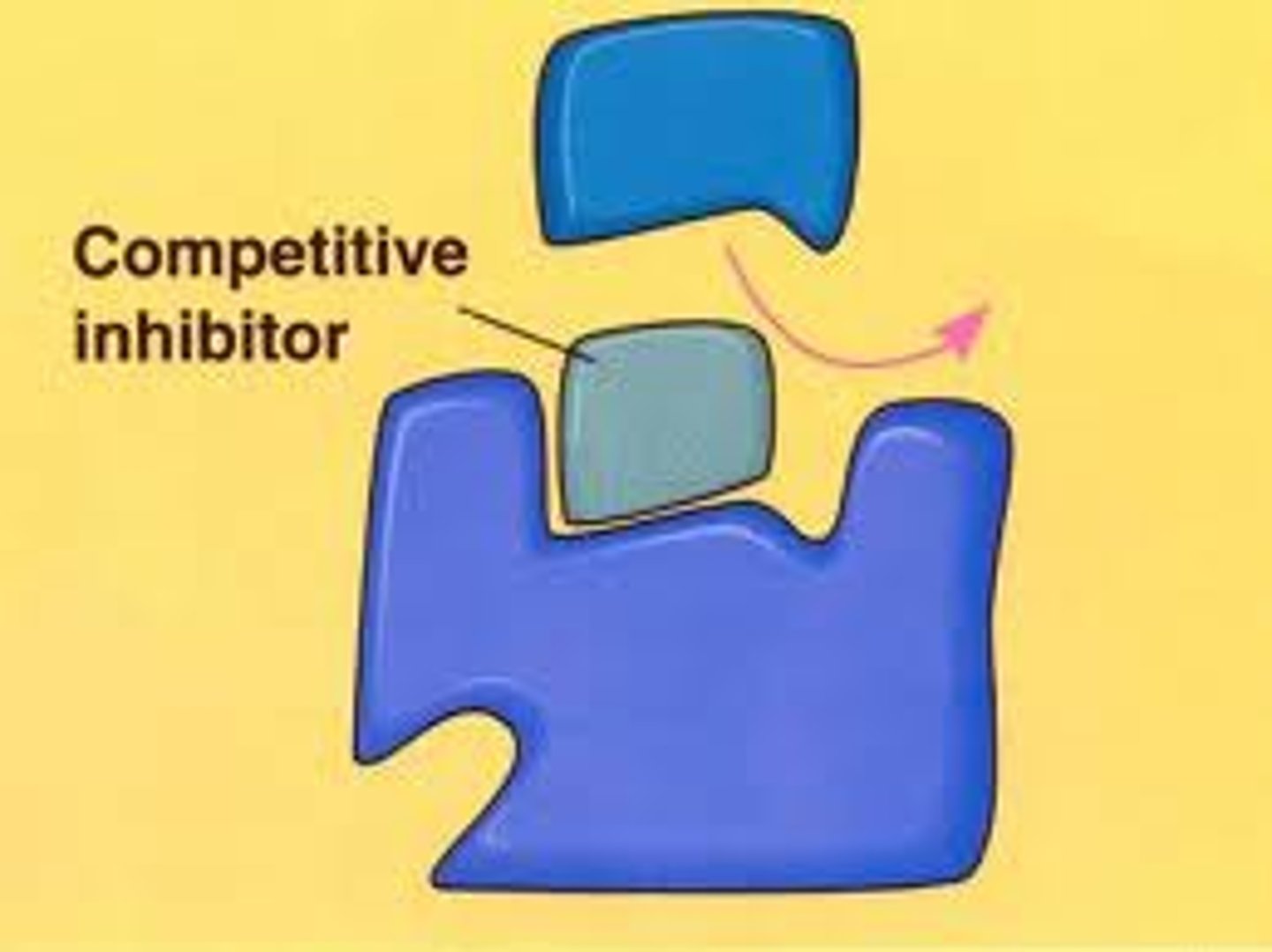
Competitive inhibitor
Competes with substrate for the active site.

Antimetabolites
Competitive inhibitors used to treat bacterial infections.
Sulfanilamide
Competes with PABA, inhibiting(preventing) bacterial growth.
Irreversible inhibition
Enzyme activity destroyed by covalent bond with inhibitor.
Covalent modification
Enzyme activity modified by forming or breaking covalent bonds.
Zymogens
Inactive enzyme precursors activated by covalent modification.
Proteases
Digestive enzymes that hydrolyze proteins from inactive forms.
Trypsinogen
Zymogen activated to trypsin for protein digestion.
Proinsulin
Inactive form of insulin, activated by peptide removal.
Cofactor
Non-protein molecule required for enzyme activity.
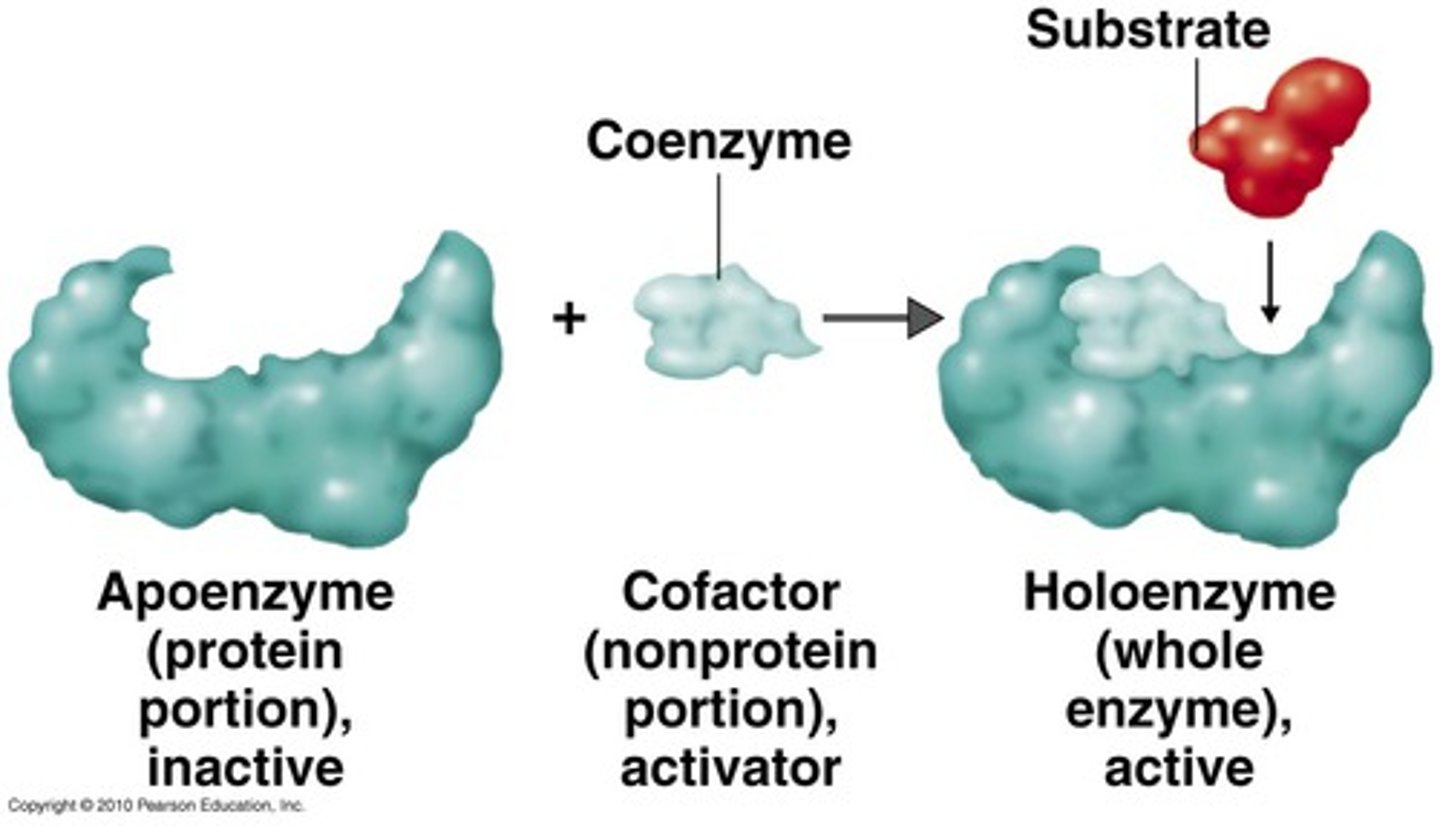
Coenzyme
Small organic molecule, often a vitamin, aiding enzymes.
Carboxypeptidase
Enzyme requiring Zn2+ cofactor for peptide bond hydrolysis.
Vitamins
Organic molecules essential for health, required in trace amounts.

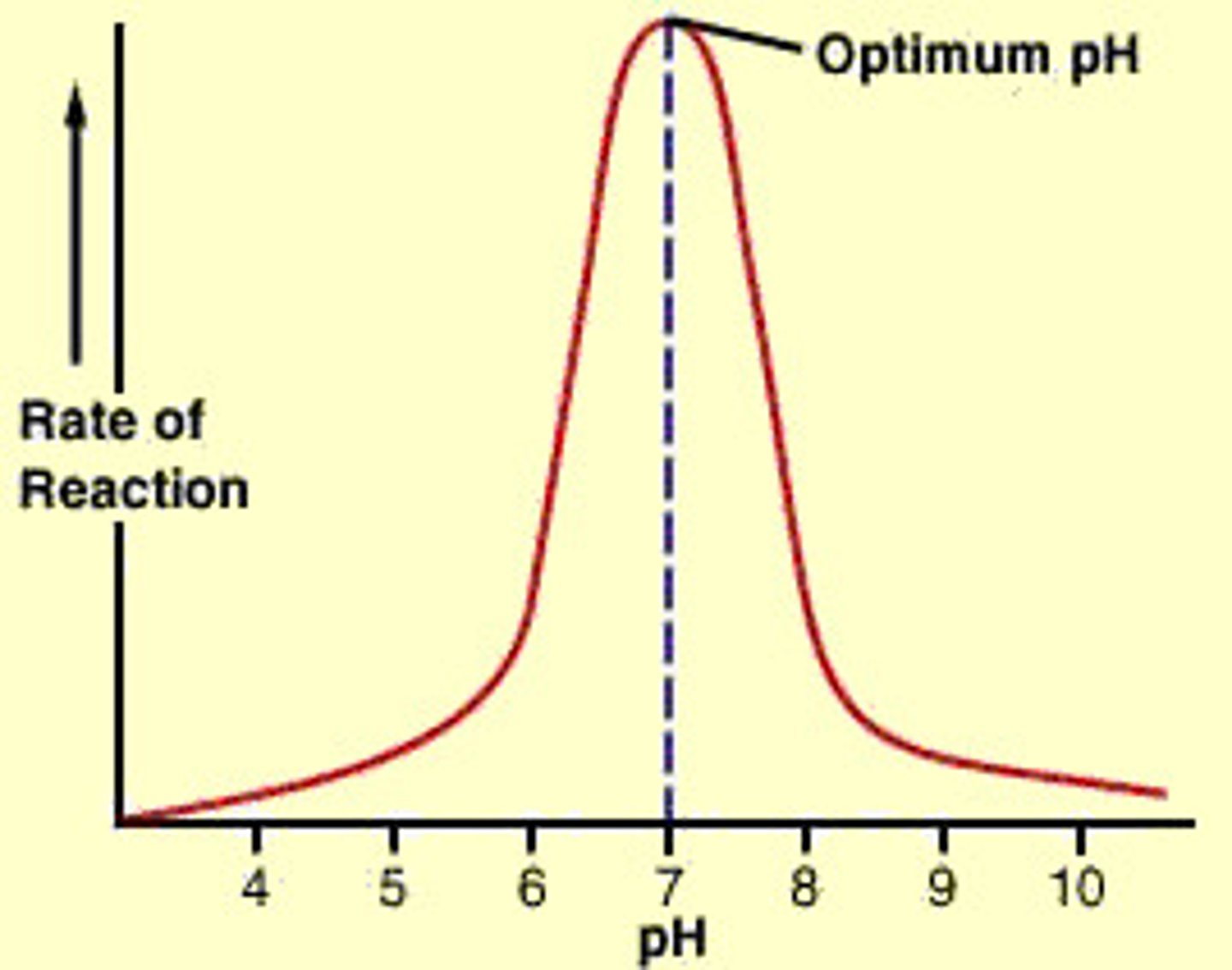
Optimum pH
pH level where enzymes function best, around 7.4.
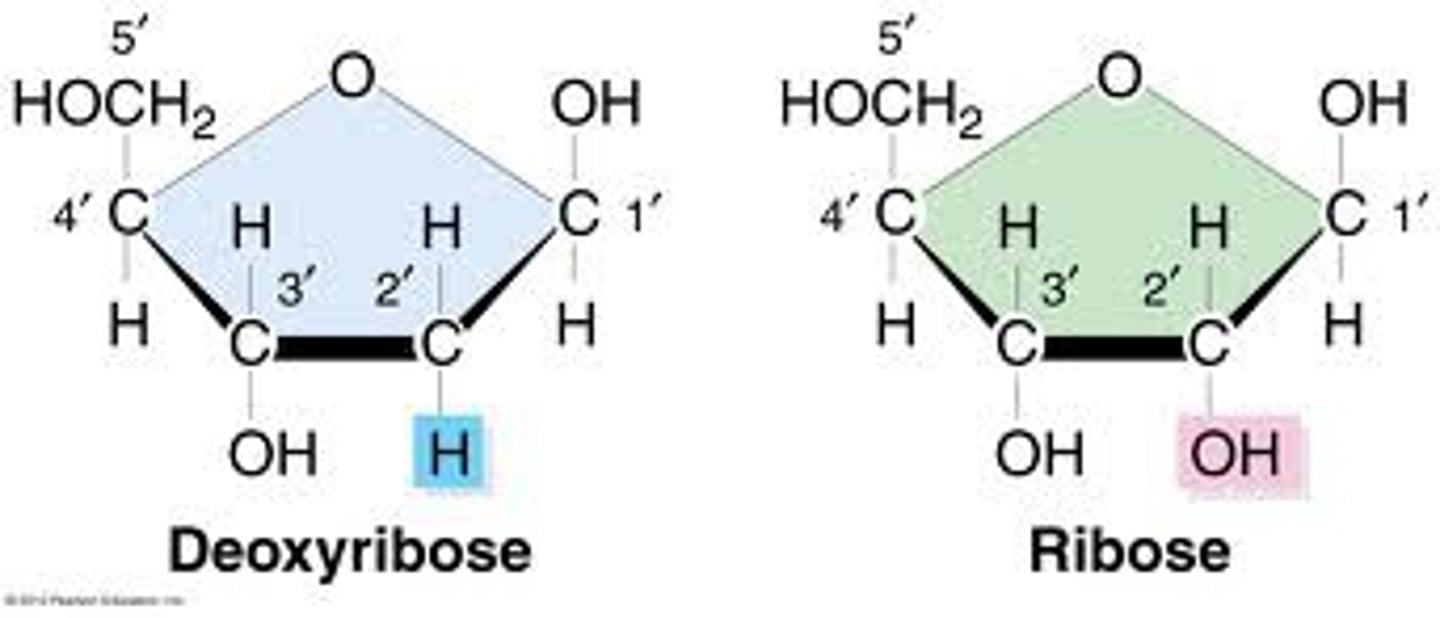
Carbohydrates
Major energy source, made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen.

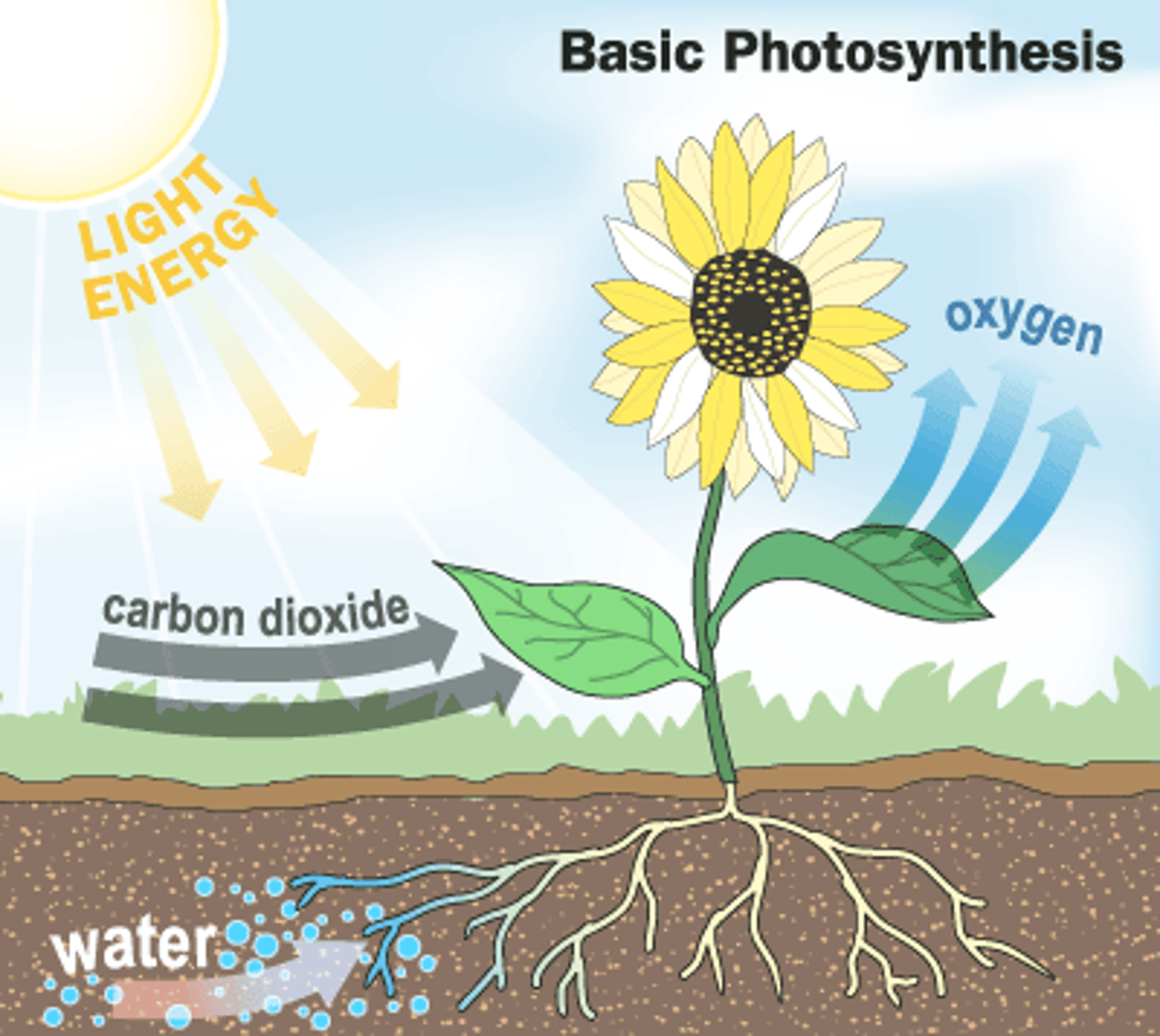
Photosynthesis
Process plants use to produce glucose from CO2 and H2O.
Saccharides
Another term for sugars, referring to carbohydrate structure.
C-terminal aromatic amino acid
Target of carboxypeptidase during peptide bond hydrolysis.
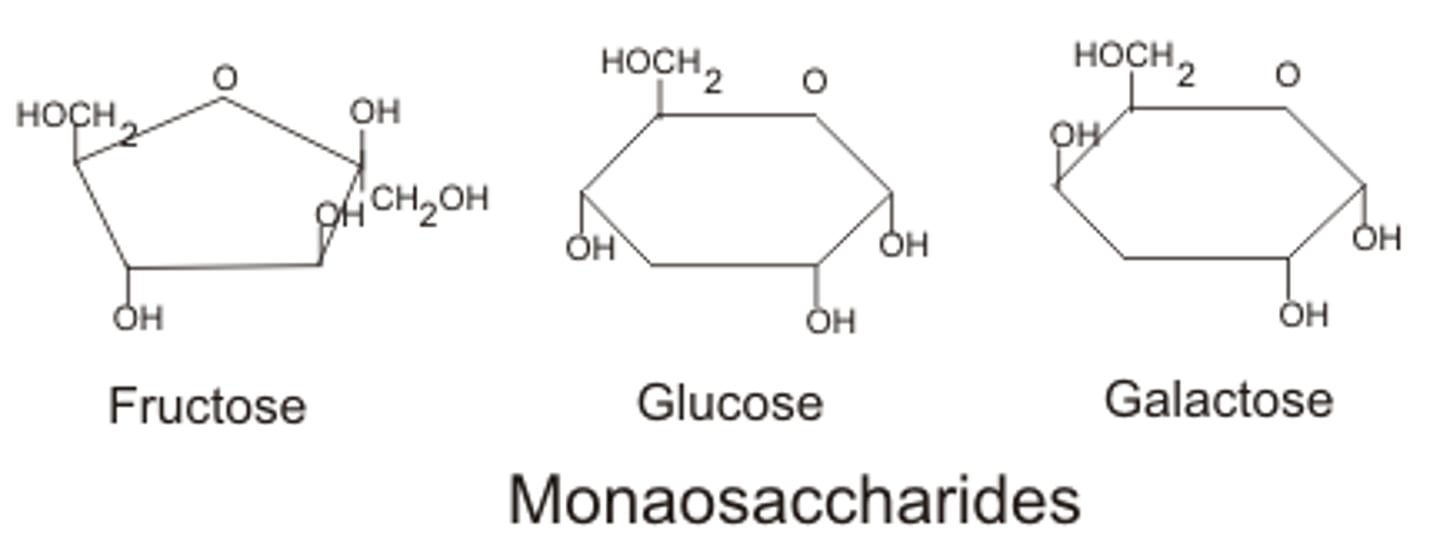
Monosaccharides
Simple carbohydrates, single sugar units.
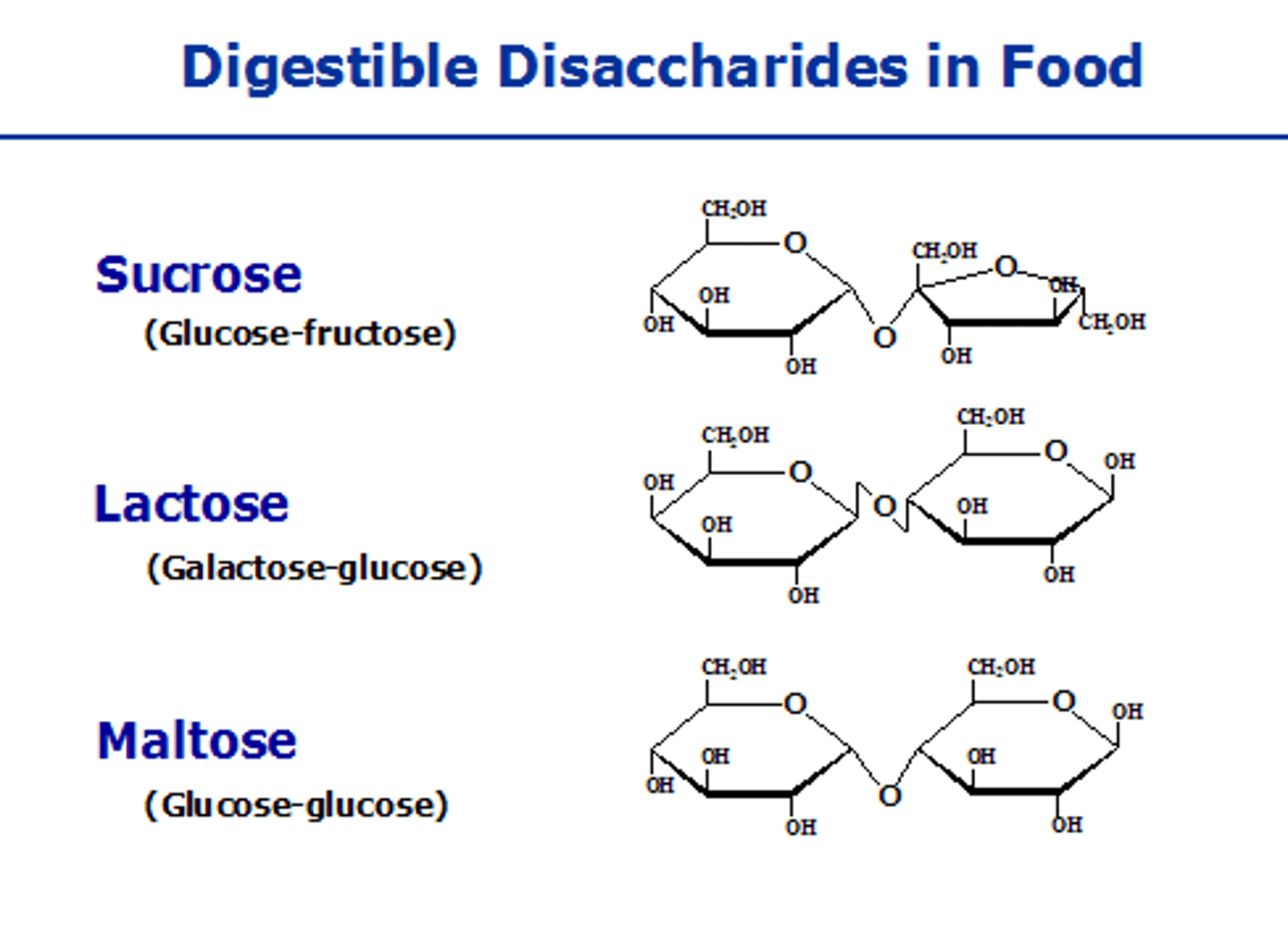
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharides linked together.
Polysaccharides
Many monosaccharides linked together.
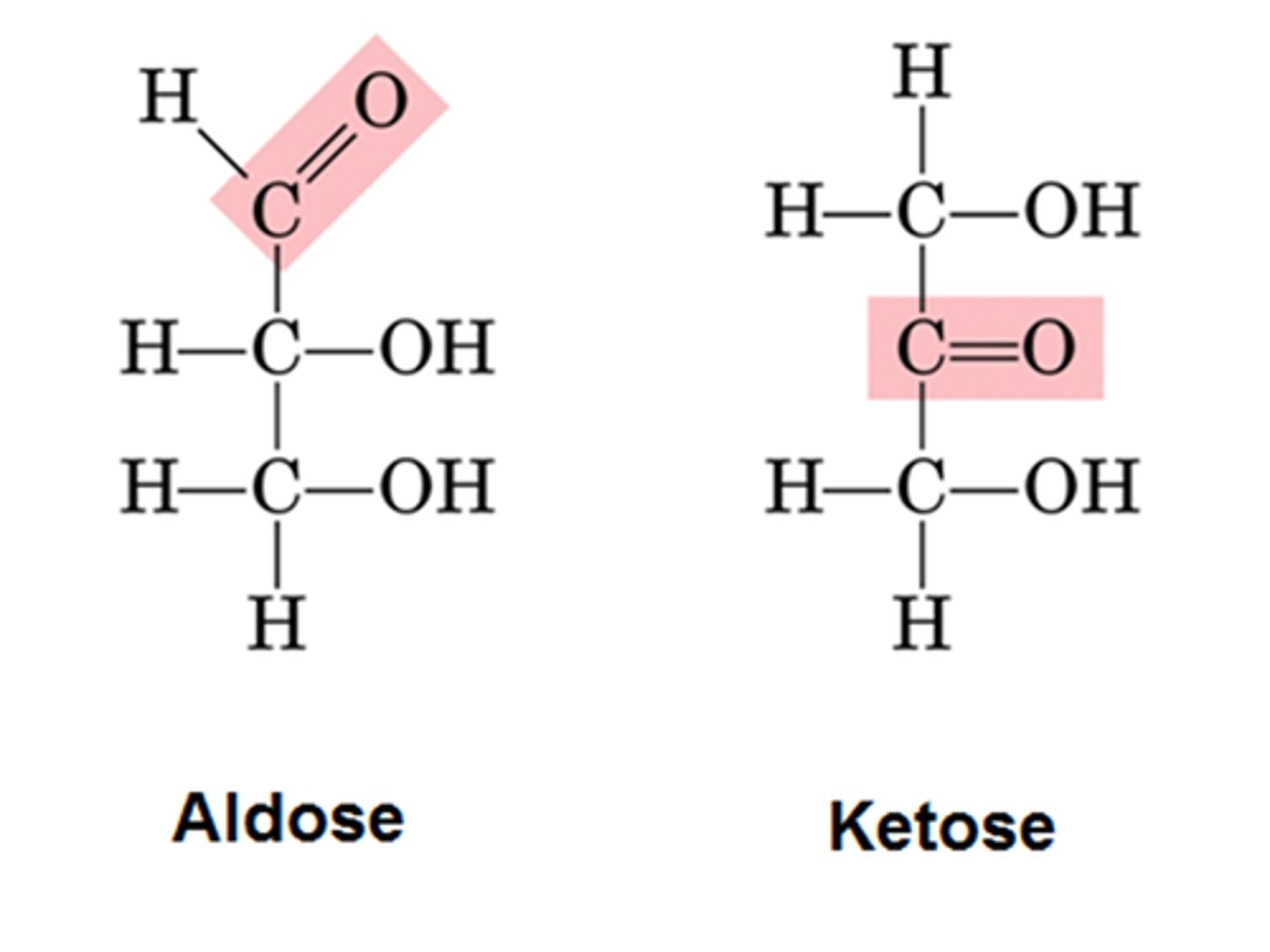
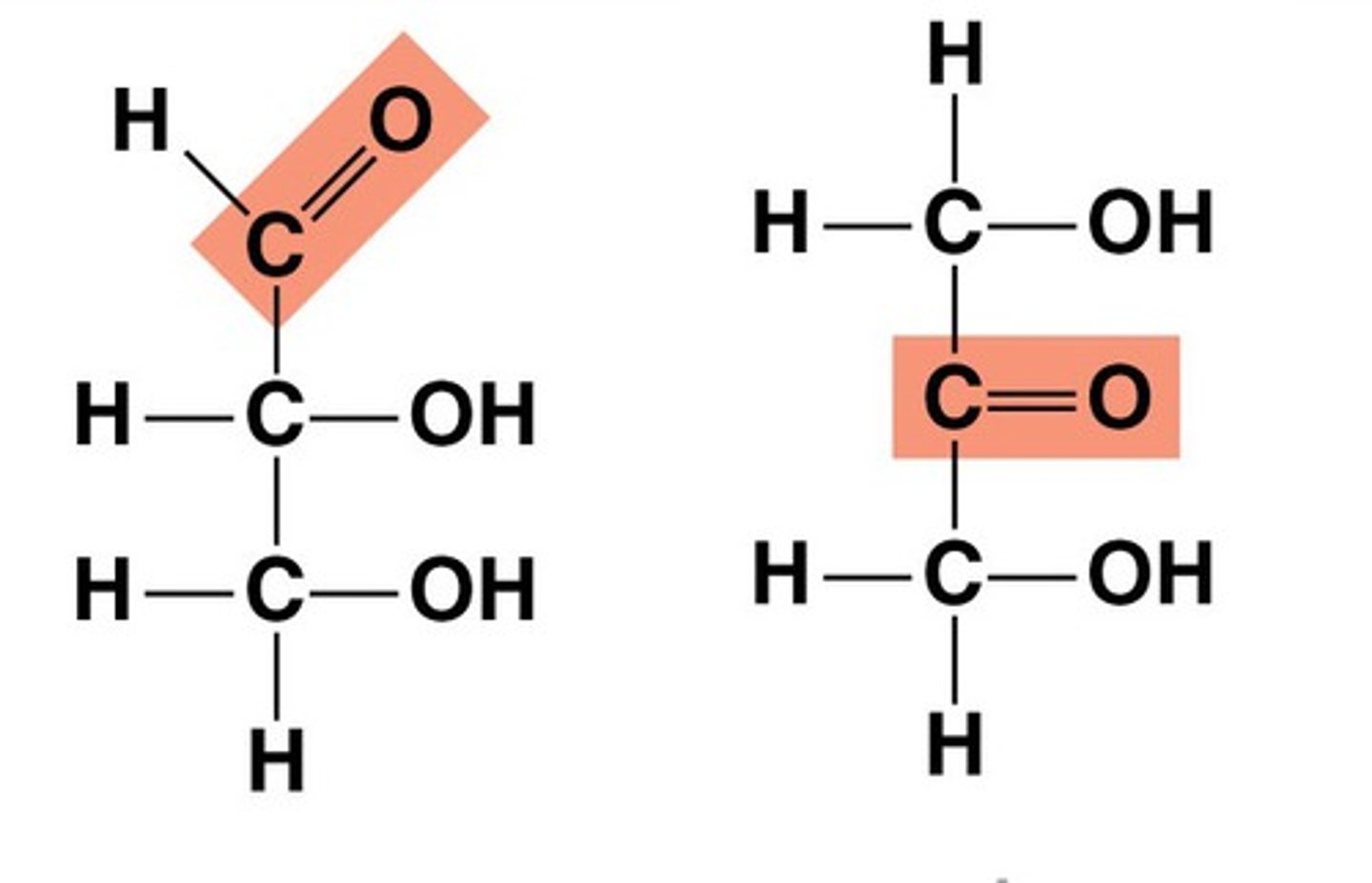
Aldoses
Monosaccharides with an aldehyde group.
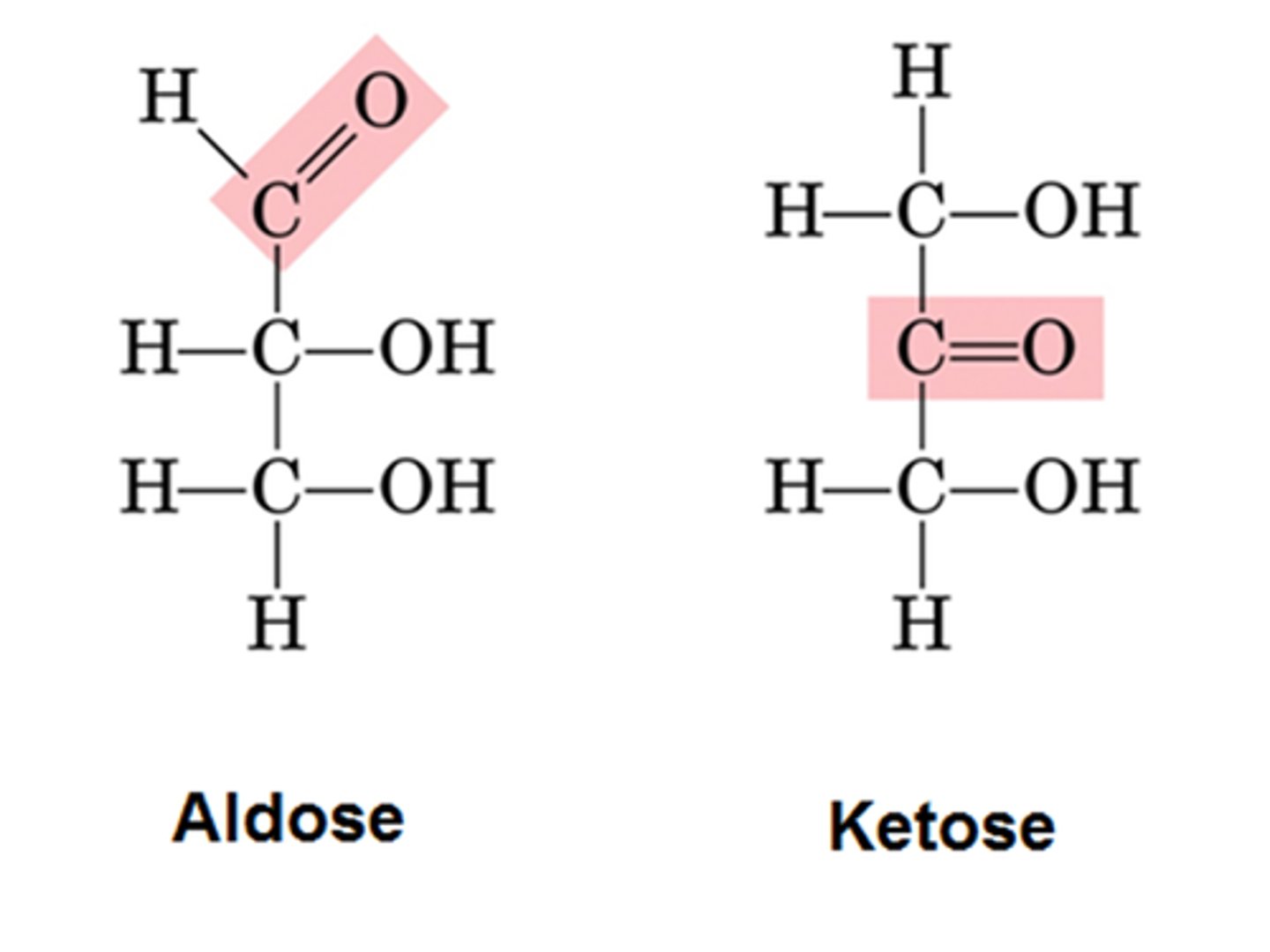
Ketoses
Monosaccharides with a ketone group.
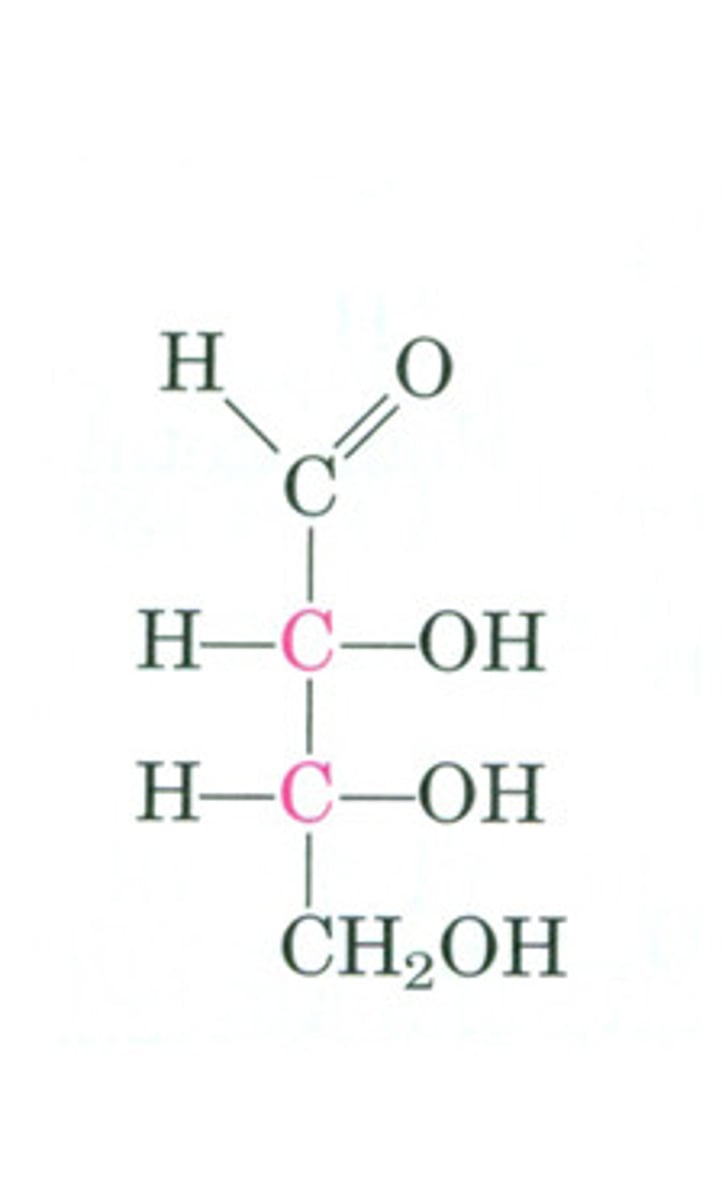
Triose
Monosaccharide with three carbon atoms.
Tetrose
Monosaccharide with four carbon atoms.
Pentose
Monosaccharide with five carbon atoms.
Hexose
Monosaccharide with six carbon atoms.
Aldopentose
Five-carbon saccharide with an aldehyde group.
Ketohexose
Six-carbon saccharide with a ketone group.
d-Glucose
Most common hexose, known as blood sugar.
d-Galactose
Aldohexose obtained from lactose in milk.
Galactosemia
Condition due to missing enzyme for galactose conversion.
d-Fructose
Ketohexose, sweetest carbohydrate, found in fruits.
High-fructose corn syrup
Sweetener made from sucrose hydrolysis.
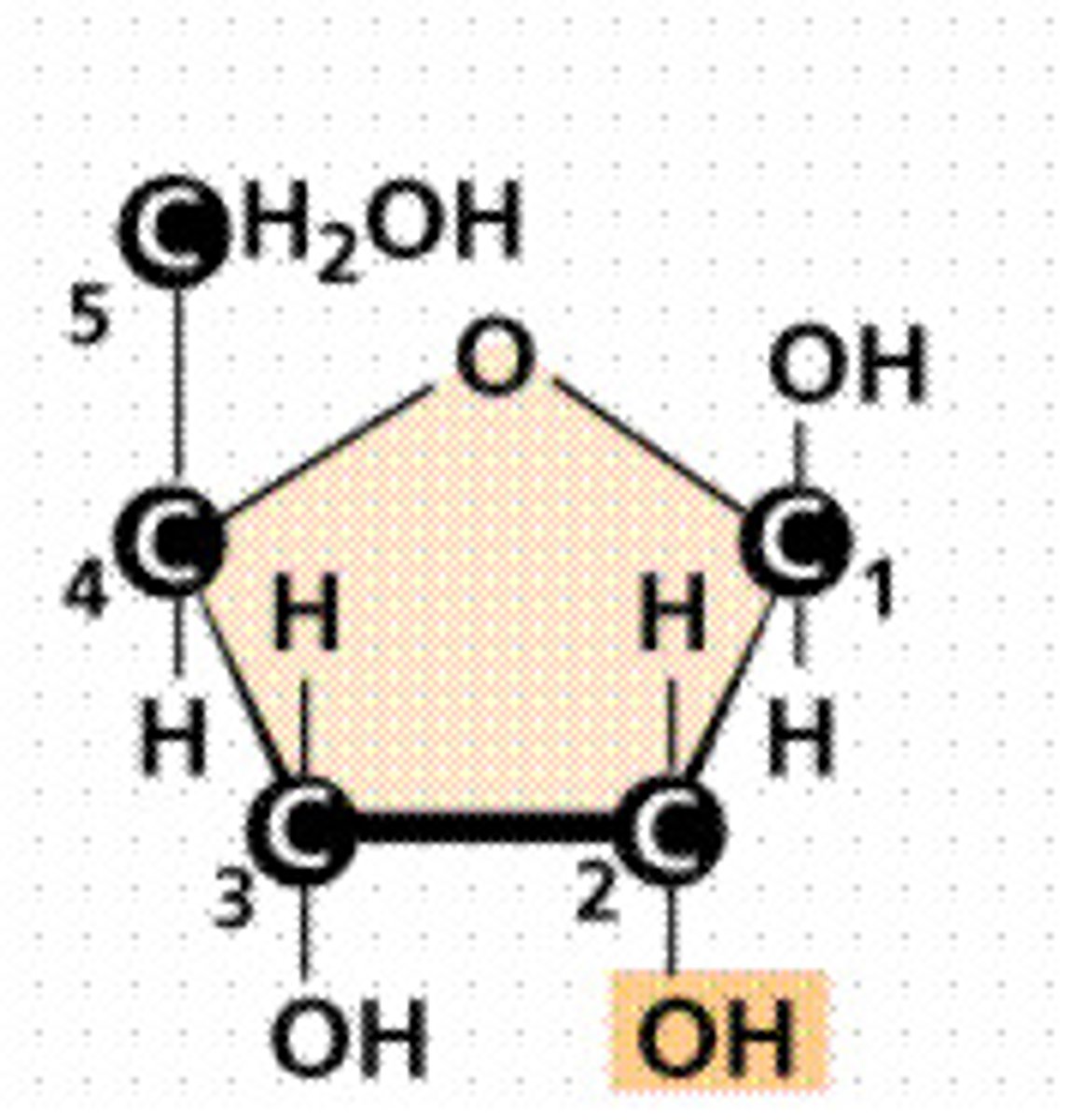
Haworth structures
Cyclic forms of sugars from carbonyl and hydroxyl reaction.
Fischer projection
2D representation of carbohydrates showing stereochemistry.
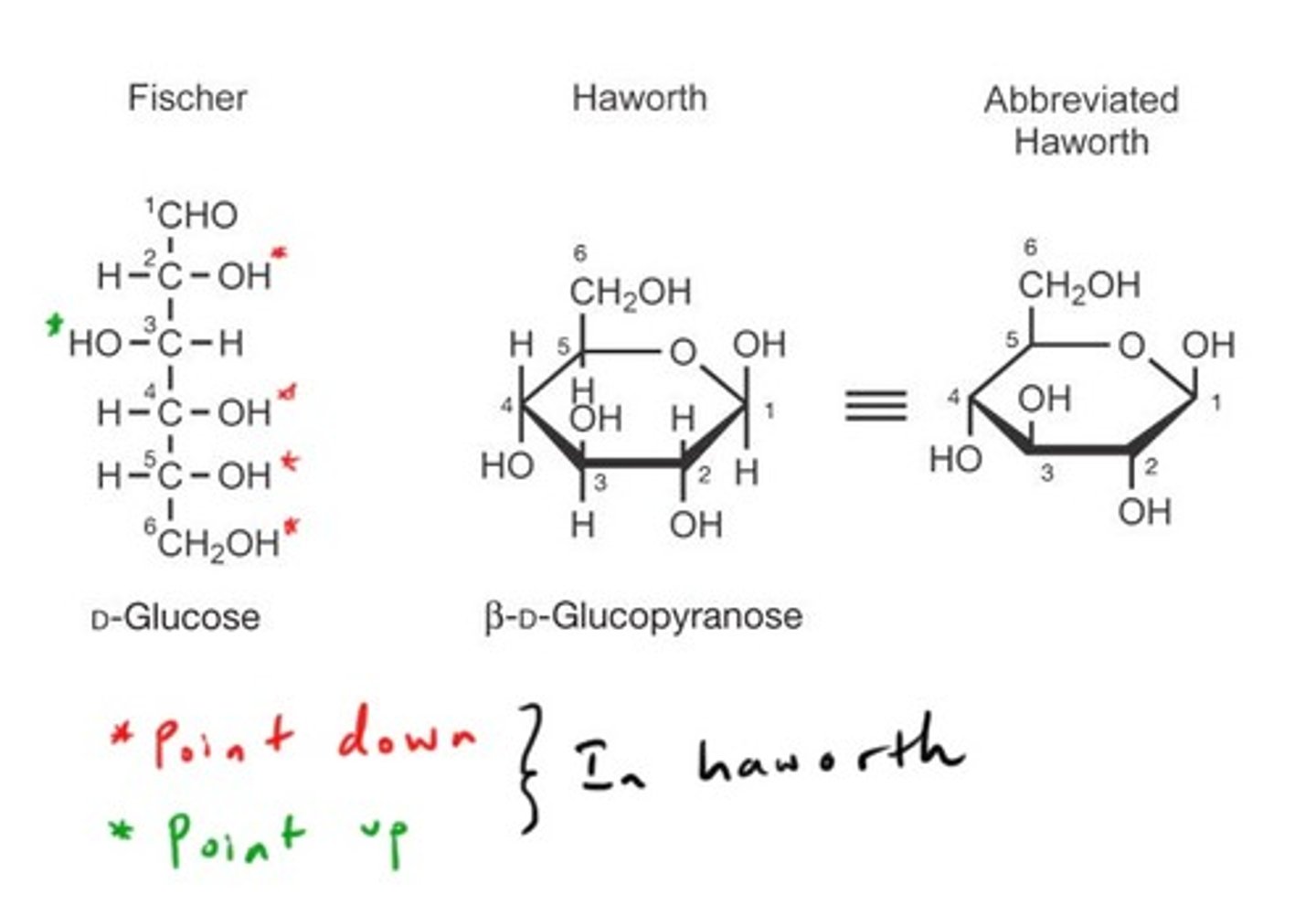
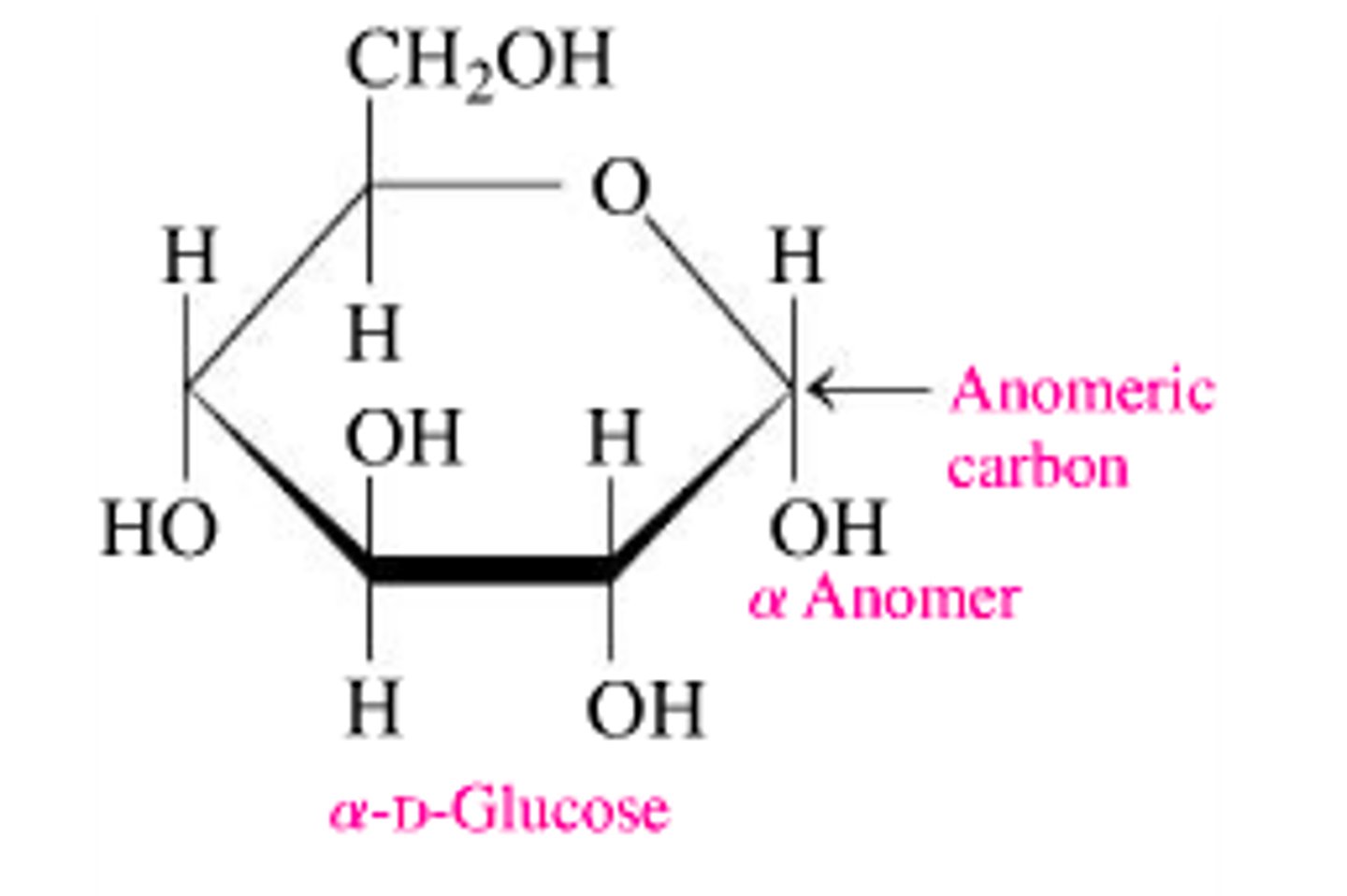
α-anomer
Cyclic form with -OH group below the ring.
β-anomer
Cyclic form with -OH group above the ring.
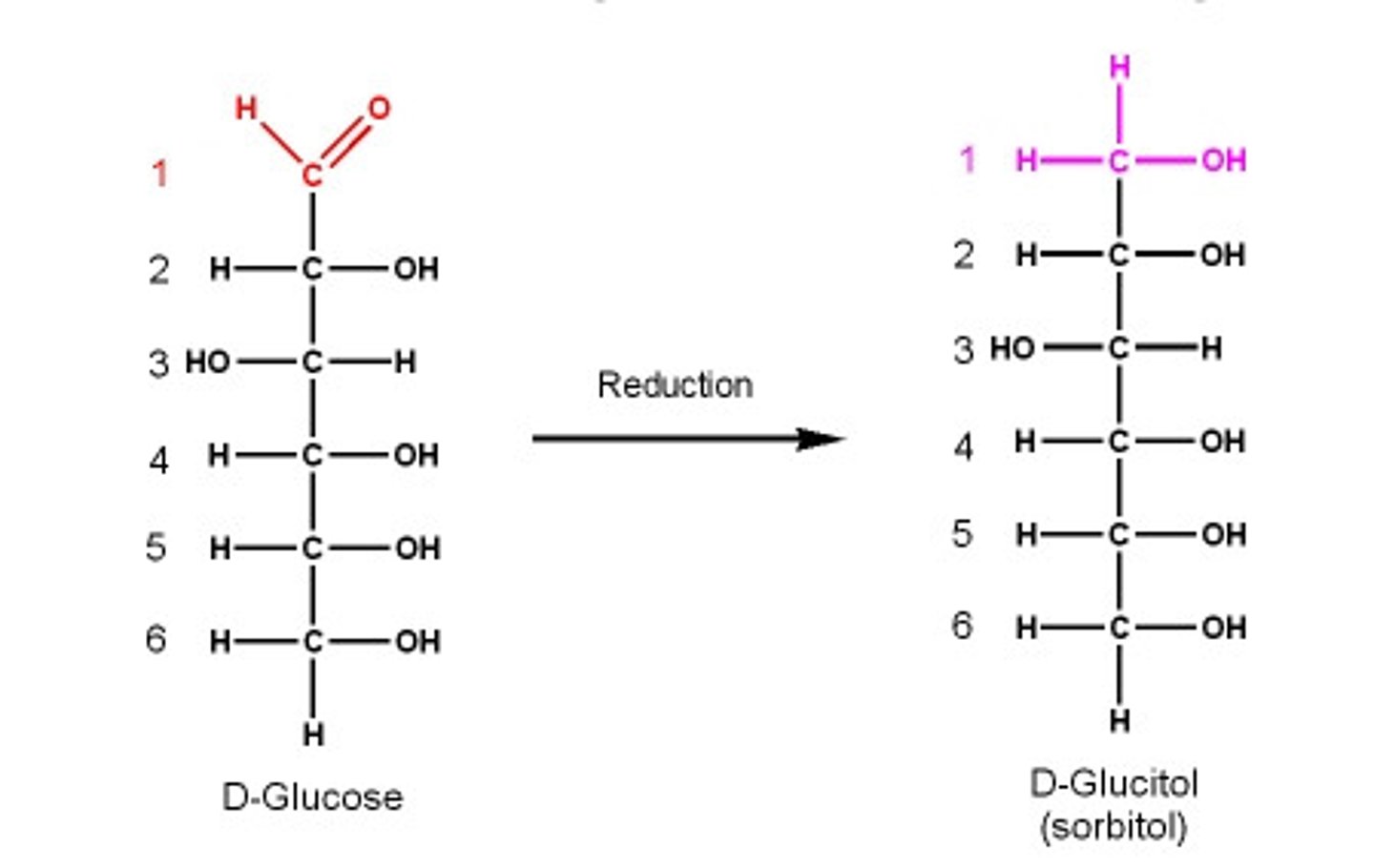
Sugar alcohols
Reduced carbohydrates used as sweeteners in products.
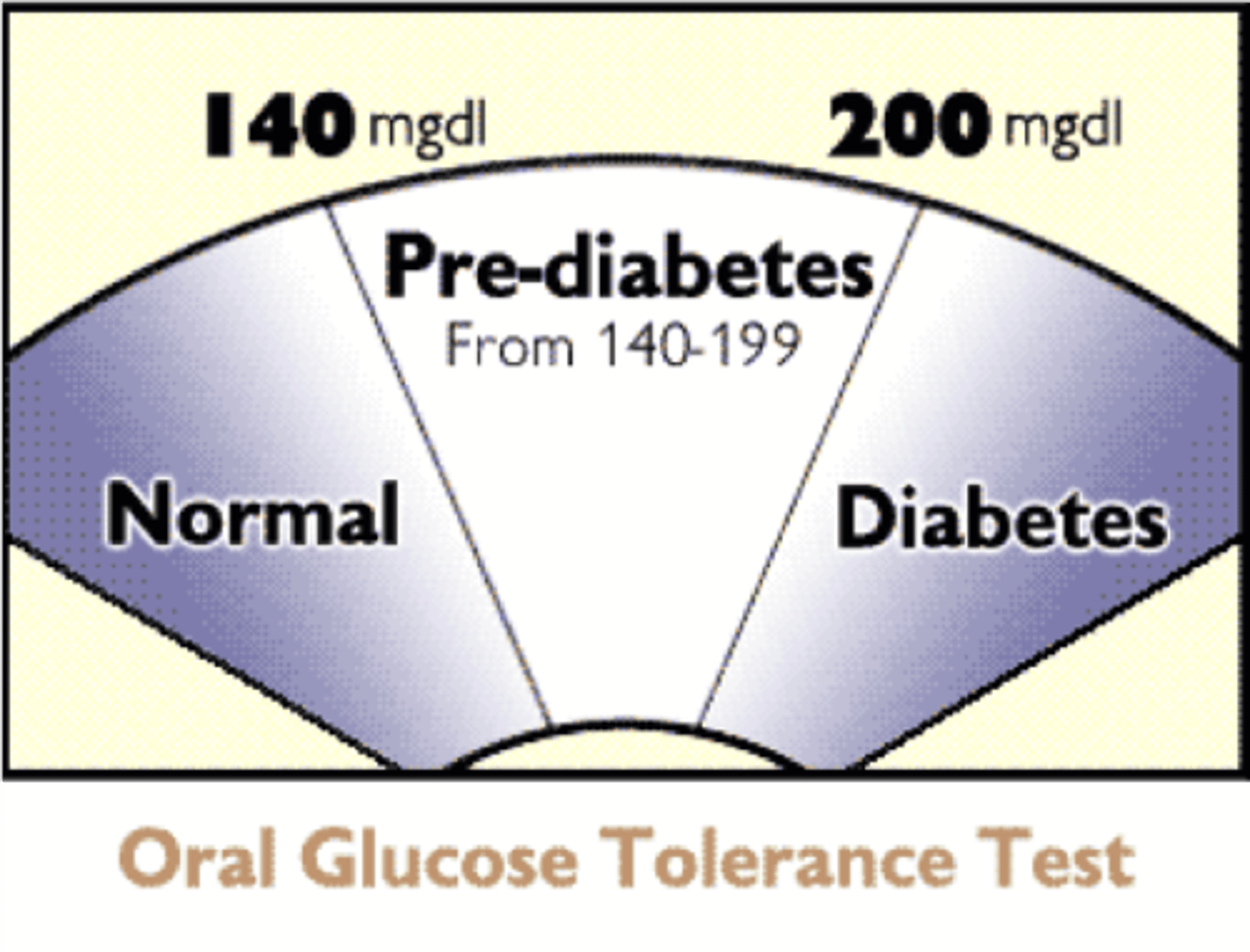
Glucose tolerance test
Measures blood glucose after glucose ingestion.
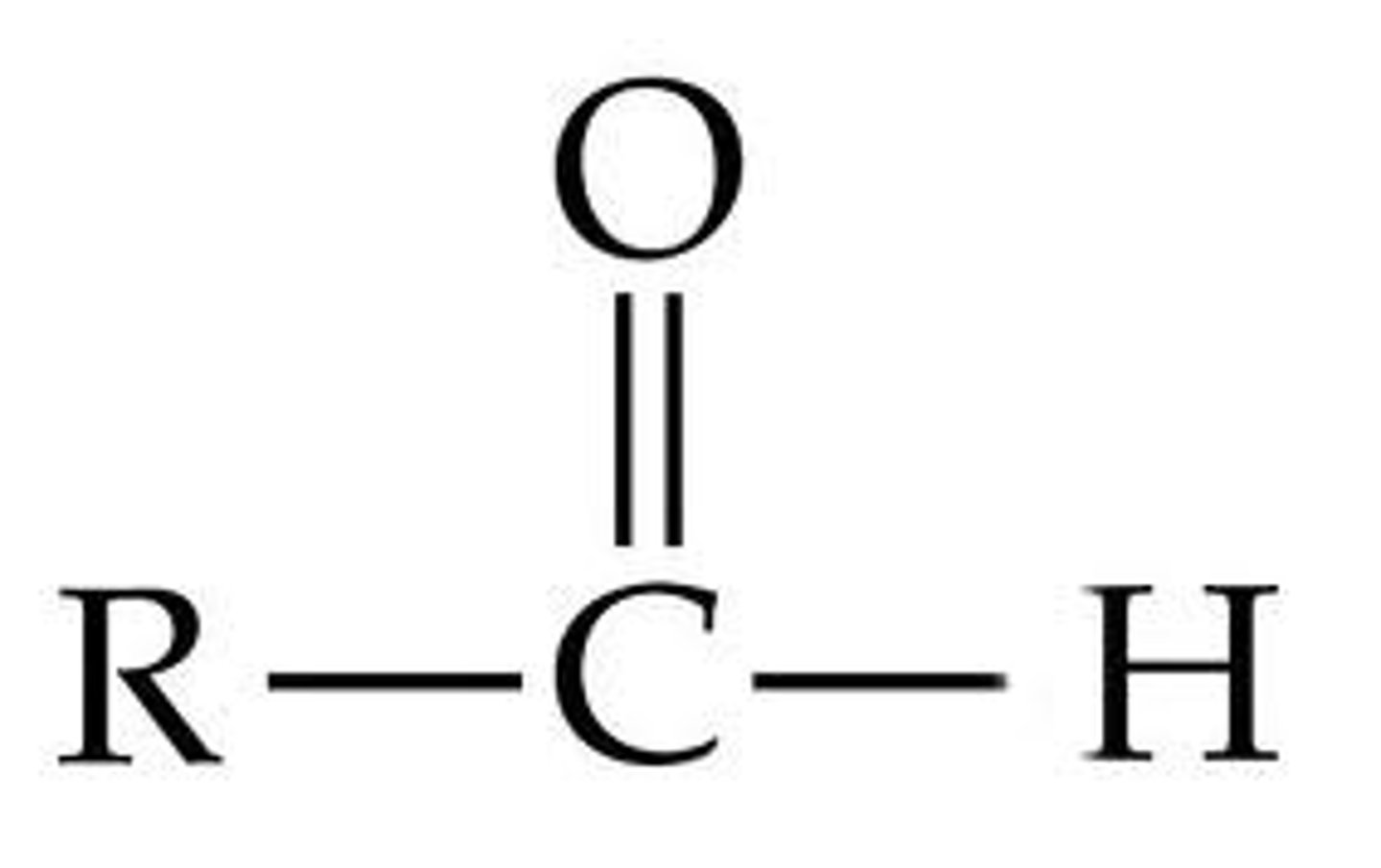
Aldehyde group
Functional group with a carbonyl and hydrogen.
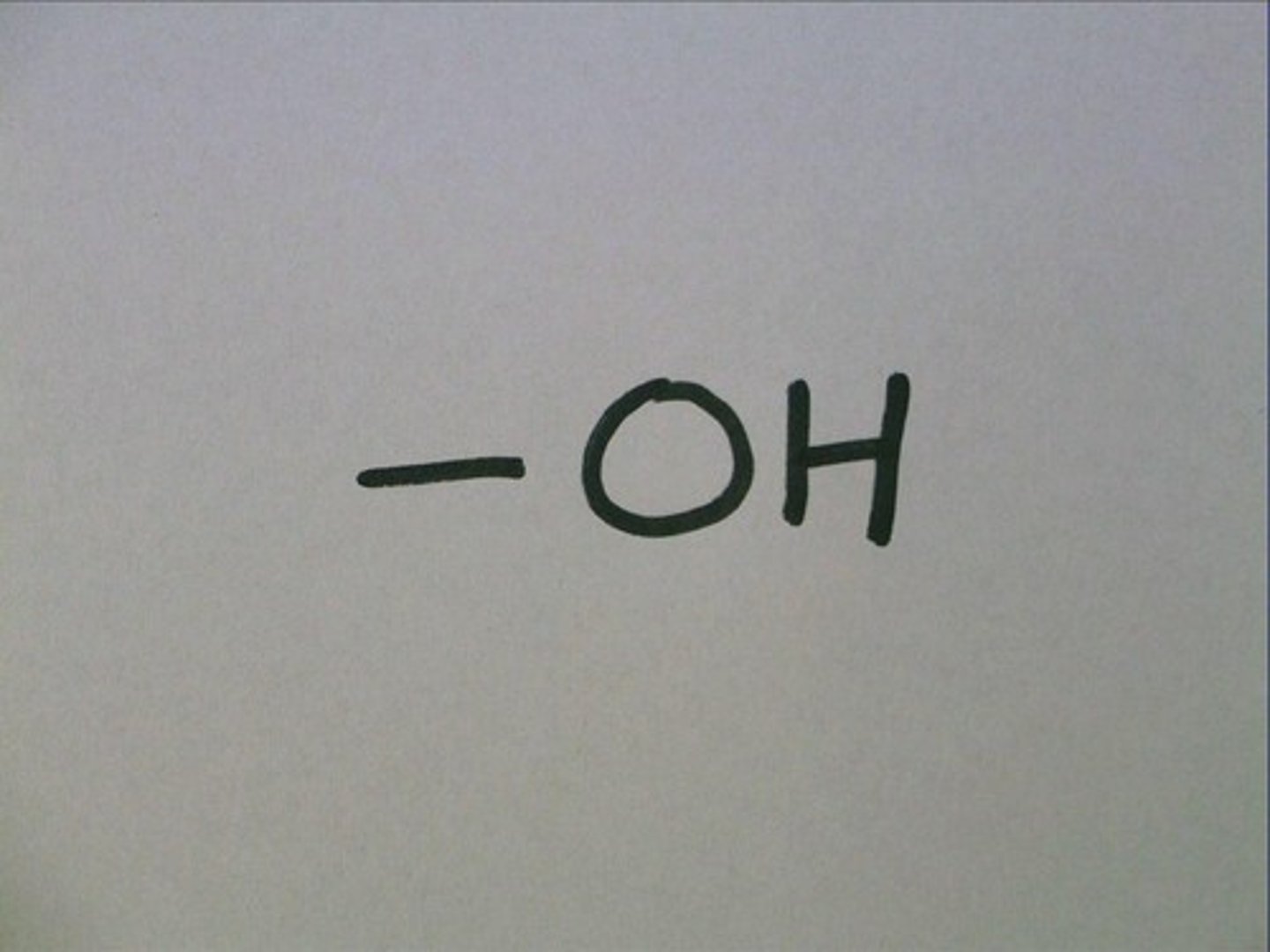
Hydroxyl group
Functional group containing an -OH group.
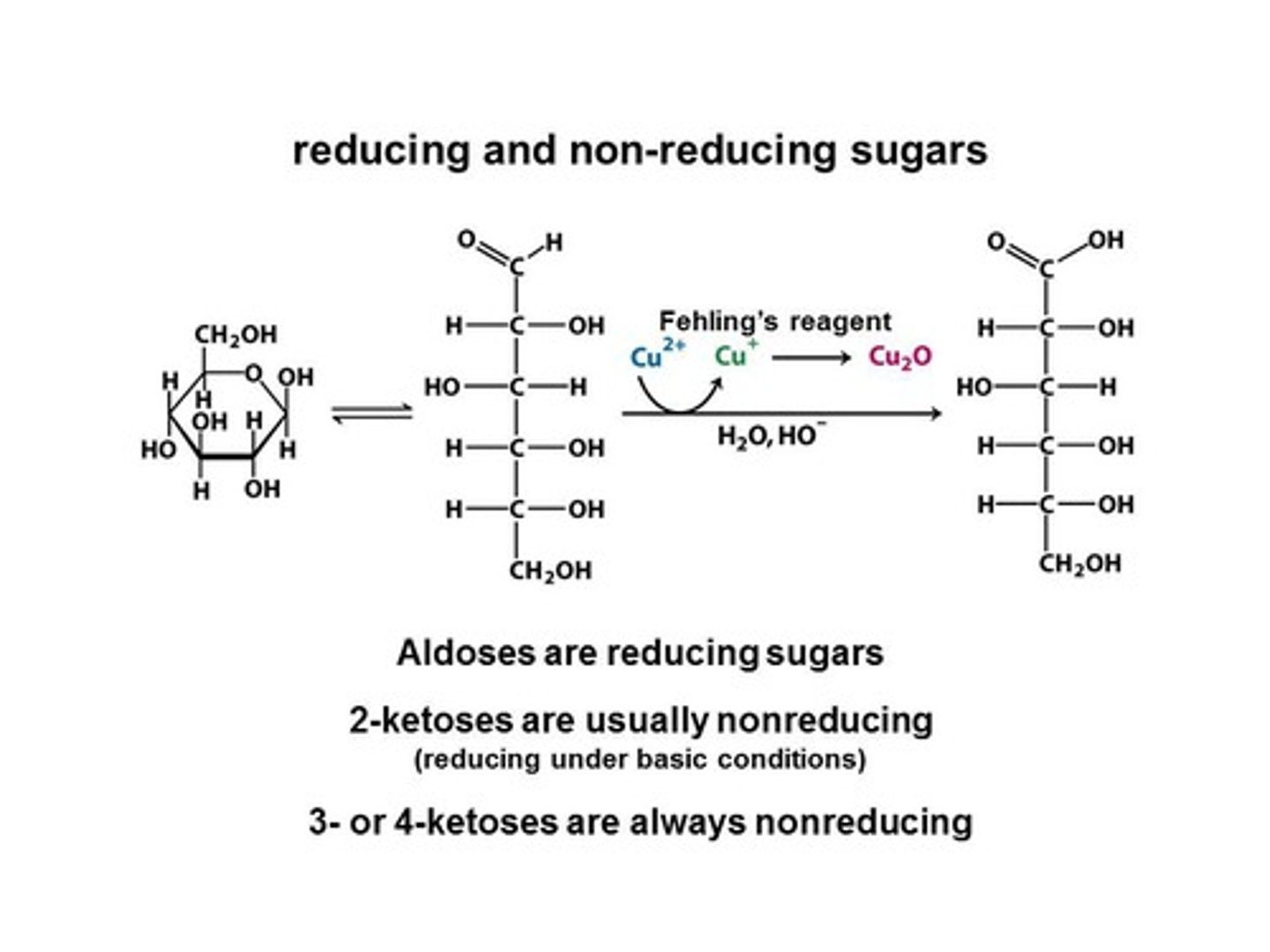
Sugar acids
Carbohydrates(H) oxidized to carboxylic(0H) acids.
Benedict's solution
Oxidizing agent for reducing sugars.
Reducing sugar
Carbohydrate that reduces another substance.
Fructose
Ketohexose with a ketone group.
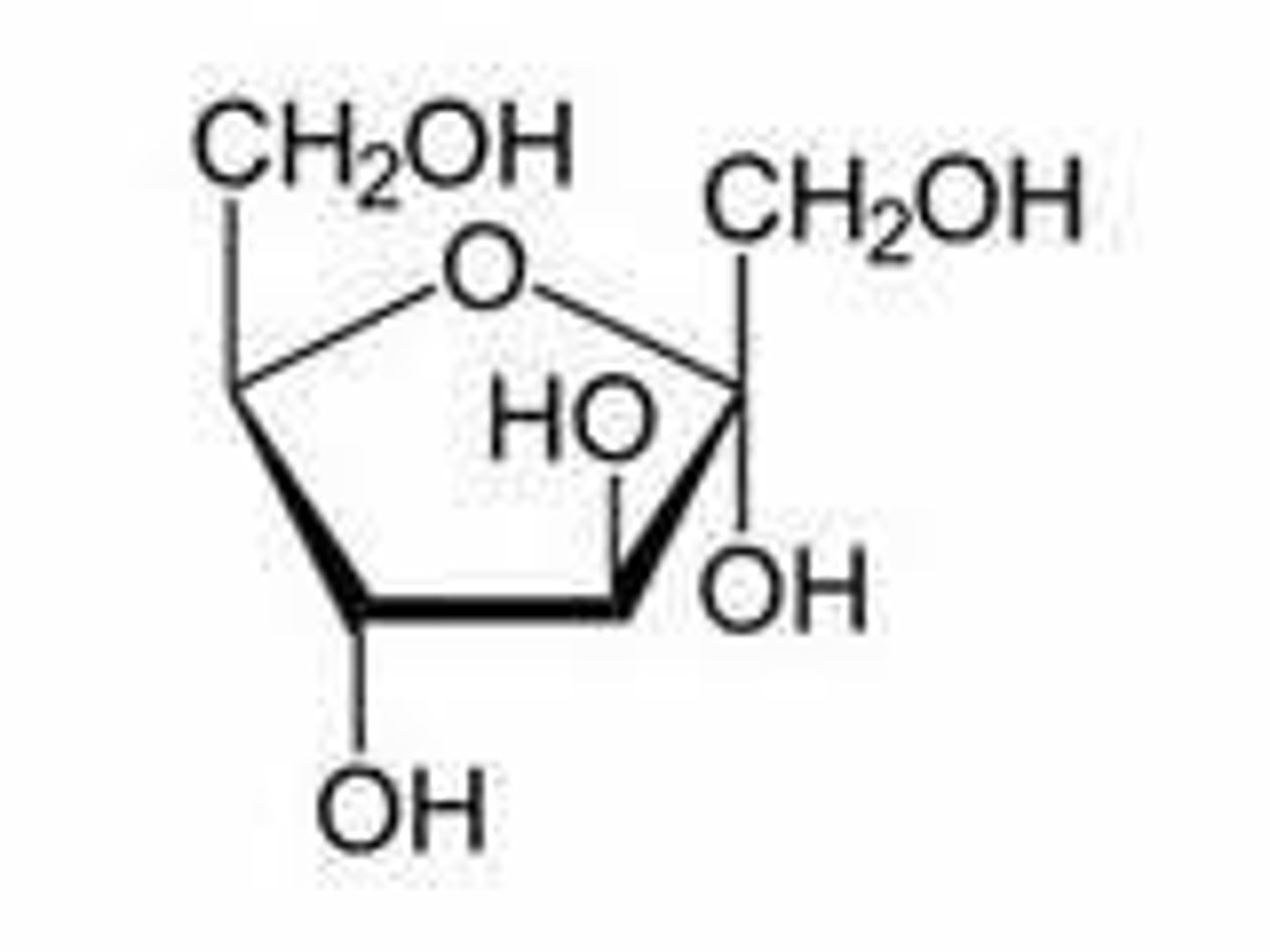
Ketohexose
Hexose with a ketone functional group.
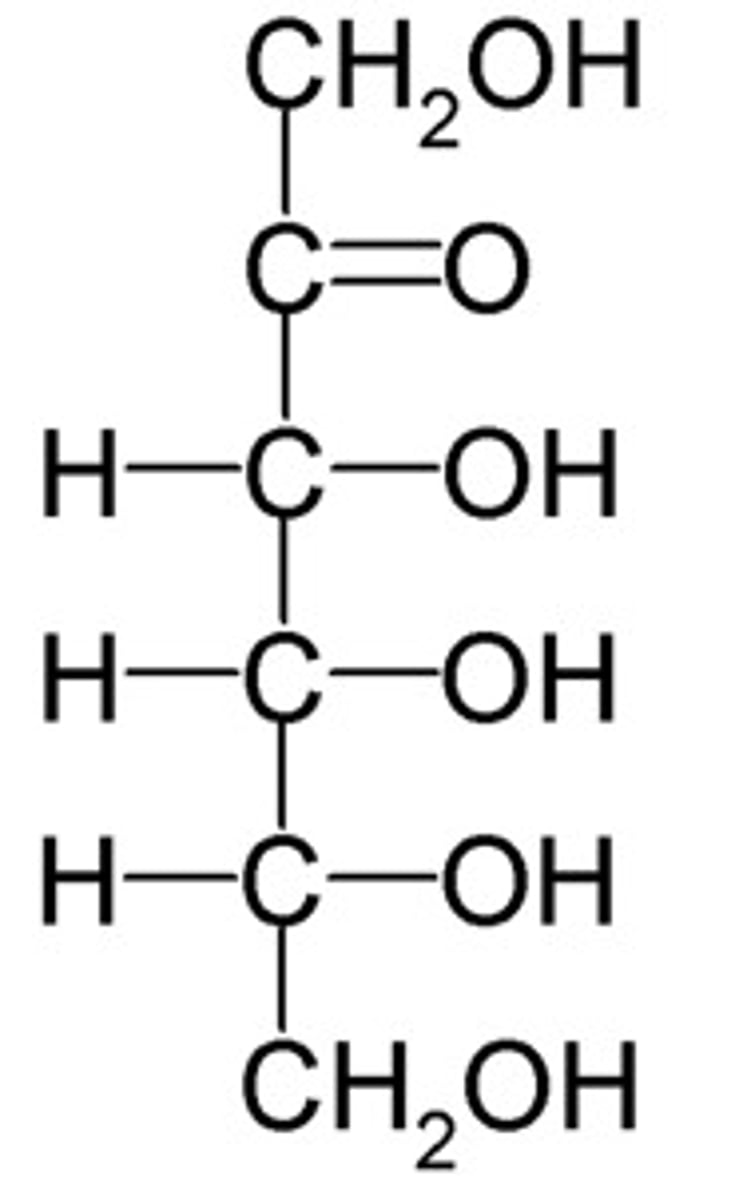
Glucose
Aldose that can be oxidized easily.
Sugar alcohols
Reduced monosaccharides, also called alditols.
D-sorbitol
Sugar alcohol derived from D-glucose.
D-xylitol
Sugar alcohol derived from D-xylose.
D-mannitol
Sugar alcohol derived from D-mannose.
Disaccharide
Carbohydrate formed from two monosaccharides.
Glycosidic bond
Covalent bond linking monosaccharides.
Lactose
Disaccharide of galactose and glucose.
Maltose
Disaccharide known as malt sugar.
α-(1→4)-glycosidic bond
Bond between carbon 1 and 4 of glucose.
β-(1→4)-glycosidic bond
Bond in lactose between galactose and glucose.
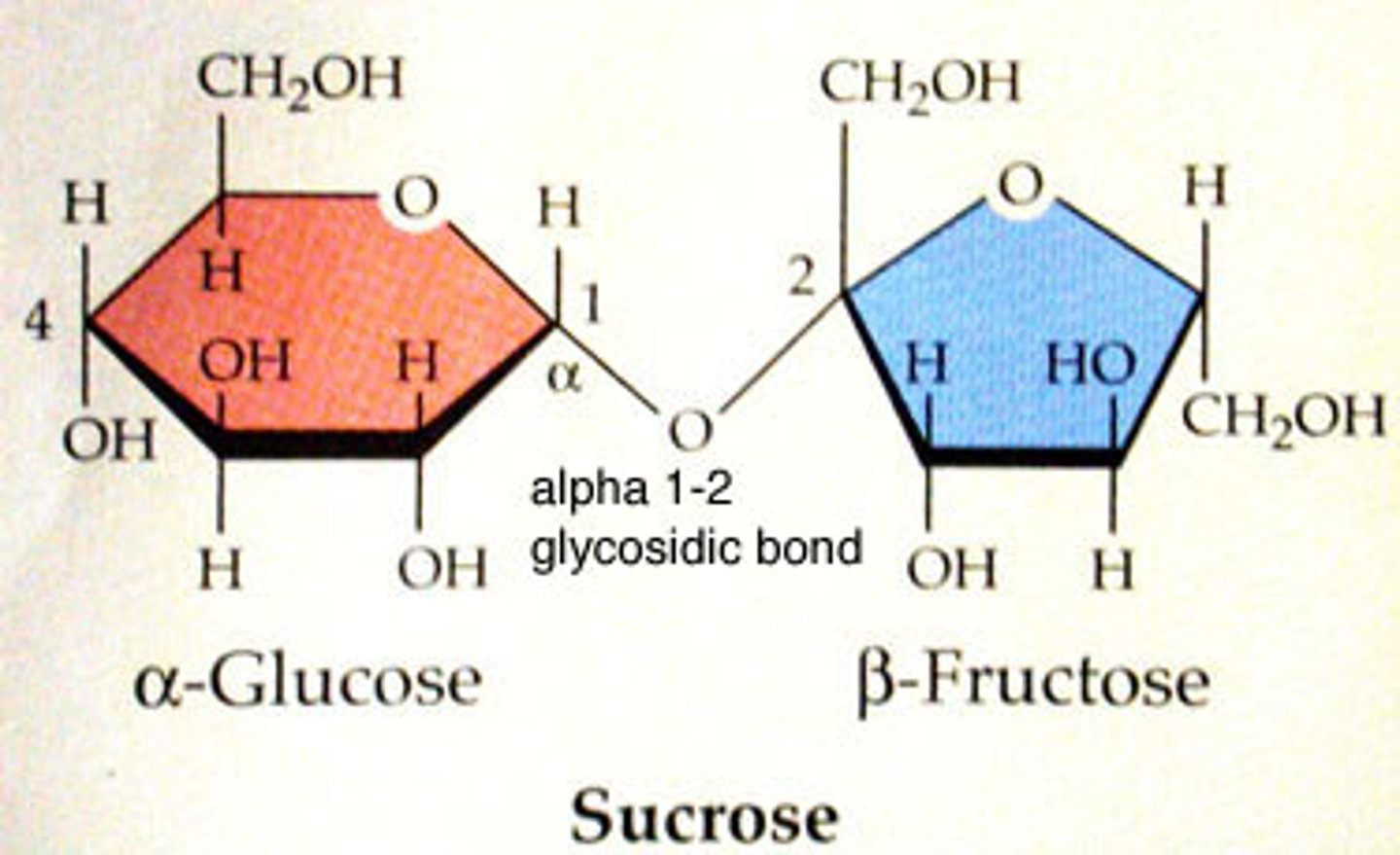
Sucrose
Disaccharide of glucose and fructose.
α,β-(1→2)-glycosidic bond
Bond between glucose and fructose in sucrose.
Sucralose
Chlorinated derivative of sucrose, artificial sweetener.
Aspartame
Noncarbohydrate sweetener made from amino acids.
Sweetness scale
Sucrose assigned a sweetness value of 100.
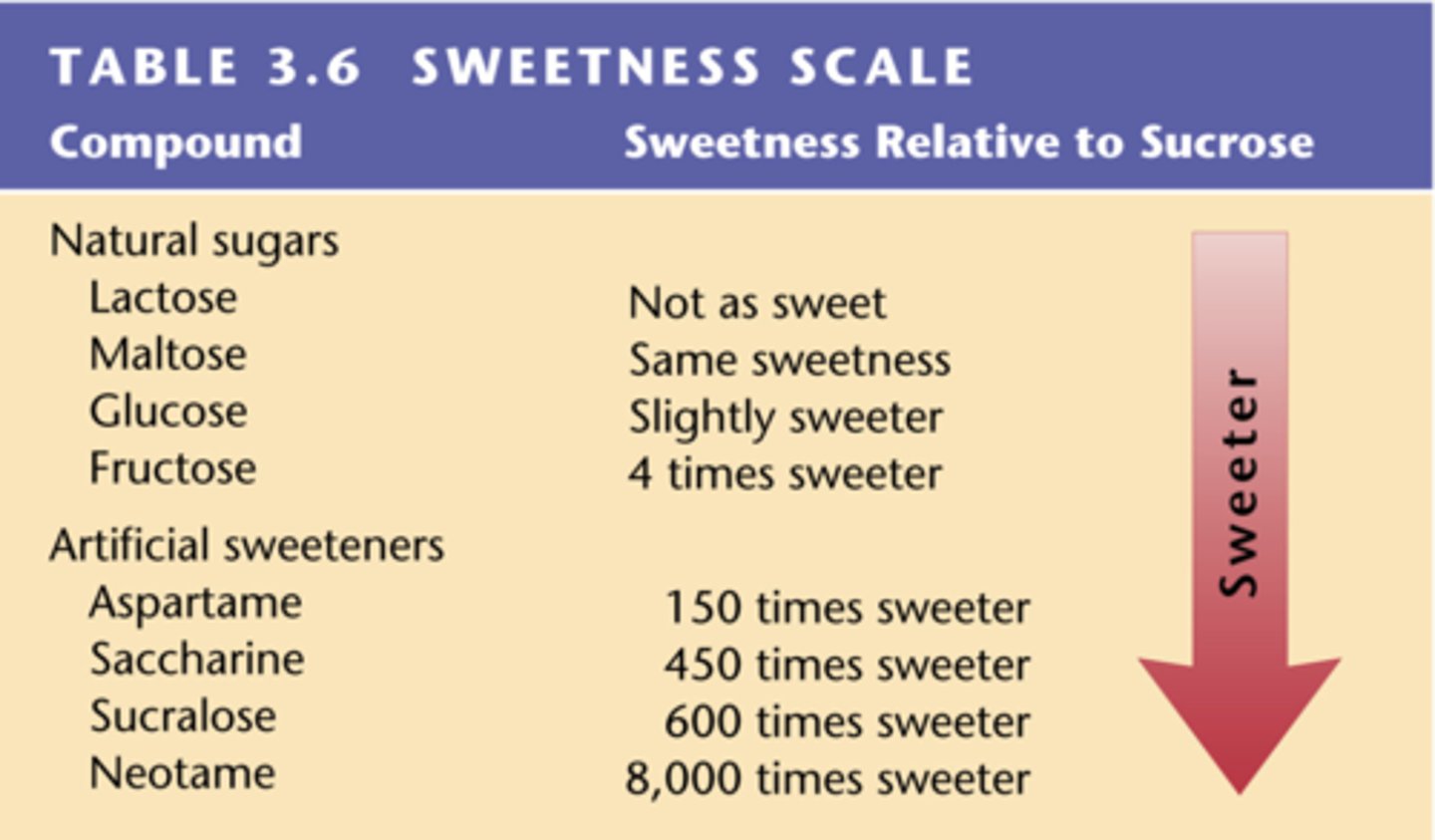
Neotame
Artificial sweetener 10,000 times sweeter than sucrose.
Saccharin
Noncarbohydrate sweetener, banned in Canada.
Lactose
Disaccharide of α-D-Glucose and β-D-Galactose.
Maltose
Disaccharide of two α-D-Glucose units.
Sucrose
Disaccharide of α-D-Glucose and β-D-Fructose.
Melibiose
Disaccharide of α-D-Galactose and α-D-Glucose.
Glycosidic bond
Covalent bond linking monosaccharides in carbohydrates.
α-(1→6)-glycosidic bond
Bond linking α-D-Glucose and α-D-Galactose in melibiose.
Cellulose
Polysaccharide of glucose with β-(1→4)-glycosidic bonds. >>> humans lack cellulose