Astronomy MASTER STUDY GUIDE #3 - Semester 2
1/49
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Galaxy mass measurements show that galaxies need between ______ times more mass than can be observed to explain their rotation curves.
3 and 10
Why are galactic lobes often observed to be “swept back?”
Rapid motion through space
“Starburst galaxies” show evidence of massive, recent activity, clearly the result of ______.
a collision
What does this diagram suggest (graph of star formation rate after the Big Bang)?
Most stars formed a few billion years after the Big Bang.
The Milky Way’s enormous death spirals are called the:
Sagittarius streams
Mergers of two spiral galaxies probably result in an:
elliptical galaxy
All quasars that we see are more than ___ billion years old.
1
The most distant observations show “structure” on a scale of ___ Mpc, but nothing on a scale larger than that.
200-300
Light from quasars passes through hundreds of gas clouds on its way to us. This result is known as the:
Lyman-alpha forest
Instead of light from a source traveling in a straight line, it is bent by the presence of a massive body. This is known as:
gravitational lensing
The largest structure in the universe is known as the:
Sloan Great Wall
The universe is believed by many scientists to be homogeneous and ______.
isotropic
The concept that the entire sky should be as bright as the surface of the Sun, although it is not, is known as:
Olbers’s paradox
Where was the Big Bang?
It was everywhere.
Which demonstration is often used to demonstrate the Big Bang and inflation?
Inflating a balloon
At our estimated density of ______, the universe will likely ______.
9 × 10^-27 kg/m³; expand forever although slower and slower
Assuming space is homogeneous, three possibilities exist for its structure:
closed, flat, and open
In a closed universe, you can travel in a straight line and ______.
End up back where you started
Given what we do know, the age of the universe works out to be about:
13.7 billion years old
What was accidentally discovered in 1964 as two astronomers tried to remove “noise” from their observations?
cosmic microwave background
As the universe cooled, it went from being radiation dominated to being dominated by:
matter
What can we say about the average temperature and density of the universe as time has gone on?
Both decreased.
If we extrapolate the Big Bang back to the beginning, it yields a:
singularity
We understand what happens back to about ___ seconds after the Big Bang.
10^-43
The era of time considered in the previous question (first 10^-43 seconds after the Big Bang) is known as the ______ era.
Planck
At 10^-4 seconds after the Big Bang, electrons, positrons, muons, and neutrinos were still in equilibrium. This is called the ______ era.
Lepton
The six types of quarks include:
up, down, charm, strange, top, bottom
Heavy Hydrogen is also known as ______.
Deuterium
Two “problems” discussed in the cosmos included:
horizon and flatness
Which of the following is not an “agreed upon” characteristic of life?
Ability to access sunlight
Why is there so little known about Earth’s first billion years?
Crystal activity did not allow preservation in rock record.
Which experiment can recreate the nucleotide and amino acid formation that Earth might have experienced?
Urey-Miller
Another popular idea is that life arrived first on Earth from:
comets or meteors
Multicellular organisms first appeared on Earth about how long ago?
1 billion
Which neighboring planet had liquid water flowing on the surface in the past (and recently observed)?
Mars
A series of variables that are multiplied together to estimate the chances for intelligent civilization is known as the:
Drake equation
An interstellar probe heading out of the Solar System containing a plaque explaining our purpose and location is:
Pioneer 10
Which of the following is not a variable in the equation used to estimate chances for other intelligent life?
Number of solar systems which contain a Jupiter-like planet
Which of the following is considered to also be a large-scale measure of structure in the universe?
pencil beam
Which is the best definition/meaning of “isotropic?”
The same in all directions
Which chart did we explore that accurately describes the main predicted outcomes for the fate of the Cosmos?
Something similar to this graph
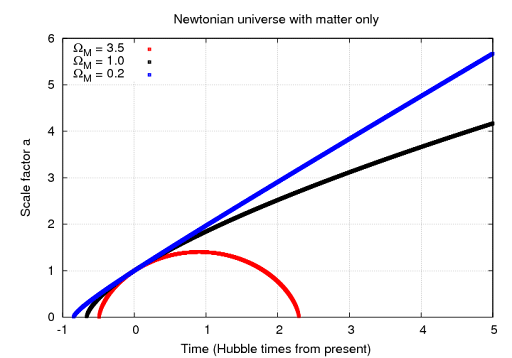
Although dark matter does not interact directly with radiation, it will interact through the ______, leading to tiny “ripples” in the cosmic background radiation.
gravitational force
The horizon problem is best described as:
Regions in opposite directions in the universe were very similar to each other when the radiation we now observe left them, but there has not been enough time since the Big Bang for them ever to homogenize with one another, so why then should they look the same?
The flatness problem was simplified using a balloon and an:
ant
Radio signals inadvertently emitted by humans via broadcast towers would appear to have a ______.
24-hour period
Life on Earth that can live or even thrive in the most harsh environments are called ______ and are used to change the way we think about discovering life elsewhere.
extremophiles
Although Mars has been (and continues to be) our best change for finding life within our own Solar System, where else might life be, albeit a “long shot?”
Moons of outer planets
Why do we know so little about Earth’s first billion years?
The planet was too active, lava flows destroying rock record.
There are ___ phases of cosmic evolution.
7
In searching for life elsewhere in the universe, perhaps one of the most important things we need to do first is:
Define what we mean by “life”