4.2.5.2 Supply Side Policies
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
expectations, monetary/fiscal policy, supply of credit, and household wealth, as well as global events
Other factors that shift AD include changes in:
changes in unit labour costs and other production costs, commodity prices, exchange rates, gov. tax and subsidies, price of imports
Other factors that shift AS include:
change in FofP costs
what shifts SRAS curve
change in FofP quality/quantity
what shifts LRAS curve
Supply-side improvements
Actual increases in the economy’s productive potential, which may result from policies OR naturally from market forces or private sector actions.
tech firm develops AI that boosts productivity, firms invest in more efficient machinery, improved administration
Application for supply-side improvements
may be independent of gov. action, often driven by private sector, reflects actual results
key features of supply-side improvements
supply-side policies
Deliberate actions taken by the government to increase the productive capacity (LRAS) of the economy.
tax cuts to incentivise, spending on education/training, deregulation, privatisation
application for supply-side policies
Planned and implemented by gov., aim at long term returns, interventionist/market based, takes time to take effect
key features of supply-side policies
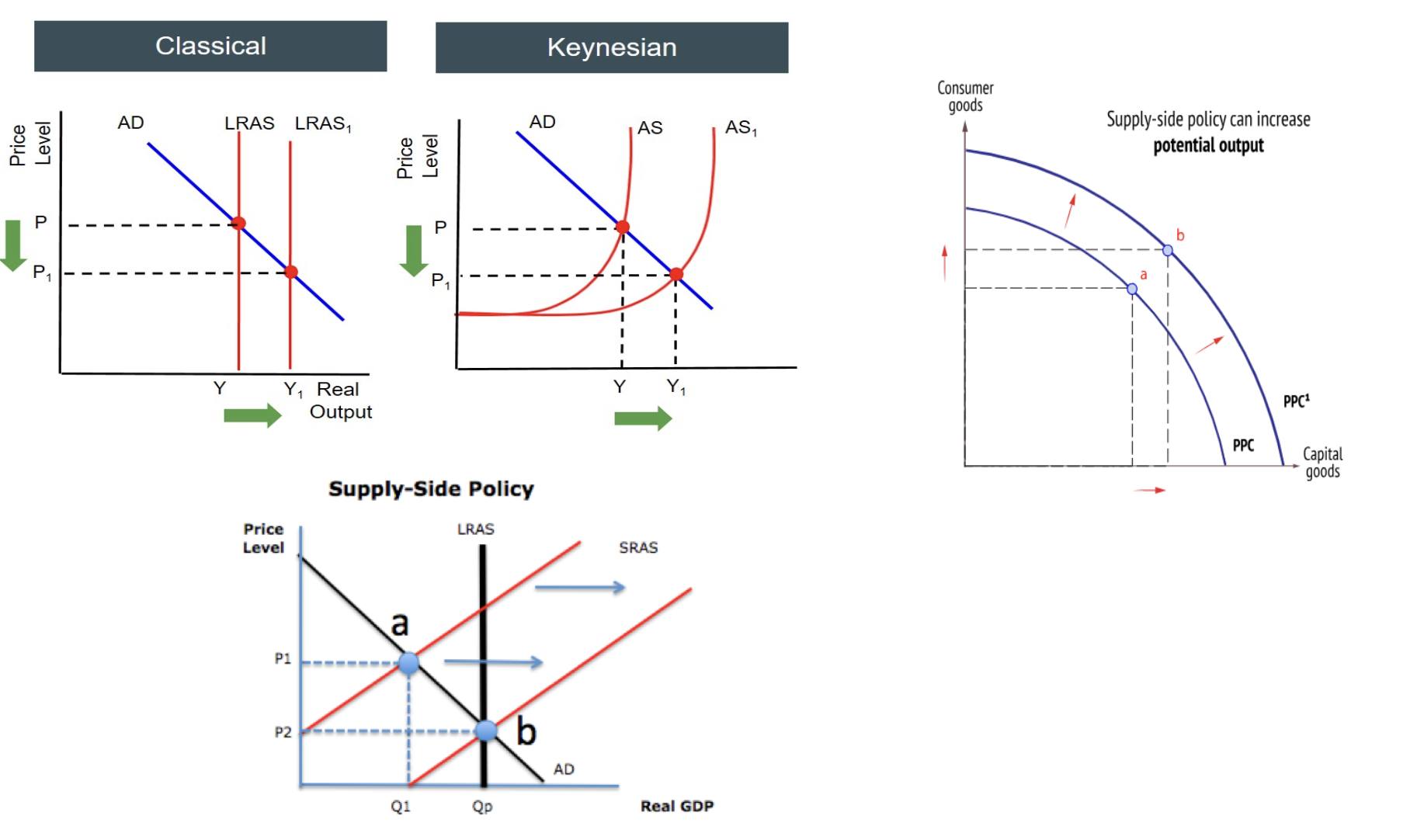
classical, keynesian, PPF
How would you show, in a diagram, the use of supply side policy?
misallocation of resources, time lags, lack of private sector response, inefficiency in public services
why may supply-side policies not lead to supply-side improvements?
broad(across entire economy) or targeted(specific sectors of the economy)
supply-side policies can either be:
target supply-side policies
Specific policies aim to reduce the bottlenecks in an economy
bottleneck
slows down the production of a whole economy and means we cannot operate at full capacity.
port is too small, a road network too congested, a broadband network too slow
application for bottleneck
market based, interventionist
two types of supply-side policies
market based
Type of supply-side policy that aims to remove inefficiencies or lack of incentives by letting the market function by removing barriers to the efficient working of the free market.
interventionist
Type of supply-side policy aimed to correct the market failures, where there is an under-provision of certain goods/services, so the government should act to encourage long term thinking.
efficiency, productivity, incentives to work and invest, labour skills and flexibility
what do supply-side policies focus on
AD/AS diagram: change in LRAS, PPC curve: outward shift
how do you show supply side polices on a diagram